
NNB Nutrition's Pürest Creatine achieves "not detected" levels for nasty contaminants like DHT and DCD that plague generic creatine -- at nearly half the price of other premium sources. Finally, clean creatine that won't break your budget.
Creatine monohydrate remains the most researched and effective sports nutrition ingredient ever developed, with benefits spanning muscle growth, strength, recovery, and cognitive function.[1] Yet despite decades of research confirming creatine's safety and efficacy, a significant problem persists: manufacturing quality varies dramatically across suppliers, leading to contamination with compounds that have no place in a daily supplement.
NNB Nutrition Announces Pürest Creatine: Cleaner Creatine at a Better Price
NNB Nutrition is addressing this issue head-on with the launch of Pürest Creatine, debuting at SupplySide Global 2025. The new ingredient sets an industry benchmark, achieving the lowest levels of dicyandiamide (DCD), dihydrotriazine (DHT), and creatinine, all verified through third-party testing and supported by transparent certificates of analysis for every production lot. The value proposition is compelling: premium purity at nearly half the price of other high-purity creatine sources.
For formulators and brands seeking to differentiate in a crowded category, Pürest Creatine offers a competitive advantage that resonates with increasingly educated consumers who understand that not all creatine is created equal.
This article explains the creatine manufacturing problem and how NNB is cleaning up the category, but first, sign up for our NNB Nutrition news alerts to get updated on other new products, studies, and developments:
Subscribe to PricePlow's Newsletter and Alerts on These Topics
The Manufacturing Problem: Corner-Cutting Creates Contamination
The synthesis of creatine monohydrate involves a multi-step chemical process: adding acetic acid to sodium sarconsinate solution, introducing cyanamide, cooling to promote crystallization, and filtering to isolate the final product.[2] When manufacturers prioritize cost reduction over quality control -- using lower-grade chemical precursors, inadequate purification steps, or aggressive processing conditions -- several problematic byproducts accumulate.
EFSA's technical evaluation notes that inferior starting materials or insufficient water during recrystallization directly increase impurity formation, a manufacturing reality that separates premium from generic production.[3]
Creatine isn't a micro-dosed ingredient, either. When you're taking 5 grams of a substance, if it's only 96% pure, then you're getting 200mg of "other stuff"... that's no small amount!
These manufacturing shortcuts don't just compromise product quality; they introduce contaminants that regulatory bodies have flagged as safety concerns. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) established maximum recommended levels for three key impurities in creatine products, yet testing of generic creatine consistently reveals violations of these guidelines.
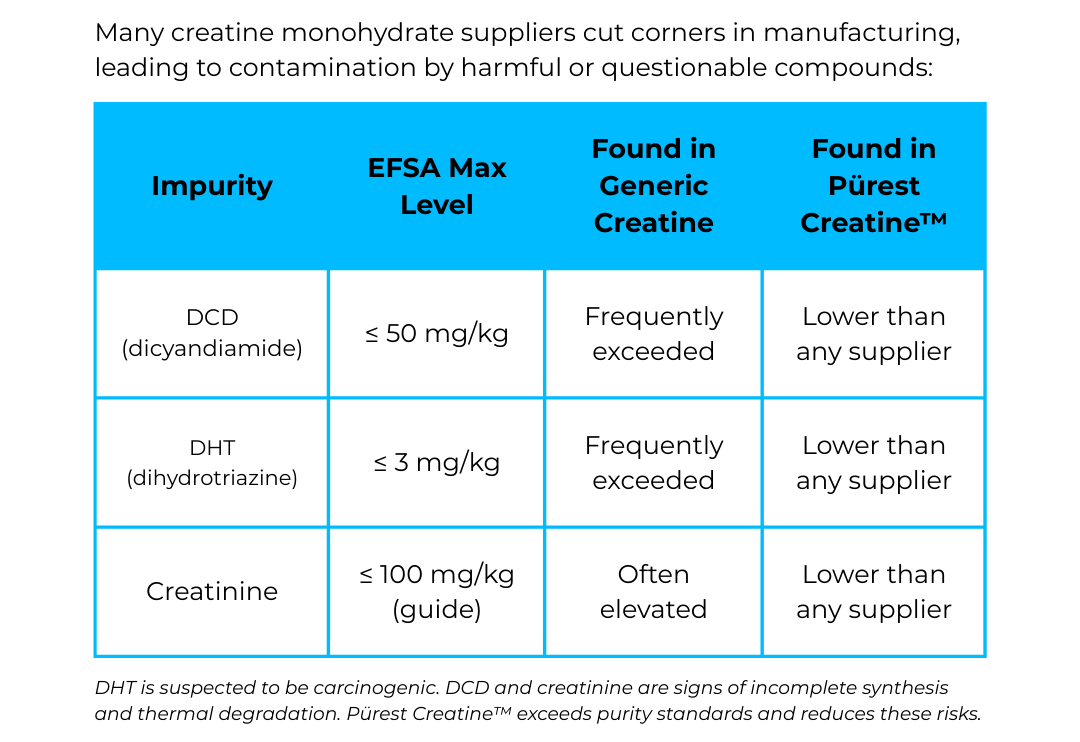
Side-by-side analysis showing how manufacturing shortcuts lead to contamination in standard creatine sources, while NNB's proprietary process achieves levels below detection limits for all major impurities.
The stakes extend beyond regulatory compliance. Water quality during manufacturing directly impacts ingredient purity. Regions with compromised water sources produce ingredients with elevated heavy metal content, requiring extensive filtration and purification protocols that many manufacturers skip to reduce costs. Clean water produces clean ingredients, but only when manufacturers implement the necessary quality control measures.
Understanding the Contaminants: What's in Your Creatine?
-
Dicyandiamide (DCD): The Quality Control Indicator
Dicyandiamide serves as a synthetic precursor in creatine manufacturing and should be removed almost entirely during proper purification. EFSA recommends DCD levels not exceed 50 mg/kg in finished creatine products.[3] Generic creatine frequently violates this threshold, with testing revealing levels exceeding 100 mg/kg.
While DCD isn't acutely toxic at trace supplement levels, animal studies demonstrate potential kidney and liver effects with chronic high exposure. More importantly, the presence of elevated DCD signals inadequate manufacturing quality control, a red flag indicating other purification failures may exist.
NNB Nutrition's marketing material highlighting their premium creatine ingredient's key selling points, including ultra-low impurity levels, competitive pricing, and versatile applications across sports nutrition and cognitive health formulations.
For consumers taking standard 5g daily doses, DCD exposure from contaminated creatine remains relatively low. However, research demonstrates that higher creatine doses (up to 20g daily for combating sleep deprivation) provide significant cognitive benefits.[4] Loading 20g grams for 5 days is still sometimes employed as well. At these elevated intake levels, impurity exposure scales proportionally, making manufacturing purity increasingly critical.
To put DCD exposure in regulatory perspective, EFSA established a tolerable daily intake (TDI) of 1 mg/kg body weight per day for dicyandiamide when used as a monomer in food packaging materials.[3] Even if consuming 3g daily of creatine at EFSA's maximum allowable DCD level (50 mg/kg), total DCD exposure would be less than 150µg per day -- equivalent to 2.5 µg/kg body weight for a 60kg person. This represents just 0.25% of the established TDI, demonstrating substantial safety margins even at maximum allowable contamination levels. Pürest Creatine's "not detected" status eliminates this exposure entirely.
Pürest Creatine achieves "not detected" status for DCD, meaning levels fall below the detection threshold of validated analytical methods -- substantially better than the 50 mg/kg maximum recommendation.
-
Dihydrotriazine (DHT): The Carcinogenic Concern
Dihydrotriazine (the other DHT) represents the most serious contaminant in poorly manufactured creatine. EFSA recommends DHT levels at or below 3 mg/kg because DHT-related compounds are suspected carcinogens. Testing of generic creatine products reveals DHT levels exceeding 110 mg/kg, more than 35 times the recommended maximum.
The formation of dihydrotriazine occurs when specific reaction pathways during synthesis aren't properly controlled. Premium manufacturers employ proprietary synthesis methods that avoid these hazardous byproduct-generating pathways entirely. This isn't a filtration issue that can be solved downstream... it requires fundamental changes to the manufacturing process itself.
Complete overview showing how manufacturing shortcuts create contamination in standard creatine, NNB's proprietary advantages, research-backed benefits, and head-to-head purity comparisons with generic and premium alternatives.
For consumers supplementing with creatine daily, potentially for years or decades given creatine's long-term safety profile, minimizing exposure to suspected carcinogens becomes paramount. Pürest Creatine achieves "not detected" status for dihydrotriazine, providing manufacturers and consumers with confidence that this contaminant has been eliminated from the final product.
-
Creatinine: The Thermal Degradation Marker
Creatinine is creatine's breakdown product, formed when creatine experiences thermal stress or degradation. While creatinine itself isn't harmful (the body naturally produces it as part of creatine metabolism), elevated creatinine levels in finished creatine products serve as a purity indicator. EFSA guidelines recommend creatinine levels at or below 100mg/kg.
High creatinine content signals one of two manufacturing failures: incomplete synthesis or thermal degradation during processing. Some manufacturers accelerate drying processes using higher temperatures to reduce production time and costs, but this thermal stress converts creatine into creatinine. Lower creatinine means consumers receive more actual creatine per serving rather than its degraded form.
Generic creatine testing frequently reveals creatinine levels approaching or exceeding 100mg/kg. Premium sources achieve levels around 50mg/kg. Pürest Creatine specifies creatinine at or below 30mg/kg -- substantially lower than both generic and premium competitors, indicating superior manufacturing quality control.
-
Heavy Metals: The Water Quality Connection
Heavy metal contamination in creatine stems primarily from water quality during manufacturing. Lead contamination has emerged as a concern with creatine produced in regions where water sources contain elevated heavy metal levels. Without extensive filtration and purification, these contaminants transfer directly into the final ingredient.
Pürest Creatine addresses this systematically. Every production lot undergoes testing for lead, arsenic, cadmium, and mercury. The specification requires lead levels at or below 1.0 ppm, demonstrating that proper water treatment and quality control eliminate this contamination pathway. The principle is straightforward: dirty water produces dirty ingredients, but rigorous purification protocols ensure clean outputs regardless of input water quality.
How Pürest Creatine Achieves Industry-Leading Purity
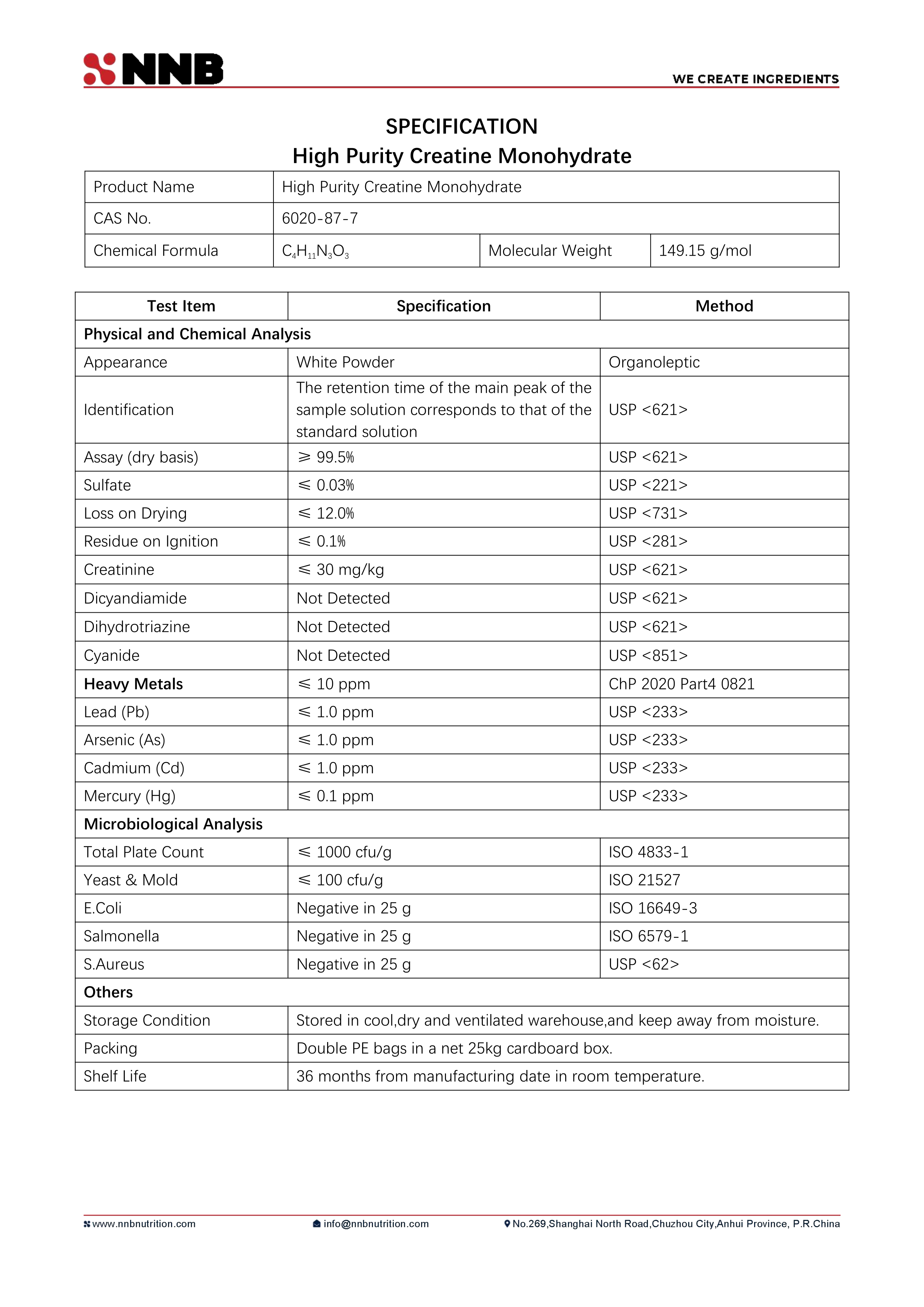
Official specification document detailing chemical analysis parameters, heavy metal limits, and microbiological testing standards that demonstrate the ingredient's pharmaceutical-grade quality and regulatory compliance.
NNB Nutrition's approach to creatine manufacturing centers on three core principles:
- Proprietary Synthesis Methods: Rather than using conventional reaction pathways that generate hazardous byproducts, Pürest Creatine employs a proprietary synthesis process that avoids DCD and DHT formation entirely. This isn't about better filtration after synthesis; it's about preventing contamination from occurring in the first place.
- Gentle Processing Without Harsh Residues: The manufacturing process avoids aggressive solvents and high-temperature drying that create thermal degradation. This controlled approach maintains creatine integrity while minimizing creatinine formation.
- Comprehensive Quality Control: Every production lot undergoes testing for all major contaminants and heavy metals. Certificates of analysis provide batch-level transparency, allowing brands to verify purity for every lot they purchase. This isn't sampling-based quality control; it's universal testing that ensures consistency across all production.
The Numbers: Pürest Creatine vs. The Competition
Third-party testing using the universally recognized USP method reveals substantial differences across creatine sources:
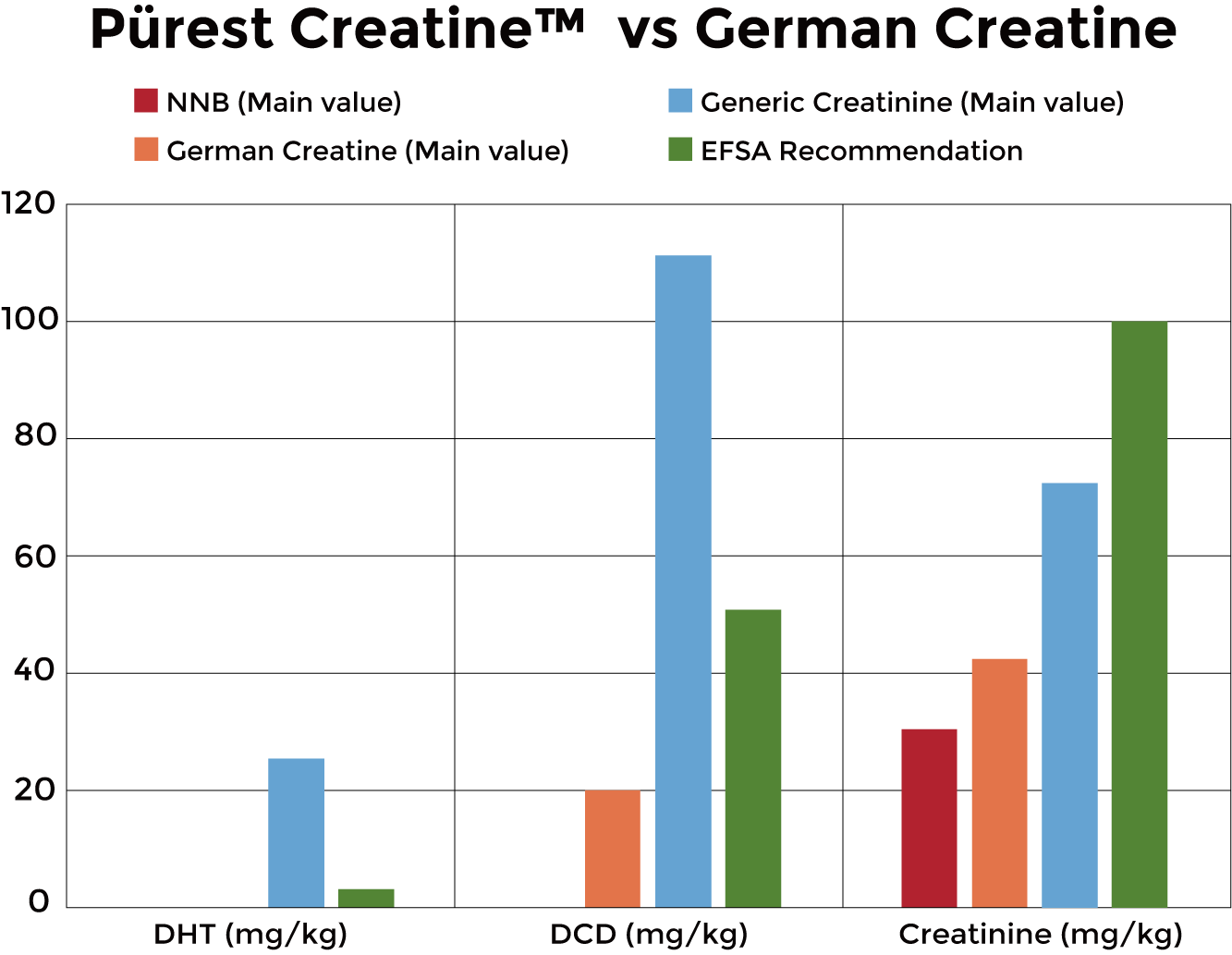
Bar graph demonstrating measurable contamination levels across different creatine sources, with Pürest Creatine achieving the lowest impurity profile compared to premium German and generic alternatives.
Generic Creatine:
- DHT: ~110 mg/kg (37× the EFSA recommended maximum)
- DCD: ~100 mg/kg (2× the EFSA recommended maximum)
- Creatinine: ~100 mg/kg (at the EFSA guideline threshold)
Other Premium Creatines:
- DHT: ~20 mg/kg (7× the EFSA recommended maximum)
- DCD: ~50 mg/kg (at the EFSA recommended maximum)
- Creatinine: ~50 mg/kg (half the EFSA guideline)
Pürest Creatine:
- DHT: Not Detected (below detection limits)
- DCD: Not Detected (below detection limits)
- Creatinine: ≤30 mg/kg (less than one-third the EFSA guideline)
The data demonstrates that even premium creatine sources contain measurable levels of contaminants that Pürest Creatine eliminates entirely. For formulators developing products at higher dose ranges, whether for athletic performance, cognitive enhancement, or longevity applications, these purity differences become increasingly meaningful.
Premium Purity Without Premium Price
The traditional creatine market presents formulators with an uncomfortable choice: select affordable generic creatine with contamination concerns, or invest in premium sources at substantially higher costs. Pürest Creatine disrupts this paradigm by delivering industry-leading purity at nearly half the price of other high-purity creatine sources.
This pricing strategy creates opportunities for brands across market segments:
- Mass-Market Brands can upgrade from generic creatine to ultra-pure sourcing without significant cost increases, using purity as a differentiation point in crowded categories.
- Premium Brands can maintain high-quality formulations while improving margins, or invest savings into additional active ingredients that enhance product efficacy.
- Emerging Brands gain access to best-in-class creatine quality that was previously restricted to brands with larger purchasing volumes and higher budgets.
The value proposition extends beyond raw material costs. Brands using Pürest Creatine gain access to marketing-friendly messaging around purity, transparency, and quality control... attributes that resonate with educated consumers who understand the creatine quality spectrum.
Why Creatine Purity Matters: The Performance and Safety Case
The extensive research on creatine supplementation -- over 500 peer-reviewed publications -- confirms remarkable consistency in benefits when using pure creatine monohydrate:[1,5]
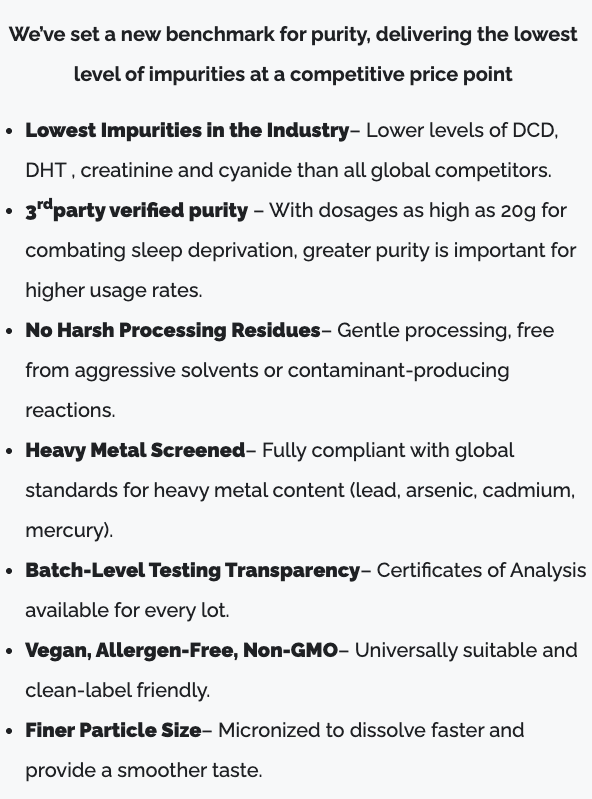
NNB's comprehensive quality advantages including industry-lowest impurities, third-party verification, gentle processing methods, and universal clean-label compatibility for diverse formulation applications.
- Strength and Muscle Growth: Meta-analyses show creatine users gain an average of 2.2 kg more fat-free mass than placebo groups during 12 weeks or less of training.[6] Strength improvements appear as early as two weeks into supplementation.[7]
- High-Intensity Performance: Creatine monohydrate enhances short-duration, high-intensity performance by approximately 5-15%.[8]
- Recovery Enhancement: Research demonstrates that creatine supplementation reduces creatine kinase (CK) levels (a marker of muscle damage) by 18-27% at 24-48 hours post-training compared to placebo.[9]
- Cognitive Support: Creatine supplementation improves cognitive performance following supplementation, with the brain's high energy demands making it responsive to increased phosphocreatine availability.[10-12]
- Cellular Hydration and Thermoregulation: Studies confirm creatine's role in improving cellular hydration status and supporting thermoregulation during exercise.[13]
These benefits depend on actual creatine content and purity. When consumers purchase creatine expecting 5g of pure creatine monohydrate per serving but receive a product with elevated creatinine (creatine's degraded form) or contaminated with manufacturing byproducts, they're not getting what they paid for, neither in terms of efficacy nor safety.
The International Society of Sports Nutrition's position stand affirms that creatine monohydrate is safe when consumed at recommended dosages, with long-term studies extending up to five years showing no adverse effects on kidney or liver function in healthy individuals.[2] However, this safety profile assumes high manufacturing purity: free from DCD, DHT, heavy metals, and excessive creatinine. That's normally what the studies get (highly-tested, pure material from the most prominent chemical companies), but is it what's in everyone's generic creatine supplement?
Formulation Applications and Stacking Strategies
Pürest Creatine's ultra-pure profile makes it suitable across performance, cognitive, and longevity-focused formulations:

Walk into any GNC or Vitamin Shoppe and you'll see the supplement revolution in action. NNB Nutrition's ingredients like MitoBurn and CaloriBurn are now in bestselling products across the shelves. The era of fairy dusting is over -– educated consumers demanded better, and they got it.
- Pre-Workout and Intra-Workout: Combine with HydroPrime® glycerol for enhanced hydration and cell volumization. Stack with FlowTech™ beta-alanine for complementary endurance support and buffering capacity.
- Nootropic and Cognitive Formulations: Creatine's brain energy metabolism benefits synergize with ingredients like GeniusPure® (Alpha-GPC) or NeuroFlow® for comprehensive cognitive support.
- Strength and Muscle Growth Products: Pair with DL 185® (a novel strength and muscle growth dileucine peptide ingredient from NNB) for synergistic muscle protein synthesis and performance enhancement.
- Longevity and Healthy Aging: Creatine's neuroprotective effects and muscle preservation benefits align with longevity-focused formulations, working alongside ingredients like NMN, spermidine, and L-ergothioneine.
- Standalone Products: The competitive pricing enables profitable creatine monohydrate standalone products that compete effectively with generic alternatives while offering demonstrable purity advantages.
The standard 5g daily serving remains effective for most applications, though research supports higher doses (up to 20g) for specific use cases like cognitive performance during sleep deprivation, making ultra-low impurity levels increasingly important at elevated intake ranges.
Available Now: Launch at SupplySide Global 2025
Pürest Creatine makes its official debut at SupplySide Global in Las Vegas, October 28-31, 2025. NNB Nutrition will showcase the ingredient alongside its comprehensive portfolio of research-backed, clinically validated ingredients for sports nutrition, cognitive health, and longevity applications.
For formulators and brands seeking to elevate product quality without sacrificing margins, Pürest Creatine delivers a compelling solution: industry-leading purity verified through third-party testing, supported by transparent certificates of analysis, and available at competitive pricing that makes premium quality accessible across market segments.
The ingredient is vegan, allergen-free, and non-GMO, with a micronized particle size for improved dissolution and a smoother taste profile. Full technical documentation, including specifications and certificates of analysis, is available through NNB Nutrition's technical support team.
The Bottom Line

NNB Nutrition returns to SupplySide Global 2025 at Booth #5154 with their latest innovations! Experience OnSwitch energy drink featuring high-dose MitoBurn L-BAIBA, taste SweetVantage natural sweetener, and explore their longevity platform. Don't miss this showcase of premium functional ingredients!
Creatine monohydrate's efficacy and safety are beyond question... when manufacturing quality is properly controlled. The difference between generic creatine and ultra-pure sources isn't marginal, it's the difference between "not detected" and "37 times the recommended maximum" for suspected carcinogens.
Pürest Creatine resolves the quality-versus-cost dilemma that has forced formulators to compromise. By achieving the industry's lowest impurity levels through proprietary synthesis methods and comprehensive quality control, while maintaining pricing at nearly half the cost of other premium sources, NNB Nutrition has created an ingredient that meets the demands of both formulators and consumers.
For an industry increasingly focused on transparency, testing, and quality, Pürest Creatine sets a new standard: one where premium purity doesn't require premium pricing, and where brands can confidently deliver the cleanest, most effective creatine available.
Subscribe to PricePlow for more on Pürest Creatine and NNB Nutrition's ingredient portfolio, including upcoming third-party laboratory test results and formulation guides:







Comments and Discussion (Powered by the PricePlow Forum)