Nitric oxide (NO) is one of the most popular targets for supplementation. The vast majority of pre-workout formulas now include some kind of NO booster, and stimulant-free workouts focus primarily (and sometimes exclusively) on achieving the highly sought-after pump that comes with NO-mediated vasodilation.
Vasodilation can be a great thing. When your arteries expand in diameter, it decreases cardiovascular resistance, thus alleviating cardiac strain, lowering blood pressure, and reducing heart rate at all levels of exertion – including rest.

Fitnox is a patented dietary supplement ingredient from Aurea Biolabs that's made from three botanical sources that's great at facilitating nitric oxide production.
In other words, a good pump is more than cosmetic, and can actually help improve athletic performance.[1] Upregulating vasodilation can be a boon for health, too – its effects can help mitigate a person's risk of high blood pressure, stroke, and heart attack.[2]
Nitric Oxide: More Than Just A Pump
All of that is certainly impressive, but it turns out there's even more to NO signaling!
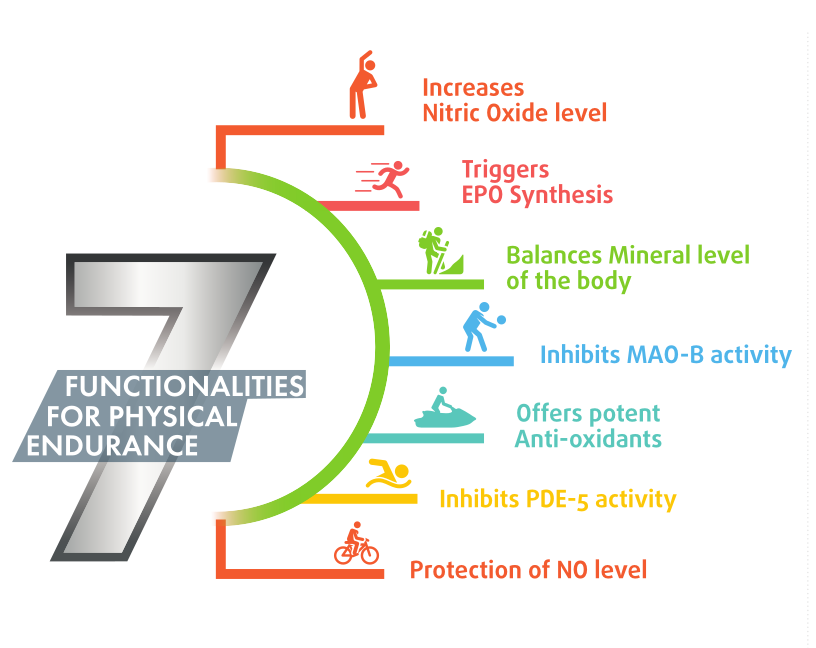
Research shows that boosting nitric oxide can also:
- Improve mitochondrial health<[3] – which has profound implications given the link between mitochondrial dysfunction and aging[4]
- Restore normal sleep duration[5]
- Improve sleep quality[6,7]
- Increase insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance[8,9]
Impaired NO production is also commonly observed in type 2 diabetes,[10] and seems to be a contributing factor to many diabetic symptoms.
Introducing Fitnox: More Than Just A Nitric Oxide Booster
This sets the stage nicely for our discussion of Fitnox, a patented ingredient developed and sold by Aurea Biolabs. It's a technology-driven ingredient incorporating the bioactive constituents from three botanical sources.

Fitnox is made from key constituents of Kaempferia parviflora (Thai Black Ginger), Moringa oleifera, and Pomegranate Extract
The evidence discussed below shows that Fitnox is great at facilitating the production of NO. But as we'll see, just like there's a lot more to NO than the pump, there's a lot more to Fitnox than just NO boosting. Fitnox is designed to enhance multiple dimensions of athletic performance and recovery, and we think it could confer some important health benefits as well.
To understand how it works, let's take a quick look at each of its three constituents, and then get into its specific research. But first, sign up for our Fitnox news alerts so that you can get notified when we have new products or studies related to the ingredient:
Subscribe to PricePlow's Newsletter and Alerts on These Topics
Let's discuss the three major sources in Fitnox, and look at research related to their effects on nitric oxide production:
-
Kaempferia parviflora (Thai Black Ginger)
Thai Black Ginger (Kaempferia parviflora) is the headliner constituent of Fitnox – it's primarily responsible for Fitnox's NO-boosting effect.
Sometimes referred to as krachaidum or krachai dum, the Kaempferia parviflora (KP) plant is native to Thailand, where it has been used medicinally for centuries.[11] It's rich in polymethoxyflavones, a class of flavonoids with shockingly broad and powerful effects.
In a 2022 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study that tracked the effects of 360 milligrams Kaempferia extract supplementation in adolescent athletes over a 12 week period, researchers found the following benefits:[11]
- Increased grip strength in both hands – 10% more in the right hand, and 5% more in the left
- 9% greater back leg strength
- 4% greater hip and upper body flexibility
- 1.4% faster 50 meter sprint
They also found that the athletes taking KP were more resilient to stress on a number of measures.[11]
The big one, though, was KP's effect on cardiorespiratory fitness. By week 12, the KP group had a 7% higher VO2max than the placebo group, which is a pretty huge effect size when it comes to VO2max.[11] They also had a 4% lower resting heart rate.[11]
The proposed mechanisms of action behind KP's wide-ranging athletic benefits include:
- Upregulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) gamma[12]
- Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)[13]
- Increased fat burning[14] and decreased fat storage[15]
- Increased mitochondrial biogenesis and ATP production[16]
- Vasodilatory effects[17]
- Anti-inflammatory effects[18]
Whenever we see any of these effects, in a natural ingredient, we take note. Here, we have several mechanisms of great interest to active nutrition consumers.
Not all NO is created equal, but KP doesn’t care
Specifically, KP has been shown to increase the activity of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS),[19] the good kind of NO production, while decreasing the activity of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), the bad NO.[20]
This is exactly what we want – eNOS causes vasodilation and its benefits, while iNOS is inflammatory.[21] Additionally, a systematic review published in 2017 found that there were no adverse effects up to 1.35 grams per day.[22]
-
Moringa oleifera
Sometimes called the horseradish tree because its roots taste similar to horseradish, Moringa oleifera is an incredibly rich source of potent phytochemicals.
A great source of quercetin
Moringa is particularly high in quercetin,[23] a powerful antioxidant that's become popular in immunity supplements because it acts as a zinc ionophore,[24] allowing zinc to enter cells and exert its beneficial effects. Quercetin can significantly reduce inflammation by downregulating the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) inflammatory pathway.[23,25] It also inhibits the NLRP3 inflammasome, which is responsible for downstream cytokine production.[26]
Quercetin's antioxidant activity makes it great at protecting and stabilizing the NO molecule, which ultimately increases NO bioavailability.[27,28] This mechanism is part of quercetin's significant anti-hypertensive effect.[29,30]
But quercetin doesn't just improve NO signaling – it also inhibits angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2),[31] an enzyme responsible for triggering vasoconstriction, which is the opposite of vasodilation. Additionally, some viruses use ACE2 docking for cellular entry.[32-34] This means that the quercetin in the Moringa portion of Fitnox may provide immunity benefits thanks to ACE2 inhibition while also supporting the vasodilation effects that healthy advocates seek.
So the quercetin in Moringa can both increase the dilation of blood vessels and prevent their constriction, which ultimately has a strong vasodilatory effect.
Chlorogenic acid
Moringa also contains lots of chlorogenic acid,[35] another powerful antioxidant with anti-diabetic, anti-carcinogenic, anti-inflammatory and anti-obesity effects.[36] Chlorogenic acid can also improve NO bioavailability[37] so effectively that it can significantly reduce blood pressure in humans in high enough doses.[38]
Thanks to these powerful bioactive constituents among others, Moringa has been shown to upregulate eNOS[39] while downregulating iNOS,[40] just like KP does.
Muscle-protecting effect
A look at how Fitnox is built, using Polar-Nonpolar-Sandwich (PNS) Molecular Technology described at the bottom of this article
But besides reducing inflammation, helping improve cardiovascular health and function, and fighting oxidative stress, Moringa is also great for preventing muscle damage.
In one particularly interesting study using rats, researchers chemically-damaged their muscles with a drug called dexamethasone, and then subjected them to a 10-day exercise regimen designed to help their muscles recover. By the end of the study, the rats who took Moringa did much better on physical activity and coordination tests than the non-Moringa group.[41] These results indicate that Moringa can both limit damage to muscles caused by exercise, and accelerate recovery after the fact.
In another study where rats were administered valproic acid, which damages muscle tissue through oxidative stress, Moringa was found to reverse the biochemical changes associated with muscle damage.[42]
This is to say that the primary idea behind including Moringa in Fitnox is to help muscles cope with and recover from exercise.
Phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) inhibition
NO boosting is not the only way that Moringa can help improve cardiovascular function. Key constituents of Moringa have been shown to inhibit phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5), an enzyme responsible for triggering smooth muscle relaxation in certain blood vessels – most notably, those used for erections.
In their 2015 rat study, a team of researchers described the process of PDE-5-induced vasodilation:
"Nitric oxide penetrates the cytoplasm of smooth muscle cells and interacts with guanylyl cyclase, catalyzing conformational changes which in turn induce the conversion of guanosine 5'-triphosphate (GTP) to 3'-5'-cyclic guanosine monophosphate. cGMP in turn phosphorylates several proteins, resulting in decreased intracellular calcium levels causing the relaxation of arterial and trabecular smooth muscle, resulting in arterial dilatation, venous constriction, and the rigidity of penile erection. The inactivation of cGMP via PDE-5 decreases the dilation of arterial vessels and the constriction of venous blood vessels and increases penile tumescence."[43]
By inhibiting PDE-5, you can prevent cGMP from triggering vasoconstriction.[43] This has an overall vasodilatory effect.
Monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) inhibition
Moringa has also been shown to inhibit monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B), an enzyme responsible for degrading monoamine neurotransmitters.[43] Inhibiting MAO-B can extend the action of those neurotransmitters.
In particular, MAO-B inhibition can increase dopamine levels,[43] so Moringa is probably playing a large role in the dopamine-boosting effects of Fitnox that we'll discuss later on.
While Fitnox is normally added to pre-workout and cardiovascular support supplements for its ability to support nitric oxide levels, this can add a new dimension to the ingredient that's great for the mental/cognitive side of training.
-
Pomegranate (Punica granatum) Extract
Pomegranate extract (PE) is, like the other two Fitnox constituents, a potent NO-boosting ingredient. Pomegranate extracts and juices have been shown to increase serum NO levels,[44-50] improve blood flow,[48] and reduce blood pressure.[51]
Pomegranate can significantly decrease vascular inflammation, while boosting blood levels of both nitrates and nitrites,[45] which are key for NO production.
The antioxidant compounds responsible for pomegranate's ability to increase eNOS expression include oleanolic acid, ursolic acid, and gallic acids.[46,47]
Plus, the antioxidant activity of pomegranate can – once again – stabilize the NO molecule, protecting it from degradation via oxidative stress.[52]
Ergogenic benefits
Studies show that pomegranate has the potential to improve athletic performance, and is "ergogenic for intermittent running, eliciting beneficial effects on blood flow."[48] It can also increase the efficiency of oxygen utilization during exercise.[49]
Anabolic, muscle-protective action
Research shows that urolithin B, a key bioactive constituent of pomegranate peel, has muscle-protecting and anabolic effects. In one 2018 study, urolithin B was found to "have a testosterone-like effect and to favorably regulate muscle protein balance."[53]
Ursolic acid, another bioactive found in pomegranate peel, exerts anabolic effects through mTOR activation and IGF-1 upregulation.[54]
Fitnox Research
As you can see, there is a lot going on with the three botanical extracts that comprise Fitnox. A comprehensive discussion of everything that's in them, and everything they do, is, frankly, beyond the scope of this article. Still, we've touched on the major points, and the discussion, thus far, should give you the background you need to put Fitnox research into context.
So what does research on the finished ingredient say?
-
Randomized Controlled Study – 250mg Fitnox Increases Nitric Oxide (NO) Production (2017)
In one 2017 study, titled "Natural sports supplement formulation for physical endurance: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study,"[55] researchers set out to assess the endurance-boosting capabilities of Fitnox.
Measurements of serum nitrate and nitrite levels
One important aspect of this study, and the reason we're leading the Fitnox research section with it, is that the researchers directly measured participants' serum nitrate and nitrite levels.
This is about as close to a direct measurement of serum nitric oxide as you can get: NO is a highly unstable molecule and only produced in small amounts, making it difficult to measure. But nitrates and nitrites are needed for the NO synthesis pathway,[56] so their presence lets us infer the extent of NO activity. The more nitrates and nitrites in a person's blood, the more NO activity there has been.
The study design was simple: 24 healthy men, aged 18 to 55, randomized to receive either 250 milligrams of Fitnox or 250 milligrams of starch capsules (the inert placebo control) for three weeks. At the beginning and end of the study period, researchers drew blood from the participants before and after exercise.
Nitrate and nitrite boosting
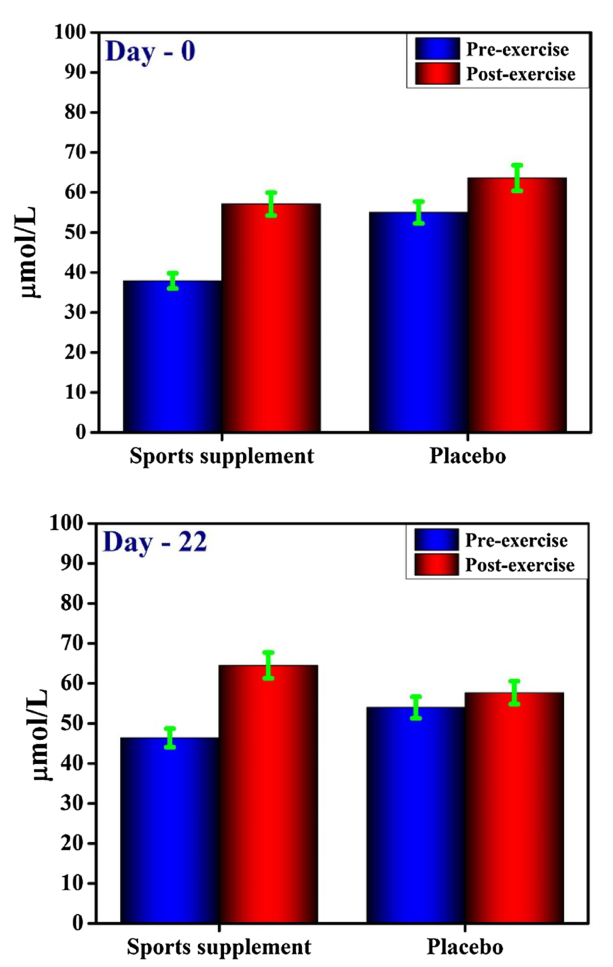
Here's what they found in the Fitnox group, with respect to blood and saliva nitrate and nitrite activity:[55]
Taken from Figure 8 in the study, Fitnox brought impressively increased nitrate levels between pre- and post-exercise measurements.[55]
- Blood nitrate levels increased:
- Before exercise by 45% (6.7 to 9.7 μmol/L)
- After exercise by 81% (8.8 to 15.9 μmol/L)
- Blood nitrite levels increased:
- Before exercise by 94% (37.5 to 73.1 μmol/L)
- After exercise by 89% (42.5 to 80.3 μmol/L)
- Saliva nitrate levels increased:
- Before exercise by 31% (6.5 to 8.5 μmol/L)
- After exercise by 22% (8.9 to 10.9 μmol/L)
- Salive nitrite levels increased:
- Before exercise by 22% (37.9 to 46.4 μmol/L)
- After exercise by 13% (57.1 to 64.5 μmol/L)
As you can see, these are pretty huge gains. They suggest a significant increase in overall NO activity.
Endurance-boosting
The study authors also measured subjects' performance during the exercise protocol.
The exercise consisted of treadmill running at specific heart rates – the subjects did one running test while maintaining 40% of their maximum heart rate, and another at 80%. In these tests, the men ran for five minutes while maintaining the target heart rate.
Fitnox conferred the following improvements to exercise performance:
- In the 40% HR test:
- 3.62% more distance covered
- 4.92% longer time to exhaustion
- In the 80% HR test:
- 18.53% more distance covered
- 9.76% longer time to exhaustion
The researchers also found that the Fitnox group had significantly lower levels of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), the enzyme responsible for converting pyruvate into lactic acid – compared to the placebo group, they had 9% less after exercise on day 22.[55]
Since lactic acid is a major contributor to muscular fatigue, the results provide some insight into how Fitnox can increase endurance and improve recovery.
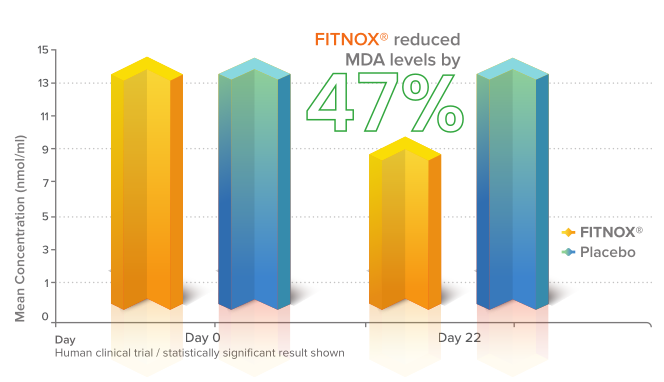
Reduced oxidative stress – NO stabilization
Subjects in the Fitnox group also had lower levels of malondialdehyde (MDA). Since MDA is a byproduct of lipid peroxidation caused by oxidative stress, MDA levels are often used as a measure of oxidative stress. That the average MDA level of the Fitnox group declined by an incredible 47% from day 0 to day 22,[55] shows its impressive antioxidant capacity.
Again, the antioxidant profile of Fitnox is key to its NO-boosting effect: All three of its constituents (but particularly Moringa and pomegranate) have the ability to stabilize the notoriously unstable NO molecule, thus extending its action and increasing bioavailability.
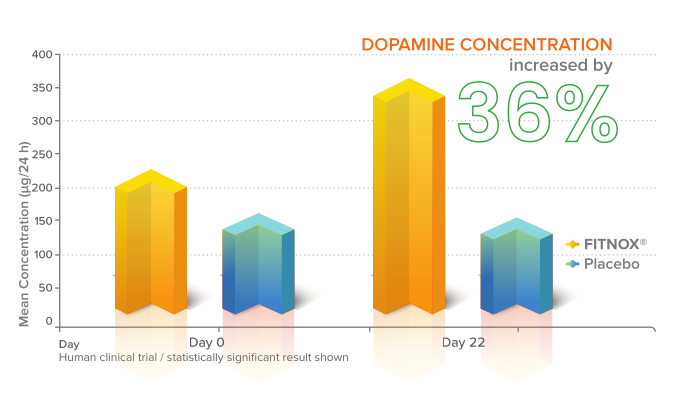
Dopamine boost
Fitnox can seriously boost dopamine,[55] giving it some potential nootropic effects that may play quite well with other related ingredients.
The last big finding from this study was a pretty impressive boost to dopamine production in the Fitnox group. Their baseline dopamine level increased by 36% from day 0 to day 22.[55]
Dopamine is famous as the pleasure, focus, and motivation neurotransmitter, but the study authors point out that it does a lot more than that: Dopamine also affects blood flow to the brain, protects the gastrointestinal tract, and supports normal immune function.[55]
In other words, the significant dopaminergic activity of Fitnox is a potential boon for health, not just athletic performance.
- Blood nitrate levels increased:
-
Randomized Single-Dose Study (2017)
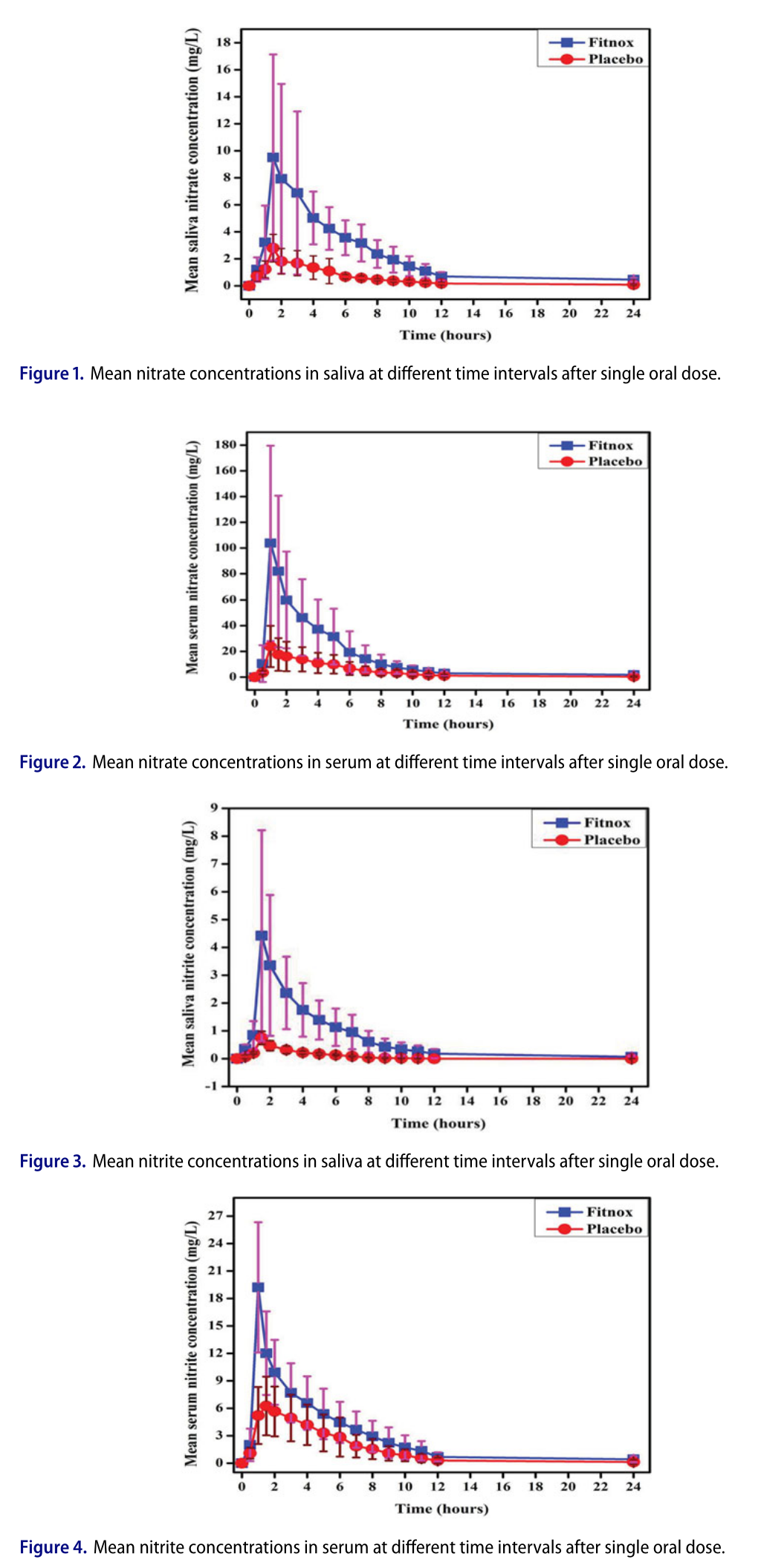
In another double-blind, placebo-controlled study from 2017, 24 healthy men between the ages of 18 and 55 were randomized to one of two groups: one received 250 milligrams of Fitnox, the other 250 milligrams of the starch capsule placebo.[57] The main difference between the two studies is that this one looked at the effects of a single Fitnox dose, instead of long-term administration.
Blood and saliva samples were taken from the subjects at 0, and 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, and 24 hours after dosing and were analyzed for nitrate and nitrite content.[57] Throughout the 24-hour study period, the subjects consumed a low-nitrate diet in order to minimize the risk of confounding dietary variables.
Fitnox leads to some very impressive increases in serum and plasma nitrate and nitrite levels after just one use.[57]
With so many more data points, the researchers were able to model the pharmacokinetic effect of Fitnox on nitrate and nitrite levels with greater precision. One advantage of taking so many samples was they were able to create reasonably precise approximations for the integrals of the curves, also known as area under the curve (AUC).
Researchers use AUC to measure the total effect of a drug or substance over time – the higher the AUC, the more of an effect the active compound is thought to have.
The researchers found that with Fitnox, nitrate and nitrite levels spiked higher, and stayed elevated longer, in both blood and plasma compared to the placebo.[57]
In the Fitnox group, average serum nitrate AUC was 390.65 h.µg/mL, compared to an average serum nitrate AUC of only 100.08 for the placebo group.[57] Average serum nitrite AUC was 66.74 h.µg/mL, compared to only 33.16 for the placebo group.[57]
Saliva nitrate AUC was 54.58 h.µg/mL for Fitnox, compared to 13.11 for placebo. Saliva nitrite was 16.68 vs 1.90.[57]
In other words, compared to the placebo group, the Fitnox groups saw AUC increases of:
- 390% for serum nitrate
- 416% for saliva nitrate
- 201% for serum nitrite
- 878% for saliva nitrite
These results indicate that a single 250-milligram dose of Fitnox can significantly increase NO activity in the body for at least 12 hours.[57]
Moreover, peak concentration was higher and duration of effect was longer for the Fitnox group in all four assays.[57]
Technical Details: Polar-Nonpolar-Sandwich Molecular Technology
The last technical aspect of Fitnox we want to discuss is its use of Aurea Biolabs' Polar-Nonpolar-Sandwich (PNS) molecular coating.
The idea behind PNS is elegant. The core active ingredient (in the case of Fitnox, Black Ginger Extract) gets sandwiched between a hydrophilic element and a lipophilic element.
To fully absorb and metabolize a supplement involves, at various stages, dissolution in both water and fats. By giving each black ginger molecule hydrophilic and lipophilic groups to interact with its surrounding environment, PNS helps increase overall absorption rate and, hence, bioavailability.
This isn't just theoretical – there's a peer-reviewed study from 2017 showing that curcumin packaged with PNS is significantly more bioavailable than ordinary curcumin.[59] While there's no curcumin here, the study shows a proof-of-concept of the technology that may be applied to others, including Fitnox.
Additionally, this is a technology that's 100% bioactive-driven. There are no excipients or additives. In the case of Fitnox, there are three components and three components only: Moringa, Black Ginger, and Pomegranate.
Last, Fitnox has received self-affirmed GRAS status, as reviewed by an independent expert panel using detailed scientific methods.
Products Containing Fitnox
Below is a list of articles written on the PricePlow Blog with Fitnox formulated inside:
PricePlow Articles with Fitnox
We've been big fans of Merica Labz F-Bomb and Impel Nutrition Vain, both of which are incredible stimulant-free pre-workout supplements built to boost nitric oxide levels.
Conclusion: We need to see more Fitnox
The research shows that Fitnox is an awesome ingredient with tons of potential, and we expect to see more of it in the coming years. Its bonafides as an NO-boosting and ergogenic ingredient are fairly well-established at this point.
What we want to see now is additional research into some of the "off label" benefits of Fitnox, like the anabolic effects we expect to see on account of its pomegranate-derived bioactive constituents.
We'd also love to see a study analyzing the effect sizes of Fitnox supplementation on PDE-5 inhibition. If they're as big as we think, that would make Fitnox a potential sexual health and wellness supplement.
But until then, we believe there's enormous potential from Fitnox in the pre-workout space -- both stimulant-based and stimulant-free. You can read more on AureaBiolabs.com and sign up for our news alerts from Aurea Biolabs below - this company has a very impressive group of ingredients recently launched, and the next ones we'll cover are even more fascinating.







Comments and Discussion (Powered by the PricePlow Forum)