For decades, Animal Pak has been supporting athletes worldwide, with a massive "pak" of vitamins, minerals, and more meant for serious training. Over time, Universal Nutrition has expanded their Animal lineup, disclosing more and more of their formulas.
On the training side, one of our recent favorites include Animal Primal, and Animal Cuts Powder, all great products to take pre workout.

Animal Juiced Aminos has been updated! We now get a nourishing electrolyte blend, as well as the inclusion of tryptophan!
Animal Pak was recently updated in 2023 -- now with fewer pills -- but that wasn't the only Animal product to get an upgrade:
Animal Juiced Aminos: Now with Hydrating Electrolytes
The above list of supplements includes some incredible pre-workout options, but what about during your workout? When the wheels start coming off and the muscles start breaking down, what does Team Animal have to keep the aminos flowing?
Their answer is Animal Juiced Aminos, an enhanced amino acid supplement that goes beyond your standard BCAA formula... but with a unique twist in the EAA and department.
We originally covered Juiced Aminos in 2021, where we were proud to be able to disclose the product's dosages. But now in 2023, we have some updates, and that includes a fully disclosed formula and added electrolytes for hydration!
It's all covered below, and available at a very affordable price, as shown on PricePlow below:
Universal Animal Juiced Aminos – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.
Note: Check the label offered at each retailer to see if you're getting the new formula! There may be some great deals on the old formula for a while, too.
This area is reserved for Team PricePlow's upcoming Product Update video.
Subscribe to our channel and sign up for notifications so you catch it when it goes live!
Animal Juiced Aminos Ingredients (2023 Update)
Below is the updated label:

And this time around, it's a full spectrum of essential amino acids -- previous versions of Juiced Aminos didn't have L-Tryptophan (we explain why below), but this one does. Let's get into it:
-
Anabolic BCAA & EAA Matrix - 6000mg
-
Instant BCAA Blend (L-Leucine, L-Isoleucine, L-Valine) - 5000mg
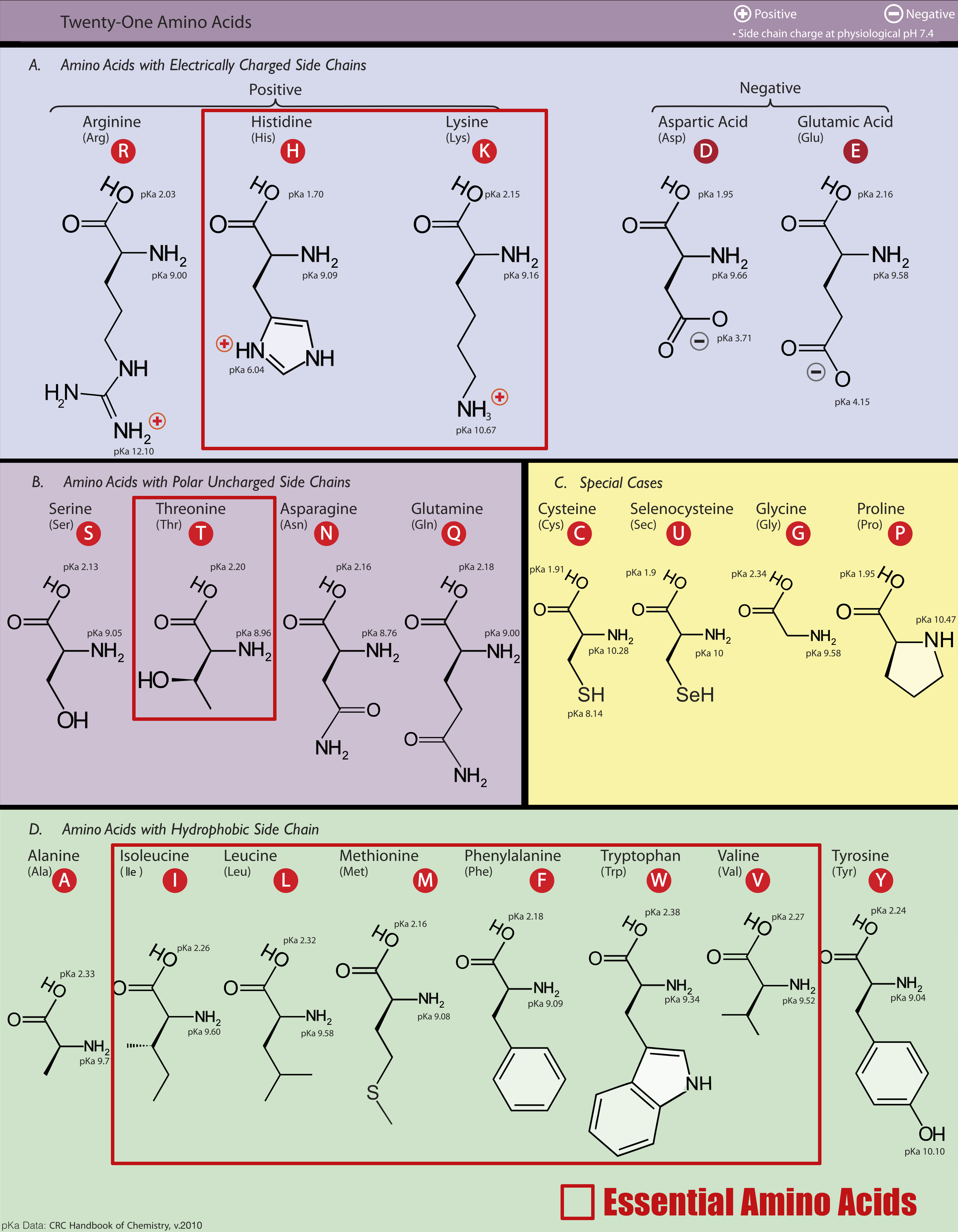
Amongst these primary amino acids, the essential amino acids are in red. Leucine, Valine, and Isoleucine are the three Branched-Chain Amino Acids.
To kick the Juiced Aminos label off, we have the tried-and-true 5 gram dose of the three BCAAs, leucine, isoleucine, and valine. The label doesn't specifically state the dosages, but Animal's website claims the standard 2:1:1 ratio, meaning we have 2.5g leucine, 1.25g isoleucine, and 1.25g valine.
Supplementing the three BCAAs bring anti-catabolic properties (they prevent muscle breakdown, especially when your brain and body need amino acids) that also help fight fatigue.[1-6] Leucine is well-known as the main BCAA, as it initiates mTOR signaling to promote muscle protein synthesis (MPS).[7-9] This is why leucine is almost universally the highest-dosed amino.
We love the BCAAs, but we love them even more when they're combined with other essential amino acids - and that's what we have with Juiced Aminos. Let's dig deeper:
-
Other EAAs - 1000mg
-
L-Lysine HCl - 500mg
Lysine supports protein synthesis but is also pivotal for collagen production, healthy immune function, red blood cell formation, and even wound healing.[10-12] It's notably the other ketogenic amino acid next to leucine, which means it won't get turned into glucose.
-
L-Phenylalanine - 125mg
Phenylalanine is critical for our feel-good neurotransmitter and catecholamine production -- especially dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine. Having this around is always a great idea, especially since these downstream neurotransmitters can boost fat oxidation.[13,14]
-
DL-Methionine - 125mg
Methionine is critically important in genetic instructions, and is the first amino acid of several peptide chains. It's also a methyl donor and can convert to cysteine, hugely important for the immune system.[15] While critically important, it's also the worst-tasting EAA, and we're always impressed when brands don't bury it at the end with scant doses.
-
L-Arginine HCl - 100mg
The big change-up from your standard amino acid supplement, arginine is a precursor for nitric oxide production.[16] Originally, it was a replacement for melatonin precursor tryptophan in Juiced Aminos, but now you get both arginine and tryptophan, which is discussed below.
-
L-Threonine - 75mg
Threonine serves as a precursor for two other important amino acids, glycine and serine. It's also used by the immune system and collagen synthesis.
-
L-Histidine - 50mg
Histidine is an important precursor for anabolic pathways, and helps combine with the beta alanine in your pre workout for the production of endurance-boosting carnosine.[17]
-
L-Tryptophan - 25mg
Tryptophan is a crucial amino acid for humans as it serves as a precursor to serotonin through the intermediary amino acid, 5-Hydroxytryptophan (or 5-HTP). Subsequently, serotonin can be transformed into melatonin. Serotonin aids in the regulation of behavior and mood elevation, while melatonin facilitates better quality sleep, two vital components of proper recovery.
The tryptophan story with Universal / Animal
This is a new addition to Juiced Aminos. Why wasn't it in the previous version? The answer is actually very interesting, and is provided at the end of Episode #080 of the PricePlow Podcast with Animal / Universal Nutrition's Vice President of Products, Jason Budsock.
Unofficial holder of the "World record cement deadlift", it's Jason Budsock, VP of Products at Animal / UniversalUSA, who joins us for Episode #080 of the Podcast!
Animal was one of the first -- if not the first -- company to put out an essential amino acid supplement in the form of Animal Nitro. It included a 6 gram EAA dose that copied what had been performed in one[18] of two studies published in 1999 and 2000.[18,19] However, those studies didn't include tryptophan because it was banned in some countries (due to a contamination concern in Japan that's long been cleared up[20,21]). So since the amino acid wasn't used in the study, Animal didn't include it in their amino acid formulas either!
Being an old-school kind of company, Universal stuck with what worked in those studies, until it became abundantly clear that tryptophan does have several benefits (as outlined above), and it was only disincluded from those studies because of regulatory issues long since resolved.
So now you know. Check out that podcast with Jason for more great Animal history sometime -- let's keep moving forward:
-
-
-
Juiced Hydration & Performance Blend - 3.5g
Now that we know the doses of the Juiced Performance Blend, we can see that we have a beyond clinical dose of taurine, which is worth a bit of a deeper dive:
-
L-Taurine - 1.25g
Taurine is an ingredient known as an osmolyte - it helps the body maintain appropriate water balance across and between cells. It's a conditional amino acid: while the body can make it, we almost universally do well with more.[22]
In terms of mechanism, all pathways aren't fully understood, but taurine reduces oxidative stress, improves muscle contractions through better calcium signaling, boosts endurance (discussed below), and helps the body produce bile for better fat digestion.[22-24]
Taurine and endurance
A recent systematic review looked at studies where taurine supplementation was tested on endurance, and noted fantastic improvements when using anywhere from 1-6 grams[24] -- and we're well into that range here. Even more interesting, the effect was shown on the first use!
Focus and nitric oxide
Taurine can also improve cognitive performance and focus. A recent study showed that it restored function of GABA receptors, decreased neuroinflammation, stimulated synaptic function, and more.[23]
Finally, we've even seen improvements with nitric oxide levels and bioavailability, which may work alongside the arginine in here.
-
Betaine Anhydrous - 1.25g
Betaine pairs well with taurine, as it is also an osmolyte and improves water transfer and "cell volumization".
-
L-Glutamine - 1g
Finally, we have a small hit of glutamine, which may improve endurance in some athletes,[25] can reduce soreness and help recovery,[26] and provide some gut health.[27] There are also immune system benefits to be had.[28]
-
-
Electrolytes
-
Sea Salt - 250mg
Sodium is the primary electrolyte lost in sweat, with approximately 0.9 grams lost per liter of sweat, while the next biggest loss is potassium at only 0.2 grams per liter. Failure to replenish lost sodium through sweating can result in sodium deficiency, which can be problematic since sodium is required for muscular contractions and inadequate sodium levels can hinder muscle function.
The biggest share of sodium in Juiced Aminos comes from sea salt.
-
Monopotassium Phosphate - 100mg
When it comes to sodium intake, the crucial factor is an adequate amount of potassium intake as well. While salt is the electrolyte that we lose the most when sweating, we lose potassium as well, and it's important to maintain a good balance between the two. Potassium levels play a role in regulating cardiovascular function and bone density.
-
Sodium Bicarbonate - 100mg
Have you tried the Animal Primal pre-workout yet?
For an additional source of sodium, Animal added 100 milligrams of sodium bicarbonate to juiced aminos to make sure electrolyte recovery is as smooth as possible after a hard workout.
-
Magnesium Oxide - 25mg
This is just a small dose of magnesium, which is important for metabolism (glycemic control / insulin sensitivity) and blood pressure. However, note that this is only going to yield 10 milligrams -- 2% recommended daily value -- and you will almost certainly want to get more from another form, since nearly everyone is magnesium deficient these days.
-
Calcium Carbonate - 25mg
Many forget that calcium is also an electrolyte -- it's important for nerve transmission (especially muscle contraction signaling), maintenance of water balance, metabolism, and cardiovascular homeostasis.
Again, this is a small dosage, so you'll want to check with your diet to see if you need more. If you consume a lot of dairy, like what's in Animal Whey, you may actually be good to go!
-
Flavors Available
With the 2023 version of Juiced Aminos, we have a new Fruit Punch flavor, in addition to the others on the menu:
Remember, as the creators of the Animal brand, Universal Nutrition manufactures their own supplements in a cGMP facility in New Jersey, and has long earned the trust of athletes worldwide.
Synergy between performance and recovery
With Animal Pak, Animal pioneered an approach to a more holistic approach to athletic health. This legacy is continued with Juiced Aminos, which contains every amino acid vital to recovering fully and properly, which is, in turn, key to realizing all of those hard-fought gains in the gym.
On top of the recovery benefits, Juiced Aminos also takes aim at improving performance. With a hefty dose of taurine paired with betaine and glutamine -- and now electrolytes -- this formula is hard to beat for an all-encompassing amino acid blend.
With the prices and flavor profile that Animal offers, there's really no reason to take a straight BCAA supplement anymore. They're no less expensive than this, and don't provide as much anabolic or endurance support. At that price, you're simply better off getting the added benefits of a big dose of taurine and some extra glutamine and betaine to top off your pre workout.
Look to stack this with Animal Pump (stimulant-free) and Animal Primal (stimulant-based) or Animal Cuts Powder (for the dieters) and sip on Juiced Aminos to keep the EAAs flowing. This way, your muscles don't have to part with their precious aminos when things start breaking down and you're not ready to stop yet... because you're too busy training like an Animal.
Universal Animal Juiced Aminos – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.









Comments and Discussion (Powered by the PricePlow Forum)