Bare Performance Nutrition was founded in 2012 by Nick Bare while he was studying nutrition at the Indiana University of Pennsylvania. That wasn't all, though: Nick was also preparing to enter the U.S. Army as an infantry officer. Since getting out of the military, he's kept up with his training as a hybrid athlete.

A perfect way to start your day - with a clinically-backed 250mg dose of Cognizin® Citicoline in BPN's Strong Multivitamin!
This focus on strength and endurance, combined with the military experience, is a great representation of where the supplement industry is heading. Traditionally, consumer supplements have been focused on strength, power, and muscle building – standard meathead stuff (which, don't get us wrong, we love). But now, thanks largely to the influence that military veterans like Nick are having on mainstream fitness culture, we're seeing average supplement consumers and amateur athletes alike focus more on balanced performance.
Dreams of deadlifting 1,000 pounds are giving way to dreams of deadlifting 600 and running a 6 minute mile, and the industry is responding to the growing demand for products that can help ordinary people become athletic generalists.
Bare Performance Nutrition's Strong Multivitamin – The First To Use Cognizin® Citicoline
Of course, sometimes it's easier said than done. Certain product categories are so simple in concept that they seem to resist reinvention – and the humble multivitamin is definitely one of them.
Yet, even here, Bare Performance has found a way to make things better. That's because the Bare Performance Nutrition Strong Multivitamin is the first (that we know of) to use Cognizin® citicoline, a patented and trademarked form of choline from Kyowa Hakko that we've covered several times before on the PricePlow Blog and will recap today.
In addition to using Cognizin®, BPN's multi has some other special features, like Sensoril ashwagandha for stress management and chromium, an important glucose regulator.
Let's get into how this works, but first, check the PricePlow news and deals:
Bare Performance Nutrition Strong Multi-Vitamin – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.
This area is reserved for Team PricePlow's upcoming videos.
Subscribe to our channel and sign up for notifications so you catch it when it goes live!
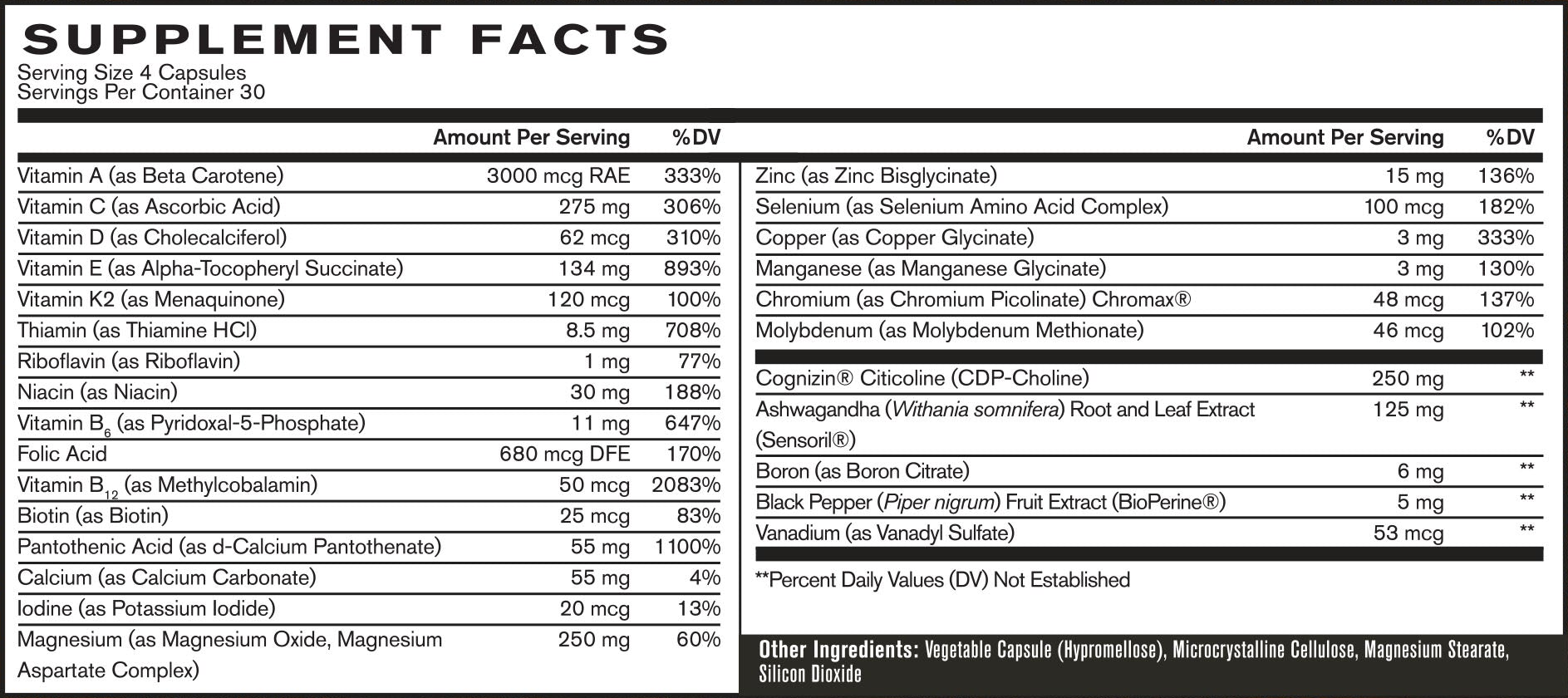
BPN Multivitamin Ingredients
In a single 4-capsule serving of the multivitamin from Bare Performance Nutrition, you get the following:
-
The Extra Ingredients: A Special Focus on Brain Health
Since the goal of any good multivitamin is to optimize health, multivitamins from premium brands usually include some extra supplemental ingredients that can improve some specific aspect of daily wellness. This is where we'll focus:
-
Cognizin® Citicoline (CDP-Choline) – 250 mg
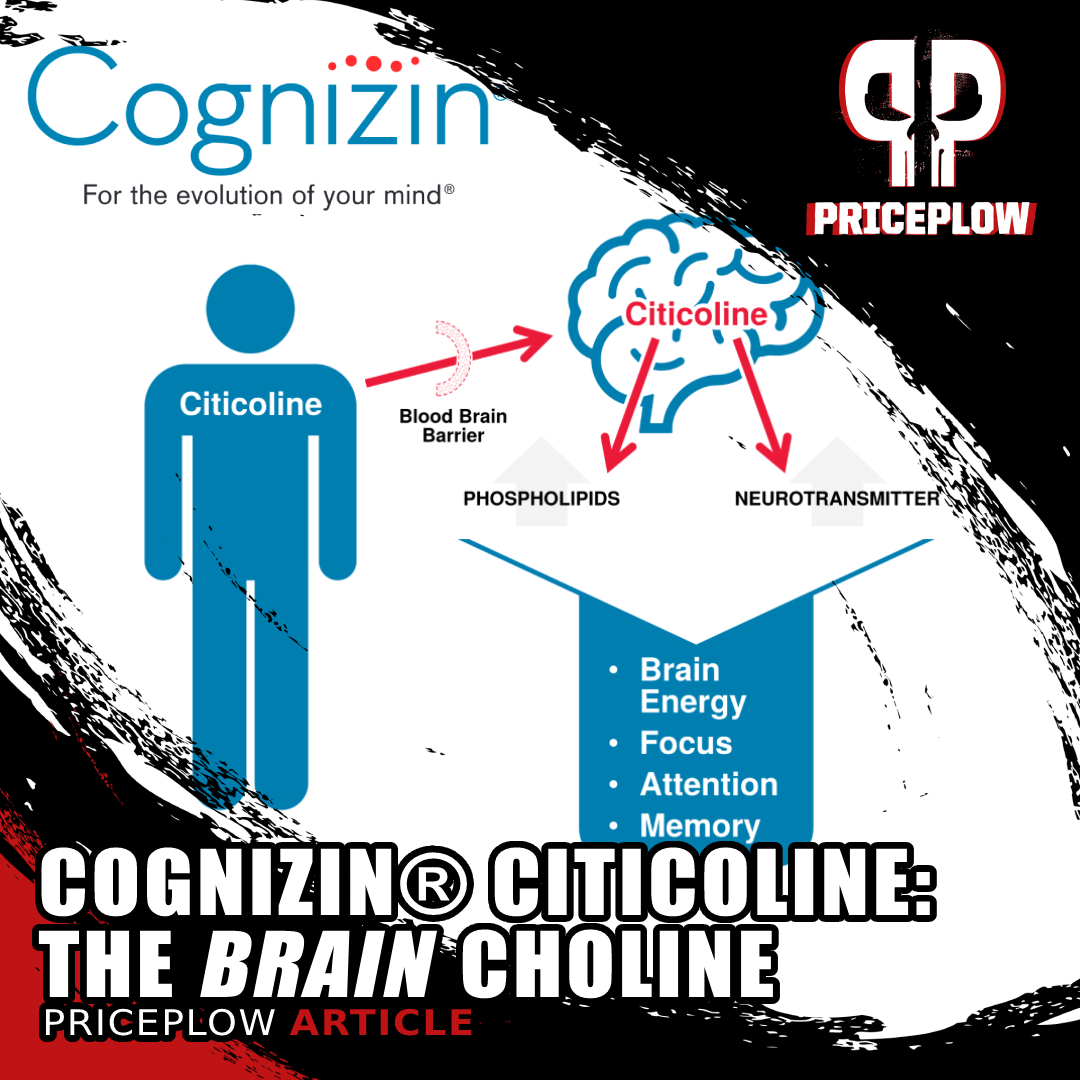
Cognizin® Citicoline is dubbed the The Brain Choline not just because it provides choline, but because it also supplies cytidine, which is also needed for the synthesis of phosphatidylcholine
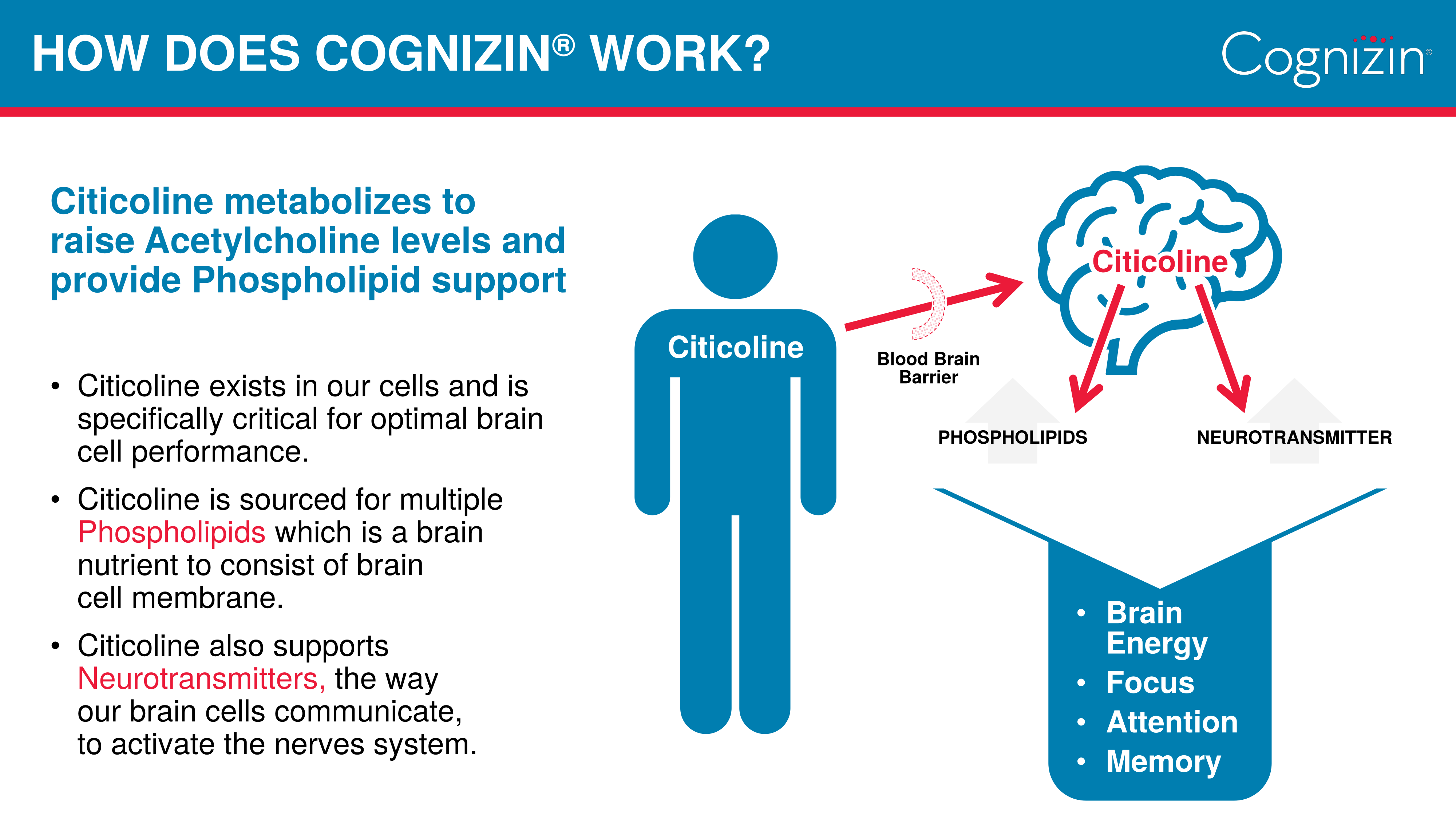
Choline is a necessary component for the synthesis of phospholipid bilayer membranes, the outer layer and barrier to entry for all of your body's cells.[1] This, in itself, is enough to make choline absolutely indispensable for optimal health and performance, but as if that weren't enough, choline is also a precursor to acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that governs the essential cognitive processes of learning and memory consolidation.[2]
Increasing acetylcholine synthesis reliably improves cognitive performance – not only when it comes to intellectual skills, but also cognitive motor skills like balance and coordination.[3,4]
But Cognizin® isn't just generic choline – it's citicoline, a molecule formed from choline and cytidine. Citicoline, unlike ordinary choline, is a direct precursor to phosphatidylcholine (PC), a phospholipid that's crucial for brain health and function.[5] In fact, citicoline availability is normally the rate-limiting factor in PC synthesis![6] Citicoline's ability to upregulate PC was confirmed by an MRI study that directly measured an increase in factors associated with PC production.[7]
Compared to other supplemental forms of choline, citicoline is the only one that's able to promote both acetylcholine and phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine, and phosphatidylserine -- the three brain cell membranes![7] See the image inset below for a graphic depiction.
Cognizin® specific research
The latest study performed on Cognizin® Citicoline was published in 2021, showing improved memory in healthy older adults.[9]
Randomized controlled trials performed specifically using Cognizin® have found that the patented and trademarked form of citicoline can support:
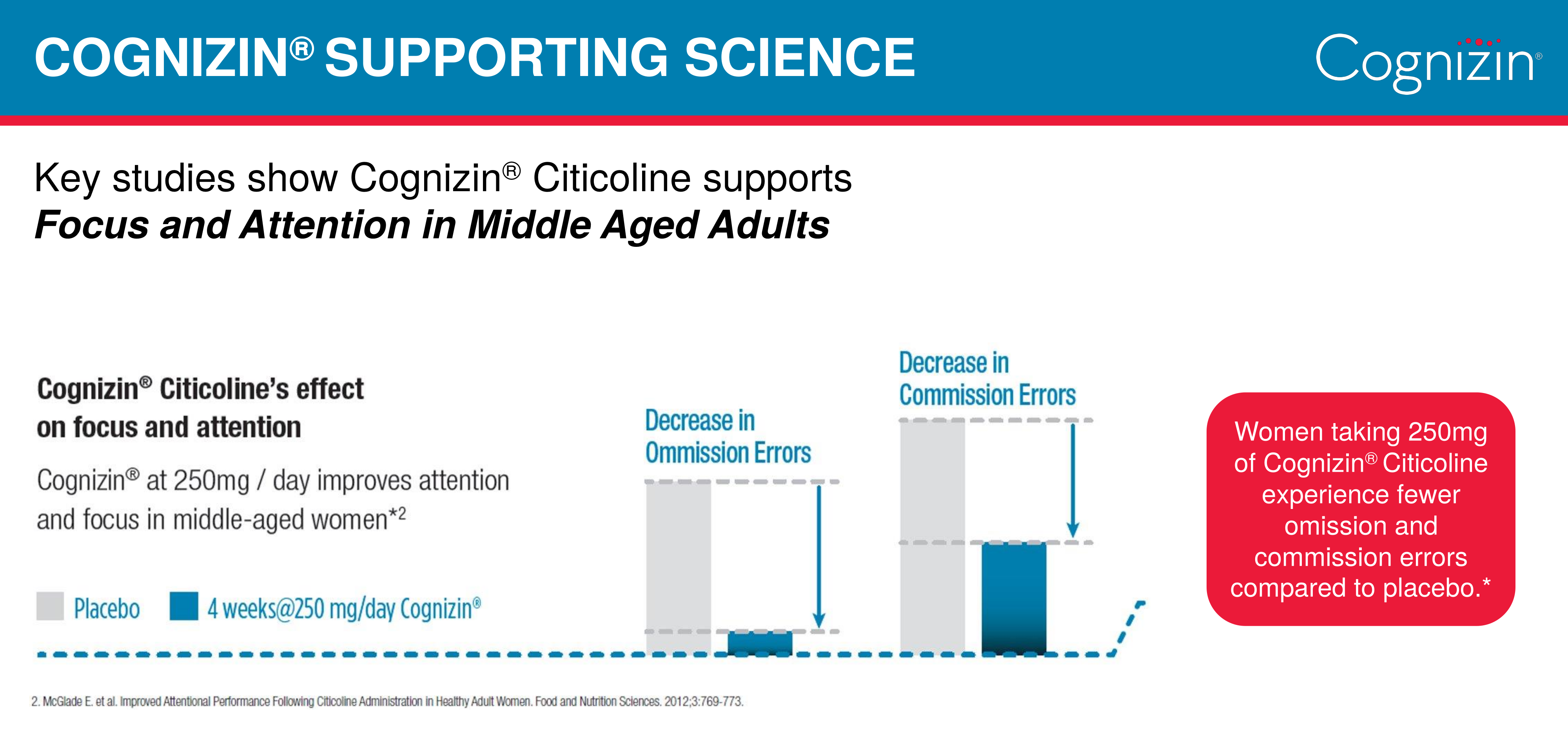
- Focus and attention (250+ milligrams)[8,10-12]
- Reduced errors while on task (250+ milligrams)[8,10]
- Brain and cognitive health (250+ milligrams)[8,10,12-14]
- Memory (500+ milligrams)[9]
- Energy utilization in the brain (500+ milligrams)[7,13,15,16]
- Acetylcholine production[11,15,17]
We're big on any branded ingredient company that supports this amount of research - as mentioned in PricePlow Podcast #118 by Joey Savage of Glaxon at SupplySide West 2023, one thing we love about Kyowa Hakko is their ability to provide "data data data"... and more data.
Supports memory in older adults
For instance, the most recent study published using Cognizin® showed statistically significant changes in memory scores in older adults.[9] We covered it in in an article specifically analyzing the data: "Research Study: Cognizin® Citicoline Improves Memory in Older Adults".
There's lots more to say about this awesome ingredient, including mechanisms and why it's superior to other forms of choline. If you want an in-depth analysis of how it works, check out our comprehensive article Cognizin® Citicoline: The Brain Choline.
A perfect match for a multivitamin
Ultimately, we're extraordinarily excited that a major brand has chosen to include this novel ingredient in a multivitamin, which is where we believe it belongs! After all, choline is an essential B-vitamin... and the popular products that contain Cognizin®, like pre-workout supplements and energy drinks, aren't always used every day. A multivitamin is.
-
Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) Root and Leaf Extract (Sensoril) – 125 mg
Ashwagandha is an adaptogen, meaning it can help normalize certain hormonal or metabolic processes. For example, if you have too much cortisol, an adaptogen could lower it, but also raise your cortisol if it's too low. This context-dependent ability makes adaptogens a powerful tool for optimizing performance, health and wellness.
Ashwagandha, in particular, is great for managing cortisol levels, and multiple studies have demonstrated its efficacy for managing both mental and physical stress.[18-21] Ashwagandha does this by regulating the hypothalamic-pituitary axis (HPA),[18] the hormone synthesis mechanism that's in charge of creating stress and adrenal hormones like cortisol, adrenaline, and noradrenaline.[18]
Besides keeping cortisol levels in an appropriate range, ashwagandha can also increase testosterone production in men.[18]
Anti-obesity
Staying or getting lean is a goal for many people today, so it will probably interest you to learn that ashwagandha increases the body's proportion of brown adipose tissue (BAT), a metabolically active kind of body fat that has the potential to burn calories as heat under certain conditions – e.g., after exposure to cold temperatures.[22] In the long run, this can help prevent unwanted weight gain.
What's Sensoril?
Sensoril is a patented ashwagandha extract consisting of whole leaf and root extract. Most ashwagandha extracts are root-only, which is unfortunate since the leaf contains withaferin A, one of ashwagandha's most powerful phytochemicals. By using Sensoril, Bare Performance is ensuring you get the dose of withaferin A that you should from ashwagandha supplementation.
-
Boron (as Boron Citrate) – 6 mg
Boron is a lesser-known mineral that nevertheless seems to play an important part in the production of both testosterone and vitamin D.[23] Since vitamin D itself can increase testosterone,[24] this means that boron has both a direct and indirect effect on serum testosterone.
Besides helping your body produce vitamin D, boron also extends vitamin D's half-life, which means the extra vitamin D you make will have an even greater impact on your health.[25] Plus, remember, we're talking about a multivitamin – there's already 310% of the vitamin D daily value being served here, which will synergize nicely with this dose of boron.
One small 2011 study found that boron supplementation can increase free testosterone, while decreasing estrogen.[23] Granted, this study had a sample size of eight, which is pretty small, so it ought to be taken with a grain of salt. Contrarily, there are concerns that high-exposure boric acid may be a reproductive toxin and is dose-dependently associated with testicular toxicity and reduced sperm counts in animal studies,[26] so it's important to consider both sides and total intake.
Still, there's plenty of evidence showing that boron can upregulate vitamin D and improve the body's uptake of magnesium, which is another mineral that's important for optimal testosterone levels.[27]
-
Black Pepper (Piper nigrum) Fruit Extract (BioPerine) – 5 mg
Kyowa Quality: Tested Dietary Supplement Ingredients Made in the USA! (BioKyowa)
Black pepper extracts are standardized for an alkaloid called piperine, which helps your body absorb nutrients more efficiently. Piperine does this by inhibiting certain stomach enzymes that ordinarily break down those nutrients before the nutrients have a chance to reach your intestines, where they could be absorbed into the bloodstream.[28]
Piperine can also improve insulin sensitivity by activating glucose transporter 4[29] and prevent fat from building up in the liver.[30] So while it's often used for absorption, there are metabolic benefits in tow.
Piperine is also a powerful antioxidant.[31]
-
Vanadium (as Vanadyl Sulfate) – 53 mcg
Vanadium is a trace mineral[32] that's important for glycemic control. Research has shown that supplemental vanadium can increase insulin sensitivity and help regenerate pancreatic beta cells in diabetic rats.[32] Vanadium's effect on hepatic (liver) insulin sensitivity makes it especially good for fighting the metabolic syndrome that's linked to type 2 diabetes.[33]
It's not totally clear how vanadium works, but it seems to actually mimic the hormone insulin,[34] thus directly facilitating appropriate glucose disposal.
-
-
Vitamins and Minerals
Of course, the core of any multivitamin is its vitamin and mineral content. We're glad to see Bare Performance using the best forms of certain vitamins and minerals:
- Cholecalciferol vitamin D (vitamin D3), which is better at increasing serum vitamin D than ergocalciferol (vitamin D2)[35]
- Menaquinone (MK-7), the most bioavailable form of vitamin K2[36]
- Methylcobalamin B12, instead of the less expensive but less effective cyanocobalamin. Besides acting as a potent methyl donor, methylcobalamin is also a bioidentical form of B12, unlike cyanocobalamin[37]
- Amino acid chelated forms of zinc, selenium, copper, manganese, molybdenum, and chromium. Chelated minerals are more bioavailable across the board than their non-chelated counterparts.[38-41]
Here are the basic nutrients you'll get from the Bare Performance multi:
-
Vitamin A (as Beta Carotene) – 3,000 mcg RAE (333% DV)
-
Vitamin C (as Ascorbic Acid) – 275 mg (306% DV)
-
Vitamin D (as Cholecalciferol) – 62 mcg (310% DV)
-
Vitamin E (as Alpha-Tocopheryl Succinate) – 134 mg (893% DV)
-
Vitamin K2 (as Menaquinone) – 120 mcg (100% DV)
-
Thiamin (as Thiamine HCl) – 8.5 mg (708% DV)
-
Riboflavin (as Riboflavin) – 1 mg (77% DV)
-
Niacin (as Niacin) – 30 mg (188% DV)
-
Vitamin B6 (as Pyridoxal-5-Phosphate) – 11 mg (647% DV)
-
Folic Acid – 680 mcg DFE (170% DV)
-
Vitamin B12 (as Methylcobalamin) – 50 mcg (2,083% DV)
-
Biotin (as Biotin) – 25 mcg (83% DV)
-
Pantothenic Acid (as d-Calcium Pantothenate) – 55 mg (1,100% DV)
-
Calcium (as Calcium Carbonate) – 55 mg (4% DV)
-
Iodine (as Potassium IOdide) – 20 mcg (13% DV)
-
Magnesium (as Magnesium Oxide, Magnesium Aspartate Complex) – 250 mg (60% DV)
-
Zinc as (Zinc Bisglycinate) – 15 mg (136% DV)
-
Selenium (as Selenium Amino Acid Complex) – 100 mcg (182% DV)
-
Copper (as Copper Glycinate) – 3 mg (333% DV)
-
Manganese (as Manganese Glycinate) – 3 mg (130% DV)
-
Chromium (as Chromium Picolinate) Chromax – 48 mcg (137% DV)
-
Molybdenum (as Molybdenum Methionate) – 46 mcg (102% DV)
Conclusion: A Cognitive-Boosting Multivitamin!

Kyowa SSW 2023 Panel: Branded Ingredients and Collaborative Competition with Dan, Joey, and Chris of Ghost, Glaxon, and Nutrabolt
It may seem like a small thing, but again, this is yet another industry trend toward a more holistic formulation philosophy. In the early days of the industry, the focus was all about physical health and performance. Cognitive support was usually an afterthought. But now, thanks to a spate of new research and a whole suite of new ingredients derived from it, industry leaders like Nick are optimizing for brain health everywhere they possibly can.
Bare Performance Multivitamin is a great entry in this product category. We love seeing the inclusion of extra ingredients focused on cortisol regulation and glucose disposal, as these are two increasingly problematic aspects of most modern Americans' personal health.
Bare Performance Nutrition Strong Multi-Vitamin – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.









Comments and Discussion (Powered by the PricePlow Forum)