
Choline is an essential nutrient that provides the backbone of the learning neurotransmitter acetylcholine; learn which form is the best for your needs.
Choline is an essential nutrient for the human body required for the optimal functioning of all cells. It's also a common ingredient included in all kinds of supplements, including pre workouts, intra workouts, and nootropic focus formulas.
Sadly, most individuals are sorely lacking in choline due to a poor diet, especially vegans, since the foods with the highest concentrations of choline are typically animal-based (dairy, meat, eggs, and seafood).[1,2]
There's several types of choline supplements available in standalone bulk supplements and as part of more comprehensive formulas. Knowing which one is the most effective can be tricky, and the same goes for knowing what the proper doses of these various forms are. We've got all that covered for you and more as we help you determine what form of choline is best.
The long story short, is that we've become believers in citicoline (CDP-Choline) over the course of time. It's always been most experiential, but now in the 2020s we see large amounts of evidence supporting it at lower doses (250 milligrams but even more at 500 milligrams) and fewer potential side effects.
Before we get to the best types of choline, let's do a quick refresher on what choline does with regards to enhancing your brain function and focus while training!
Choline – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.
What does choline do?
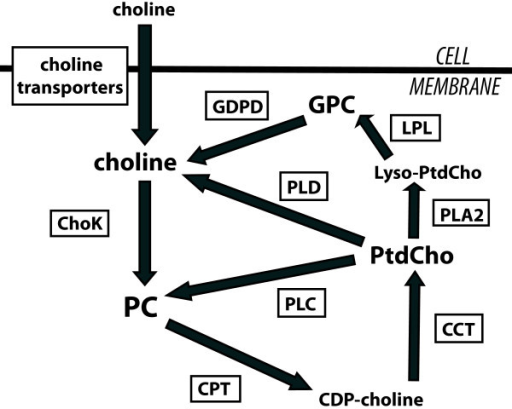
Schematic drawing of choline phospholipid metabolism and its regulatory enzymes illustrates the metabolic reactions associated with modulation of choline-containing metabolites.
As we stated up at the beginning of this article, choline is essential for the healthy functioning of virtually all cells in your body. It's used in the synthesis of phospholipids, which support a cell's structural integrity and signaling functions.[1] The human body can synthesize choline endogenously in the liver (as phosphatidylcholine), but the amount required by the body exceeds the amount it naturally produces,[3] which is why it's important to get more choline through the diet or supplementation.
More pertinent to its role as a nootropic-enhancing compound, choline also serves as a precursor for the synthesis of acetylcholine ("the learning transmitter").[1] Acetylcholine is vital to memory, mood, muscle control (i.e. the mind-muscle connection), and a number of other important brain and nervous system functions.[4,5] Those lacking adequate amounts of the compound may experience difficulty learning or recalling memories due to chronically low acetylcholine levels.
Deficiencies of choline can impart serious consequences including complications of the liver, muscle, and lymphocytes.[1] Lacking in choline may also affect expression of genes involved in cell differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis (programmed cell death), as well as adversely impact the development of the brain and nervous systems in growing animals.[1,6] When your diet is low in choline, you are literally programming your body to stop thriving and start dying.
Suffice it to say choline is something you DO NOT want to be deficient in, which is part of the reason it's so widely available and commonly supplemented. But, there's several different forms to choose from when purchasing a choline supplement, and knowing which is the most effective for your needs will go a long way to ensuring you choose the right one and consuming the right dose.
Types of Choline
-
Lecithin
Certain such as eggs and soy products are naturally rich with lecithin. Some processed foods, including certain chocolates and even protein powder, contain added lecithin, but the choline content of these is generally on the lower end of the spectrum.
Lecithin (derived from soy or sunflower) is really the only means vegans have for obtaining choline, but typically requires additional supplementation to significantly increase acetylcholine levels.[2] That being the case, lecithin is generally not regarded as an effective means to enhancing cognition or focus, or preventing certain neurodegenerative diseases like the other forms of choline which we'll cover in a bit.[7] FYI, if you are vegan and want to use lecithin as your choline source, you'll have to eat upwards of 100g lecithin to get any appreciable increase in choline concentrations.[8]
-
Choline Bitartrate
Choline Bitartrate is the cheapest and most widely available form of choline for purchase. It contains 41% choline by weight, which gives you roughly 410mg choline for every gram of choline bitartrate that you consume. The bitartrate form is also the most commonly used form of choline in pre workout supplements and nootropic formulas, usually in the 500-1,000mg range. Research is mixed on its nootropic benefits, but it does yield some other benefits for the body, particularly in regard to the liver.[9-11]
Studied doses: 1-3g per day
NutraBio Choline Bitartrate is trusted and third-party lab-tested, and uses VitaCholine form.
-
Choline Citrate
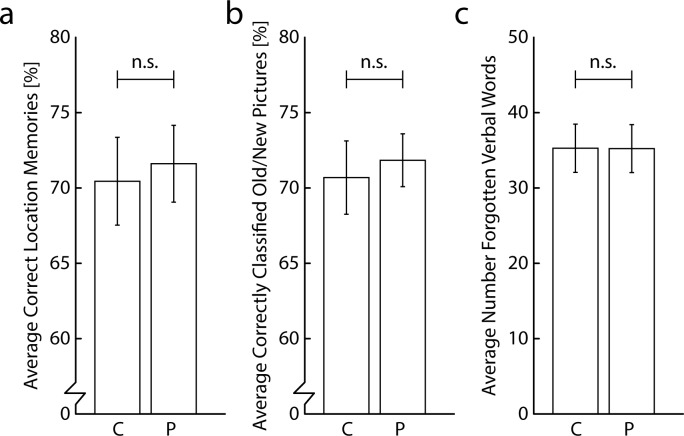
Choline bitartrate is incredibly affordable, but may not always deliver the best results as evidenced here in the graph showing that it did NOT perform better than placebo in memory testing.[11]
Another cheaper salt of choline, choline citrate contains roughly 50% choline by weight, a bit more than the bitartrate version. Not much research has been conducted on the citrate form of choline in regards to nootropic benefits, but many users believe it is more effective than the bitartrate form due to increased uptake by the body.
There is a study conducted in patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) who were given 1200mg intravenously two times per week that showed improvements.[12] Subjects receiving the treatment experienced less paresthesia and greater muscle strength in lower extremities, as long as 3 years after the trial was conducted. Additionally, one of the patients was a commercial pilot who was able to return to flight duty.[12]
Note that choline citrate powder is very sour, and is generally unenjoyable to use on its own unless added to something very sweet.
Recommended Dose: None, honestly.
There is very little choline citrate on the market anymore after research has shown the next two forms to be so much better, but your best shot is with SNS Choline Citrate.
-
Citicoline (CDP-Choline)
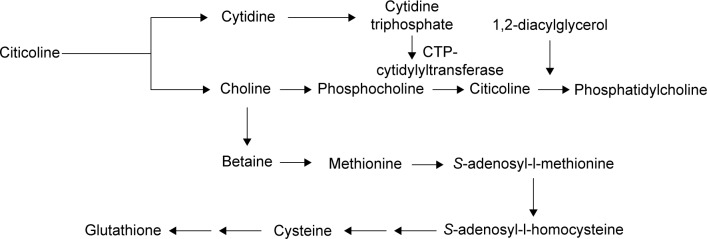
Citicoline, chemically known as Cytidine 5′-diphosphocholine (CDP-Choline), is one of the premium forms of choline that has quite a bit of research in animals as well as humans demonstrating its nootropic and neuroprotective benefits. It's only 18-19% choline by weight, but is able to pack a nootropic punch because it's essentially two nootropics in one (uridine and choline).
Upon digestion, Citicoline is broken into cytidine and free choline.[14] Cytidine is quickly converted to uridine which can cross the blood-brain barrier and exert its own nootropic benefits. CDP-Choline also is naturally-occurring in the body and used as an intermediary in the synthesis of phosphatidylcholine.
Research into Citicoline is rather extensive and impressive. It's shown great efficacy in studies regarding cognitive decline associated with neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's, as well as the impairment brought on by cerebral ischemia, stroke, and other traumatic brain injuries.[13]
Citicoline also potentiates neuroplasticity, increases cognition, improves learning, and boosts production of norepinephrine and dopamine levels in the CNS.[15] While this is an awesome form of choline, CDP-choline is more expensive than bitartrate and citrate.
You can read even more in our article titled "Cognizin® Citicoline: The Brain Choline".
Recommended dose: 250-500mg / day
Citicoline – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.
-
Alpha GPC
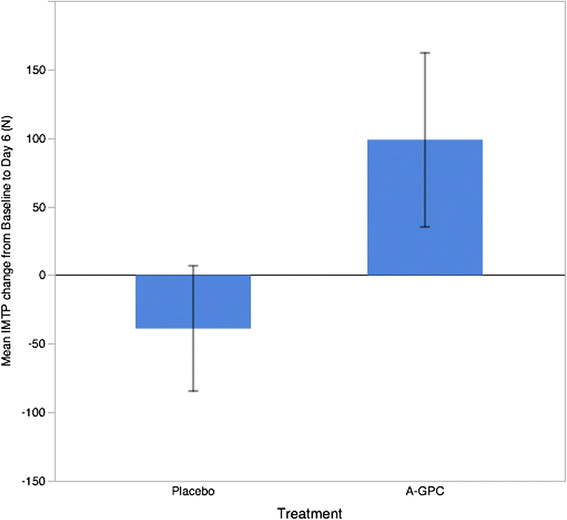
Alpha GPC isn't just good for enhancing brain function, it can also deliver some big strength gains (when dosed at 600mg).
The last form of choline you'll come across most commonly is L-alpha glycerophosphocholine (Alpha-GPC). Like citicoline above, Alpha GPC is one of the more bioavailable and well-studied forms of choline. The big difference here is that Alpha GPC is "40% choline by weight", but if using it in a powdered form, it needs to be bound to 50% silica (Alpha-GPC itself is a goopy mess). This lowers the powdered formulas from 40% choline by weight to 20% choline by weight, while CDP is 18-19% - similar when in powdered form. Alpha GPC can be found in the brain as well as dairy products, but it's typically synthesized by purifying soy lecithin.
Similar to CDP-Choline, Alpha GPC has been studied rather heavily and brings a number of nootropic benefits as well as a few other interesting ones. In regards to nootropic effects, Alpha GPC has been shown to increase acetylcholine production, enhance cognition, combat neurodegenerative disease, and improve memory.[16-19]
As for some of its other fringe benefits, Alpha GPC also has been noted to increase strength and power during training and elevate post-workout growth hormone (GH).[20-22] It might also exert a mild stimulative effect due to its ability to increase dopamine in the brain.[23]
Recommended dose: 300-600mg per day, but make sure you're aware that the powders are 50% silica-bound, and the labels of those supplements should say "Alpha GPC 50%". So 600mg of Alpha-GPC 50% is really 300mg Alpha-GPC, which yields an actual 121mg choline.
NutraBio Alpha GPC – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.
Which form is best?
The "best" form of choline may come down to how much you're willing to spend, but this is an area where we think spending more is worth it, because inferior forms lead to increased side effects (potentially due to conversion to TMAO). You can get the nootropic benefits from citicoline at a much lower dose than the bitartrate form, and with fewer concerns.
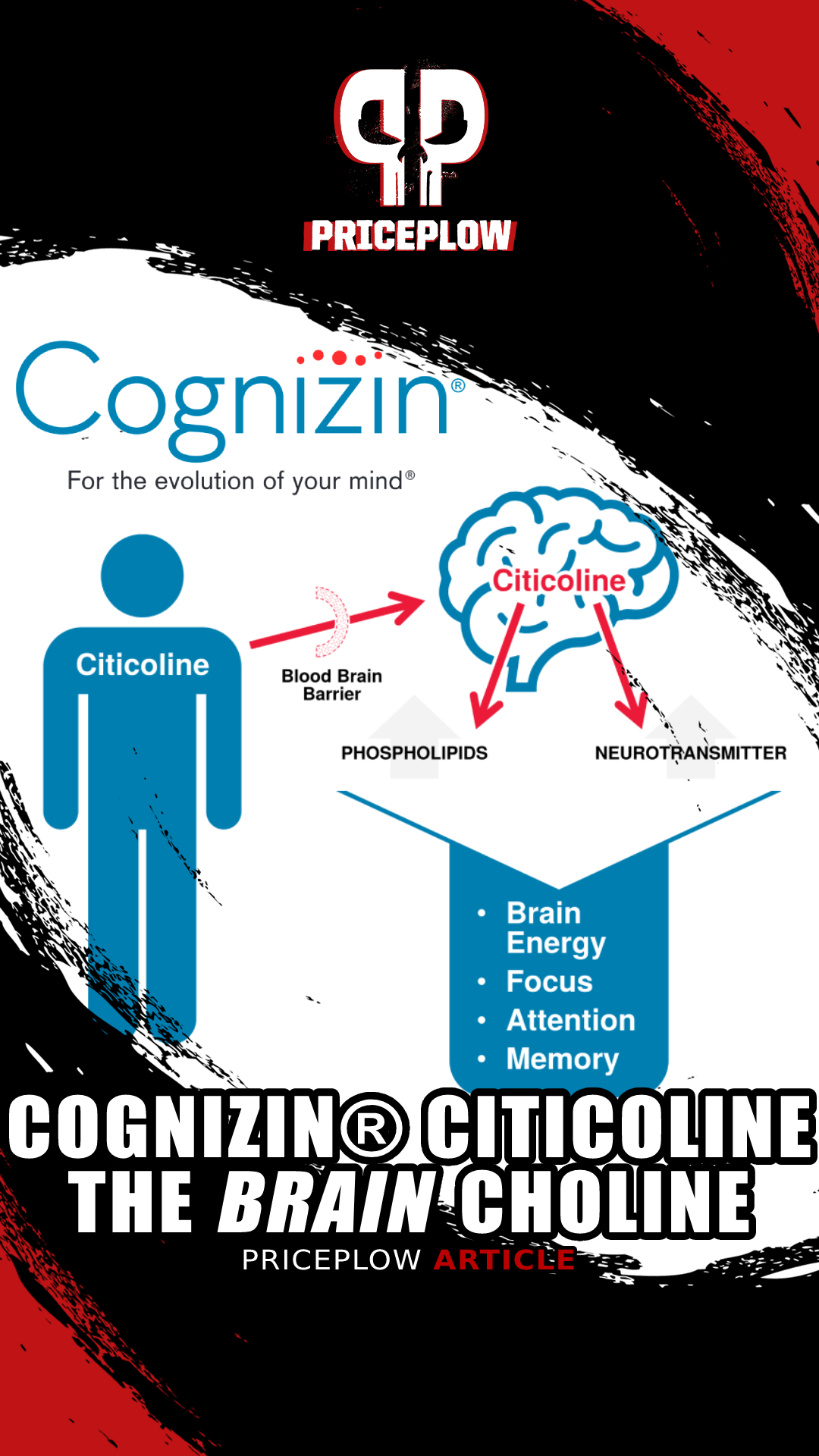
Cognizin® Citicoline is dubbed the The Brain Choline not just because it provides choline, but because it also supplies cytidine, which is also needed for the synthesis of phosphatidylcholine
From personal experience, we've noticed the most pronounced effects from supplementing with CDP-Choline / citicoline. Although these are a touch more expensive, they're potency and effectiveness more than make up for the cost.
Stacking Choline
While choline is great on its own, it also benefits from being stacked with a number of other ingredients which synergize with it and potentiate its effects in brain.
-
Caffeine + Choline
Caffeine is awesome for everything -- energy, mood, focus, and it's also great to pair alongside choline, which is why some many of our favorite nootropic formulas include caffeine and choline-based ingredients together.
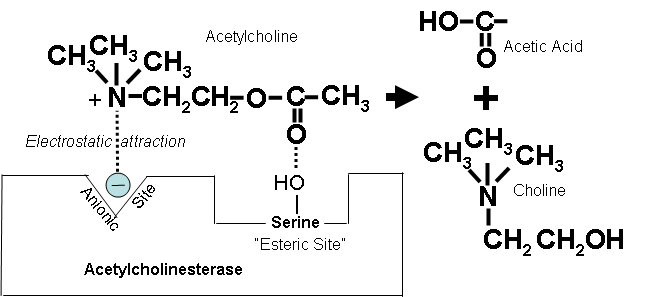
Caffeine has been shown to potentiate the effects of choline in the body, as well as inhibits acetylcholinesterase, resulting in increased production of acetylcholine that also stays active longer in the body.[24,25]
Recommended dose of Caffeine: 100-300mg depending on your preference / tolerance
-
Acetyl-L-Carnitine + Choline
Combining ALCAR and Choline is like matching Louisiana red beans and rice... it's a match made in heaven. These two contribute the two halves of acetylcholine, with ALCAR supplying the acetyl group and choline-based compounds providing the back half. As a bonus effect, you also might experience some increased fat loss and muscle gain too, at least if you were already carnitine-deficient (vegans and elderly).[26]
Recommended dose of ALCAR: 1-2g
-
Huperzine A + Choline
Huperzine is a potent inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase, the enzyme that degrades acetylcholine. Using huperzine along with a choline supplement not only increases production of acetylcholine, but also ensure the amount that is produced also stays around longer to exert its effects in the body.
Recommended dose of Huperzine: 100-200mcg
Takeaway
Whew! Did you make it to the end?
Choline is simply awesome stuff and you should want it as part of your daily supplement regimen, even if you're not a big nootropic nerd like we are.
As diets go more extreme - from vegan to keto - certain ones put you in severe deficiencies. In this case, it's vegans who are at risk, and choline is most definitely something that you do not want to be deficient in. But basically everyone benefits from supplementing this compound.
We prefer to go with CDP-Choline as it exerts the most potent / noticeable effects in terms of heightening focus, attention, and cognition -- but with fewer downsides.
Choline – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.




Comments and Discussion (Powered by the PricePlow Forum)