
There's a reason why dark chocolate and its flavonols are continually hailed as super foods: (-)-epicatechin
For years, we've continually heard that dark chocolate is one of Mother Nature's true superfoods. Yet every article and daytime TV show we see just never seems to have enough convincing science explaining why you should take it seriously.
The reason chocolate is so medically exciting is because of epicatechin, the natural flavonol from cocoa beans that does most of the heavy lifting in the research on dark chocolate.
If this is your first time hearing about it, it won't be your last - a wave of supplements containing this incredible ingredient have started to take the supplement world by storm, and it's popularity has only just begun.
TL;DR
Epicatechin is quite a beneficial flavonol, found in foods already generally recognized as healthy (berries, apples, dark chocolate, ginger, grape seeds / wine, even ephedra!)
Dark chocolate is the most popular source, but dieters must weigh the cons (increased calories) against the pros (general cardiovascular health, insulin benefits, and others).
-
For general health, ~40g daily of high-quality 70-85% dark chocolate will yield several benefits. Recommended products are discussed.
This will provide roughly 30mg epicatechin, but ~200 calories, so dietary adjustments must be made to avoid weight gain.
-
For more aggressive anabolic / muscle growth purposes, higher doses of 200mg or more epicatechin are typically used, but this is less proven in research (yet very promising).
Such doses will lead you to pure epicatechin-based supplements discussed at the bottom of this page.
Update in February 2015: A new study published this year shows that it is safe to use and there were no side effects observed.
Update March 2016: We've found a study analyzing the epicatechin content of various dark chocolate bars, and have updated our suggestions.
What is epicatechin?
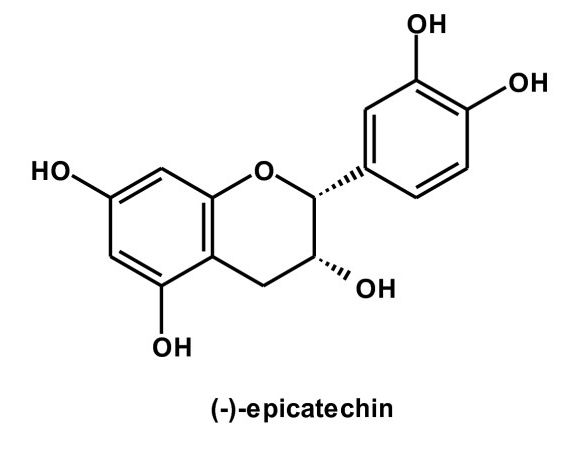
Epicatechin's structure looks similar to other known catechins like the popular EGCG from green tea, but it has a whole new batch of benefits and properties
Cocoa extract and several other foods have been found to have a number of bioactive compounds, also known as flavonols, which have a unique ability to improve both health and performance. Of the many flavonols found in cocoa extract[1], one particular flavonol known as epicatechin appears to stand head and shoulders above the rest for its health and performance boosting properties.[2]
Epicatechin is more formally known as (-)-epicatechin, pronounced "minus epicatechin". It is most prevalent in natural sources of cocoa, ranging from 1.5-2.8mg of epicatechin for every gram of cocoa.[1,3,4] The "darker", more pure, and less processed the chocolate is, the higher the concentration of flavonols inside.
When ingested in efficacious amounts (as discussed in the dosage section below), epicatechin provides benefits such as
- increased blood flow and nitric oxide levels,
- better insulin sensitivity,
- appetite suppression (based on a new study published August 2016!),
- lower cholesterol levels (due to antioxidant activity),
- improved blood pressure,
- more elastic skin,
- and it even has potential anabolic (muscle-building) properties, with possible myostatin-inhibiting abilities!
Each of these benefits is discussed in the benefits section below.
Various sources
Cocoa isn't the only source of epicatechin, it's just the most popular and easily obtained. You can also get it from the following:

How appropriately fitting that one of the most potent sources of this healthy compound, Chinese Hawthorn Berry, is literally unheard of in the Western World. This is a "kabob stick".
- Chinese hawthorn berries (140mg/100g)[5]
- Ginger (56mg/100g)[6]
- Fava beans / broad beans (22.51mg/100g)[7]
- Blackberries (11.48mg/100g)[7]
- Apple cider (9.03mg/100mL apple cider)[7]
- Apples (8.33mg/100g)[7]
- Green and Black Tea (~4mg / 100mL)[7]
- Blueberries (~5mg/g)[7]
- Red Wine (3.78mg/100ml)[7]
- Ma Huang (ephedra - concentration varies)[8-10]
Thanks to the epicatechin and other flavonols inside, a well-rounded diet of the above foods (which frequently find themselves touted in health magazines) do happen to have more benefits.
While caloric intake and macronutrient tracking is still the most important facet of dieting, clearly not all calories are built the same, as you'll see from the benefits discussed below.
Epicatechin Benefits
Getting back to the benefits listed above, in no particular order:
-
Enhanced Nitric Oxide Production
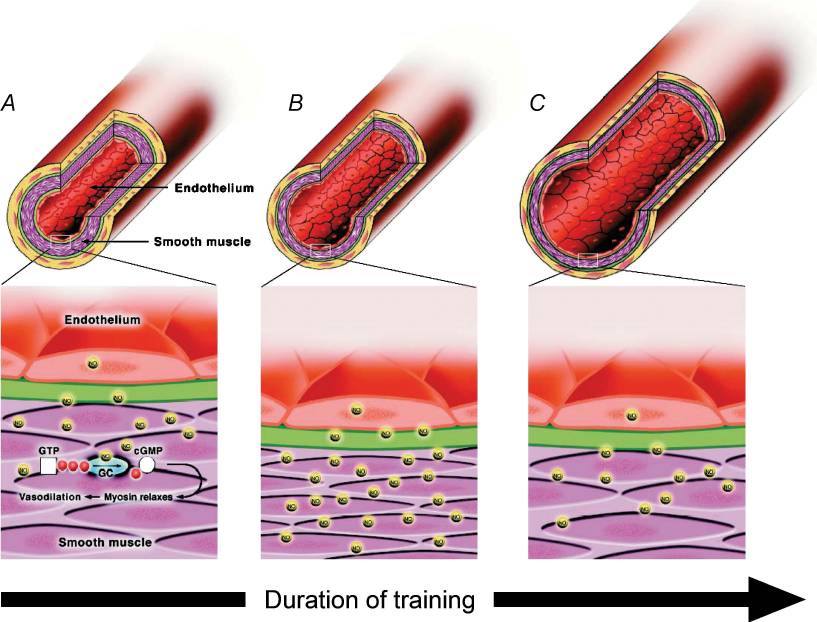
Hypothesized response of arteries to increased flow and shear stress following varying durations of exercise training[11]
Nitric Oxide (NO) is a molecule that essentially tells our blood vessels to "relax", allowing for increased blood flow and circulation. This relaxation is known as vasodilation - the widening of the blood vessels.
These effects are beneficial for a myriad of reasons, such as cardiovascular effects (lowering blood pressure[12]) to improved athletic performance.[11] Improved NO production increases what's known as the anaerobic training threshold – or more simply put -- more reps in the gym. And it's not only beneficial in the gym, it's great for cardiovascular health in general. One great benefit is the reduction of blood pressure thanks to the widening of said blood vessels.
So how does epicatechin affect your NO levels?
(-)-Epicatechin's NO connection
One research study had participants ingest 30g of dark chocolate (70% cocoa) per day, and in 15 days, their serum nitric oxide levels were 54% higher.[13] This is compared to no change in the white chocolate placebo group.
Another study found that epicatechin has the unique ability to elevate your NO levels by inhibiting processes that break NO down.[14] The benefit of this is that you keep your NO levels elevated for longer periods of time, bringing the benefits of athletic and cardiovascular benefits along with it.
Can more NO boost actual muscle growth? If it lasts long enough...
If you're a hard training athlete, you should understand how motivating "the pump" is the when you work to gain strength and build muscle. There are several factors that influence your ability to achieve that pump during training, but one of the most important is your body's production of nitric oxide to improve blood flow and deliver that pump.
But does this ultimately build muscle?? Is it worth using as a next-generation muscle building supplement?
Perhaps, if it lasts long enough. Nitric oxide's most powerful effect on muscle growth comes from it's ability to increase the production of satellite cells. Satellite cells are essentially cells that have no assignment which are called into action to repair and rebuild our muscle cells when damage occurs.
However, as we age the amount of available satellite cells begins to decrease, along with our ability to recover from intense muscle damage - such as the type that occurs during intense training. New evidence suggests that nitric oxide actually increases satellite cell growth.[15]
In practical terms: Epicatechin has the ability to activate the body's muscle building machinery and potentially lead to some beneficial results.
But let's be real here: it's first going to come down to your diet and training. You can eat all the dark chocolate in the world, if you're not getting the proper amount of quality protein alongside your calorie number, you're not going to build muscle.
But there just might be another way epicatechin can result in more muscle...
-
Muscle Growth and Strength
In your body, myostatin essentially acts as a muscle growth regulator, and essentially prevents muscles from growing too big too fast. Conversely, another substance known as follistatin acts as a myostatin regulator, preventing myostatin levels rising too high, thus allowing controlled rates of muscle growth to occur.
Inhibiting myostatin levels has long been the holy grail of muscle-building and muscle-building supplements. To put it mildly, many are excited about new evidence from a recent epicatechin-based trial that was done on both humans and mice.
The epicatechin - myostatin / follistatin connection
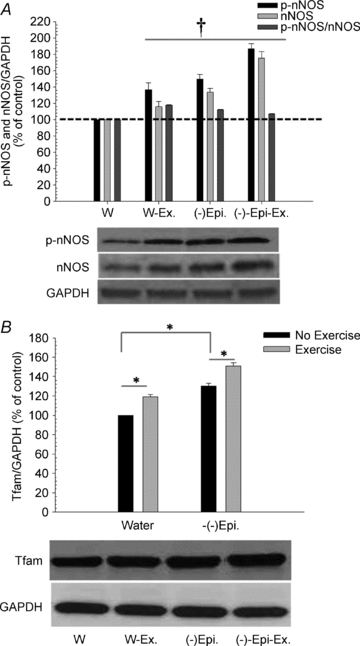
A pilot study used six middle-aged participants (roughly 40 years old) of average weight, and gave them 1mg of epicatechin per kg of body weight twice per day. This is roughly 170mg (-)-epicatechin per day for a 185lb male.
In just one week, their follistatin increased by 49.2%, while their myostatin levels decreased by 16.6%![16]
Of course, this was a very limited pilot trial, with only six participants and one week, but it's extremely promising to say the least. There were also increases in hand grip strength (by 7%), but there was no placebo-based control.[16]
Worth noting, those same researchers first experimented on young mice, who showed a 15% reduction in myostatin yet no change in follistatin levels when providing the same dosage as the humans.
Don't jump to conclusions, but it's at least promising
Needless to say, we're cautiously optimistic when it comes to (-)-epicatechin's ability to increase size and strength, and for those of you who wish to remain natural and have a budget to experiment with new extracts, this should be at or near the top of your list.
February 2015 Update: Another Great Follistatin study
In January 2015, researchers published a new pilot study targeting an initial safety analysis in 17 healthy humans, using epicatechin in ranges of 50-200mg per day, either taken in one large dosage at a time, or spread twice daily.[17]
No subjects had any side effects, but more importantly for this section, the average day 5 follistatin levels were ~2.5 times higher than day 1![17]
This was simply a pilot study, so there are longer studies on the way, but it's further exciting news. If follistatin levels remain that high in healthy humans (and we cannot guarantee they will), this truly does have mass-building potential.
We get more and more excited about this extract with every new study published, and will keep this page up to date as it comes in.
-
Muscular Endurance
The more epicatechin given to these mice, the more incredible their nitric oxide parameters - even without exercise.[18] This source goes on to show other charts, such as mitochondrial protein and tension strength, all with similarly impressive results.
In addition to the potential muscle and strength building benefits of epicatechin, there also appears to be an ability to improve muscular endurance as well.
According to a study published in The Journal of Physiology, rats given that same 1mg/kg of epicatechin daily for fifteen days had a significant increase in their endurance capacity.[18]
In addition to increasing the amount of exercise they were able to perform, another study found that gains in endurance capacity made during epicatechin supplementation were able to be maintained without training as long as supplementation continued. In fact, the data shows that gains were able to be maintained without exercise for up to fifteen days after supplementation was stopped.[19]
Conceivably, epicatechin has the ability to allow users to complete more reps, train longer, and allow them to main their gains with supplementation, even during moderate periods away from the gym, which could possibly be useful in the case of injury or taking a week off (some workout plans encourage this every few months as a form of "strategic deconditioning" in order to stave off overtraining, burnout, and plateaus).
Once again, this is all promising but not certifiably proven in humans. The pilot study has proven that (-)-epicatechin is worthy of more intense research, but already has users jumping into the fray with some products listed below, and they are successfully yielding results on some.
-
Blood Glucose Regulation
There may not be a single hormone more important to building muscle and burning fat than insulin. In the body insulin is responsible for shuttling glucose out of our bloodstream, and into our muscle cells. Once insulin enters into the muscle cell it triggers a reaction that causes the cells to begin our muscle building process, known as protein synthesis.
Easy there! Just because cocoa flavonols may lower blood pressure doesn't mean that the sugar and fat it's processed with in milk chocolate won't do even more damage in the opposite direction...
However, although insulin's anabolic presence is essential for muscle, too much insulin can be disastrous for both our health and our physiques. When insulin is constantly present in the bloodstream due to excessive carbohydrate consumption, muscle cells begin to become desensitized and no longer allow glucose to be removed from the bloodstream, resulting in high blood sugars. This causes the accumulation of unwanted body fat in addition to setting the stage for the development of type-2 diabetes and other cardiovascular conditions as well.
Where (-)-epicatechin comes in
According to a study published in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, ingesting 100 grams of dark chocolate daily showed the ability to significantly increase insulin sensitivity and glucose dispersal.[14] This means that epicatechin actually makes our cells more efficient at processing glucose, allowing us to recover faster from intense workouts, build muscle more effectively, and limit the gain of unwanted body fat.
The extracts are not yet marketed for these reasons, but if your diet is consistently poor in epicatechin-based foods, it could be worth supplementing before carb-containing meals even if you're dieting and not going after muscle growth.
-
Appetite Suppression Capabilities
A new study published August 2016 shows appetite suppressive capabilities too! We continually see more and more good news with this ingredient and have to update this post all the time.
Following from the above point, dieters should be excited about a new 2016 study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition titled Epicatechin, procyanidins, cocoa, and appetite: a randomized controlled trial. This study showed that "nonalkalized cocoa mixture was associated with an acute decrease in food intake only after being supplemented with epicatechin."[20]
They went on to say that "It is possible that epicatechin at a dose of >1.6 mg/kg body weight, alone or in concert with appropriate catalytic cocoa compounds, may be useful for helping people control their food intakes."[20]
Stating the Obvious: Dieters should avoid the chocolate sources though
Of course, large quantities of chocolate is going to be the exact opposite of what dieters want, so in this case, high-epicatechin supplements without the fats and sugars may be what you want. Dieters are keen to look at the new Ghost Size supplement discussed in our epicatechin supplements section lower on this page.
-
Brain and Heart Health Benefits
Moving beyond the athletic health and nitric oxide enhancement, epicatechin has been shown to have significant benefits for improving both general heart health and brain function.
As we know, epicatechin has the ability to increase blood flow due to its ability to stimulate nitric oxide production, leading to aforementioned cardiovascular benefits.
LDL Cholesterol improvements
Beyond the two research studies cited above suggesting benefits due to improved nitric oxide levels, a third study used 100g of dark chocolate (containing 88mg flavonols) for just two weeks, which decreased blood pressure and serum LDL cholesterol - but white chocolate placebo did not.[21] The method of action was likely due to its antioxidant behavior.
Cocoa-eating tribes have ridiculously low cardiovascular disease
CocoaVia (a Mars product) discussed below is a great way to get cocoa's flavonols in without the caloric onslaught of chocolate or other foods
Even more interesting, scientists at The University of California – Davis studied a group of coastal Indians known as Kuna to determine why they have dramatically lower rates of cardiovascular disease than the general population.
The researchers concluded that it was their regular consumption of flavonol rich cocoa, which is particularly high in epicatechin, which caused them to remain relatively free of heart disease.[22]
To be fair, indigenous coastal populations also eat a lot of fish, which also promotes healthy cardiovascular function[23], but the researchers specifically called the cocoa consumption to attention.
2015 Update: One month of cocoa flavanols improves cardiovascular output
A new study named the "Flaviola Health Study" published on September 9, 2015 by researchers from the University of Dusseldorf showed that taking 450mg cocoa flavanols 2x/day significantly improved endothelial function (measured as flow-mediated vasodilation (FMD)), plasma lipids, and blood pressure.[24]
Their statistical analysis showed that it significantly lowered the 10-year risk of coronary heart disease and the chances of death from such diseases!
It only took two weeks of flavanol consumption to improve FMD levels, The study was double-blinded / placebo-controlled and was performed on 100 healthy, middle-aged men and women.
Cognitive mental enhancement too!
Other studies have found that the increased blood flow from epicatechin extends all the way up to the brain, and was actually shown to improve cognitive performance as well![25]
By applying the Framingham Risk Score, CF predicted a significant lowering of 10-year risk for CHD, myocardial infarction, CVD, death from CHD and CVD.[24]
The first part of this pilot study provided 150mg of total cocoa flavanols to subjects for five days, and then made them perform a cognitive task. The participants' BOLD signals (blood-oxygen level dependent) were improved, theoretically indicating more neurotransmission and brain activity.[26]
In the second part of the study, the researchers gave a single high dose of flavonols (450mg) and noted the cerebral blood flow, which coincides with all of the above results.
Since this was just a pilot study, there can definitely be more to the cognitive support, and it's just not yet measured or understood yet. Or, it just has to do with the improved blood flow in general. Needless to say, cocoa-derived flavonols, the majority of which consist of epicatechin, have shown scientists nothing but great results.
Dosage
Actual products are discussed below, but the quick guide for common dosages is below:
-
For general health:
Both Lindt 70% and 85% are our favorite sources of epicatechin and other cocoa flavonols. See why below -- this post has been updated to show that 70% contains more epicatechin!
~30-40g of dark chocolate that has not been processed with alkali (or the Dutch Process) and is at least
85%70-85% cocoa is ideal.You can also help yourself with a cup of green tea, a cup of berries, an apple, and an optional small glass of wine each day.
-
For the athletic and muscle-building benefits:
At least ~200mg of total epicatechin daily, taken with or without food. Doses can be spread across the day.
At this point, you'd need a nearly stupid amount of calories (even if it came from perfect 100% dark chocolate), so it's time look at the epicatechin supplements suggested below.
Why not alkali-processed chocolate?
Not all dark chocolates are created equal.
It turns out that cocoa "processed with Alkali" or "Dutch processed" loses much of its flavonol content due to this alkalization - as much as 60%![27,28]
And simply because we want more epicatechin and less fat, sugar, and calories, you should look for a chocolate bar that contains at least 85% 70% cocoa. By the time you ate enough milk chocolate to get enough flavonols, you'd be doing far more metabolic damage than its worth.
Depending on the rest of your diet, you could possibly get away with eating as little as 25 grams of a dark chocolate to supply the body with ample amounts of epicatechin, but if you're not eating any of the above foods, consider bumping it closer to 40g of dark.
Epicatechin products and supplements
There are two different reasons you might be here, so see the appropriate section below (quick link to the stronger muscle-building supplements here).
-
For general / cardiovascular health:
Updated March 26, 2016: We've been told about a study published in 2014 titled "Determination of Catechin and Epicatechin Content in Chocolates by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography"[4] which tested various dark chocolates for their catechin and epicatechin content. This post has been updated to reflect those numbers.
The study cited above shows the following table:[4]
Product Serving Size Catechin Epicatechin[4] Cocoa Powder (Natsol Laboratories) N/A 0.20% 0.28% Lindt Excellence, 90% cocoa 40 6.04 mg 17.32 mg Lindt Excellence, 85% cocoa 40 4.80 mg 22.76 mg Lindt Excellence, 70% cocoa 40 7.84 mg 28.56 mg Ghirardelli Chocolate, 86% cacao 45 4.50 mg 23.85 mg Ghirardelli Chocolate, 72% cacao 38 5.78 mg 27.70 mg Ghirardelli Chocolate, 60% cacao 38 4.79 mg 17.78 mg Godiva Chocolatier, 85% cacao 40 5.20 mg 31.68 mg Safeway Select chocolate, 85% cacao 40 4.76 mg 10.52 mg Safeway Select chocolate, 72% cacao 40 4.84 mg 14.64 mg Green & Black's chocolate, 50% cocoa 40 3.28 mg 11.92 mg Bournville Cranberry chocolate, 50% cocoa 33 1.49 mg 3.76 mg Bournville Rich Cocoa chocolate, 50% cocoa 33 1.09 mg 3.60 mg So it turns out that this post's earlier assumptions were wrong - Lindt 70% Dark Chocolate is actually better than Lindt 85% Chocolate in terms of flavonol content!
Godiva's 85% tested the best, but their prices are far higher, so for the best mix of value, taste, and catechin content, we're sticking with Lindt. You can now choose between Lindt's 70% or their 85%, but note that 70% will have more sugar and carbs (yet also taste better). Schedule it into your diet accordingly.
Also realize that the store brand stuff just isn't worth the savings.
(End of 2016 update)
We asked popular dark chocolate manufacturers which of their products were not alkalized with the Dutch process. The results:
- Lindt's 70% dark chocolate is the more pure product without alkalinization (confirmed by Lindt via email). This seems to be the best value overall, too, and is our personal selection.
Lindt 70% Dark Chocolate – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.
- Eating Evolved is a small brand with some delicious dark chocolates that come in various flavors, but they are very expensive for the price.
We enjoy their packaging, which says "Chocolate: It's FOOD, not candy"
But if you want to avoid the caloric content and don't want to take the more aggressive pills below, there's another product you should consider, then:
-
Mars Inc has a concentrated cocoa flavonol product named CocoaVia.[30]
This product contains 375mg cocoa total flavonols per serving, and comes in several different forms such as capsules, different dark chocolate bars, and drink mixes. This means you can just take one serving per day and be done with it. The capsules state that each serving also contains 20mg natural caffeine from the cocoa content.
-
Endangered Species Dark Chocolate
Endangered Species Chocolate does not use the Dutch Alkaline process[31,32].
Note: This is a correction to this piece on October 5, 2015 - we misread the original social media response from Endangered, and apologize for that mistake.
In our loser's bracket is Ghirardelli, who failed to respond to our requests over both social media[33] and email.
Considerations
Regardless of which option you choose (CocoaVia vs. Lindt 70), you're looking to run at a bit over $1.00/day.
Count for the caloric "damage"
Remember, when it comes to weight loss, calories are still king - so if you take the dark chocolate approach, note that you have just added 200 calories to your diet, and need to remove those 200 calories elsewhere or else you will gain weight.
- Lindt's 70% dark chocolate is the more pure product without alkalinization (confirmed by Lindt via email). This seems to be the best value overall, too, and is our personal selection.
-
For anabolic muscle building support and athletic performance:
This is why most of our readers are here, so let's get to it:
-
Competitive Edge Labs' Epi-Plex
Dollar for dollar, this is by far the best deal on this page. Epi-Plex uses piperine (black pepper extract) to increase absorption, alongside it's 300mg epi in just one capsule.
If you're going for raw epicatechin and looking for bang-for-buck, Competitive Edge Labs is the place to get it!
Competitive Edge Labs Epi-Plex – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.
-
Ghost Size
This is the most complete muscle-building supplement for an all-around creatine / epicatechin combination -- with the incredible flavoring support from the masters of flavor at Ghost!
Ghost Size – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.
-
Are there any side effects to cocoa flavonols?
This section updated in February 2015:
A pilot study published in January of 2015[17] that was performed on healthy humans with pure (-)-epicatechin showed that,
(-)-EPI was safe to use, with no observed adverse effects, and our findings suggest that increases in NO metabolites, mitochondrial enzyme function and plasma follistatin levels may underlie some of the beneficial effects of cocoa products or (-)-EPI as reported in other studies.[17]
In that study, there were 17 participants who received either large single doses of 50, 100, or 200mg epicatechin or doses of 50mg twice daily. They were all fine, and had several of the benefits explained above, such as the follistatin boost.
Side effects of cocoa supplements?
Although uncommon, some do experience gastrointestinal distress from taking cocoa supplements. Some varieties of supplemental cocoa will also contain caffeine, as it is natural occurring in the plant, so take note.
This shouldn't be enough caffeine to trigger any issues, but if you're ultra-sensitive to the stimulant, you're wise to stick to the epicatechin-only supplements.
For instance, the CocoaVia product shown above contains 20mg caffeine.
Allergic reactions are also possible. Those with, or who may be allergic to cocoa should avoid taking dark chocolate or cocoa supplements.
Conclusion
Epicatechin is a truly unique supplement that has the ability to naturally boost health and performance, and we believe this is only the beginning of a nice little revolution in the nutrition and supplement industries.
Let us not forget its potential ability to help drive glucose into muscle cells instead of fat cells, keeping insulin and blood sugar levels in check - this may actually be the most underrated use of it yet!
But for now, its alleged ability to decrease myostatin, while simultaneously increasing follistatin, effectively opens up a new gateway for muscle growth, which is likely why most of our readers are here.
So to those of you looking for gains, stack it in with your favorite protein powder and leave comments below on how the results go!
Ghost Size – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.







Comments and Discussion (Powered by the PricePlow Forum)