It's been exactly a year since NutraBio launched their Natural Series, where they released their Natural Pre Workout and Natural Intra Blast, which are stevia-sweetened versions of the massively-dosed NutraBio Pre Workout and Intra Blast supplements.

NutraBio returns to its Natural Series, soon to take on the challenge of naturally sweetening their EAA platform blend!
These two products joined NutraBio's Natural BCAA and Grass-Fed Whey Isolate, and they're all powered by stevia and sometimes some added monk fruit extract or cane sugar for the sports series.
A busy brand...
Since then, Mark Glazier and the industry's most transparent brand has been pounding the pavement with an insane amount of product releases, such as EAA Energy (which includes a new cherry limeade flavor), the new Dragon Fruit flavor systems (which now includes focus-enhancing intra workout supplement Alpha EAA), the Breakfast Series Whey Protein Isolate flavors, Curcumin Advanced, and even single-ingredient products like KSM-66 Ashwagandha and Alpha-GPC.
Back to the Natural Series: EAAs for everyone
But what about our natural friends out there? The flavored powders listed above all have sucralose. Turns out NutraBio's been busy for you too -- on top of a really cool and unique Matcha Green Tea flavor Grass-Fed Whey Isolate (where the flavor is a beneficial active ingredient!), the team wants to get more essential amino acids into your hands too!
Introducing EAA Natural
And with that, they're launching EAA Natural, which is starting as an unflavored, unsweetened version, but will soon have flavors as well -- so sign up for our NutraBio news alerts below! After that, we'll get into the ingredient label here:
NutraBio EAA Natural – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.

Below, you'll see the same amino blend as EAA Pure, EAA Energy, and Alpha EAA... but with one major thing missing: Sucralose!
The long story short is that EAA Natural uses the same 10.55g base formula as Alpha EAA, EAA Energy, and EAA Pure (an in-store retailer exclusive). This is an incredible thing, because we have 8.2g of EAAs consisting of 6g BCAA, meaning there's a large 2.2g of non-BCAA EAAs... tough for anyone to flavor, let alone without sucralose!
In addition, there's endurance-enhancing taurine, high-quality CocoPure coconut water for hydration, and AstraGin to amplify absorption.
Sucralose-free dieters often miss out on these quality formulas, and sometimes don't get in enough protein in general, missing out on some of the best protein powders (and oftentimes avoiding beef). This makes EAA Natural a great idea for these types of dieters, because these aminos are essential -- they must be ingested via diet and/or supplementation!
Here we'll quickly break down what each amino does:
-
BUILD: Full Spectrum EAA-BCAA Matrix (8.2g)
-
BCAAs — 2:1:1 (fermented) (6g)
The original flavor is unflavored, but we also expect to see flavors with stevia (and probably cane sugar like Natural Intra Blast has)
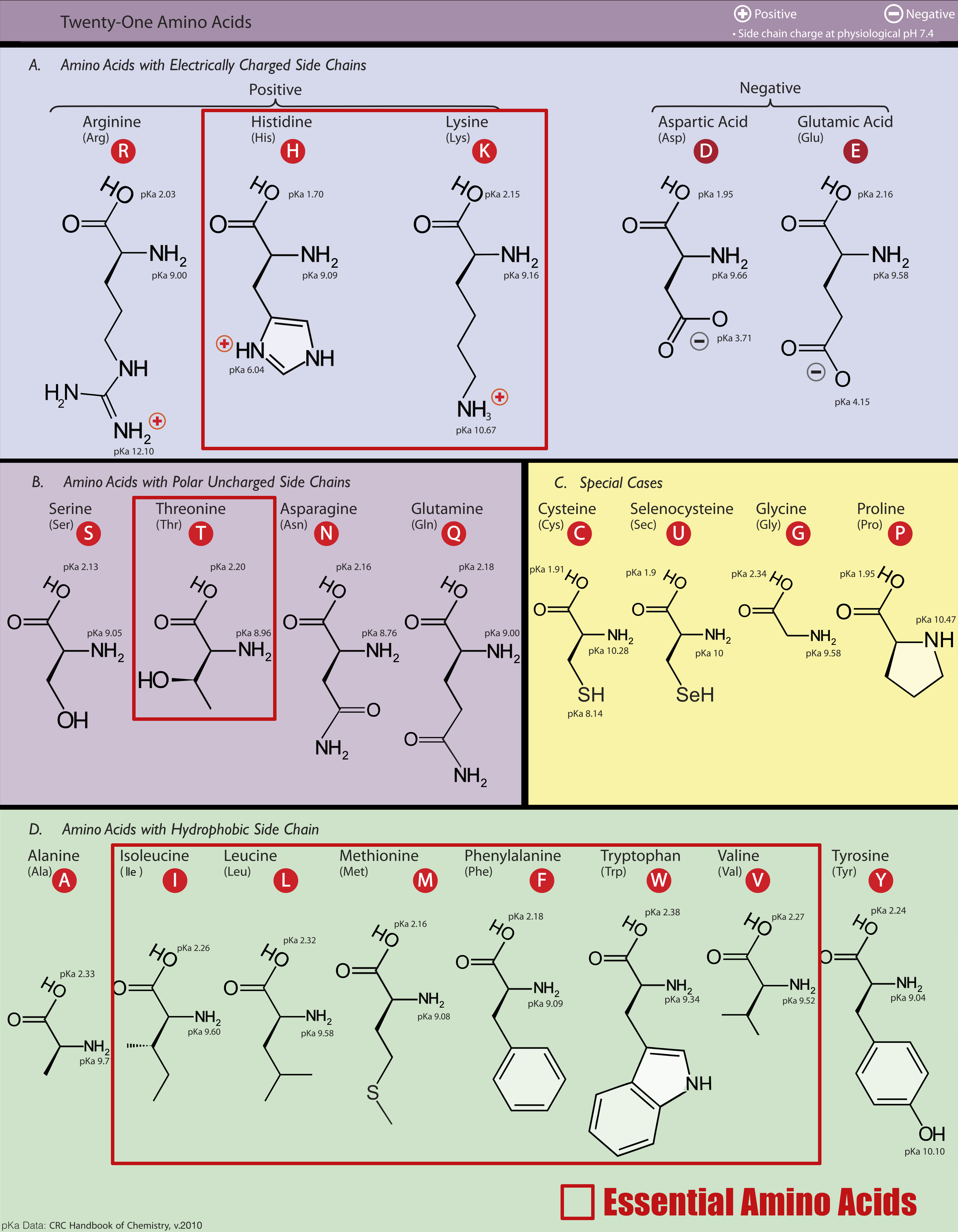
The branched chain amino acids, or BCAAs, consist of the three amino acids leucine, isoleucine, and valine.They're combined in the time-tested 2:1:1 leucine:isoleucine:valine ratio.
Leucine is the powerhouse BCAA, since its effects are most associated with muscle protein synthesis (MPS) in cells. This happens via mTOR pathway (mechanistic target of rapamycin).[1] The mTOR pathway plays a critical role in cell proliferation and growth, and mTORC1 is the branch of that responsible for the development of muscle tissue.[2]
Isoleucine shares a base structure with leucine (hence its name) and also plays a role in muscle protein synthesis -- just not as much as leucine. An added benefit, though, is that it helps muscle cells take glucose up during exercise, which is definitely what we like.[4]
The least-studied of the three is valine, and it plays an essential role creation of glycogen.[5] This is helpful during long workouts when your body has exhausted its liver and muscle glycogen stores. This could be why BCAAs have been shown to be beneficial for endurance:
BCAA benefits
Amongst these primary amino acids, the essential amino acids are in red. Leucine, Valine, and Isoleucine are the three Branched-Chain Amino Acids.
On top of boosting stamina and endurance, BCAAs help reduce delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS). The benefits are subtle but helpful, since part of the game is to get back out there and train hard the next day, keeping volume high and thus performance high.[6] BCAAs may even help dieters burn fat, but it still requires caloric deficit.[7] On that note, it's important to remember that BCAAs contain calories!
The 6g dose alone is better than many BCAA supplements out there, and we have a long way to go in this formula!
Next it's time to talk about the functions of the other six essential amino acids - aminos we must get from diet. BCAAs function best when combined with a full spectrum of essential amino acids,[8] so it's critical to get them all in - why not supplement them all together too?!
Thankfully, the two that NutraBio has highest-dosed are also greatest for muscle protein synthesis:
-
Lysine (850mg)
Lysine is a ketogenic amino acid that supports muscle protein synthesis, immune system function, hematopoietic organs, and the formation and production of collagen -- which helps injury recovery. Lysine is part of the carnitine shuttle, something that's seriously critical to fatty acid breakdown and transport.[9]
-
Threonine (850mg)
Threonine is also seriously important for muscle development, since it acts as a precursor for glycine and serine, which in turn are two amino acids needed during said development. Meanwhile, threonine itself helps with collagen synthesis and the immune system. To top it off, it synergizes with with methionine to oxidize fat.[10]
-
Phenylalanine (300mg)
Phenylalanine is one of the "fun" amino acids, since it helps us produce catecholamines such as dopamine, epinephrine, and norepinephrine. It can also convert to PEA (phenethylamine), a molecule that elicits great mood through a dopamine boost. This makes it a "feel good" amino.[11-12]
-
Histidine (300mg)
Histidine is important because what it turns into is important. The body can convert it to histamine, and that can then become carnosine. Carnosine is interesting because it takes on intracellular protons that would otherwise cause cell damage.
You know the beta alanine in pre workouts (such as NutraBio's Natural Pre Workout) -- well, that beta alanine works alongside histidine in producing the carnosine, and it's incredibly helpful for endurance as it 'scrubs' acids from the sore muscle cells, and we postulate that it's synergistic with beta alanine because of that.[13] Meanwhile, histidine is critical for the brain, immune system, and blood vessel operation.[14-15]
-
L-Tryptophan (75mg)
Another of the "feel-good" aminos, Tryptophan is known for being a precursor to serotonin, and thus can help you sleep better (or conversely, not getting enough can make you sleep terribly). Serotonin is also involved in mood, well-being, and cognition. Don't worry about it making you fall asleep - it needs to get converted to melatonin first, and that happens at night. Tryptophan also seems to have very important roles in memory formation and learning.[16-17]
-
DL-Methionine (25mg)
Last but not least is Methionine, which is great because it provides a desperately-needed sulfur atom to athletes who are oftentimes deficient. The con to that pro is that the sulfur doesn't taste so great, so we normally see it dosed lower, and that's what we have here. This makes it possible to get a stevia-sweetened EAA going.
Biochemically, methionine is a known as a methyl donor, and it's the first amino acid in any peptide chain. Mammals convert methionine to cysteine, which is essential for immune response.[18]
Since so many of us are deficient in sulfur, this is a very important thing to get in.
-
-
Taurine (1200mg)
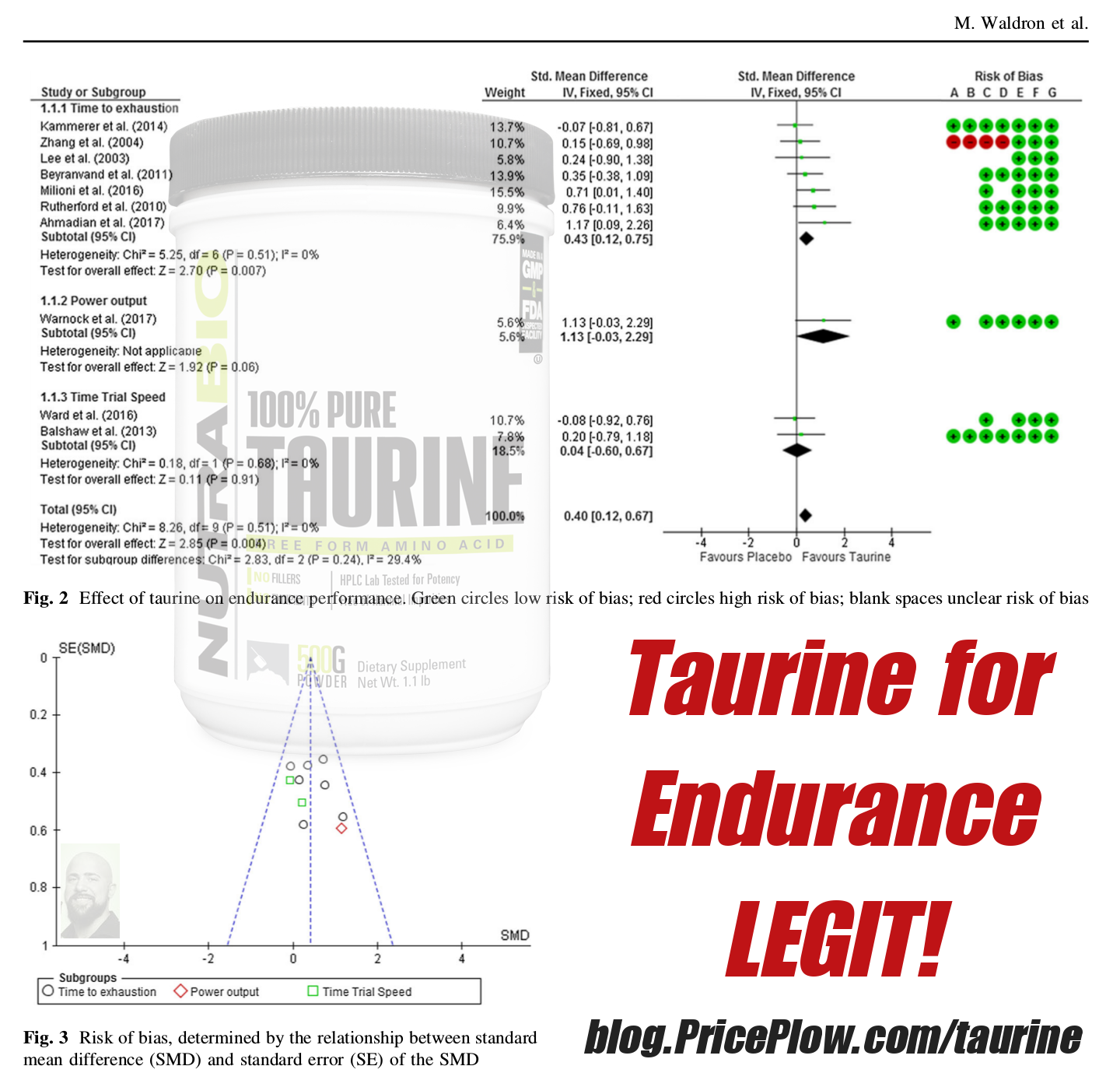
Taurine is an organic acid (not technically an amino acid) that provides a ton of endurance-boosting benefits that we covered in a meta analysis showing taurine boosting endurance. The ingredient boosts your aerobic exercise capabilities,[19] and we posit that it is due to its use as an osmolyte, which assists with water transfer amongst cells. 500mg to 2g are all clinical doses, and NutraBio split that right down the middle here.
Taurine, long used for a 'filler' amino acid, turns out to be legit for endurance... and after a single use!
To top it off, taurine is a good antioxidant and boosts hydration due to the osmolyte mechanism above.[20]
-
L-Alanine (600mg)
L-Alanine is a non-essential amino acid that that helps fight fatigue and stress. It was put into EAA Natural for two likely reasons: first, to help give a bit of a performance assist during that hard training... but second... it tastes good!
The ingredient assists with protein building and helps supply the body with energy in times of oxidative damage (ie cardiovascular activity).[21,22] This means it helps support muscle development, and is yet another amino acid that's important to the immune system.
-
CocoPure - coconut water powder (500mg)
CocoPure is NutraBio's take on coconut water powder, and it comes with a story. When Mark Glazier was looking for coconut water ingredient suppliers for his fall 2018 EAA Pure / EAA Energy launches, he realized just how terrible these "coconut water powders" are - they're nothing but sugar water!
But CocoPure lives up to its name -- it's 90% pure coconut water powder by weight, per Glazier and Team NutraBio... as opposed to the other junk they found on the market that was as bad as 36% CWP by weight, with the majority 64% coming from nasty carriers like maltodextrin.
A better coconut water carrier
Another industry scam uncovered by Mark Glazier and his fearless team: that 'coconut water powder' doesn't have much coconut water in it!
To make coconut water powder, the coconut water gets spray-dried onto a “carrier”. That enables you to make a liquid into a powder, but it also yields a lower effective dose per gram. Some methods and ingredients are simply better than others, and many on the market use blood sugar spiking maltodextrin!
CocoPure avoids that by using a tapioca carrier. It only takes up 10% of the final powder's weight. Hopefully Mark Glazier will explain more later on!
Back to the topic at hand, athletes often use coconut water for its potassium.[23] When training hard, we can get deficient in the K atom, so coconut water powder may help replenish.
-
AstraGin (50mg)
AstraGin is an absorption enhancer made from two adaptogen ingredients, astragalus and panax notoginseng. Research shows that it works best with amino acids by improving their uptake,[24] and that's exactly what we have here in EAA Natural.
Flavors
NutraBio is launching with an unflavored and unsweetened version of EAA Natural, but more flavors are to come. Below is a list of the flavors that are in stock:
EAA Natural: NutraBio proves its EAA platform
NutraBio's been doing very much stuff, but a lot of it is sucralose-based. With this release, they show their love for their Natural Series fans, and remind them that they are not forgotten!
But further, and most important, we now see that NutraBio's built out a platform for its essential amino acid supplements. EAA Pure and EAA Energy were similar, but they released at the same time so we thought nothing of it. Then came Alpha EAA, and we realized what they were up to. They have a blend that is an incredible formulation, and they're becoming masters of flavoring on top of it.
So much so, apparently, that they're ready to release this formula with natural flavoring and sweetening, something we honestly weren't expecting with so many non-BCAA EAAs inside.
NutraBio EAA Natural – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.









Comments and Discussion (Powered by the PricePlow Forum)