In the supplement industry in general — but especially fat-burning supplements — there are a few mainstay ingredients that are backed by lots of research. These ingredients show up in tons of formulas because of their reliability. But interestingly enough, it's not that common to see all the mainstays together in the same formula.
This "back to basics" approach is why we appreciate ALLMAX Rapidcuts Thermo: Non-Stimulant Fat Burner. For the average consumer who's just getting into supplementation and doesn't know where to start, a product like Rapidcuts Thermo is definitely a good product to consider.

ALLMAX Rapidcuts Thermo takes some classic stim-free weight loss ingredients and combines them with our favorite new grains of paradise technology in CaloriBurn GP
Rapidcuts Thermo Stim-Free: Combine CaloriBurn Grains of Paradise with popular mainstream ingredients
As grains of paradise aficionados, we've found that the heated weight loss ingredient is well-accomplished in the world of sports nutrition supplements, but hasn't made as much impact in other weight loss circles.
Thanks to NNB Nutrition's innovations with CaloriBurn GP, combined with ALLMAX's use of "mainstream" Amazon-friendly ingredients such as CLA, green tea, garcinia cambogia, and green coffee bean extract, we have a stimulant-free supplement that can get marketed to the masses in North America and introduces them to our favorite fat burning spice.
This combines two weight loss generations, bridging the gap between ingredients familiar with dieters in the late 2000s and newer technologies we're more excited about now, like CaloriBurn GP. It's all covered below, but first use PricePlow to sign up for our alerts and check prices:
AllMax Nutrition Rapidcuts Thermo – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.
This area is reserved for Team PricePlow's upcoming Ingredients video.
Subscribe to our channel and sign up for notifications so you catch it when it goes live!
Rapidcuts Thermo Stimulant-Free Ingredients
Three capsules of ALLMAX Rapidcuts Thermo: Non-Stimulant Fat Burner is the daily recommended dose. In that, you get the following:
-
CaloriBurn GP (grains of paradise extract) - 40 mg
Headlined by NNB Nutrition's CaloriBurn, ALLMAX Rapidcuts Thermo takes some old-school, trusted ingredients and combines them with our favorite new grains of paradise technology
Kicking things off with the headline ingredient, CaloriBurn is a patented extract of the Aframomum melegueta, also known as grains of paradise. CaloriBurn, developed and manufactured by industry all-star NNB Nutrition,is standardized for 12.5% 6-paradol, a compound that changes the fat composition in the human body.
How does it work? First, you need some background information. There are two types of adipose (fat) tissue in the human body: white adipose tissue (WAT) and brown adipose tissue (BAT). They serve very different functions. Whereas WAT is used by the body to store energy for the long-term, to be used when calorie-intake is low,[1] BAT is responsible for a state known as non-shivering thermogenesis, which means it burns calories for heat to maintain your body temperature during cold exposure.[1]
Put simply, the more BAT you have (compared to WAT), the higher your metabolic rate will be.[2,3] And not just because BAT is burning fat: BAT can use glucose for thermogenesis as well.[4] This means that glucose uptake and blood lipids improve even in the absence of weight loss.[4]
CaloriBurn is a potent extract of Grains of Paradise, which has multiple fat burning positive effects!
6-paradol is the active ingredient in grains of paradise that drives the conversion of WAT to BAT, thus improving metabolism and aiding weight loss.
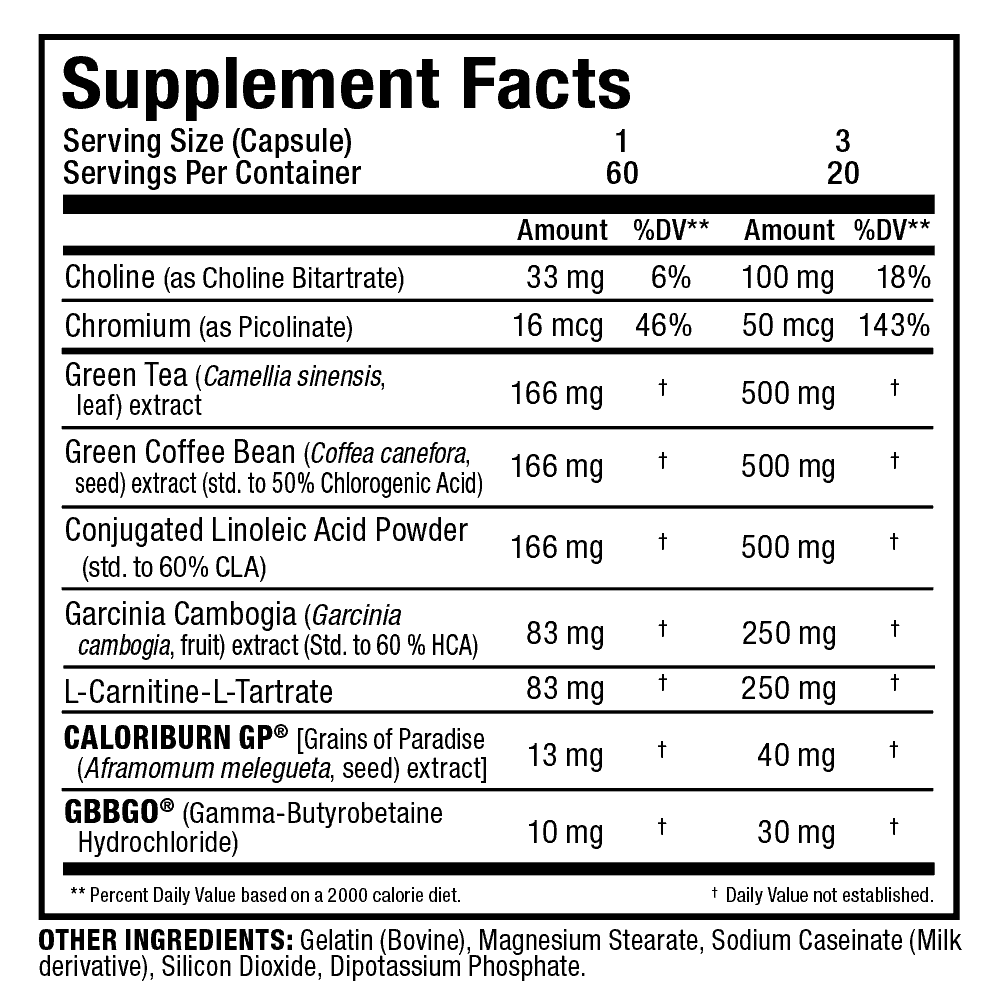
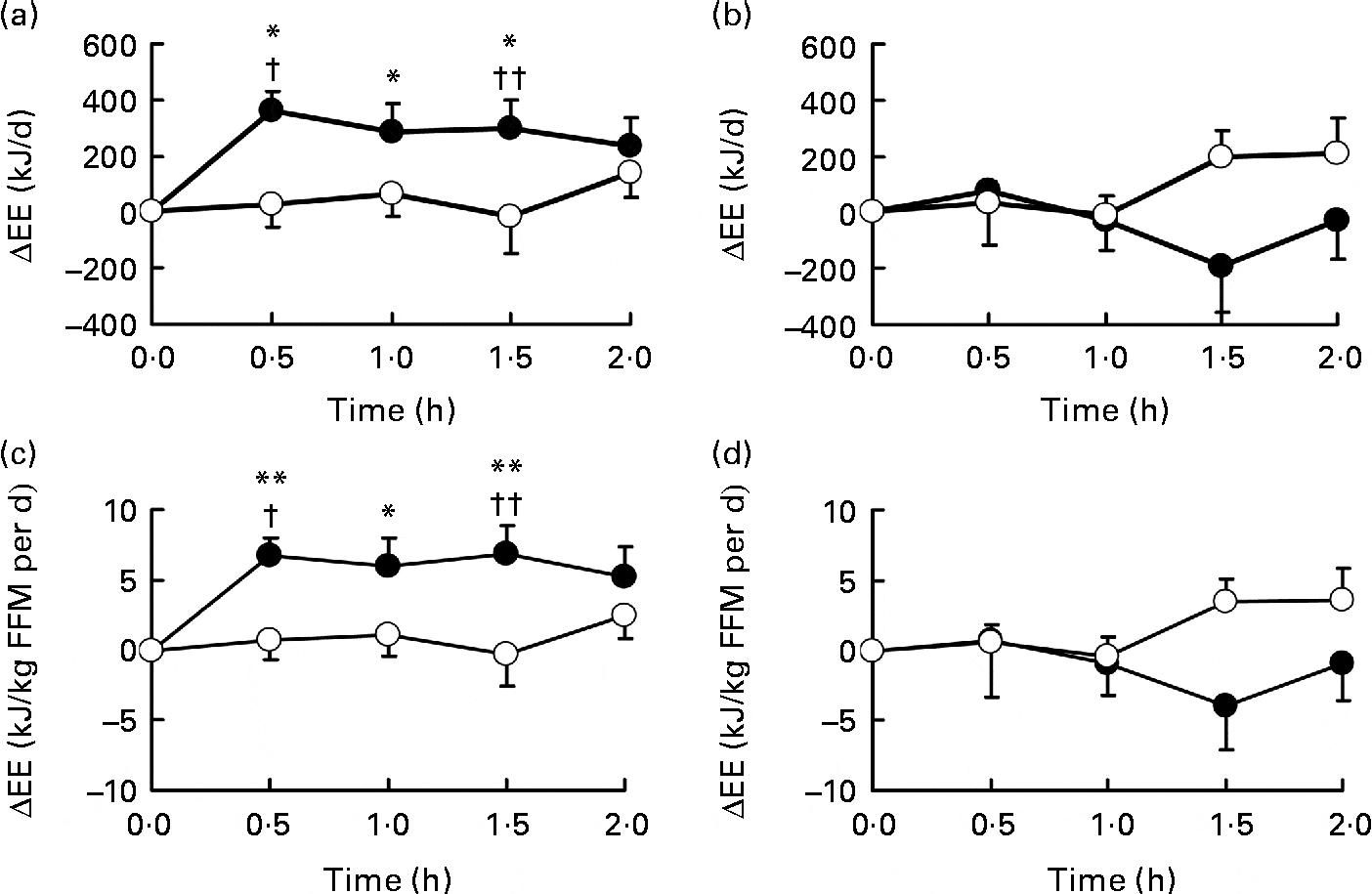
One of the great things about grains of paradise is that, unlike many widely-touted weight loss ingredients used by supplement manufacturers, there are actual human clinical trials that justify its use. Researchers gave 19 healthy men between the ages of 20 and 32 a 40 milligram dose of grains of paradise extract while measuring their energy expenditure. (Note that it's the same recommended daily dose contained in Rapidcuts Thermo.)They found that the men receiving grains of paradise had a higher basal metabolic rate than the controls, due to increased BAT activity.[5]
Energy expenditure change (ΔEE) after oral ingestion of Grains of Paradise.[3] This spice helps melt away those stubborn pounds!
Similarly, a study of grains of paradise supplementation in non-obese women was found to decrease their levels of visceral fat,[6] a particularly harmful type of fat that's linked to cortisol overproduction and chronic inflammation. This study used a smaller dose than the one suggested by Rapidcuts Thermo.
To learn more about this headline ingredient, see our articles titled CaloriBurn: NNB Takes Grains of Paradise to Hot New Heights! and CaloriBurn: NNB Takes Grains of Paradise to Hot New Heights!.
-
Green Tea extract - 500 mg
Here at PricePlow we often refer to green tea extract as a metabolic catch-all due to its numerous health benefits. At a generous 500-milligram dose, you should definitely expect to feel the following documented clinical effects of green tea extract:
- Higher levels of fat oxidation and loss of fat tissue[7]
- Improved blood circulation[8]
- Better insulin sensitivity[9,10]
- Lower blood pressure[11]
- Higher sense of overall well-being[11]
Finally, and most interestingly, green tea extract has something important in common with choline and chromium: its ability to help defat the liver. In this respect, green tea extract is actually backed and supported by clinical trials.
For example, in one 2016 study, people who took 500 milligrams of green tea extract for 90 days had significantly lower liver enzymes,[12] which is generally accepted as a proxy for liver health and function.
In another study, subjects with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease took green tea with high levels of catechins, the main class of antioxidants in green tea extract. This time, the researchers directly measured inflammation and fat in the subjects' livers and found that the tea significantly improved both metrics.[13]
-
Green Coffee Bean extract - 500 mg
Derived from green coffee, which simply refers to raw, unroasted coffee beans, green coffee bean extract (GCE) is standardized for a polyphenol called chlorogenic acid, also known as CGA.[14] Evidence is mounting that CGA has anti-inflammatory, anti-obesity, anti-diabetic, anti-carcinogenic, and antioxidant properties, in no small part thanks to its ability to improve the metabolism of both lipids and glucose.[14]
The journal Gastroenterology Research and Practice recently published a research review that found green coffee bean extract reduced the intestinal absorption of glucose and fat accumulation in the liver. The authors stated that, in their view, GCE reduces the synthesis of fat and cholesterol while also increasing the rate at which fat and cholesterol are oxidized by the body.[14]
The journal Phytotherapy Research published a study that found CGA can mobilize free fatty acids stored in body fat, thus making them available for use by the body even in the absence of co-administered caffeine. This implies that GCE could potentially aid in fat loss.[15]
-
Conjugated Linoleic Acid - 500 mg
Typically derived from dairy or red meat, conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) is an omega-6 fatty acid that has been gaining popularity as a supplement. There's good evidence for CLA's ability to improve body composition by reducing body fat.[16] Although the doses studied in that research were higher than what we see here, it should be noted that CLA is abundant in many of the foods that we at PricePlow regard as the cornerstone of a healthy, pro-metabolic diet. So having a little extra 500-milligram boost won't hurt at all.
For people who can't tolerate dairy because of a sensitivity to lactose or casein, CLA supplementation can help replace nutrients they're deprived of from a non-dairy diet, and in that case, you may want to consider getting even more.
-
Garcinia Cambogia Extract (fruit rind) standardized to 60% HCA - 250 mg
A less common but still popular stimulant-free fat-burning ingredient, Garcinia cambogia extract, derived from the fruit of that tree, is standardized for a substance called hydroxy citric acid (HCA). One interesting thing to note about the extract used in ALLMAX Rapidcuts Thermo is that it's standardized for 60% HCA -- slightly higher (and thus, presumably, more efficacious) than the 50% standardization we usually see in Garcinia extracts.
Garcinia hasn't been studied much, but what limited research that exists is promising. A team of scientists from South Africa have reported that Garcinia cambogia can help reduce appetite, increase the rate at which the body burns fat for fuel, and decrease lipogenesis, the process by which the body synthesizes new fat.[17] Additionally, Garcinia appears to increase insulin sensitivity, which implies it will help regulate blood glucose and increase satiety after meals.[17]
The benefits of Garcinia appear to go beyond weight loss: HCA, the main bioactive compound, seems to have anti-inflammatory, anti-carcinogenic, and antidiabetic properties.[17] It also potentially lowers blood triglycerides, extends the action of acetylcholine, and protects the liver.[17] The common denominator in all of this might be that HCA inhibits an enzyme called adenosine triphosphate citrate lyase, which is centrally implicated in the synthesis of triglycerides, cholesterol, and fatty acids.[17]
We're glad to see a 60% HCA extract in ALLMAX Rapidcuts Thermo since that's the concentration that seems to have the most significant health benefits.[17]
-
L-Carnitine L-Tartrate - 250 mg
Carnitine can help the body burn more fat for energy. It transports free fatty acids to the mitochondria, where they are burned as fuel and converted into ATP.[18] On the other hand, low levels of carnitine means that your mitochondria burn less fat for fuel, which obviously is not great if you're trying to lose fat.
L-carnitine tartrate is used because of its superior bioavailability and rate of action.[19] Because of its impact on metabolism, carnitine has been shown to positively affect blood glucose, insulin sensitivity, and post-exercise muscle tissue recovery.[20,21]
-
Choline - 100 mg (total yield), or 18% DV
Even though your liver is capable of synthesizing some choline for use by your body, the compound is considered an essential nutrient because the body requires more than your liver can synthesize.[22] While consuming some choline through supplementation or diet is important, most of the population doesn't get enough.[23]
With regards to fat burning, the main reason to take choline is that it's required to produce a substance that transports fat and cholesterol out of your liver.[23,24] That's important because if you're carrying around even a small amount of extra weight, chances are you have some degree of fatty liver—a condition associated with obesity and the metabolic syndrome.[25] Because fatty liver itself can impair the metabolism of glucose and lipids,[26] it's difficult to achieve a lean body composition without providing your liver with optimal support.
By helping to de-fat the liver, choline supplementation can potentially support weight loss.
This may not seem like a monster dose, but realize that the 100 milligrams is the total yield of choline in the nutrition portion of the panel! Since choline bitartrate is 41% choline by weight, there's actually somewhere closer to 240-250 milligrams of choline bitartrate inside - which is how we often see it labeled.
-
Chromium - 50 mcg
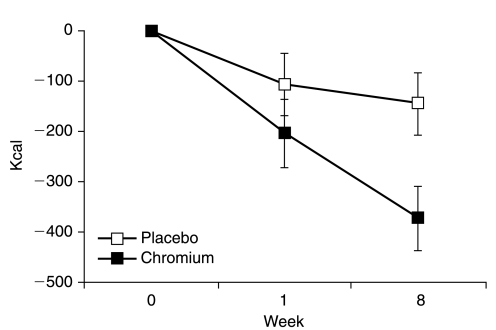
In this study, high-dose chromium picolinate had a profound effect on appetite.[27] This is why we're not against taking even more than what's provided by ALLMAX here.
Through its interaction with the insulin system,[28-30] chromium has been repeatedly shown to improve glucose and insulin sensitivity, especially in people with significant insulin resistance.[31,32] Of all forms of chromium on the market, picolinate seems to be the most effective.[32]
People who take chromium supplements have a lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes,[33] and conversely, people with diagnosed chromium deficiency have a significantly higher risk of diabetes and other metabolic disorders.[34] Much like choline, chromium has been shown to help defat tissues in places where fat does not belong,[35] such as the liver.
As shown in the nutrition facts up top, this is coming from chromium picolinate, our favorite form of chromium. In all honesty, if you have metabolic issues and aren't sure about the nutrient density of your diet, it wouldn't be a bad idea to get more chromium -- there's solid research anywhere from 200 milligrams up to 1000 milligrams. You can learn more about this ingredient in our article titled Chromax Chromium Picolinate: 25+ Years of Insulin Sensitivity Improvement.
-
Gamma-butyrobetaine hydrochloride (GBB) - 30 mg
GBB Supplements add to the "carnitine pool" by increasing the reagent -- GBB -- which goes on to make more carnitine if your body needs it!
Gamma-butyrobetaine hydrochloride (GBB) is a precursor to L-carnitine and amplifies the effects of carnitine in the body, meaning that it synergizes very well with L-carnitine L-tartrate. By increasing thermogenesis, it can accelerate the amount of fat the body burns as heat.[36,37]
Combined with CaloriBurn GP, you may find yourself sweating a bit more during exercise with this ingredient, as it pushes the "carnitine pool" to new heights, allowing for more mitochondrial benefits. We often enjoy 2 grams of carnitine per day, but can't fit that into capsules -- combining L-Carnitine with GBB is a great way to get the most out of space constraints.
To learn more about this heated and interesting ingredient, see our article titled GBB (Gamma-Butyrobetaine Ethyl Ester): Super Carnitine That Makes You Sweat?!.
Conclusion
ALLMAX Rapidcuts Thermo Non-Stimulant Fat Burner is a product with some time-tested and trusted ingredients. However, it's time to introduce readers who are searching for those ingredients to the real powerhouse - grains of paradise powered by CaloriBurn GP. This blends the "old school" with the new, and that's something we're always good with if it brings dieters a new human-researched ingredient to test out.
Realize that a few ingredients in here are what we consider "under-dosed", and if you're not eating a nutrient-dense diet, you may get serious benefits from additional carnitine, chromium, and choline. However, our take is that most readers will come for the garcinia and CLA, but leave with the grains of paradise - and that's OK by us. The way ALLMAX is marketing it, they're using it as a low-cost addition to their stacks, so the price is right as well.
If you aren't taking any other carnitine supplements and don't eat much meat, you may want to consider taking more than the recommended daily serving of three capsules per day... but don't be surprised if the grains of paradise and GBB heat you up beyond expectations!
AllMax Nutrition Rapidcuts Thermo – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.








Comments and Discussion (Powered by the PricePlow Forum)