VC-H1 from Freemen Nutra delivers real plant-based collagen peptides from hibiscus. Clinical study shows superior skin benefits at just 1.5g daily -- 1.7-4x more potent than animal collagen.
The collagen supplement market faces a fundamental contradiction: consumers spend billions annually on a protein that isn't nutritionally complete, raises ethical and sustainability concerns, and requires massive doses to show modest benefits. Animal-derived collagen contains minimal essential amino acids and lacks tryptophan entirely, and typically demands 5-15 grams daily to deliver results.[1] Meanwhile, most "vegan collagen" products offer amino acid blends or botanical "boosters" without the bioactive peptides that actually stimulate collagen synthesis. And marine collagen sources simply don't taste or smell acceptable.
Put simply, we have a multi-billion dollar problem that's long been looking for a solution -- and that solution is finally here.
Enter VC-H1 Botanic Collagen Peptides from Freemen Nutra, the first plant-based collagen alternative containing genuine bioactive di- and tripeptides proven to stimulate collagen production. Derived from organically grown Hibiscus sabdariffa, VC-H1 delivers the same collagen-stimulating peptide sequences found in animal collagen, what's known as G-X-Y-patterned di- and tri-peptides including but not limited to Pro-Hyp, Gly-Pro-Hyp, and Hyp-Gly. The novel ingredient addresses every limitation of conventional collagen supplements, all covered in this article today.
Collagen Consumers Demand Real Alternatives
The motivation for collagen alternatives extends far beyond veganism. Religious dietary requirements (halal, kosher) exclude many animal sources. Sustainability-conscious consumers criticize animal agriculture's supply chain and feed requirements. Others face allergen concerns, or simply question spending premium prices on an incomplete protein. Quality remains a barrier, with too many inexpensive and poorly-studied collagen ingredients on the market.
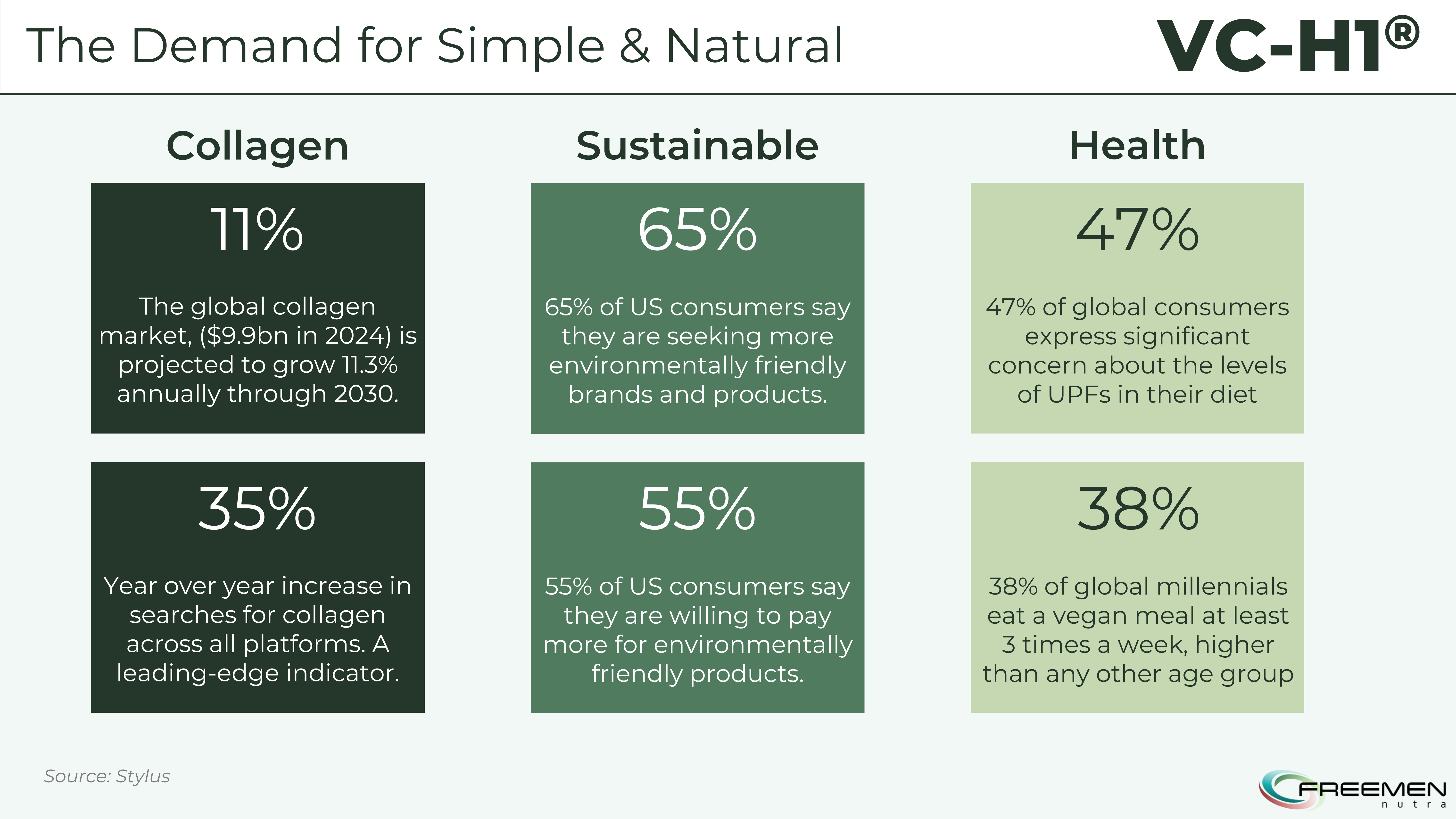
The numbers tell the story - 65% of consumers want more sustainable products, while the collagen market's explosive 35% year-over-year growth shows you're not alone in seeking better alternatives to traditional animal-based options.
Perhaps most importantly, awareness grows that collagen's benefits stem not from replacing structural protein, but from specific bioactive peptides that signal fibroblasts to synthesize new collagen. This understanding creates demand for high-quality alternatives that deliver these functional peptides without animal sourcing.
The VC-H1 Breakthrough
VC-H1 solves the collagen conundrum through three key advantages:

Peptide awareness has skyrocketed with a 550% surge in searches during 2025 alone, and now you can understand why - these mini-proteins act as cellular signals that activate your body's natural processes.
- Plant-based source: Derived from hibiscus, VC-H1 sidesteps any and all of the various dietary and ethical concerns surrounding animal collagen sources.
- Real bioactive peptides: With 85-90% di- and tripeptide content and an ultra-low 316 Da molecular weight, VC-H1 contains the actual collagen-stimulating sequences, not amino acid substitutes. In vitro studies show VC-H1 stimulates collagen synthesis at 0.1% concentration while animal collagen requires 0.25% for equivalent results, providing 1.7-4.0x superior potency.
- Clinical validation: A 12-week double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (n=98) demonstrated significant improvements in skin hydration, elasticity, wrinkle depth, and barrier function using objective instrumentation (p<0.001 across multiple measures). This represents gold-standard evidence rare in the supplement industry.
- Lower effective dose: At just 1.5 grams daily versus typical collagen's 5-15 gram requirement, VC-H1 reduces cost, improves formulation flexibility, and enables delivery formats impossible with traditional collagen powders.
This article explores the science behind VC-H1's bioactive peptides, examines the clinical evidence validating its efficacy, and investigates the mechanisms that make hibiscus-derived collagen peptides a genuine alternative rather than another amino acid blend. We'll also cover practical formulation considerations and market positioning for this breakthrough ingredient.

Meet the world's first truly botanical collagen peptide - sourced from organically grown hibiscus and delivering superior Type I collagen synthesis compared to animal sources, all while being completely vegan-certified.
Before diving in, make sure you're subscribed to our VC-H1 and Freemen Nutra news alerts, as there's more on the horizon:
Subscribe to PricePlow's Newsletter and Alerts on These Topics
The Collagen Supplement Landscape
Collagen serves as the body's primary structural protein, comprising one-third of total body protein and providing the scaffolding for skin, tendons, cartilage, bone, and connective tissue.[2] The protein's distinctive amino acid profile -- 33% glycine, 23-25% proline, and hydroxyproline combined -- gives it unique structural properties through its triple-helical configuration.
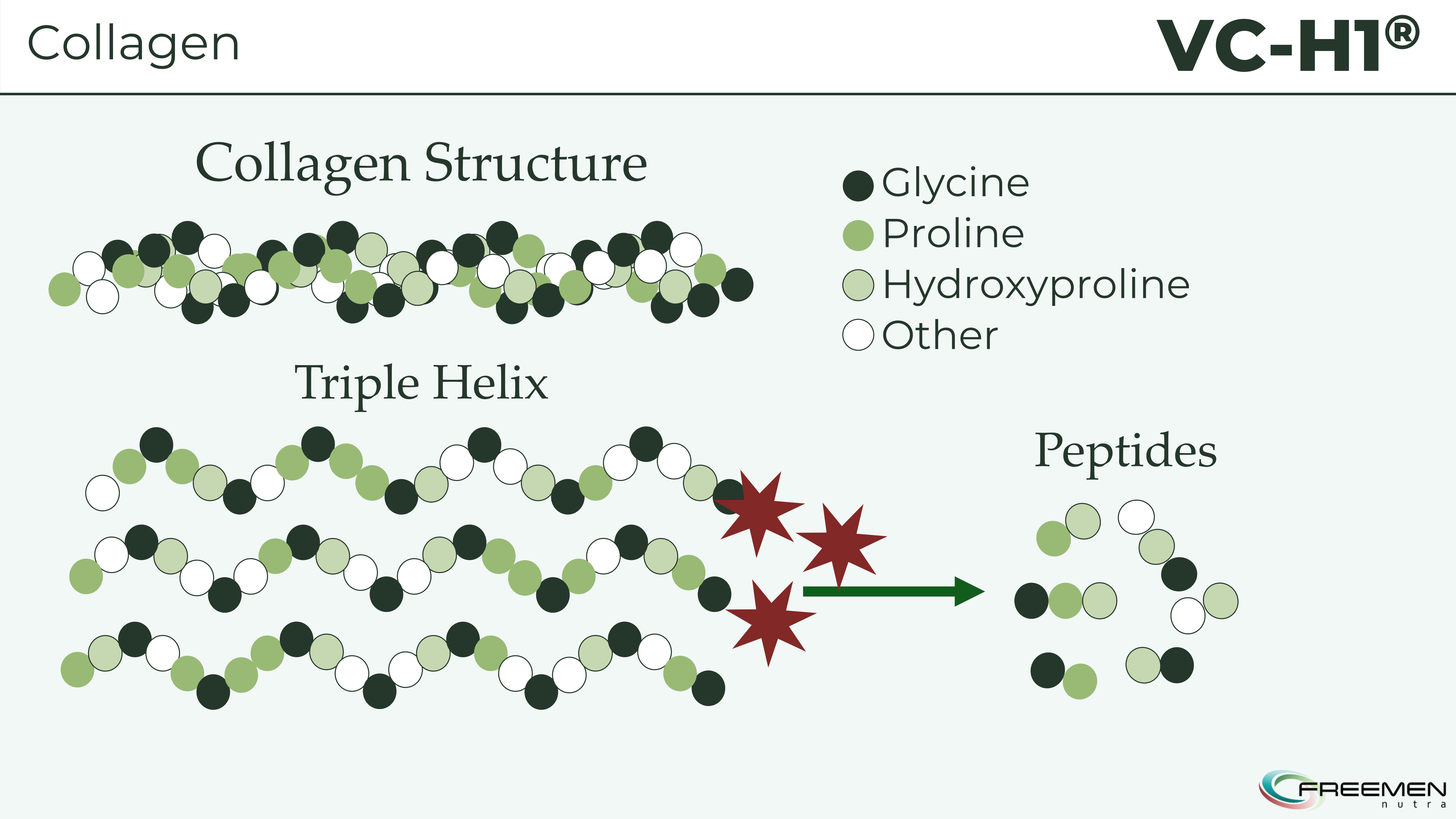
Here's how collagen's triple helix structure naturally breaks down into smaller peptides containing glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline - the same bioactive sequences that VC-H1 delivers from plant sources.
What Collagen Does (And Doesn't Do)
The clinical evidence for collagen supplementation shows clear benefits for specific applications. Multiple randomized controlled trials demonstrate that oral collagen peptides (2.5-5g daily for 8+ weeks) significantly improve skin hydration and elasticity.[3][4] Meta-analysis of 26 RCTs (n=1,721) confirmed these improvements with strong statistical significance (p<0.00001 for both hydration and elasticity).
Joint support evidence proves more modest. A 24-week RCT using 10g daily in college athletes with activity-related joint pain showed significant improvements compared to placebo,[5] while a 6-month study in adults 50+ found responder rates of 51.6% versus 36.5% placebo (p<0.05).[6] Benefits appear consistent for active individuals but remain inconsistent in diagnosed osteoarthritis.
Not a Complete Protein
However, collagen harbors a critical nutritional limitation: it's fundamentally incomplete as a protein source. With zero tryptophan content, minimal branched-chain amino acids, and low levels of other essential amino acids, collagen scores near zero on the PDCAAS (Protein Digestibility-Corrected Amino Acid Score).[1] It cannot fully support muscle protein synthesis as a primary protein source and exists as a functional ingredient, less so as a nutritional one.
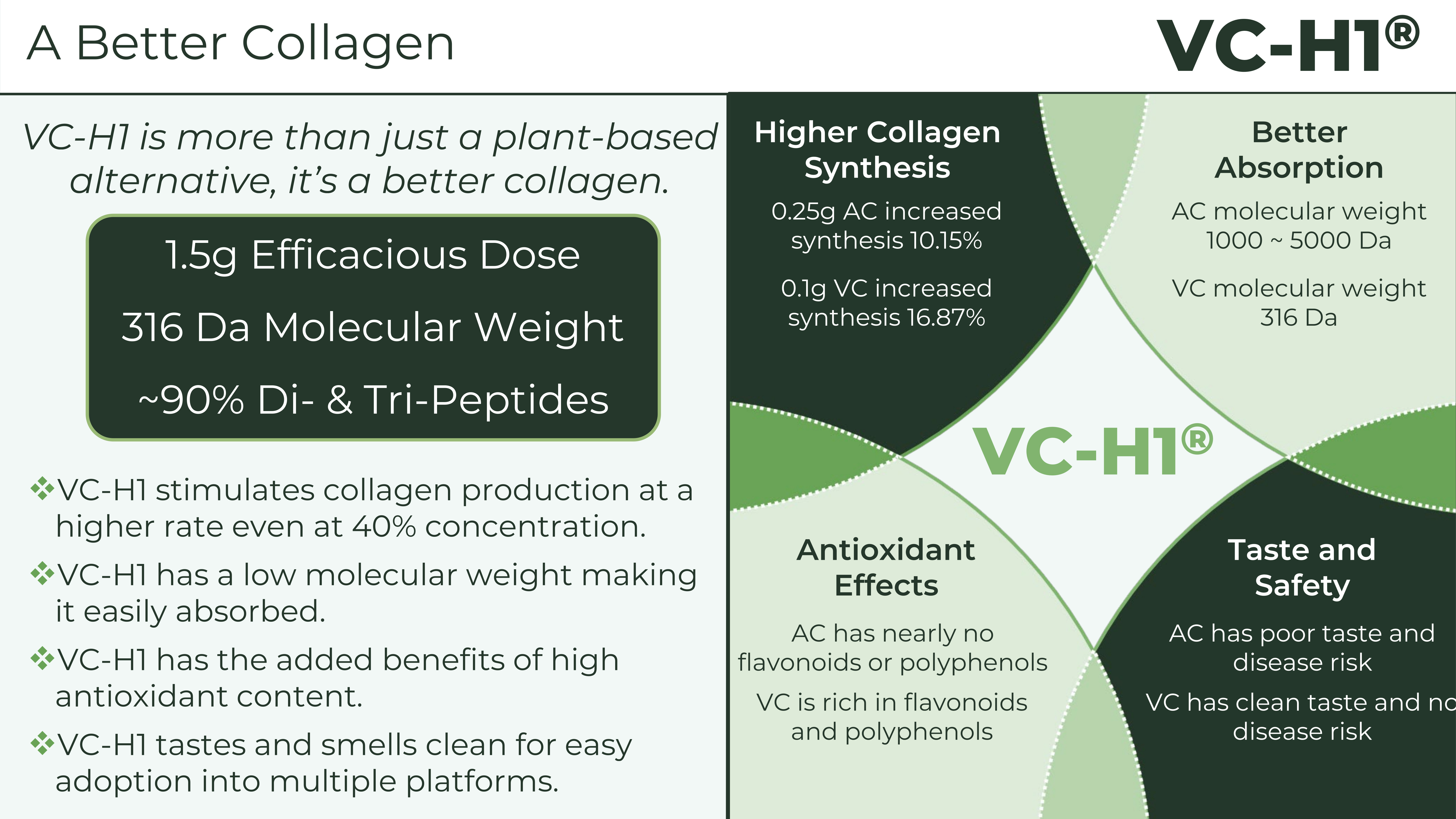
At just 1.5g effective dose and 316 Da molecular weight, VC-H1 delivers better absorption and higher collagen synthesis than animal collagen, plus you get added antioxidant benefits and clean taste without the disease risks.
The Bioactive Peptide Mechanism
Understanding how collagen supplements work requires abandoning the intuitive assumption that eating collagen becomes new collagen. The body operates far more intelligently.
When collagen degrades, whether from aging, UV damage, or mechanical stress, the breakdown releases small peptide fragments into the bloodstream. These fragments contain specific amino acid sequences, including:
- Pro-Hyp (proline-hydroxyproline)
- Gly-Pro-Hyp (glycine-proline-hydroxyproline)
- Hyp-Gly (hydroxyproline-glycine), and
- Related di- and tripeptides.
The presence of these sequences signals to fibroblasts that collagen damage has occurred, triggering increased collagen synthesis as a repair response.[7]
Hijacking the Collagen Repair Process
Oral collagen supplementation hijacks this feedback loop. Unlike most dietary proteins broken down to individual amino acids, collagen-derived peptides absorb as intact di- and tripeptides through intestinal peptide transporters.[8] Radiolabeling studies show these peptides accumulate in skin and cartilage, persisting for days post-ingestion and directly stimulating fibroblast activity.
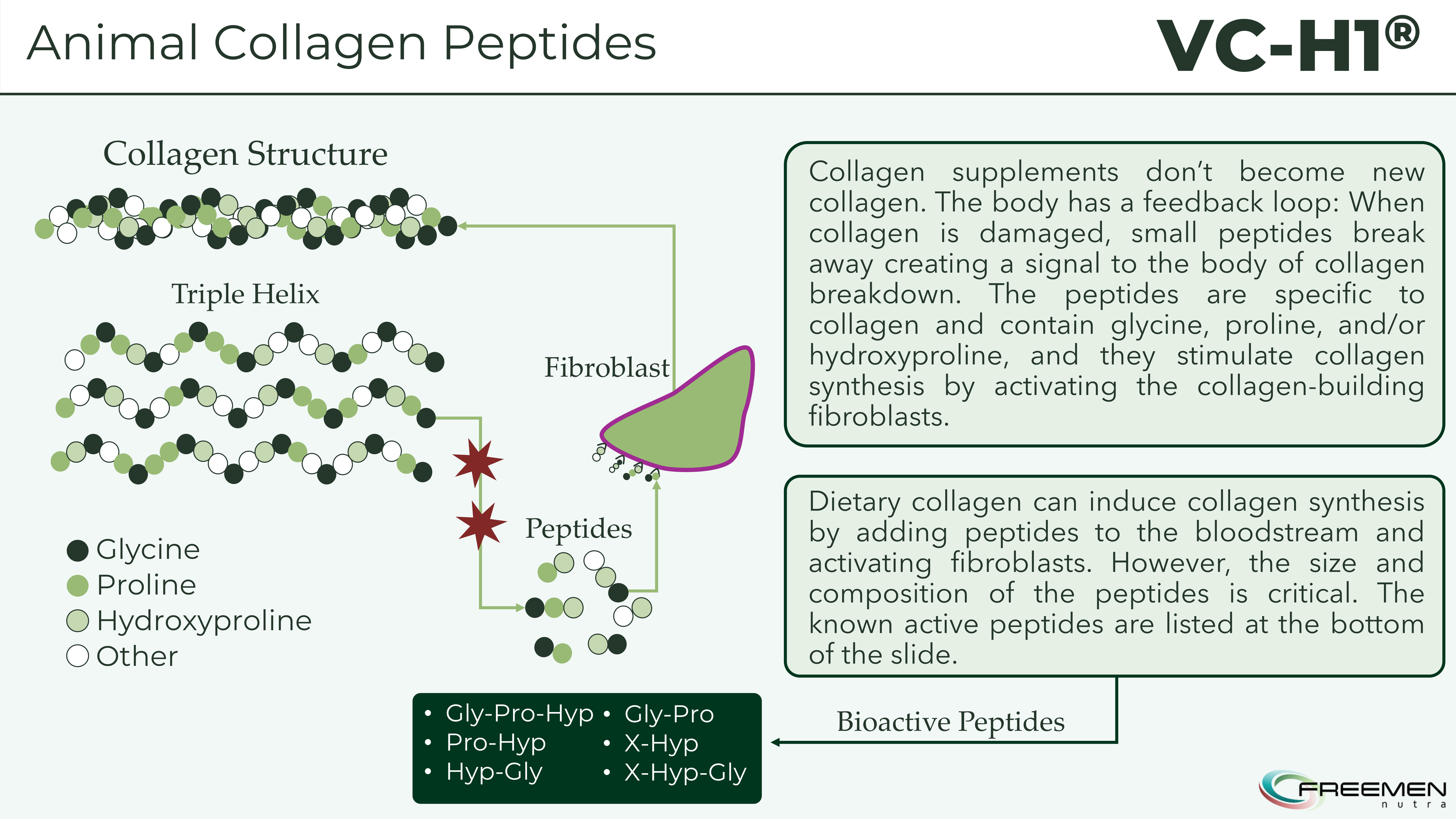
Your body doesn't just rebuild collagen from what you eat - instead, specific peptide sequences like Pro-Hyp and Gly-Pro-Hyp act as damage signals that tell your fibroblasts to start making new collagen.
The Pro-Hyp dipeptide stands out as the most abundant peptide in human blood after collagen ingestion (39% of total hydroxyproline-containing peptides).[7] In vitro studies demonstrate Pro-Hyp significantly increases fibroblast proliferation, hyaluronic acid synthase expression, and collagen production through STAT3 phosphorylation pathways. This isn't amino acid building blocks supporting synthesis, it's molecular signaling triggering a coordinated repair response.
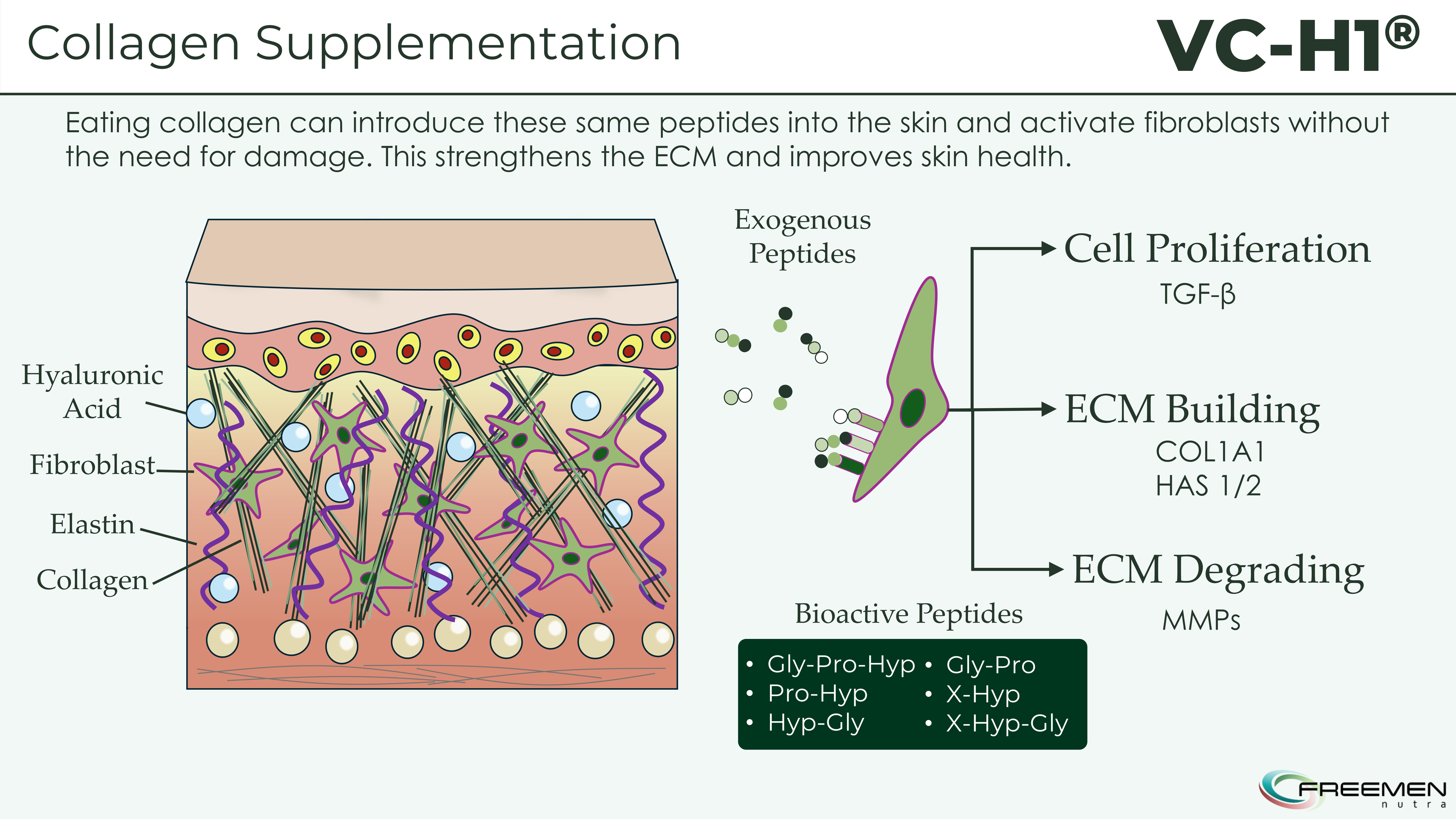
Smart supplementation bypasses the damage step - exogenous peptides from VC-H1 directly signal your fibroblasts to increase ECM production without needing tissue breakdown first.
This mechanism explains why collagen works despite its incomplete amino acid profile. The benefit derives from bioactive signaling peptides, not nutritional completeness. It also reveals the fundamental requirement for any collagen alternative: it must contain or generate these specific peptide sequences to function.
Why Consumers Want Alternatives
Consumer demand for collagen alternatives extends well beyond the vegan and vegetarian markets. Religious dietary restrictions exclude many from animal-sourced supplements (halal and kosher requirements prohibit porcine sources, while bovine sources raise concerns depending on feeding, slaughter methods, and certification). These restrictions affect billions of consumers globally.
Cost sensitivity matters more than marketers acknowledge. Quality collagen supplements at 10-15 gram daily doses can exceed $1.50-2.00 per serving, making consistent use prohibitively expensive for many consumers who often prioritize other supplements first. The growing awareness that collagen functions through signaling rather than replacement raises questions about whether massive doses justify their cost.
Perhaps most significantly, educated consumers now understand collagen's protein quality limitations. The supplement industry's evolution toward transparency means PDCAAS scores, essential amino acid profiles, and leucine content appear in product discussions. Savvy buyers recognize they're paying premium prices for an incomplete protein that won't really support muscle synthesis.
Vegan Sources Haven't Been Good Enough... Until Now
The market problem? Most "vegan collagen" products fail to address the core requirement. Amino acid blends might match collagen's glycine and proline ratios, but they lack the bioactive peptide sequences that trigger collagen synthesis. Botanical "collagen boosters" containing vitamin C, silica, and antioxidants support collagen production indirectly but don't provide the molecular signals that drive actual fibroblast activity.
Most "vegan collagen" products fall short because they use amino acid blends or plant extracts that don't contain the actual bioactive peptides your skin needs - VC-H1 stands apart with real collagen-stimulating sequences.
This gap creates opportunity for an ingredient that delivers genuine bioactive peptides from a plant source... exactly what VC-H1 accomplishes.
VC-H1: A Different Class of Collagen Alternative
VC-H1 emerges from enzymatic hydrolysis of Hibiscus sabdariffa calyx, targeting a plant protein called extensin that shares structural similarities with animal collagen. While plants don't produce collagen in the strict biochemical sense, extensin functions as a cell wall structural protein with repeating glycine-rich sequences analogous to collagen's Gly-X-Y tripeptide pattern.
The manufacturing process uses specific proteases to cleave extensin into bioactive peptides in the critical 300-400 dalton range. The result: an ultra-low molecular weight ingredient averaging 316 Da -- dramatically smaller than animal collagen peptides, which typically range from 1,000 to 5,000 Da. This size difference matters enormously for absorption and bioavailability, as smaller peptides cross intestinal barriers more efficiently and reach target tissues at higher concentrations.
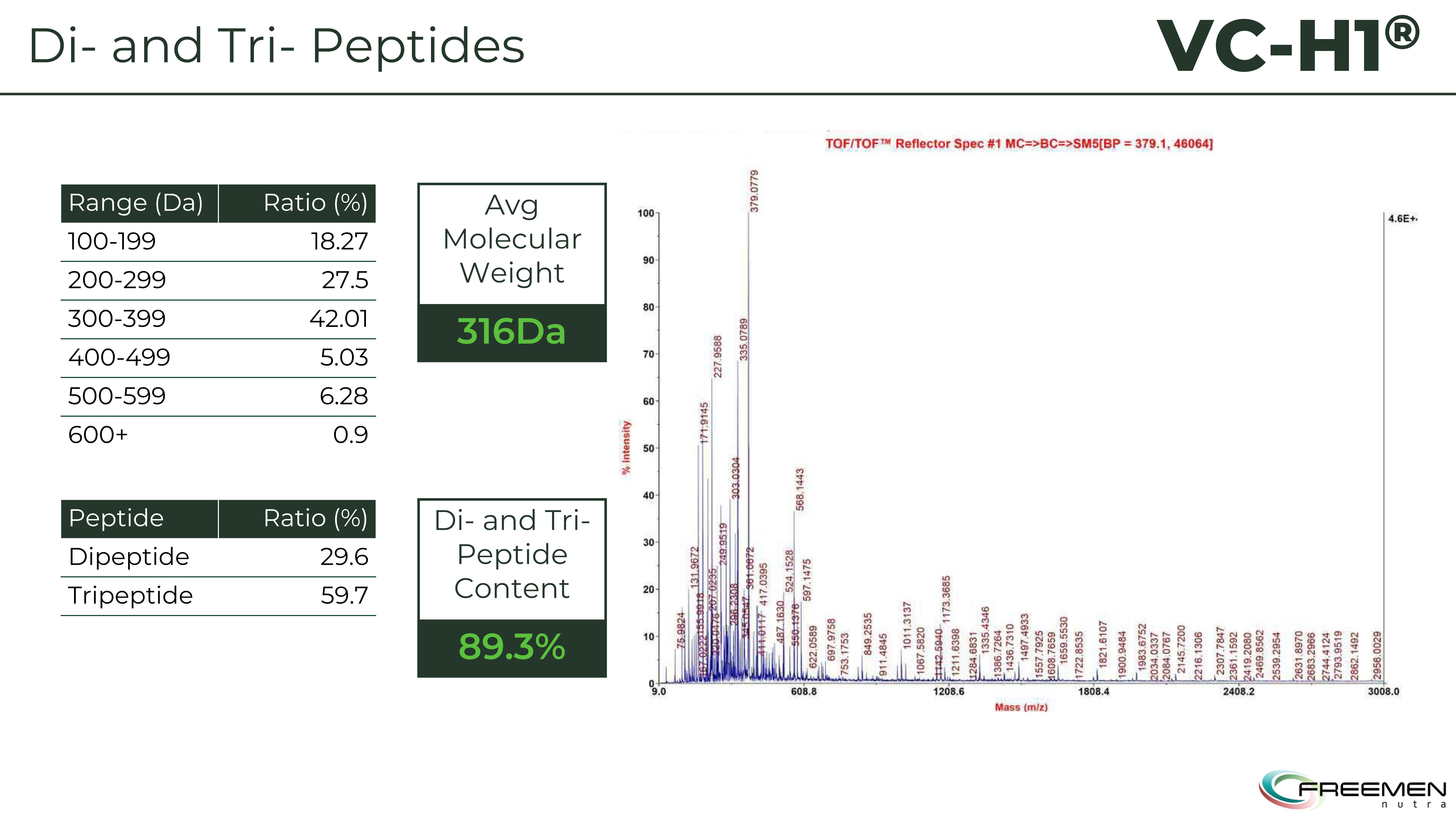
The mass spectrometry data proves it - VC-H1 contains 89.3% bioactive di- and tripeptides with an average molecular weight of just 316 Da, making it significantly more bioavailable than larger animal-derived peptides.
VC-H1's amino acid composition mirrors the functional elements of collagen:
- 22% glycine,
- 9% proline, and
- 11% hydroxyproline
This isn't coincidental. These three amino acids define collagen's structure and, critically, compose the bioactive peptide sequences that signal collagen synthesis. The ingredient contains 85-90% di- and tripeptides, the exact molecular configurations absorbed intact through intestinal peptide transporters and recognized by fibroblasts as collagen degradation signals.
VC-H1's sourcing distinguishes it from commodity botanical extracts. All hibiscus raw material originates from a dedicated 200-hectare organic farm developed by RAWGA Inc. specifically for VC-H1 production. This vertically integrated supply chain -- from seed selection through cultivation, harvest, extraction, and packaging -- ensures organic certification authenticity, eliminates adulteration concerns, and provides complete traceability. The "farm-to-tablet" approach delivers transparency rare in the supplement industry while supporting sustainable agricultural practices.
How It's Different from Other "Vegan Collagen"
The vegan collagen category suffers from what can only be called definitional chaos. Most products labeled "vegan collagen" fall into three categories, none of which deliver the bioactive peptides required for collagen synthesis stimulation:
- Amino Acid Blends attempt to mimic collagen's glycine and proline ratios using isolated free-form amino acids. These formulas might match collagen's compositional profile on paper, but they fundamentally miss the mechanism. Individual amino acids don't signal collagen synthesis, the specific peptide sequences do. Taking glycine and proline separately provides building blocks but doesn't trigger the fibroblast response that drives new collagen production. It's nutritional support, not functional signaling.
- Collagen Boosters combine vitamins, minerals, and botanicals that support collagen synthesis through indirect mechanisms. Vitamin C enables hydroxylation of proline residues (creating hydroxyproline essential for collagen stability). Silica may support connective tissue structure. Antioxidants protect existing collagen from degradation. These ingredients help, but they're cofactors and protectants, not collagen synthesis triggers. They optimize the environment for collagen production without providing the molecular signal to initiate it.
- Fermented Collagen represents a newer approach, using genetically modified yeast or bacteria to produce collagen proteins. While these products generate actual collagen (not plant analogs), the process remains expensive, the molecular weight distribution often falls in the higher ranges (reducing bioavailability), and many consumers seeking plant-based options reject GMO fermentation. The final product, though technically vegan, lacks the antioxidant co-benefits of botanical sources.
VC-H1: An Entirely New Category
VC-H1 occupies a distinct category: plant-derived bioactive peptides.
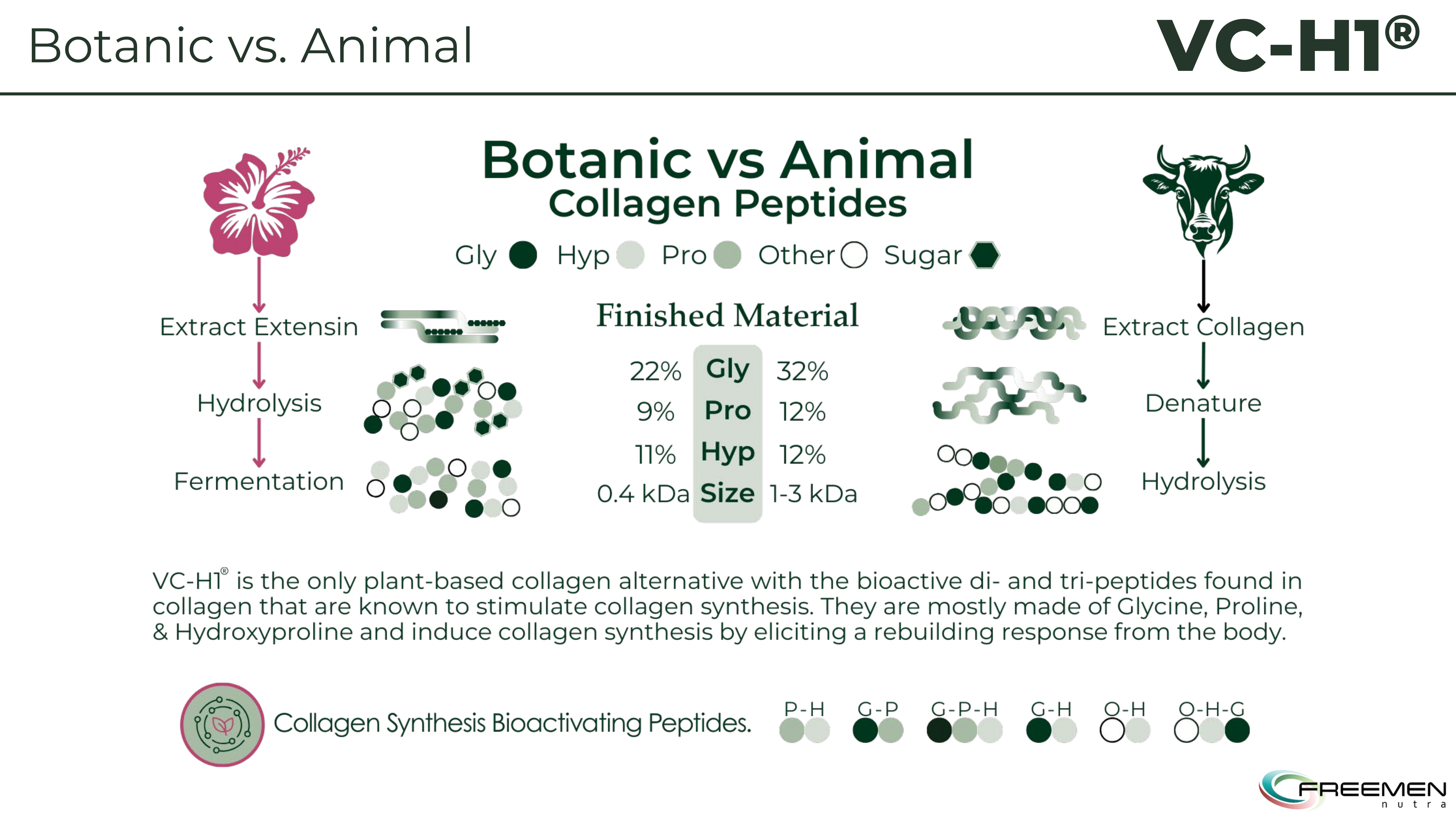
While animal collagen requires denaturing and breaking down existing proteins, VC-H1 extracts extensin from hibiscus through fermentation, creating the same bioactive peptides with better molecular weight distribution at 0.4 kDa vs 1-3 kDa.
The ingredient contains the actual peptide sequences found in animal collagen: G-X-Y patterned di- and tripeptides. These aren't mimics or analogs, they're the identical molecular structures that trigger collagen synthesis in fibroblasts. Internal in vitro studies confirm this: VC-H1 at 0.1% concentration stimulates collagen production more effectively than animal collagen at 0.25% concentration -- 1.7 to 4.0-fold superior potency depending on the animal source compared.
Smaller Peptides, Better Bioavailability
The molecular weight advantage amplifies this difference. At 316 Da average, VC-H1 peptides absorb more readily than larger animal collagen peptides. Smaller peptides mean better bioavailability, higher blood concentrations, and more efficient delivery to dermal fibroblasts where collagen synthesis occurs.
The following table breaks down the comparisons:
| Category | Mechanism | Contains Bioactive Peptides | Typical Dose | Clinical Validation |
| VC-H1 | Direct fibroblast signaling + antioxidants | Yes (G-X-Y as Pro-Hyp, Gly-Pro-Hyp, etc.) | 1.5g | RCT with objective measures |
| Animal Collagen | Direct fibroblast signaling | Yes | 5-15g | Multiple RCTs |
| Amino Acid Blends | Provide building blocks | No | 3-5g | Limited/none |
| Collagen Boosters | Cofactor support, protection | No | Varies | Limited/none |
| Fermented Collagen | Direct fibroblast signaling | Yes | 5-10g | Emerging |
The Hibiscus Advantage
Hibiscus sabdariffa brings 4,000+ years of traditional use in medicine and skincare across Asia, Africa, and the Middle East. Modern phytochemistry reveals why: the plant synthesizes an impressive array of bioactive compounds with documented skin health benefits.
The anthocyanin profile stands out, dominated by delphinidin-3-sambubioside alongside delphinidin-3-glucoside and cyanidin-3-sambubioside. These compounds belong to the anthocyanidin family, water-soluble pigments responsible for red, purple, and blue plant colors. Beyond pigmentation, anthocyanins function as potent antioxidants, scavenging reactive oxygen species that degrade collagen and accelerate photoaging.
Delphinidin-3-sambubioside specifically inhibits multiple receptor tyrosine kinases involved in cellular proliferation and inflammation.[9] Bioinformatic analysis reveals it modulates pathways related to extracellular matrix organization, cellular response to oxidative stress, and regulation of apoptosis, which are all relevant to skin aging. The compound's anti-inflammatory effects extend to reducing pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β) that stimulate matrix metalloproteinases, enzymes that actively break down collagen and elastin in aged skin.
The polyphenol content extends beyond anthocyanins to include chlorogenic acid derivatives, quercetin glycosides, and hydroxycinnamic acids. This diverse antioxidant profile provides broad-spectrum protection against multiple reactive oxygen species, UV-induced damage, and inflammatory cascades that compromise skin structure.
Organic acids, including hibiscus acid, citric acid, and malic acid, contribute additional benefits. These compounds support skin barrier function, influence pH for optimal enzyme activity, and may enhance peptide absorption through mild chelation effects that increase intestinal permeability.
Dual Mechanism that Goes Beyond Animal Collagen
VC-H1 thus operates through a dual mechanism absent in pure animal collagen:
- Primary mechanism: Bioactive peptides (G-X-Y-patterned di- and tri-peptides like Pro-Hyp, Gly-Pro-Hyp, etc.) signal fibroblasts to increase collagen synthesis through the same pathways as animal collagen peptides, as discussed above. This addresses the production side of the equation.
- Secondary mechanism: Anthocyanins, polyphenols, and organic acids protect existing collagen from degradation by neutralizing reactive oxygen species, suppressing inflammatory cytokines, and inhibiting matrix metalloproteinases. This addresses the breakdown side.
The combination creates a more comprehensive approach to collagen homeostasis than animal collagen alone, stimulating synthesis while simultaneously reducing degradation. This dual action may explain why VC-H1 demonstrates superior in vitro potency despite containing the same core bioactive peptides as animal sources.
The sustainability story completes the package. The organic farm operates with reduced chemical inputs, lower water consumption than animal agriculture, and lower greenhouse gas emissions than collagen derived from bovine or porcine sources. The vertically integrated supply chain eliminates multiple transportation steps, further reducing environmental impact. For brands seeking to align supplement formulations with sustainability commitments, VC-H1 offers evidence-based efficacy without the ecological footprint of animal-derived alternatives.
It's all great in theory, but what does the clinical evidence support?
The Clinical Evidence
VC-H1's efficacy rests on gold-standard clinical research published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences in July 2025.[10] The study employed a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled design (the benchmark for establishing supplement efficacy) conducted at Yonsei University College of Medicine in Seoul, South Korea.
From lab to clinic, VC-H1 has the studies to back up its claims - preclinical research shows superior collagen synthesis, while the human clinical trial demonstrates real improvements in hydration, elasticity, and wrinkle reduction.
Study Design and Rigor
Researchers enrolled 100 participants aged 35-60 years, all presenting with photoaged skin characterized by dryness and visible periorbital wrinkles (grade ≥3 on visual assessment scales). This age range captures early to moderate photoaging, allowing detection of measurable improvements within a reasonable timeframe. The final analysis included 98 participants (after two dropouts), with 50 subjects in the VC-H1 group and 48 in the placebo group.[10]
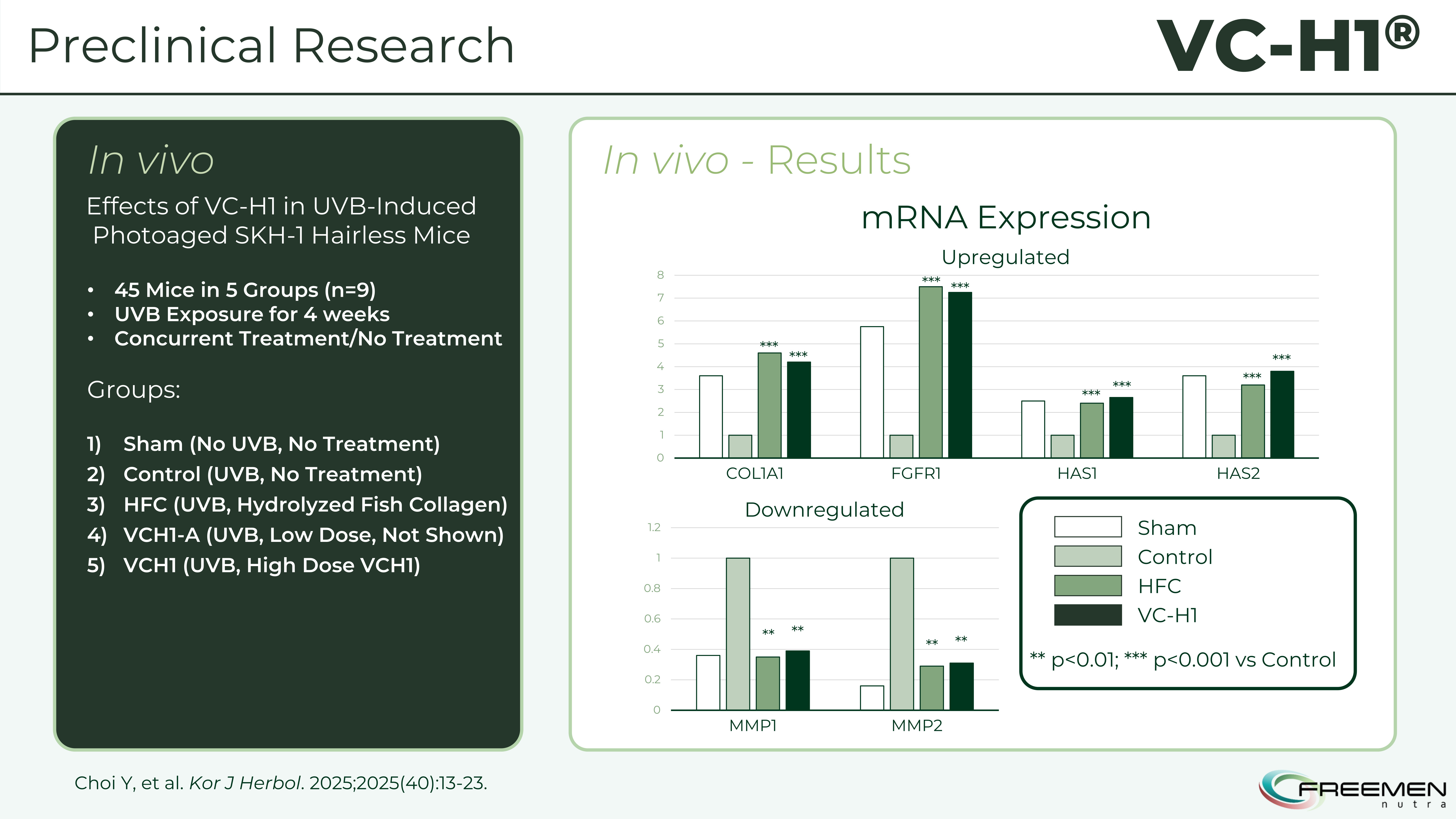
The mouse studies show VC-H1's dual protection - it upregulates collagen and hyaluronic acid synthesis genes while downregulating matrix metalloproteinases that break down existing collagen.
The trial duration of 12 weeks with assessments at baseline, 6 weeks, and 12 weeks enabled researchers to track both onset and progression of benefits. This timeframe aligns with skin cell turnover cycles (approximately 28-40 days in adults) and allows sufficient time for collagen synthesis effects to manifest in measurable tissue changes.
The study's strength lies in its reliance on objective instrumentation rather than subjective self-reporting. While participant satisfaction matters for real-world compliance, objective biomarkers provide the rigorous evidence required for scientific validation. Researchers measured skin hydration, transepidermal water loss (TEWL), deep moisture content, keratin index, and elasticity using validated dermatological instruments. Only the overall appearance assessment relied on dermatologist evaluation, though even this used standardized grading criteria.
Participants received either 1.5 grams of VC-H1 daily or an identical-appearing placebo (maltodextrin-based) diluted in water.[10] The double-blind design meant neither participants nor researchers knew group assignments until after data collection, eliminating expectation bias. Statistical analysis used linear mixed-effects models to account for individual variability and time effects, with baseline values included as covariates to reduce confounding.
Primary Outcomes: Skin Barrier Function
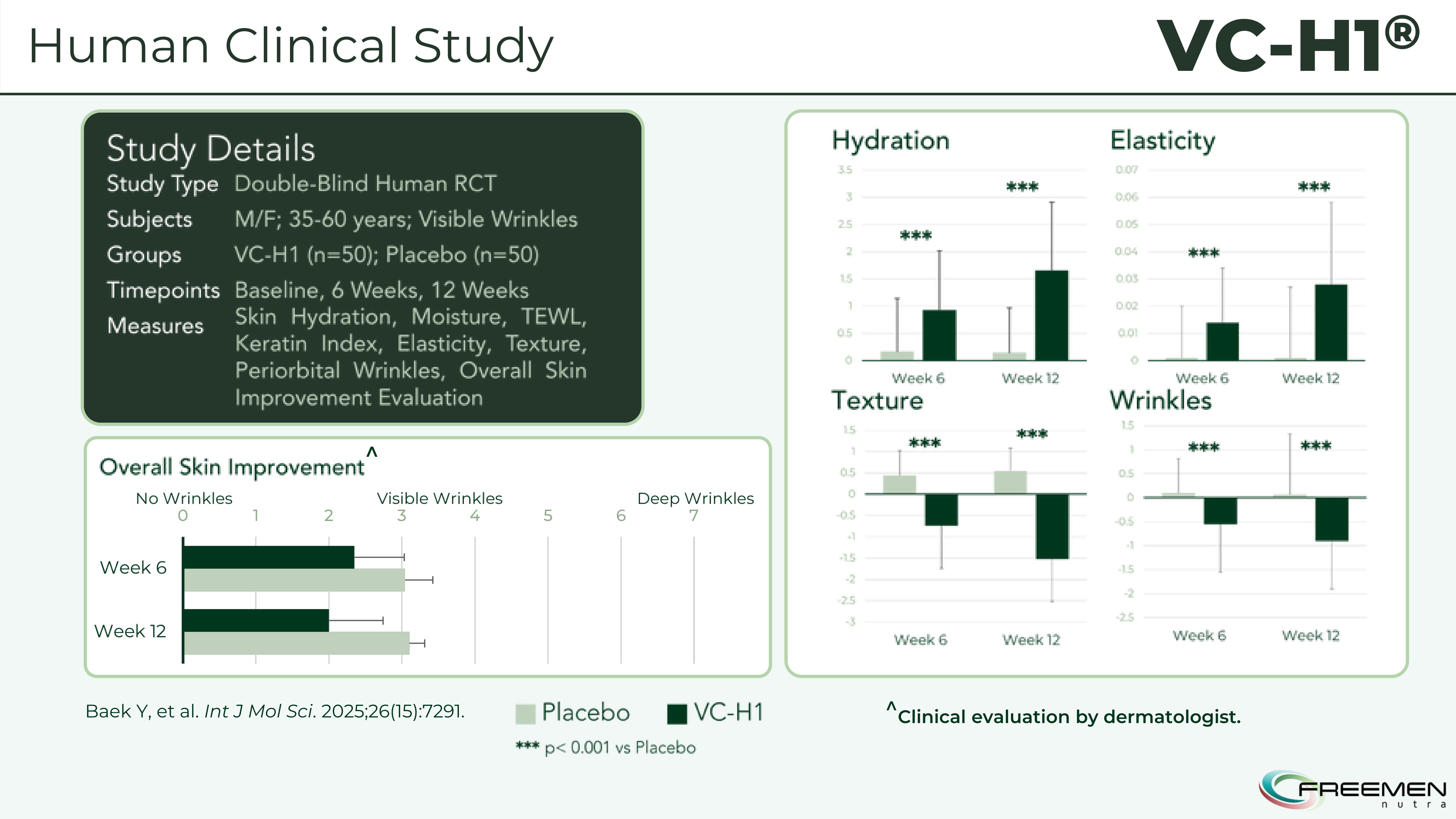
The 12-week double-blind study with 100 participants shows statistically significant improvements across the board - better hydration, elasticity, texture, and visible wrinkle reduction with p<0.001 significance levels.
-
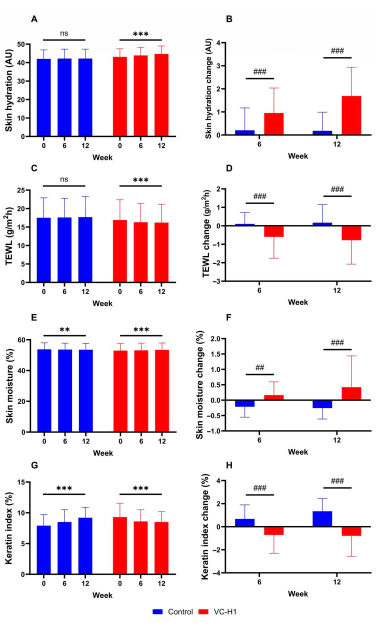
Hydration and Water Retention
Skin hydration showed dramatic improvements in the VC-H1 group compared to placebo. By week 6, hydration levels increased significantly (p<0.001), and these gains persisted through week 12.[10] The consistency across timepoints indicates sustained benefit rather than transient effects.
The comprehensive 12-week clinical data shows VC-H1's superiority across multiple skin health markers - significant improvements in hydration, reduced TEWL, enhanced moisture retention, and normalized keratin turnover.[10]
Deep moisture content similarly improved in the VC-H1 group. This endpoint measures water retention in deeper dermal layers rather than just surface hydration. The distinction matters because surface hydration can fluctuate with environmental conditions and topical product use, while deep moisture reflects actual tissue-level changes in water-binding capacity. The improvement suggests enhanced hyaluronic acid synthesis (or reduced degradation), as hyaluronic acid's exceptional water-binding properties (holding up to 1,000 times its weight in water) drive deep tissue hydration.
-
Transepidermal Water Loss
TEWL measures the rate at which water evaporates through the skin, serving as a key indicator of barrier function. Higher TEWL values indicate compromised barrier integrity, allowing excessive water loss and increasing vulnerability to irritants and pathogens. Lower values reflect better barrier function.
The VC-H1 group showed significant TEWL reduction compared to placebo, with improvements evident by week 6 and maintained through week 12 (p<0.001).[10] The magnitude of reduction indicates restoration of barrier lipid organization, improved corneocyte cohesion, and enhanced natural moisturizing factor production. These changes reflect comprehensive barrier repair, not just temporary occlusion.
-
Desquamation and Cell Turnover
The keratin index quantifies the amount of surface keratin, with elevated levels indicating irregular desquamation (shedding of dead skin cells). Photoaged skin often exhibits impaired desquamation, leading to rough texture, dullness, and clogged pores.
VC-H1 supplementation significantly reduced the keratin index compared to placebo (p<0.001), indicating improved cell turnover and more regular desquamation.[10] This improvement correlates with better barrier function, as proper desquamation requires coordinated protease activity and lipid metabolism, both of which are dependent on healthy underlying tissue.
Secondary Outcomes: Structural Improvements
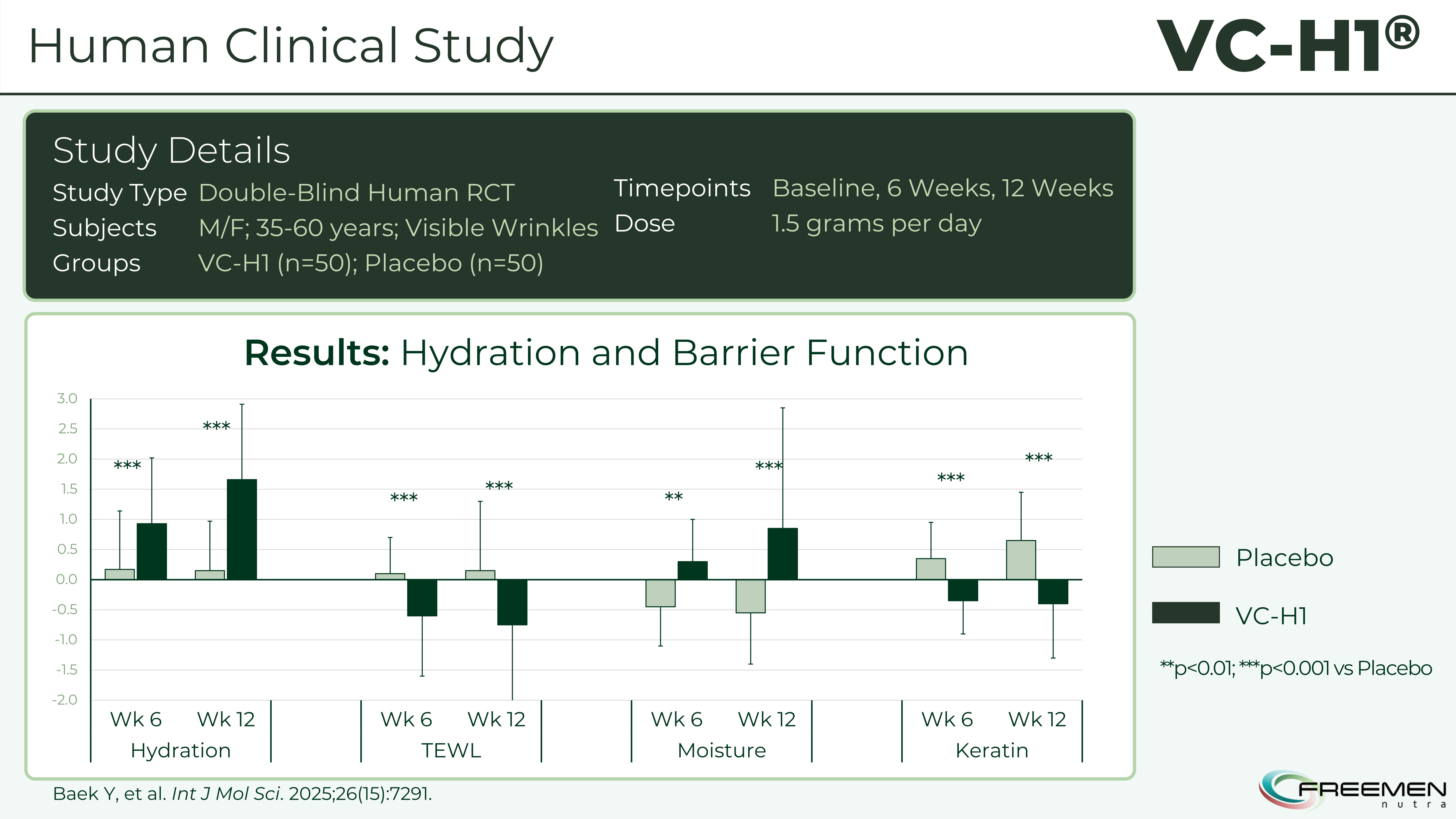
The double-blind RCT proves VC-H1's effectiveness in real people - significant improvements in hydration, TEWL reduction, moisture retention, and keratin regulation at both 6 and 12 weeks.
-
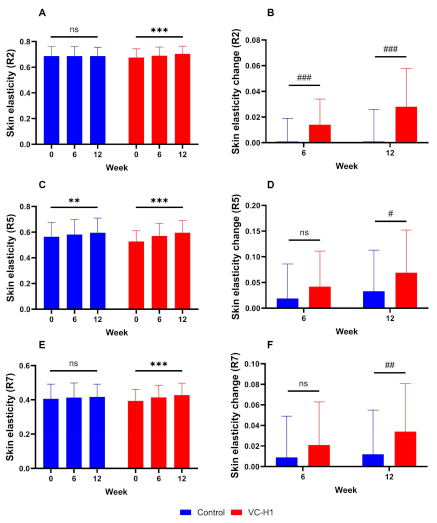
Elasticity Enhancement
Skin elasticity -- the ability to return to original shape after stretching -- depends on intact elastin fibers and the collagen network that supports them. Age and UV exposure degrade both proteins, resulting in sagging and loss of rebound.
The elasticity data proves VC-H1's structural improvements - significant gains in skin rebound and firmness measured through multiple elasticity parameters at both 6 and 12 weeks.[10]
The VC-H1 group demonstrated significant elasticity improvements at both 6 and 12 weeks compared to placebo (p<0.001).[10] Objective measurement using cutometry (which applies controlled suction and measures skin deformation and recovery) eliminates subjective bias. The improvement suggests either new elastin and collagen synthesis, reduced degradation of existing fibers, or both.
The sustained improvement through 12 weeks indicates lasting structural changes rather than temporary swelling or hydration effects that might artificially improve elasticity measurements in the short term.
-
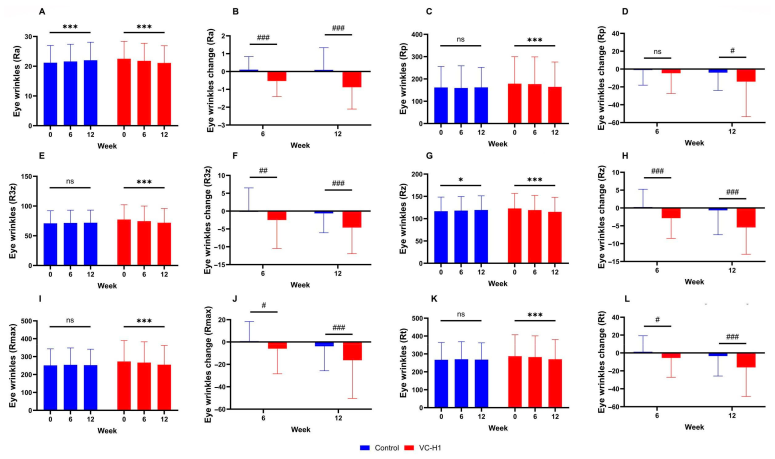
Wrinkle Reduction
Periorbital wrinkles (fine lines and deeper creases around the eyes) served as the primary wrinkle endpoint. This area experiences significant photoaging due to thin skin, high expression movement, and sun exposure.
Wrinkle depth decreased significantly in the VC-H1 group compared to placebo at both assessment timepoints (p<0.001).[10] Three-dimensional imaging systems quantified wrinkle parameters including depth, width, and total area, providing objective measurements free from observer bias.
Eye area wrinkle measurements show VC-H1's targeted anti-aging effects - significant reductions in wrinkle depth, width, and surface irregularities around the delicate eye area.[10]
The wrinkle reduction at 6 weeks, with further improvement at 12 weeks, follows the expected timeline for collagen remodeling. Initial benefits likely reflect improved hydration plumping fine lines, while later improvements incorporate actual structural changes as new collagen fills in dermal volume and supports the epidermis.
-
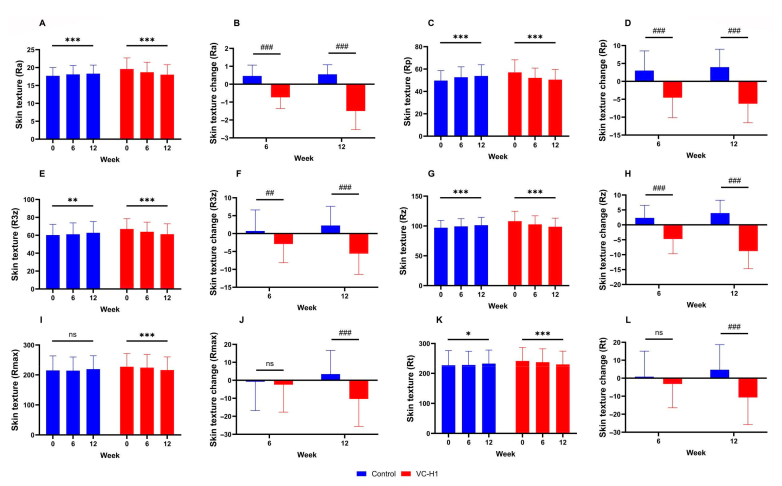
Texture and Overall Appearance
Surface texture measurements using optical profilometry showed significant smoothness improvements in the VC-H1 group (p<0.001).[10] Texture improvements reflect the combined effects of better hydration, normalized desquamation, and enhanced structural support from improved collagen and elastin networks.
Surface texture measurements using optical profilometry demonstrate VC-H1's ability to smooth skin roughness across multiple texture parameters with sustained improvements through 12 weeks.[10]
Using standardized grading scales, dermatologists' overall appearance assessments rated the VC-H1 group significantly higher than placebo at both 6 and 12 weeks (p<0.001).[10] While this measure introduces some subjectivity, the blinded nature of the assessment and use of validated scales maintain scientific rigor. The dermatologists were evaluating multiple parameters holistically: evenness, brightness, texture, firmness, and overall skin quality.
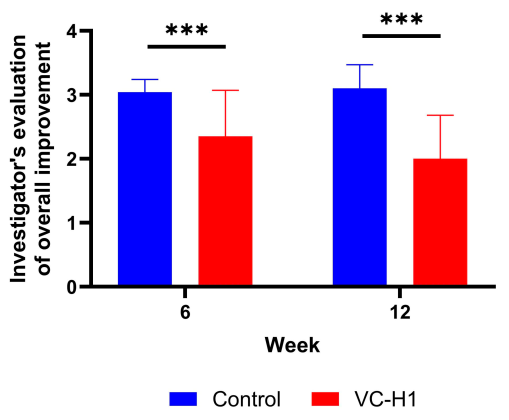
Dermatologist evaluations confirm what the objective measurements showed - VC-H1 participants scored significantly higher on overall skin appearance at both 6 and 12 weeks compared to placebo.[10]
What These Results Mean
The statistical significance demands attention. P-values below 0.001 indicate less than 0.1% probability that observed differences resulted from chance. For context, most clinical trials consider p<0.05 (5% chance) sufficient for statistical significance. The consistent achievement of p<0.001 across multiple independent outcomes provides incredibly strong evidence for real effects, especially since it was repeatedly achieved in numerous metrics.
Effect sizes matter as much as statistical significance. Small but statistically significant changes may not translate to noticeable real-world benefits. The improvements observed with VC-H1 -- visible wrinkle reduction, measurable elasticity gains, substantial TEWL decreases -- showed clinically meaningful changes that participants would perceive as actual skin improvement.
The progression from 6 to 12 weeks also reveals important insights about mechanism and optimal usage. Many outcomes showed improvements at 6 weeks that either sustained or increased at 12 weeks. This pattern suggests cumulative benefits from continued supplementation rather than a ceiling effect reached quickly. The implication: consistent long-term use likely produces better results than short-term trials.
Significant Improvement Across Several Measurements
The comprehensive improvement across barrier function, structural integrity, and appearance metrics addresses the full spectrum of photoaging. VC-H1 didn't excel in one area while failing in others, it improved hydration and elasticity and wrinkles and texture. This broad efficacy profile distinguishes it from targeted interventions that address single aging mechanisms.
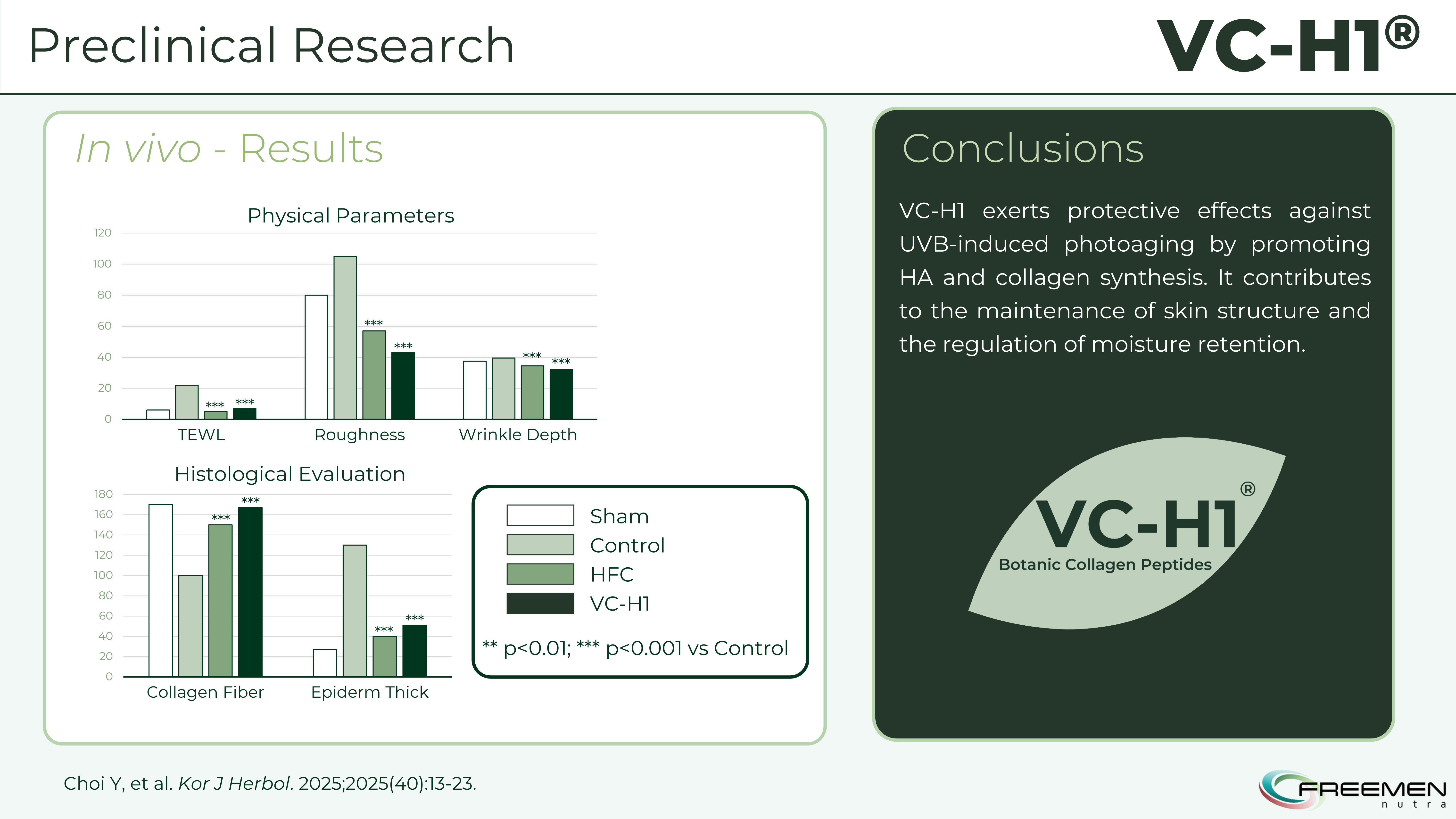
Beyond gene expression, VC-H1 delivers measurable physical improvements - reduced TEWL, decreased roughness, and increased collagen fiber density that you can actually see under the microscope.
Safety data proved equally important: no adverse effects were reported in either group throughout the 12-week study.[10] Blood chemistry, hematology, and urinalysis showed no clinically significant abnormalities. The clean safety profile at 1.5 grams daily suggests a comfortable margin for higher doses if desired, though the clinical dose already produces robust effects.
In Vitro Data
Before human trials, researchers internally compared VC-H1's collagen synthesis stimulation against four types of animal-sourced collagen peptides in cultured human dermal fibroblasts. The results established VC-H1's mechanistic superiority at the cellular level.
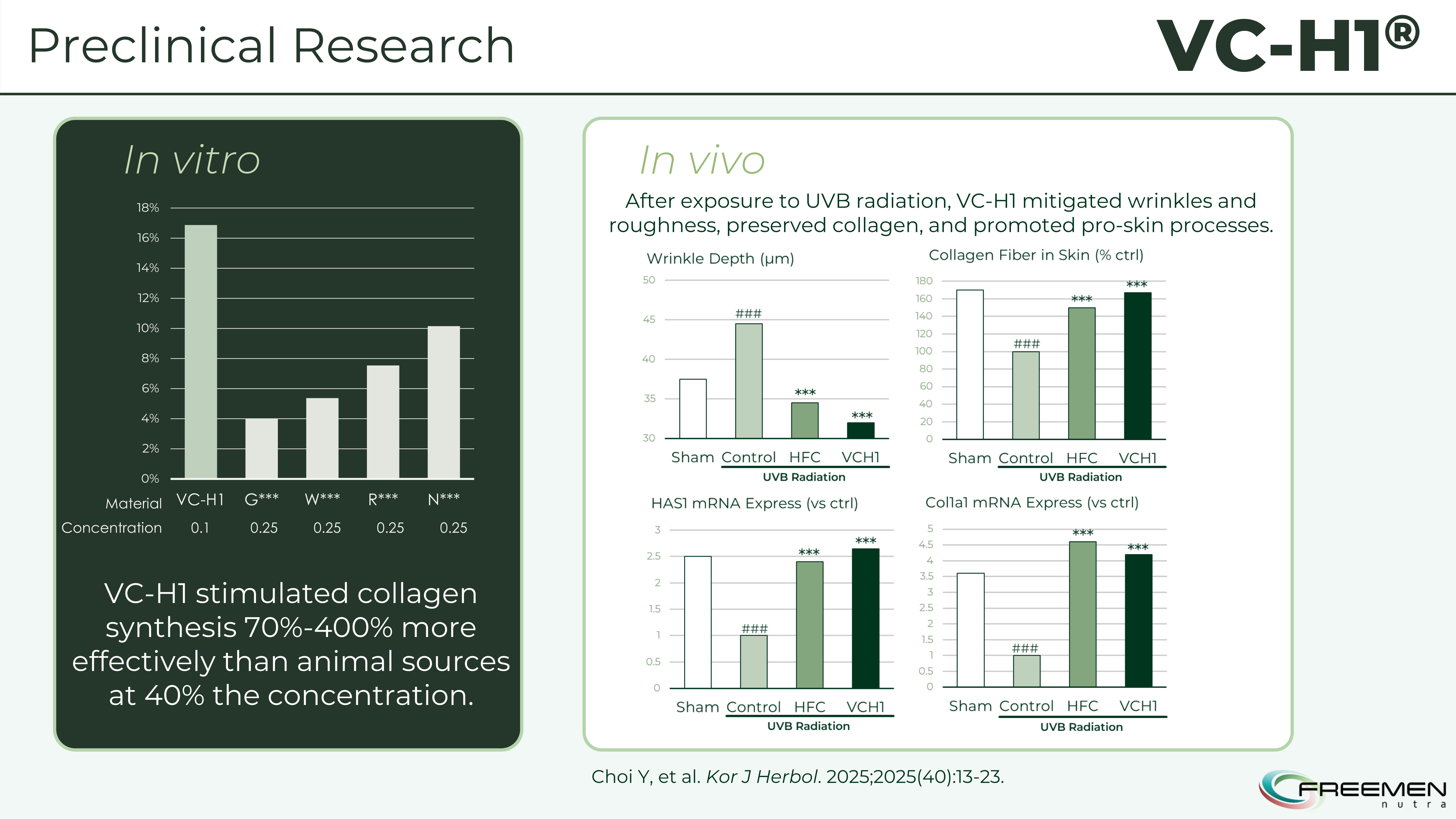
The lab data is impressive - VC-H1 stimulated 70-400% more effective collagen synthesis than animal sources at just 40% the concentration, plus it protected against UV damage and preserved existing collagen fibers.
At 0.1% concentration, VC-H1 increased collagen synthesis by 16.87% compared to untreated controls. Animal collagen at 0.25% concentration (2.5 times higher) increased synthesis only 10.15%. This means VC-H1 produced 1.7-fold greater collagen synthesis despite using 40% of the dose. When compared across different animal collagen sources, the potency ratio ranged from 1.7 to 4.0-fold depending on the specific collagen type.
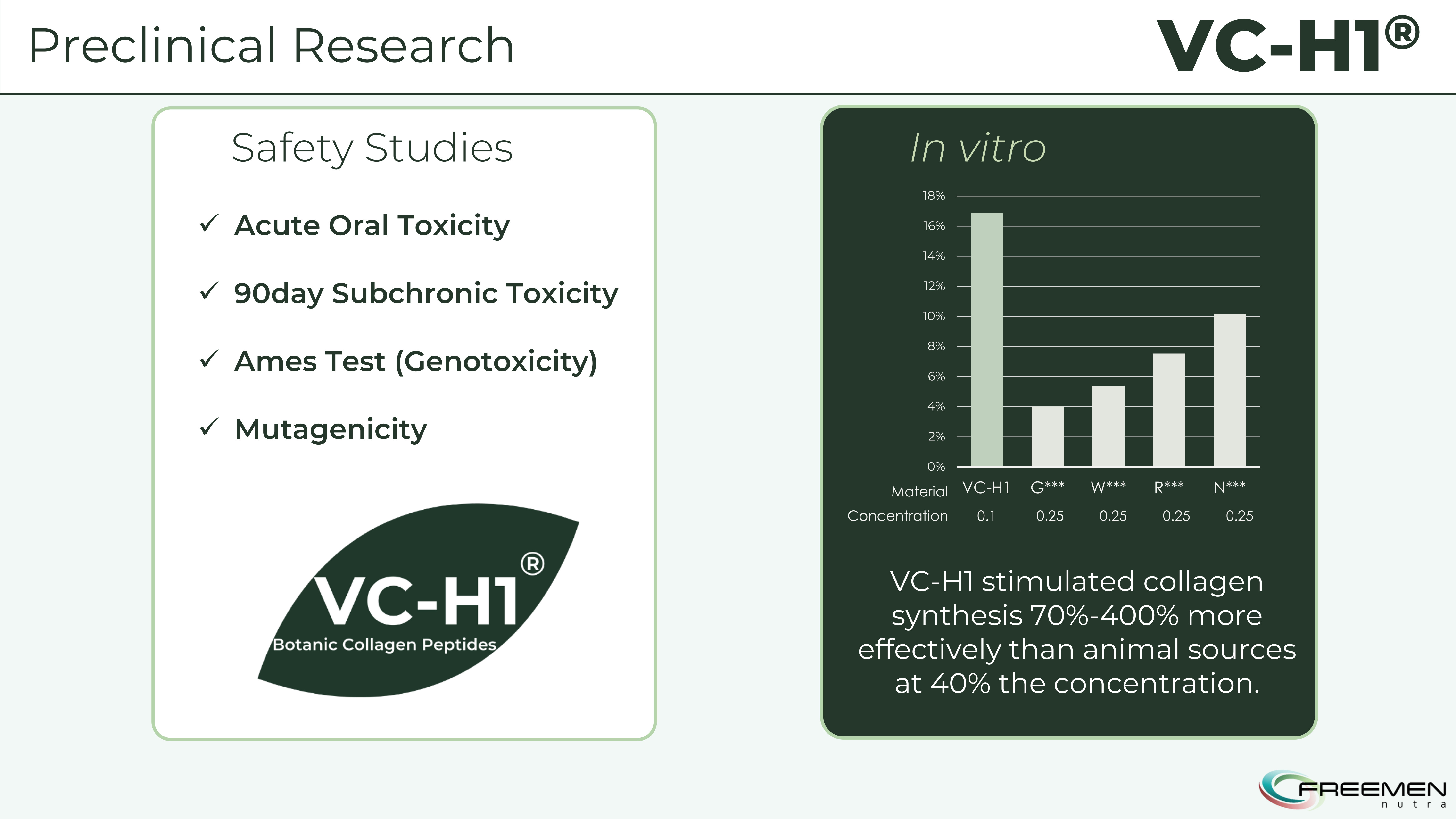
VC-H1 passes comprehensive safety testing including acute toxicity, genotoxicity, and mutagenicity studies, while delivering 70-400% more effective collagen synthesis than animal sources at lower concentrations.
The superior potency likely traces directly to molecular weight. VC-H1's average 316 Da molecular weight allows efficient absorption across cell membranes and intestinal barriers. Smaller peptides reach higher intracellular concentrations, bind more effectively to cellular receptors, and trigger stronger signaling responses. Animal collagen peptides at 1,000-5,000 Da face absorption limitations that reduce bioavailability and cellular uptake.
The in vitro data validates the human trial results by demonstrating VC-H1's direct effects on the cells responsible for collagen synthesis. The mechanism isn't indirect support or cofactor provision, it's direct stimulation of fibroblast activity at the cellular level, confirmed in controlled laboratory conditions before validation in human subjects.
This combination of rigorous human data showing comprehensive skin health improvements, backed by cellular studies demonstrating superior collagen synthesis stimulation, establishes VC-H1 as an evidence-based collagen alternative with peer-reviewed validation.
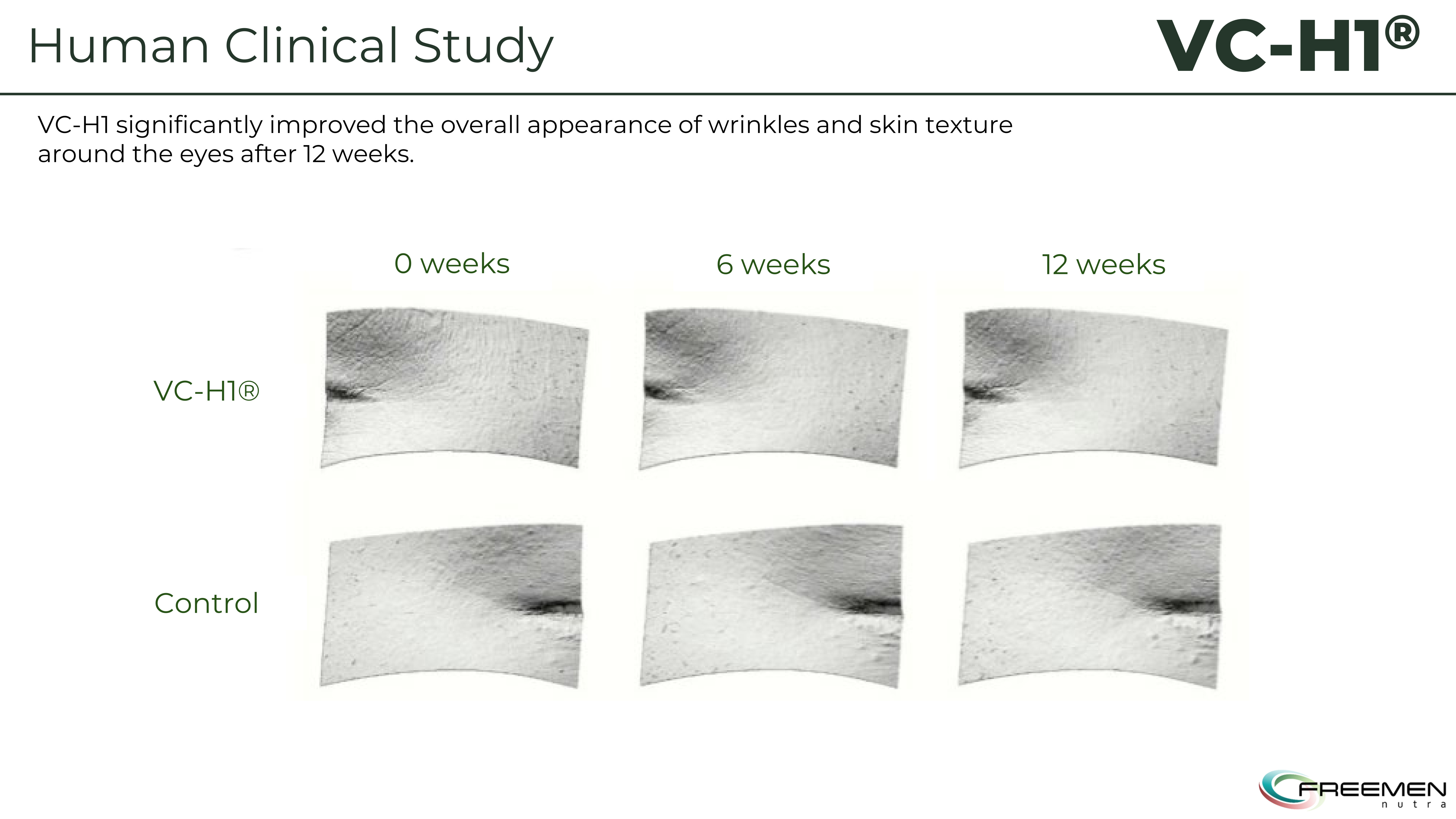
These are actual clinical trial photos showing eye area improvements over 12 weeks - you can see how VC-H1 participants experienced visible smoothing of fine lines compared to the placebo group.
Mechanisms: How VC-H1 Works
VC-H1's primary mechanism exploits the body's sophisticated collagen repair system. Under normal conditions, collagen degradation -- whether from UV exposure, mechanical stress, or enzymatic breakdown -- releases small peptide fragments into the extracellular space and bloodstream. These fragments aren't metabolic waste, they're molecular signals carrying critical information: that collagen damage has occurred.
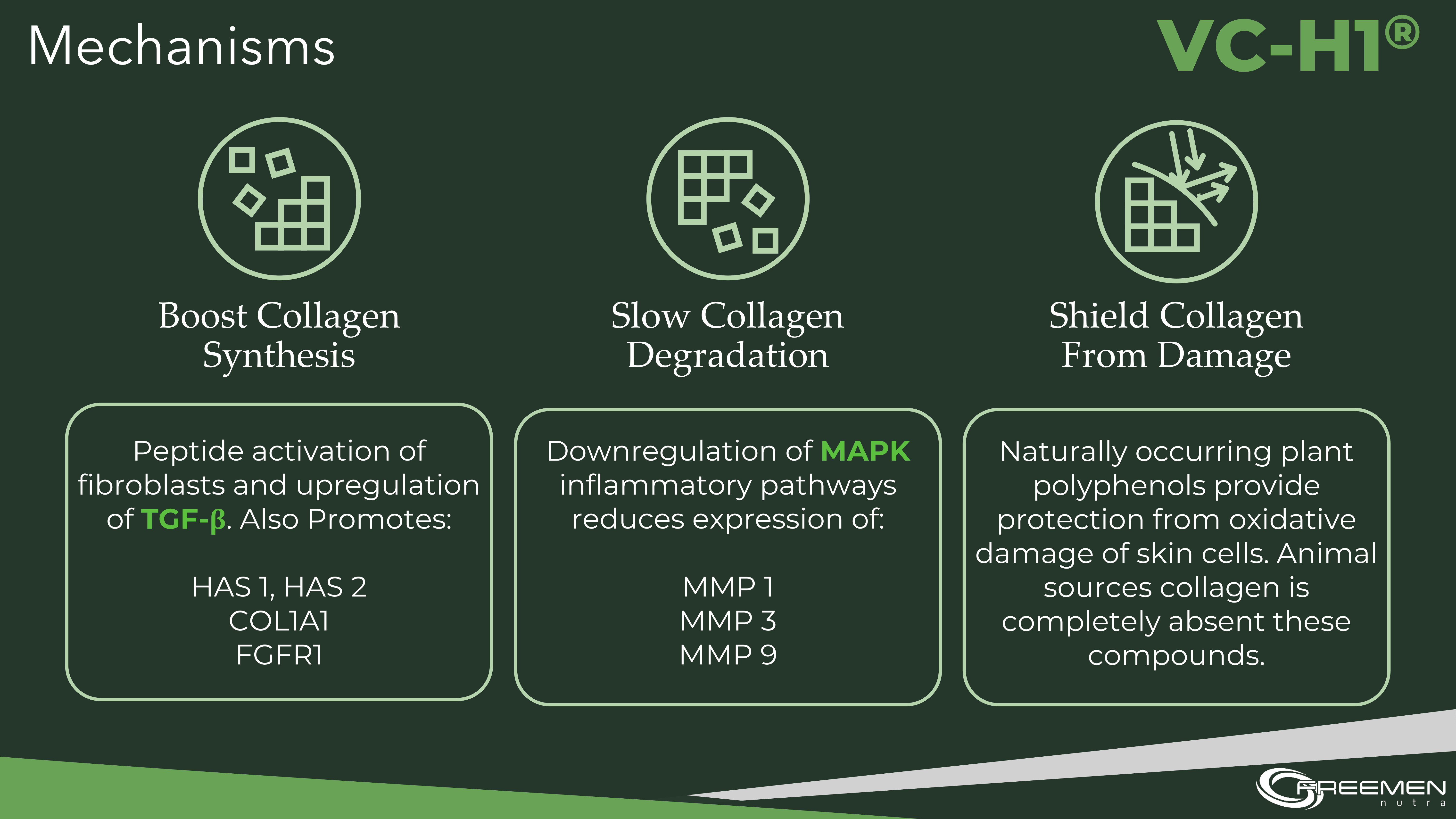
VC-H1 works through a triple approach - it boosts collagen synthesis through peptide activation, slows breakdown by reducing inflammatory pathways, and shields existing collagen from oxidative damage with natural plant polyphenols.
Taking Advantage of the Bioactive Peptide Signal
Fibroblasts, the cells responsible for synthesizing new collagen, express receptors that recognize specific peptide sequences. When G-X-Y patterned di- and tripeptides bind to these receptors, they trigger intracellular signaling cascades that upregulate collagen gene expression, increase procollagen synthesis, and enhance secretion of collagen precursors into the extracellular matrix.
Research on collagen-derived peptides demonstrates this mechanism directly. Pro-Hyp, the most abundant peptide in blood after collagen ingestion, significantly increases fibroblast proliferation and stimulates hyaluronan synthase-2 (HAS2) expression.[7] The pathway involved (STAT3) integrates and activates growth factor signals, ultimately driving both cell division and extracellular matrix production.
VC-H1 delivers these identical peptide sequences despite its plant origin. The Pro-Hyp dipeptide doesn't carry a molecular signature identifying its source -- animal or plant origin makes no difference to fibroblast receptors. What matters is the precise amino acid sequence and molecular configuration, both of which VC-H1 replicates from hibiscus extensin.
The 316 Da average molecular weight amplifies this effect through superior bioavailability. Intestinal peptide transporters (PEPT-1) preferentially transport di- and tripeptides, allowing VC-H1's peptides to cross the gut barrier intact rather than being broken down to individual amino acids.[7] Once in circulation, the smaller size enables better tissue penetration and higher local concentrations at fibroblast sites. The larger animal collagen peptides face absorption barriers that reduce the percentage reaching target tissues, explaining VC-H1's superior in vitro potency despite containing the same core signaling sequences.
Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects
While bioactive peptides trigger collagen synthesis, hibiscus-derived phytonutrients simultaneously protect existing collagen from degradation. This dual mechanism distinguishes VC-H1 from pure animal collagen, which lacks meaningful antioxidant content.

Memo-Q breaks the mold in cognitive enhancement. This silk protein-derived ingredient from Freemen Nutra has 10 human clinical trials showing memory and learning benefits across ALL ages -- from 7-year-olds to 90+ seniors. Four mechanisms, one powerful ingredient. 400-600mg daily.
The anthocyanin profile (dominated by delphinidin-3-sambubioside) provides potent reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging. UV radiation generates ROS in skin tissue, causing lipid peroxidation, DNA damage, and direct oxidation of amino acid residues in collagen and elastin. This oxidative damage weakens structural proteins, making them susceptible to enzymatic degradation.
Delphinidin-3-sambubioside neutralizes multiple ROS types including superoxide radicals, hydroxyl radicals, and hydrogen peroxide through electron donation, and without forming harmful secondary radicals. The sambubioside glycoside (glucose-xylose disaccharide) attached to the delphinidin core enhances water solubility and stability compared to aglycone anthocyanidins, improving bioavailability and extending antioxidant activity duration.[9]
Beyond direct ROS scavenging, VC-H1's polyphenols suppress inflammatory signaling. Chronic low-grade inflammation accelerates skin aging through multiple mechanisms. Pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 activate transcription factors like NF-κB, AP-1 that upregulate matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). These enzymes directly cleave collagen, elastin, and other extracellular matrix components, degrading the structural network faster than fibroblasts can rebuild it.
Hibiscus anthocyanins reduce pro-inflammatory cytokine expression in dermal fibroblasts and suppress MMP-1 (collagenase) activity through multiple pathways. These compounds prevent harmful effects that lead to excessive collagen breakdown.
The clinical trial results validate this protective mechanism. The significant TEWL reduction and improved barrier function observed in the VC-H1 group reflect preserved lipid organization and structural integrity, which are outcomes consistent with reduced oxidative and inflammatory damage. The sustained benefits through 12 weeks suggest ongoing protection, not just acute antioxidant effects.
ECM Preservation and Synthesis
Collagen doesn't function in isolation, it exists within a complex extracellular matrix (ECM) containing elastin, hyaluronic acid, proteoglycans, and structural glycoproteins. Skin health depends on the integrated function of this entire network, not just collagen content.
VC-H1 influences multiple ECM components through interconnected mechanisms. The Pro-Hyp peptide specifically upregulates hyaluronan synthase-2 (HAS2), the enzyme responsible for synthesizing high-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid.[7] Hyaluronic acid's exceptional water-binding capacity (holding up to hundreds of times its weight in water) drives the deep moisture improvements observed in the clinical trial. It also provides the hydrated gel matrix that supports fibroblast migration, proliferation, and collagen deposition during tissue remodeling.
Elastin synthesis, while less studied with VC-H1 specifically, likely benefits from improved fibroblast function and reduced MMP activity. Elastin degradation by elastases (MMP-2, MMP-9, MMP-12) contributes substantially to loss of skin elasticity with aging. By suppressing these enzymes, VC-H1's anti-inflammatory components preserve existing elastin fibers while creating an environment conducive to new elastin production. The significant elasticity improvements in the clinical trial suggest this mechanism operates effectively in vivo.
Skin barrier lipids (ceramides, cholesterol, and free fatty acids) maintain proper ratios and organization. While VC-H1 doesn't directly provide lipid precursors, the improved barrier function (reduced TEWL) indicates enhanced lipid synthesis or organization. This may occur through reduced oxidative stress that would otherwise damage lipids, improved keratinocyte differentiation driven by better underlying dermal support, or both.
The combined effects create an all-around improvement in skin architecture: increased collagen synthesis, preserved existing collagen, enhanced hyaluronic acid production, protected elastin networks, and improved barrier lipid organization. This explains why clinical outcomes showed improvements across barrier function, structural integrity, and appearance: VC-H1 addresses multiple interconnected aspects of skin health simultaneously.
Practical Applications and Formulation
With its water solubility, clean taste, and low 1.5g dose, VC-H1 works in multiple formats - from jelly sticks and powders to capsules, giving you flexibility that traditional collagen can't match.
Dosing and Usage
VC-H1 delivers clinical benefits at just 1.5 grams daily -- one-third to one-tenth the typical collagen supplement dose of 5-15 grams. This dramatic dose reduction creates immediate advantages for both brands and consumers.
For brands, lower doses mean lower raw material costs per serving, improved profitability, and greater formulation flexibility. A 1.5-gram ingredient fits comfortably in three-capsule servings, single-scoop powders, or ready-to-drink beverages where 10-15 grams of traditional collagen would create unworkable serving sizes or unpleasant texture.
For consumers, the cost-per-serving drops substantially compared to equivalent-efficacy animal collagen products. When a supplement requires one-third the material to achieve superior results, the value proposition speaks for itself. This makes consistent daily use (which is critical for optimal benefits) more financially sustainable.
Formulation Advantages
VC-H1's physical and organoleptic properties solve problems that plague traditional collagen formulations.
- Water solubility enables clean dissolution in beverages without the clumping, foam formation, or settling common with hydrolyzed collagen powders. This opens the entire functional beverage category: better ready-to-drink products, drink mixes, stick packs, and effervescent tablets.
- Neutral taste and odorless profile eliminate the need for aggressive flavor masking. Animal collagen carries distinct taste and aroma that require substantial sweeteners, flavors, and aromatics to overcome. VC-H1 disappears into formulations, allowing subtler flavor profiles, reduced sugar content, and cleaner label declarations.
- Two-year shelf stability at room temperature simplifies logistics, reduces waste from expiration, and supports global distribution without cold chain requirements. The stability extends across pH ranges and temperature variations, maintaining potency through manufacturing, storage, and consumer use.
- Format versatility expands beyond traditional powder and capsule delivery. The 1.5-gram dose fits easily into:
- Two standard capsules (750mg each) for convenient once-daily supplementation
- Single-serving powder sachets or stick packs for travel and on-the-go use
- Gummy formulations where 10+ grams of collagen would be impossible
- Functional food applications (bars, bites, chocolates) where larger doses create texture problems
- Ready-to-drink beverages in standard 8-16oz formats without viscosity issues
This format flexibility allows brands to differentiate through delivery innovation rather than being constrained to the same powder-in-a-tub format saturating the collagen market.
Stacking Possibilities
Understanding VC-H1's mechanisms reveals intelligent formulation strategies that amplify benefits through synergy rather than redundancy.
- Synergy with antioxidants: VC-H1 already provides anthocyanin antioxidants, but complementary antioxidants working through different mechanisms enhance overall protection. Vitamin C supports collagen synthesis through proline hydroxylation (creating hydroxyproline essential for collagen stability), scavenges different ROS types than anthocyanins, and regenerates oxidized vitamin E. Vitamin E protects lipid membranes from peroxidation. Combining VC-H1 with vitamins C and E creates comprehensive antioxidant coverage across water-soluble and lipid-soluble compartments.
- Complementary to traditional collagen: VC-H1 doesn't just have to replace animal collagen, it can also enhance it. The two ingredients deliver the same bioactive peptide signals but through different molecular weight distributions and absorption kinetics. Combining them may provide both immediate (VC-H1's rapid absorption) and sustained (animal collagen's gradual breakdown) peptide signaling. The added anthocyanins from VC-H1 protect the collagen both ingredients stimulate.
- Hyaluronic Acid, Minerals, and More: Many other common skin care ingredients, such as biotin and hyaluronic acid, will still work well alongside VC-H1, and can be used to further improve skin hydration status. Quality forms of zinc, such as zinc picolinate, are also great for warding off zinc deficiency, which can result in numerous skin problems.
Target Applications
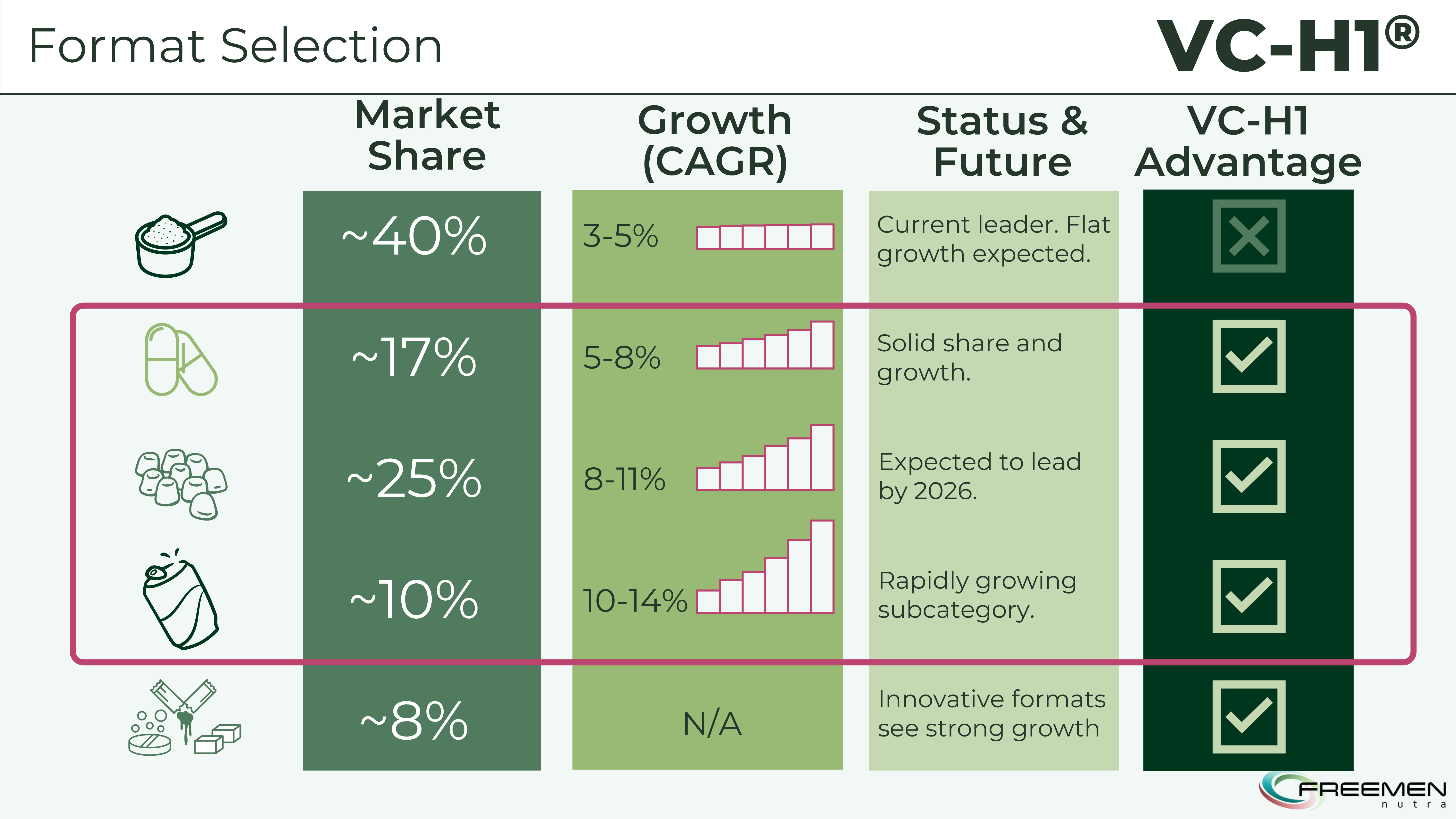
The data shows gummies and sticks leading growth at 8-14% CAGR while traditional powders plateau - VC-H1's versatile formulation advantages work across all formats, giving you flexibility in the fastest-growing segments.
VC-H1's evidence-based efficacy and clean positioning enable entry across multiple supplement categories:
- Beauty-from-within supplements targeting skin hydration, elasticity, and anti-aging serve as the primary market. The clinical validation of visible wrinkle reduction and measured elasticity improvement provides credible marketing claims in a category often reliant on weak evidence.
- Combination formulations amplify market opportunity. Pairing VC-H1 with traditional collagen creates a superior collagen product with added antioxidant benefits. Combining with hyaluronic acid, biotin, zinc, and vitamins C and E addresses skin health through multiple complementary mechanisms. The different pathways prevent ingredient redundancy while creating comprehensive formulations.
- Functional beverages leverage VC-H1's solubility and neutral profile for beauty waters, enhanced teas, collagen coffee creamers, and sports recovery drinks. The low dose enables meaningful ingredient levels without compromising taste or texture.
- Sports nutrition applications extend beyond traditional beauty markets. Connective tissue support for joint health, faster recovery from training stress, and injury prevention appeal to athletes and active individuals. VC-H1's collagen synthesis stimulation and anti-inflammatory properties align with these performance and recovery goals.
- Healthy aging formulations address broader demographics seeking to maintain vitality and physical function. Combining VC-H1 with ingredients supporting cognitive function, metabolic health, and cellular health creates comprehensive longevity-focused products.
Certifications and Clean Label

VC-H1 meets every major dietary and quality standard you could want - vegan, halal, kosher, organic, non-GMO, plus comprehensive manufacturing certifications that ensure you're getting exactly what's on the label.
VC-H1 meets modern consumers' demand for transparency, sustainability, and dietary accommodation:
- Certified Vegan, Halal, and Kosher opens markets unavailable to animal-derived collagen
- Organic hibiscus source from a dedicated 200-hectare farm ensures authentic organic certification
- Non-GMO verification pending will complete the clean label trifecta
- Farm-to-tablet traceability through vertically integrated supply chain provides transparency rare in botanical ingredients
- Sustainability credentials include reduced greenhouse gas emissions compared to animal agriculture, lower water consumption, and elimination of multiple transportation steps through vertical integration
These certifications aren't marketing add-ons -- they're fundamental to VC-H1's positioning as the ethical, sustainable, effective alternative to animal collagen.
Competitive Positioning
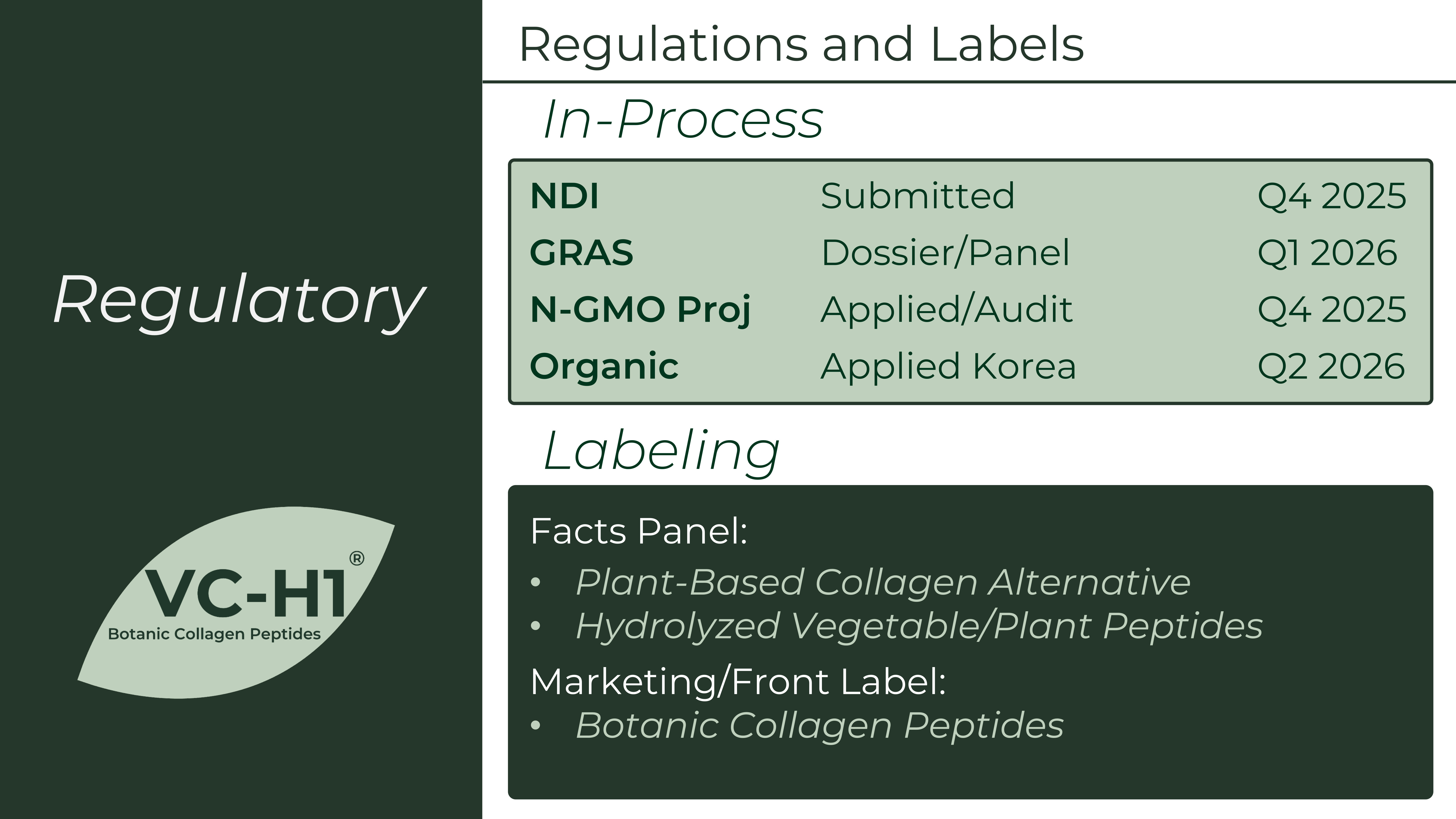
VC-H1's regulatory pathway is well underway with NDI submitted and GRAS dossier in progress - you'll be able to label it as "Plant-Based Collagen Alternative" or "Botanic Collagen Peptides" on finished products.
VC-H1's market positioning addresses diverse consumer needs that existing collagen products fail to meet simultaneously:
- Vegans and vegetarians gain the first plant-based alternative delivering actual bioactive collagen peptides with clinical validation, not amino acid blends masquerading as collagen
- Sustainability-focused buyers access proven efficacy without animal agriculture's environmental footprint
- Religious dietary observers (halal, kosher) find certified compliance with clinical evidence
- Efficacy-driven consumers receive gold-standard RCT validation with objective measures and head-to-head superiority data
- Value-conscious shoppers achieve better results at one-third to one-tenth the dose of animal collagen
The value proposition unifies botanical authenticity with scientific rigor: "Where Beauty Blooms" connects hibiscus's traditional skincare heritage with modern clinical validation. This evidence-based positioning enables professional recommendations from dermatologists, nutritionists, and healthcare practitioners who require peer-reviewed data. Premium pricing finds justification in superior efficacy, lower effective dose, comprehensive certifications, and transparent sustainability --- creating multiple entry points across beauty, wellness, sports nutrition, and healthy aging markets.
Conclusion: The Future of Collagen Supplementation
VC-H1 accomplishes what the supplement industry has sought for years: a genuinely effective plant-based collagen alternative backed by the same caliber of evidence supporting animal-derived products. This isn't marketing hyperbole, it's biochemical reality validated through double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials.
The market wants plant-based solutions, the science proves peptides drive efficacy, and VC-H1 delivers it all - 100% plant-based with 90% bioactive peptides, strong research backing, and cost-effective dosing.
The breakthrough centers on delivering actual bioactive peptides, not amino acid substitutes or indirect support nutrients. VC-H1 contains G-X-Y-patterned di- and tripeptides including but not limited to Pro-Hyp, Gly-Pro-Hyp, and Hyp-Gly -- the identical molecular signals that trigger collagen synthesis in fibroblasts. At 316 Da average molecular weight and 85-90% di- and tripeptide content, these peptides absorb more efficiently than animal collagen peptides, explaining the 1.7-4.0x superior collagen synthesis stimulation at less than half the concentration.
The clinical validation establishes a new category standard. Gold-standard RCT methodology with objective instrumentation demonstrated significant improvements (p<0.001) across hydration, elasticity, wrinkle depth, barrier function, and overall appearance at just 1.5 grams daily. Most "vegan collagen" products lack human studies entirely, yet VC-H1 meets the evidentiary bar set by premium animal collagen brands while surpassing them in sustainability, ethics, and organoleptic properties.
This convergence of efficacy and values reshapes market dynamics. Consumers no longer choose between effective supplements and ethical ones. Brands no longer sacrifice performance for clean positioning. The lower dose requirement reduces costs while enabling format innovations impossible with 10-15 gram servings.

Explore the first dietary supplement ingredient that works on the gut-brain axis, Digexin, with Freemen Nutra's Eric Withee on the PricePlow Podcast Episode #147. The data is unlike anything we've ever seen!
For formulators, VC-H1 opens opportunities across beauty supplements, functional beverages, sports nutrition, and healthy aging products. The neutral taste, water solubility, and comprehensive certifications (vegan, halal, kosher, organic) eliminate formulation constraints and market access barriers. The dual mechanism combining peptide signaling with anthocyanin protection creates differentiation in crowded categories.
VC-H1 from Freemen Nutra demonstrates that plant-based alternatives can exceed animal-derived standards when designed with rigorous science rather than compromising efficacy for positioning. As the supplement industry evolves toward evidence-based formulations and sustainable sourcing, VC-H1 establishes the benchmark for next-generation beauty-from-within ingredients where beauty truly blooms.






Comments and Discussion (Powered by the PricePlow Forum)