Since Glaxon's launch in 2019, we've followed their movements closely -- in a short amount of time, their fascinating formulations have become the envy of the industry. Every Glaxon supplement brings something new, unique, and powerful to the industry - each one standing on its own.

Get ready to fly! The Glaxon Pre Workout Diet Stack is no joke, and will keep you going even through a low-calorie month.
One thing we haven't discussed much of, however, is what happens when you stack these insane formulas. When appropriately put together, Glaxon-based stacks create some insane synergies, allowing you to throw literally everything at a goal. Standalone, their supplements are excellent. But with a proper stack, excellent transcends to phenomenal.
PricePlow's Glaxon Pre Workout Cutting Stack
When dealing with Glaxon, one of the first things you have to discuss is their potent, top-end pre workout supplement, Glaxon Specimen Yo-Yo. What's interesting is that it can bring some weight loss effects on its own, thanks to its thermogenic blend. But if we're trying to cut down, we can add more -- and that comes in the form of their stimulant-free fat burning powder, Thermal.
And of course, dieting can be a pain, especially if you're sacrificing a few carbs, but that doesn't mean you have to sacrifice the pumps. We can bring them back in a big way with Plasm Surge.
It is that stack -- Specimen Yo-Yo, Thermal, and Plasm Surge -- that we'll focus on today. You can get it directly from Glaxon and sign up for our alerts, but if it's not available, you can still piece it together using PricePlow:
Glaxon – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.
An insane pre workout stack
The goal here is simple: to annihilate workouts with a high-energy, thermogenic, fat-oxidizing blend that will keep you pumped, regardless of caloric deficit. Mix them up before training, dosing Specimen Yo-Yo to your preferred stimulant threshold, and get ready for a hell of a ride.
-
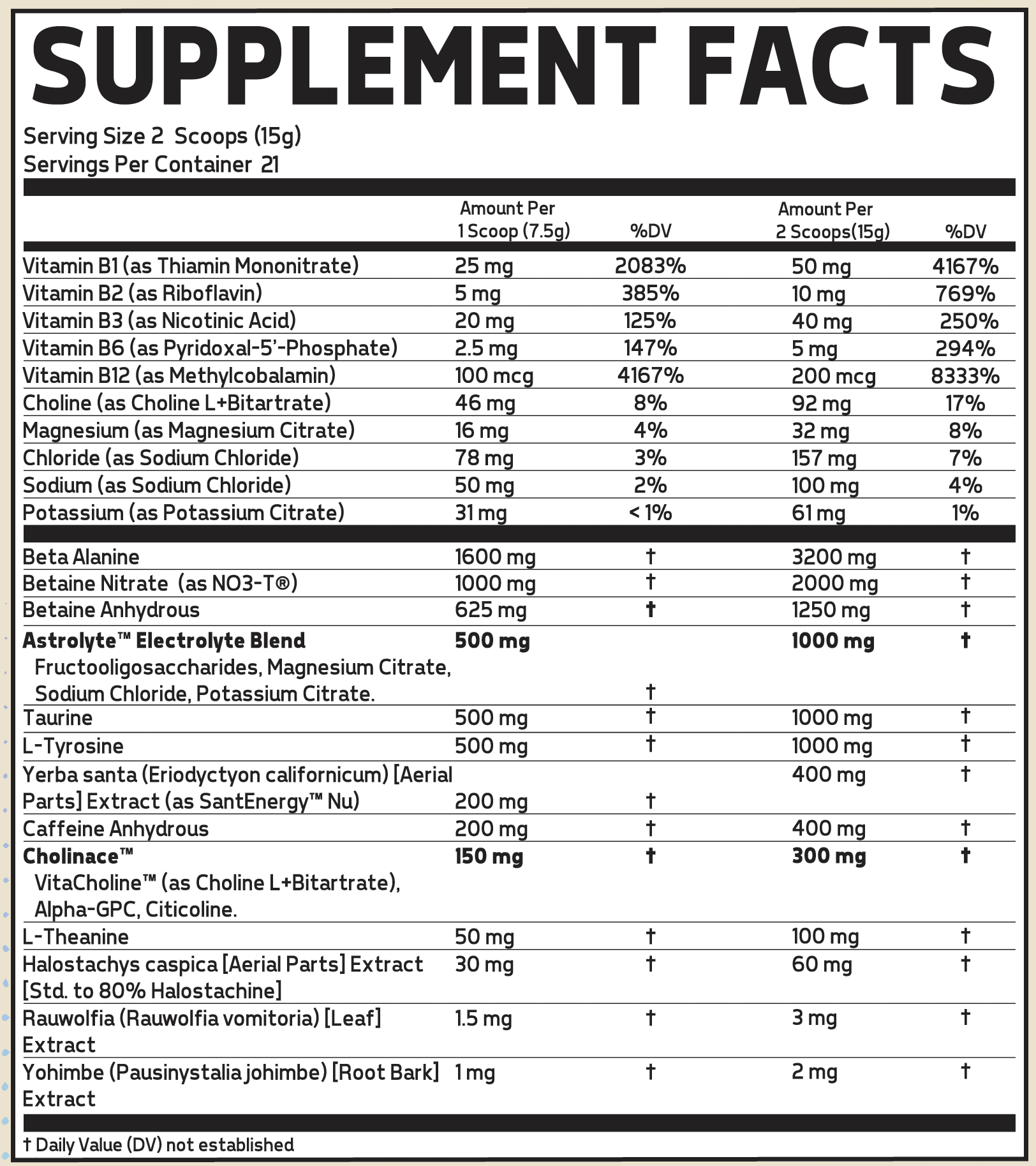
Starting with Specimen Yo-Yo
Specimen Yo-Yo is covered in detail in our article titled Glaxon Specimen V2: The Tale of Two Specimens, but the general idea is this: get ready to fly.
With Specimen Yo-Yo, we have a powerful blend that will not only provide energy, but provide thermogenesis, prevent fat storage, and decrease appetite:
- 400 milligrams of caffeine per serving, providing energy and igniting a bit of thermogenesis and fat oxidation while suppressing appetite[1,2]
- Both alpha-yohimbine and yohimbe (3mg and 2mg respectively -- two alkaloids that significantly boost energy)[3,4]
- 60 milligrams halostachine (an alkaloid similar to ephedrine that boosts energy, mood, focus, and motivation through the beta-2 receptor)[5-7]
The above is only the beginning, however. We've seen numerous studies and meta-analyses showing increased endurance from beta alanine[8,9] and taurine[10] -- and if you take advantage of that endurance effect -- you can go longer and burn more fat while you're at it.
L-Tyrosine is great for focus, but many often forget how important it is for thyroid hormone production, critical to metabolism and energy expenditure.[11,12]
There are two forms of betaine involved, getting us to a clinical dose, which has been shown to improve body composition in both men[13] and women[14] -- 3% and 3.3% body fat reductions, respectively! Betaine's fat loss data is also backed by a more recent systematic review of six studies on 195 participants.[15]
Finally, the choline provided is very useful for fat oxidation,[16-21] although it works best when synergized with L-carnitine.[22-24] And guess what ingredient comes in the next supplement we discuss?!
Do you see where we're going here? Glaxon Specimen Yo-Yo isn't just a phenomenal, high-energy pre workout -- it's one that can help you incinerate fat if you don't sabotage it with your diet!
Glaxon Specimen V2 Yo-Yo – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.
-
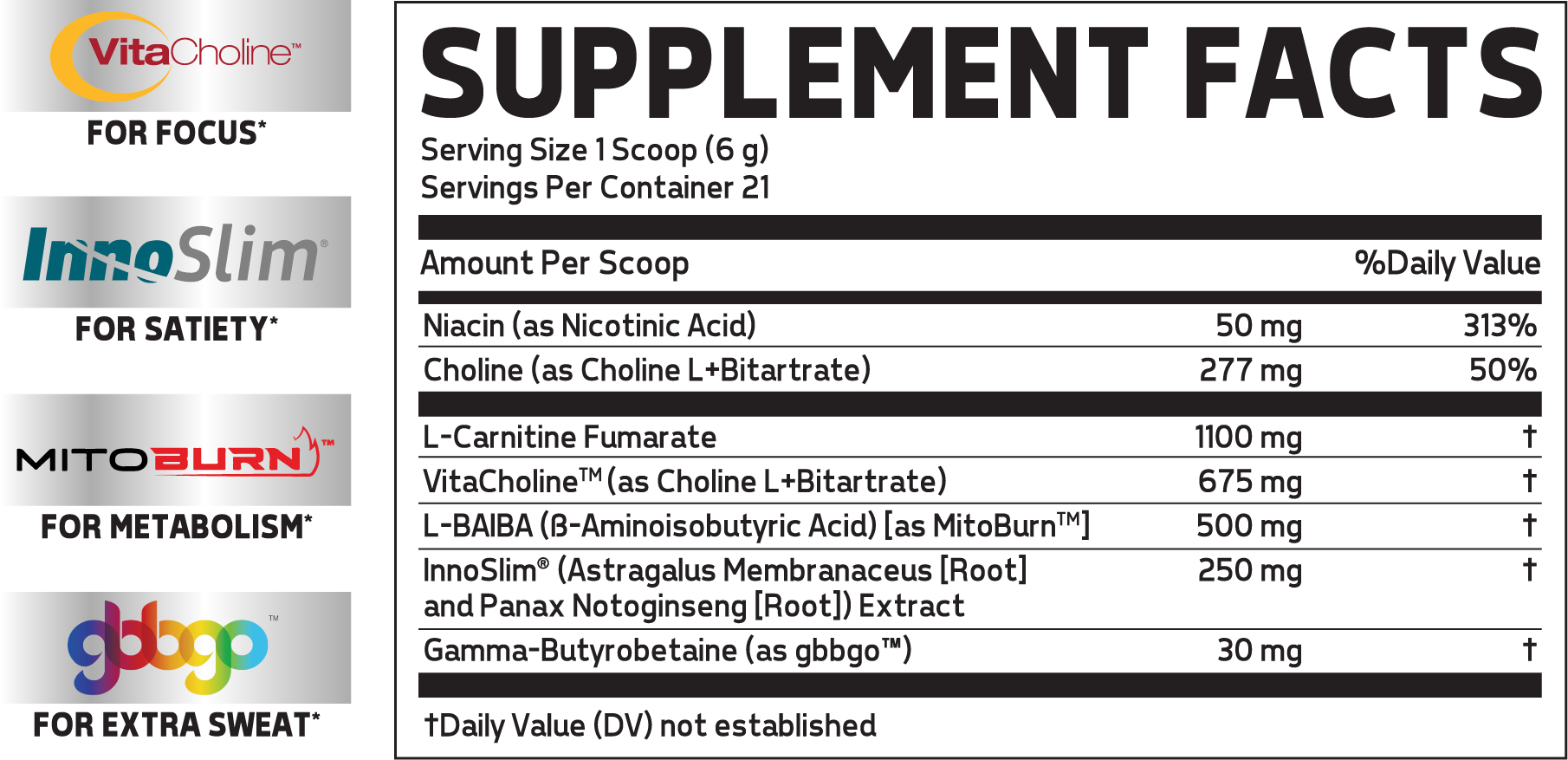
Amplifying Fat Loss with Thermal
Specimen is great, but if you really want to ramp up fat oxidation, then we add Glaxon Thermal, which we dub The Missing Piece In Your Fat Loss Stack.
Glaxon Thermal is a stimulant-free thermogenic weight loss aid that comes in powder form. This tub represents the 2021 update.
Thermal is anchored by two fascinating weight loss ingredients that we'll focus on below:
-
NNB Nutrition's MitoBurn L-BAIBA
L-BAIBA is a non-protein amino acid known as a myokine, which is a messenger sent from the skeletal muscle to carry out various actions.[25] When we exercise, L-BAIBA is released (by breaking down the BCAA L-Valine), and this signals to the rest of the body that it needs to begin preparing for exercise functions.
Based on animal research, this then goes on to get the body to carry out the following benefits:
- Increased fat oxidation[26-28]
- Ketone body production (BHB)[29]
- Conversion of white adipose tissue to more metabolically active "beige" fat[30,31]
- Better blood glucose tolerance and insulin resistance[26,28]
- Reduced inflammation[28]
- Lipid profile improvement[26]
- Promoted bone health[32]
The mechanisms are drilled down in greater detail in our Glaxon Thermal article, but what this means is that we get more exercise-based effects by kickstarting the "exercise program" faster and harder with MitoBurn.
Glaxon Thermal was the first supplement produced to use it, and continues to sell and succeed.
-
NuLiv Science's InnoSlim
Made from a patented blend of Astragalus membranaceus and Panax notoginseng, InnoSlim can inhibit small intestine glucose uptake by 41% by decreasing SGLT1 expression,[33] helping to prevent it from being stored as fat. However, it can still enhance glucose uptake into muscle cells by increasing GLUT4 activity![34]
More than ever, we understand metabolism and its critical importance. Besides exercise and cleaning up your diet from processed foods, how else can we accelerate our path back to metabolic wellness? Nuliv Science's InnoSlim is one such accelerant.
By upregulating many metabolic components (like AMPK, ACC-P, HIF-1, and adiponectin),[34] Innoslim can help to increase fatty acid oxidation.
Again, we get into far more detail in our main Thermal article linked above, but this is an ingredient we don't see in enough pre workout stacks, yet love for dieters.
On top of the anchors, Thermal is fronted by a large dose of L-Carnitine, which helps the body transport fatty acids to the mitochondria for oxidation and use.[35] A 2016 meta-analysis of nine randomized controlled studies found that L-carnitine helps dieters lose significantly more weight and improves BMI far better than placebo.[36] Two grams is generally the dose, such as in one study where it improved insulin sensitivity and blood sugar response.[37]
Worth noting that carnitine works best in those who may be deficient -- typically this means vegans and vegetarians,[38-41] seniors,[42,43] and overtrained athletes.[44] And to push carnitine even further, there's pro-carnitine GBB to get you sweating more too!
Updated in 2021, Thermal's Ingredients now sport GBB and a switch to L-Carnitine Fumarate on top of MitoBurn L-BAIBA.
Finally, there's a lot more choline in Glaxon's trademarked CholinACE blend, which will help support carnitine retention and the choline research cited above in the Specimen Yo-Yo section.
Thermal can be taken any time of the day, given that it's stimulant-free. However, we like to get our MitoBurn, choline, and carnitine in pre workout for some added fatty acid oxidation and transport effects when we want them - during training!
Glaxon Thermal – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.
-
-
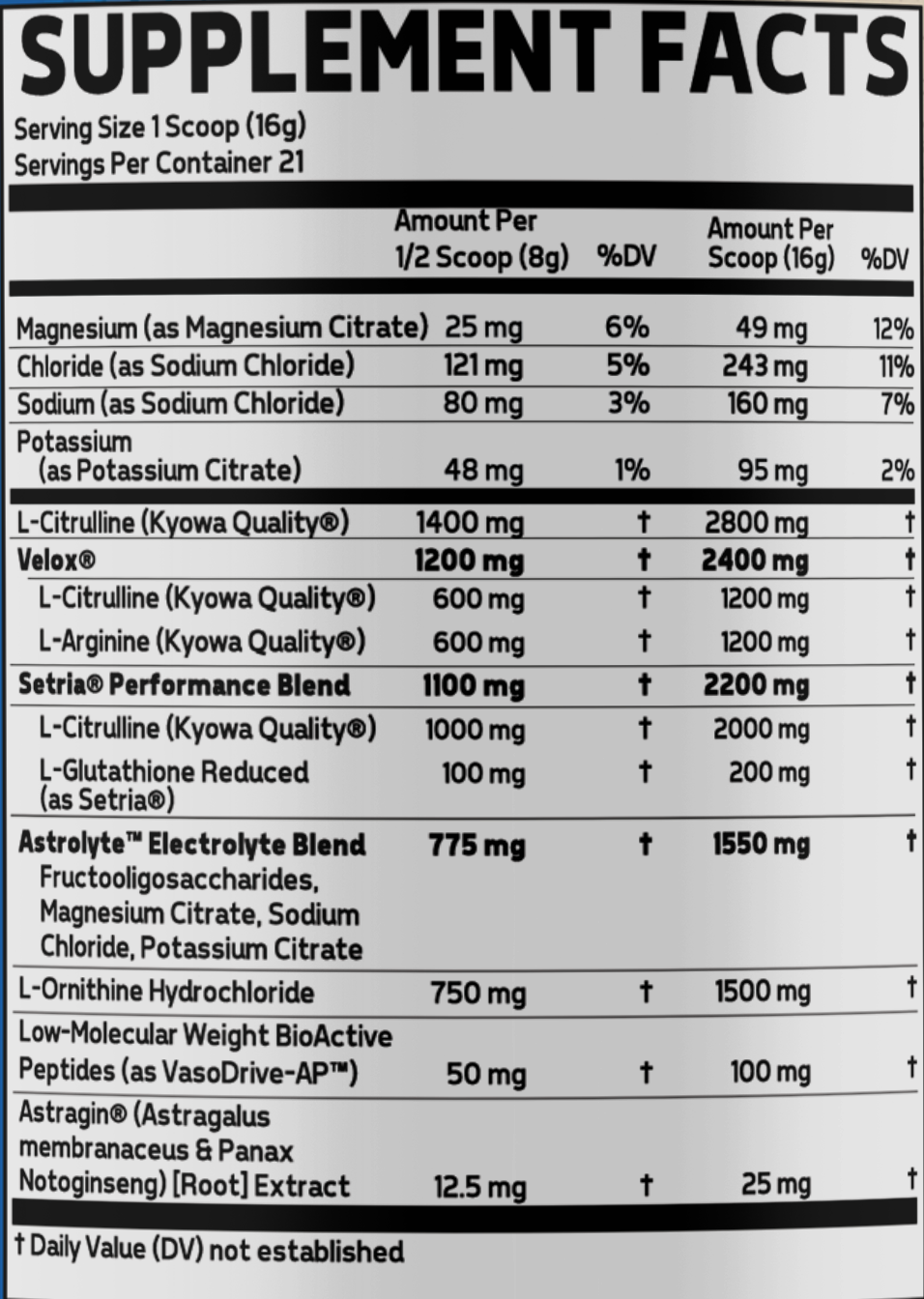
Out of this world pumps: Plasm Surge
The above two supplements are for dieters, but this one's for performance, enjoyment... and a little bit of vanity. When we're dieting and are in a caloric deficit, we often lose a bit of our pump effects -- especially if you're low-carb dieting.
To keep those pumps dialed in while bringing some performance and recovery gains alongside, we added Plasm Surge to the stack.
The nitric oxide pumps come from a huge blend of L-Citrulline and L-Arginine, which synergize to increase nitric oxide levels through the nitric oxide synthase pathway.[45-48] They're prolonged with Setria L-Glutathione, a unique antioxidant addition to the pre workout scene.
With improved nitric oxide levels, we get improved blood flow and nutrient delivery, and that blood flow leads to dialed-in pumps when we need them most.
The underrated ingredient, however, is the Astrolyte blend, which keeps us hydrated through a combination of electrolytes and fructooligosaccharides that we covered in our recent article titled Glaxon Astrolyte: Hydrating Electrolytes That Do More. If we're already low on calories, we don't want to further hamper pumps and performance by being low on electrolytes! The astrolyte blend fixes this.
This -- and more -- all synergizes with the nitrates in Specimen Yo-Yo to bring what we call "rescue pumps" for dieters, especially if you can't use a full dose of Specimen due to the stimulant load.
Glaxon Plasm Surge – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.
Diet-Driven Workouts Don't Need to be Weak

Glaxon is a unique brand, to say the least. If you thought their formulas were solid, wait until you stack them together.
If you're ready for a little bit of shred time, but aren't looking forward to the low-energy, low-pump workouts that diet season can bring, then this stack is for you. Glaxon spared no expense in creating a ridiculously unique and potent trio of supplements here, in combinations that have never before been used and have heads turning all over the industry.
Even though it's not a fat burner, Specimen Yo-Yo on its own provides incredible fat loss and appetite suppressant effects. But with the novel ingredients like MitoBurn and InnoSlim in Thermal, it takes on a whole new dimension.
Yet, even then, an extreme diet can have you feeling a bit "flat" still, even if you're energized to the max from the Yo-Yo blend. That's where Plasm Surge comes in, rescuing your pumps so that you can continue to quietly admire your progress in the mirror as we head into whatever the next month is going to bring us.
Glaxon – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.







Comments and Discussion (Powered by the PricePlow Forum)