The supplement world is always seeking that next breakthrough ingredient -- something that genuinely delivers on promised benefits with research to back it up. MitoBurn (L-BAIBA) from NNB Nutrition has established itself as exactly that kind of ingredient, thanks to its metabolic benefits as an "exercise mimetic".

New research shows MitoBurn (L-BAIBA) from NNB Nutrition significantly enhances glycogen storage after exercise. Study found 140-152% higher muscle glycogen and up to 235% higher liver glycogen. Could be a breakthrough for athletes and fitness enthusiasts!
Now, exciting new internal research from the NNB R&D team suggests MitoBurn has another powerful capability: dramatically enhancing glycogen supercompensation after exercise.
MitoBurn and Glycogen Supercompensation?!
Glycogen supercompensation refers to the body's ability to store more carbohydrates as glycogen than normal, providing additional energy reserves for intense physical activity. When properly optimized, this process can enhance athletic performance, delay fatigue, and improve recovery between training sessions. For anyone concerned with performance or body composition, finding ways to direct more carbohydrates toward glycogen storage rather than fat storage represents a significant metabolic advantage.
This effect could make MitoBurn a game-changing supplement for athletes, fitness enthusiasts, and anyone looking to optimize their body's use of carbohydrates.
Before diving into the details, make sure you don't miss future updates on MitoBurn and other innovative ingredients by subscribing to our NNB Nutrition news alerts:
Subscribe to PricePlow's Newsletter and Alerts on These Topics
What is MitoBurn? A Quick Refresher
MitoBurn is NNB Nutrition's purified, stabilized form of L-β-aminoisobutyric acid (L-BAIBA), the active isomer of BAIBA. This metabolite is naturally produced during exercise when our muscles break down the amino acid valine.
BAIBA functions as a signaling molecule, essentially telling our body that exercise is happening. This triggers a cascade of beneficial metabolic responses, even without the actual exercise. This is why BAIBA has been nicknamed the "exercise molecule."[1]
Since its launch, MitoBurn has gained popularity for supporting:[2]
- Conversion of white fat to metabolically active brown/beige fat
- Enhanced fatty acid oxidation
- Improved metabolic health markers
- Support for healthy insulin sensitivity
What makes MitoBurn special is that it delivers the active L-isomer of BAIBA, as opposed to less effective forms. It's also extremely soluble and stable, making it perfect for beverages and liquid supplements, as we recently explored in our MitoBurn in the Bottle article on its beverage stability.
But now there's a new potential benefit to add to the list: enhanced glycogen supercompensation.
New Research: MitoBurn Dramatically Boosts Glycogen Storage
Internal research from NNB Nutrition has revealed that MitoBurn supplementation can significantly enhance glycogen storage following exercise and carbohydrate consumption.
This study, while not yet peer-reviewed or published, provides fascinating preliminary data on MitoBurn's potential for optimizing how our bodies store and utilize carbohydrates.
The Study Design
The researchers used 40 male ICR mice divided into five groups:
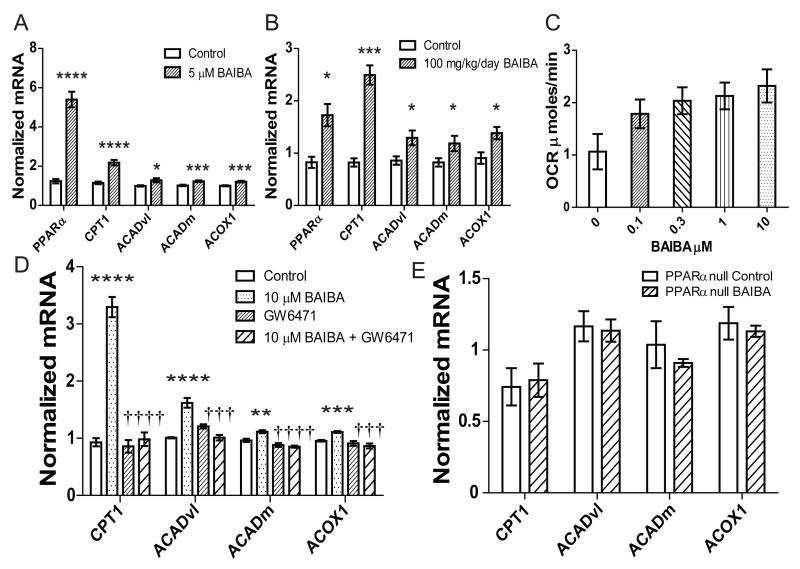
Multiple experimental panels showing BAIBA significantly increases expression of key fatty acid oxidation genes in both cell culture and live animal models. The data demonstrates dose-dependent metabolic activation through PPARα pathways, supporting BAIBA's role in enhancing energy utilization.[1]
- Control (sterile water)
- Exercise control (sterile water)
- Exercise + carbohydrate/protein (glucose + casein)
- Exercise + carbohydrate/protein + 200mg/kg MitoBurn
- Exercise + carbohydrate/protein + 400mg/kg MitoBurn
The mice were supplemented with their treatments for 28 consecutive days. On the experimental exercise day, the mice ran on a treadmill at 25m/min for 90 minutes. Immediately after exercise, the mice in groups 3-5 received glucose and casein protein. After 30 minutes of recovery, tissues were harvested to measure muscle and liver glycogen content.
The Results: Massive Increases in Glycogen Storage
The results were nothing short of remarkable:
Muscle Glycogen:
- The 200mg/kg MitoBurn group showed 140.2% higher muscle glycogen content compared to the exercise + carb/protein group
- The 400mg/kg MitoBurn group showed 152.3% higher muscle glycogen content
Liver Glycogen:
- The 200mg/kg MitoBurn group showed 147.3% higher liver glycogen content compared to the exercise + carb/protein group
- The 400mg/kg MitoBurn group showed an incredible 235.2% higher liver glycogen content
What makes these results particularly interesting is that they occurred just 30 minutes after carbohydrate consumption – a remarkably rapid response.
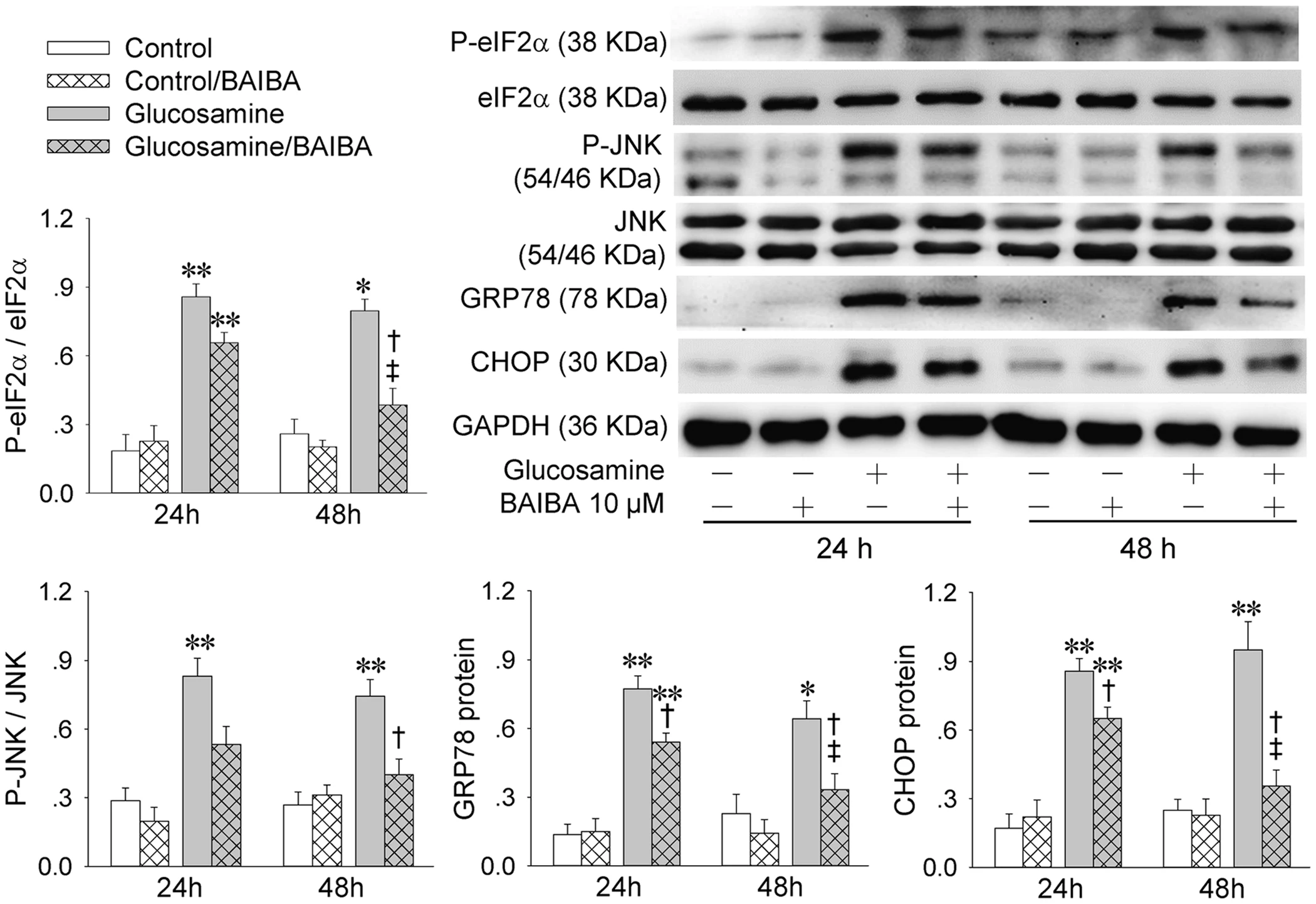
Laboratory analysis showing how BAIBA treatment significantly counteracts glucosamine-induced cellular stress. Western blot results demonstrate reduced phosphorylation of stress markers at both 24 and 48-hour timepoints, supporting BAIBA's protective effects on metabolic health.[3]
Human Equivalent Dosages
Converting the effective doses from this study to human-equivalent doses:
- 200mg/kg in mice converts to approximately 16.2mg/kg for humans, or about 1,134mg (1.1g) for a 70kg person
- 400mg/kg in mice converts to approximately 32.4mg/kg for humans, or about 2,268mg (2.3g) for a 70kg person
While these are higher than typical supplemental doses, they're well within the safety profile established for MitoBurn (which we'll discuss later).
Why Glycogen Supercompensation Matters
Glycogen is the body's stored form of carbohydrates, primarily found in muscles and liver. It's the primary fuel source for high-intensity exercise and plays a crucial role in endurance performance. When glycogen stores are depleted, performance suffers dramatically -- this is the dreaded "bonk" or "hitting the wall" that athletes fear.
Glycogen supercompensation refers to the process of deliberately increasing glycogen storage beyond normal levels. Traditionally achieved through carb-loading protocols, this strategy helps maximize available energy for demanding physical activities.
But MitoBurn appears to take glycogen supercompensation to another level by enhancing the body's ability to store carbohydrates as glycogen rather than fat. This has several potential benefits:
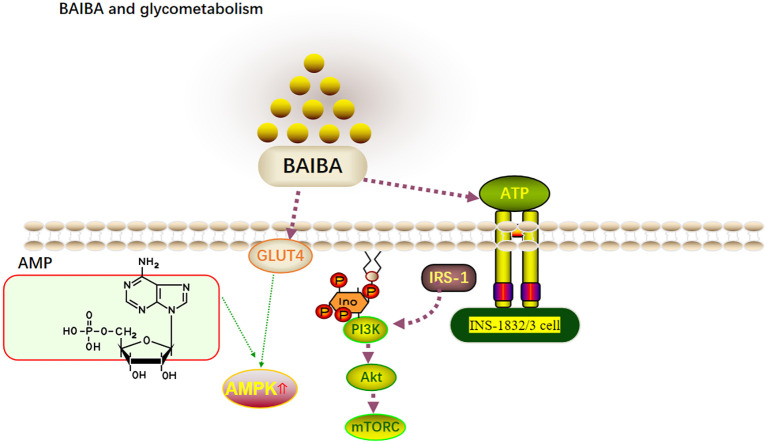
BAIBA activates multiple cellular pathways that enhance glucose transport and utilization. This signaling cascade involves GLUT4 translocation and AMPK activation, helping explain the compound's benefits for glycogen storage and energy metabolism.[2]
- Improved Nutrient Partitioning: More carbohydrates stored as glycogen means fewer calories diverted to fat storage
- Enhanced Performance: Higher glycogen reserves translate to more available energy during workouts or competitions
- Faster Recovery: Accelerated glycogen replenishment speeds recovery between training sessions
- Body Recomposition Potential: Supporting the use of calories for fuel and glycogen storage rather than fat accumulation
The significant increases in both liver and muscle glycogen are particularly notable. Muscle glycogen primarily fuels working muscles during exercise, while liver glycogen helps maintain blood glucose levels between meals and during overnight fasting.
Possible Mechanisms: How Does MitoBurn Enhance Glycogen Storage?
While the exact mechanism behind MitoBurn's glycogen-enhancing effects wasn't determined in this study, we can make educated hypotheses based on what we know about BAIBA's action in the body.
BAIBA is known to:

MitoBurn L-BAIBA Powder is nearly tasteless, with just a smidgen of bitterness that's easily covered up.
- Activate AMPK: This "energy sensor" plays a key role in cellular energy homeostasis and can enhance glucose uptake into muscle cells[4]
- Improve Insulin Sensitivity: Better insulin function means more efficient glucose transport into cells where it can be stored as glycogen[3]
- Enhance Mitochondrial Function: Improved energy efficiency may allow for greater glycogen synthesis[1]
Other possibilities include the ability to increase expression of glucose transporters and optimize enzymatic activity.
Regardless of the exact mechanism, the results suggest that MitoBurn creates a metabolic environment that strongly favors glycogen formation over fat storage when carbohydrates are consumed after exercise.
Strategic Implementation: Timing and Stacking
This can be used by anyone from endurance athletes to strength athletes to team sports events... and before bodybuilding events too!
Based on the study design, the optimal strategy for leveraging MitoBurn's glycogen-enhancing effects would include:

MitoBurn L-BAIBA from NNB Nutrition is remarkably soluble at 737g/L -- making it perfect for RTDs and liquid supplements! While most ingredients struggle in beverages, MitoBurn thrives.
- Consistent Supplementation: The study used 28 days of consistent supplementation before the test day
- Exercise First: Perform some form of glycogen-depleting exercise
- Carb + Protein Intake: Consume carbohydrates with protein shortly after exercise
- Timing: The study showed benefits as soon as 30 minutes after carbohydrate consumption
This protocol could also be effective when implemented around holidays or other occasions when carbohydrate intake is likely to be higher.
Potential Stacking Options:
MitoBurn could potentially be stacked with other ingredients for enhanced effects:
- GlucoVantage® (Dihydroberberine): For improved glucose disposal and insulin sensitivity
- Chromium: For additional support of insulin function
- Alpha-lipoic acid: For enhanced glucose uptake
Safety Profile: Is This Much MitoBurn Safe?
The human-equivalent doses derived from this study (1.1-2.3g per day) are higher than what's typically found in most supplements (250-500mg). However, toxicology data for MitoBurn is reassuring.
Internal safety studies conducted according to OECD guidelines have demonstrated:
- An LD50 (median lethal dose) greater than 2000 mg/kg body weight in acute oral toxicity studies
- Non-mutagenic in bacterial reverse mutation assays
- Non-clastogenic/non-mutagenic in in vitro micronucleus tests at concentrations up to 2000 μg/mL
These findings place MitoBurn in "Category 5" of the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS), indicating relatively low toxicity.
These safety data suggest that higher doses could be explored for specific applications, especially around exercise and carbohydrate consumption.
Conclusion: MitoBurn’s Expanding Potential
The new research on MitoBurn's ability to enhance glycogen supercompensation adds another impressive capability to this already remarkable ingredient. By significantly improving the body's ability to store carbohydrates as glycogen rather than fat, MitoBurn offers exciting possibilities for athletes, fitness enthusiasts, bodybuilders, or those simply looking to better manage their metabolism during periods of higher carbohydrate intake.

NNB Nutrition has finally brought us a trusted and tested form of L-BAIBA, which we call an "exercise signal" that kickstarts incredible metabolic processes! It's known as MitoBurn and it helps kick-start the 'exercise program'!
While we await peer-reviewed publication of findings like these, the preliminary data suggest that MitoBurn may be even more versatile than previously thought. Its safety profile and near-decade of safe use, combined with its exceptional solubility (as covered in our MitoBurn in the Bottle article), positions MitoBurn as an increasingly valuable tool in the supplement arsenal.
For anyone looking to optimize their body's handling of carbohydrates, enhance recovery, or improve nutrient partitioning, MitoBurn appears to offer a research-backed approach worth considering.



Comments and Discussion (Powered by the PricePlow Forum)