Your organs work harder than Congress -- and actually get things done -- now it's time to protect them.
In the never-ending pursuit of gains, enhanced performance, and peak physiques, we often overlook the silent workhorses making it all possible - our vital organs. 'Merica Labz has answered the call with their latest creation, Organ Defender, a comprehensive organ support formula packed with proven ingredients to keep your body's command centers functioning at optimal levels.

Your organs work harder than Congress! 'Merica Labz Organ Defender delivers comprehensive support with NAC, Milk Thistle, Red Yeast Rice, and more. Keep your liver, heart, brain and eyes functioning at peak levels while you push your limits.
With the same bold, unapologetic approach we've come to expect from 'Merica Labz, Organ Defender stands ready to provide your hardworking organs the backup they deserve. And in true 'Merica fashion, they've wrapped it all in label artwork that's as eye-catching as the formula is effective, featuring a ripped older gentleman in jorts who looks suspiciously like a senior US Cabinet official...
Let's dive into what makes this product the constitutional right of anyone serious about their internal health.
'Merica Labz Keeps Your Freedom Organs Free
Whether you're pushing your limits in the gym, following an aggressive supplement regimen, or simply battling the daily toxins of modern life, your organs need backup. Organ Defender isn't just another supplement, it's tactical support for your body's most crucial systems.
Think of it as preventative maintenance for your internal machinery. Just as you wouldn't run your car into the ground without an oil change, your liver, kidneys, heart, and other vital organs deserve regular support to continue running at peak performance.
If you want to stay updated with 'Merica Labz and be notified when they drop their next freedom-fueled creation, sign up for PricePlow's 'Merica Labz news alerts:
Merica Labz Organ Defender – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.
'Merica Labz Organ Defender Ingredients
Each serving (3 capsules) of Organ Defender provides the following:
-
N-Acetyl-L-Cysteine – 600mg
N-Acetyl-L-Cysteine (NAC) leads the Organ Defender formula with a substantial 600mg dose, and for good reason. This powerhouse ingredient is the acetylated form of cysteine, a semi-essential amino acid that serves as the rate-limiting building block for glutathione, which is often called your body's "master antioxidant".[1]
NAC works through multiple mechanisms to support organ health:
-
Glutathione replenishment
NAC directly boosts glutathione production in your liver and other tissues.[2] This matters because glutathione is critical for detoxification processes and protecting cells against oxidative damage. When your glutathione levels drop (which happens during intense exercise, exposure to environmental toxins, or with age) your organs become more vulnerable to stress and damage.
-
Direct antioxidant effects
Beyond supporting glutathione production, NAC itself acts as a free radical scavenger, directly neutralizing harmful reactive oxygen species (ROS) that can damage cellular components.[3]
-
Liver protection
Your liver processes everything from the supplements you take to the toxins you encounter. NAC has been shown to protect liver cells from oxidative damage and is actually the standard medical treatment for acetaminophen (Tylenol) overdose, which can cause severe liver damage.[4]
-
Cardiovascular support
NAC may help support healthy blood vessels and cardiovascular function by improving nitric oxide bioavailability and reducing oxidative stress in the vascular system.[5]
-
Respiratory health
If you're training hard, you'll appreciate that NAC supports respiratory function by acting as a mucolytic (breaking up mucus) and reducing inflammation in the airways.[6]
The 600mg dose in Organ Defender is in line with doses shown to be effective in research. Merica Labz does what they do best here, providing legitimate support rather than window dressing. This makes NAC an excellent cornerstone for any organ support formula, especially for those pushing their physical limits.
-
-
Red Yeast Rice Powder (Monascus purpureus) (seed) - 600mg
Red yeast rice delivers one of the heaviest-hitting cardioprotective ingredients in Organ Defender's formula with a substantial 600mg dose. This traditional fermented food has been used in Chinese medicine for over 1,200 years, but its modern applications for cardiovascular support have made it a standout ingredient in health supplements.[8]
The "magic" happens when the Monascus purpureus yeast ferments rice, creating a range of bioactive compounds including:
- Monacolins - Particularly monacolin K (chemically identical to lovastatin!), which inhibits HMG-CoA reductase, the key enzyme in cholesterol production[9]
- Polyketides - Including pigments with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties[10]
- GABA - A compound that helps regulate blood pressure[10]
Red yeast rice delivers multiple cardiovascular benefits:
- Cholesterol management - Multiple studies show it can reduce total cholesterol by about 35 mg/dL and LDL cholesterol by about 28 mg/dL[11]
- Anti-inflammatory effects - Helps reduce C-reactive protein (CRP) and other inflammatory markers linked to cardiovascular disease[12]
- Blood pressure support - Some studies suggest modest blood pressure lowering effects when combined with conventional therapy[13]
The 600mg dose in Organ Defender is large enough to deliver clinically significant benefits while maintaining an excellent safety profile.[12] This makes red yeast rice a perfect complement to other cardiovascular-supporting ingredients in the formula, working together to keep your freedom-pumping heart and circulatory system in peak condition.
-
Hawthorn Berry Extract (4:1) – 500mg
Hawthorn (Crataegus spp.) is a traditional medicinal plant with an extensive history spanning thousands of years. This bright red berry isn't just visually striking, it's packed with bioactive compounds that make it a cardiovascular powerhouse in 'Merica Labz Organ Defender.
Hawthorn berry powder delivers a concentrated dose of flavonoids, oligomeric procyanidins, and triterpenoids that work synergistically to support heart health and cardiovascular function.[14]
The cardiovascular benefits of hawthorn are well-documented. Research shows it possesses positive inotropic effects (increases heart contraction strength) and vasodilatory properties that can improve coronary blood flow, making it particularly valuable for cardiovascular support.[15]
This ingredient has a multi-faceted approach to heart health:
- Antioxidant protection: Hawthorn's flavonoids, including epicatechin and hyperoside, are potent antioxidants that protect LDL cholesterol from oxidative damage, a key factor in maintaining arterial health.[16]
- Lipid regulation: Multiple studies show hawthorn can help maintain healthy cholesterol levels by promoting cholesterol breakdown in the liver.[17]
- Endothelial protection: Hawthorn helps preserve the integrity of vascular endothelium (the critical inner lining of blood vessels), which is essential for proper circulation.[16]
So we've supported the liver and the heart -- up next? The brain!
-
Bacopa Monnieri Extract (Whole Herb) (std. 50% Bacosides) - 300mg
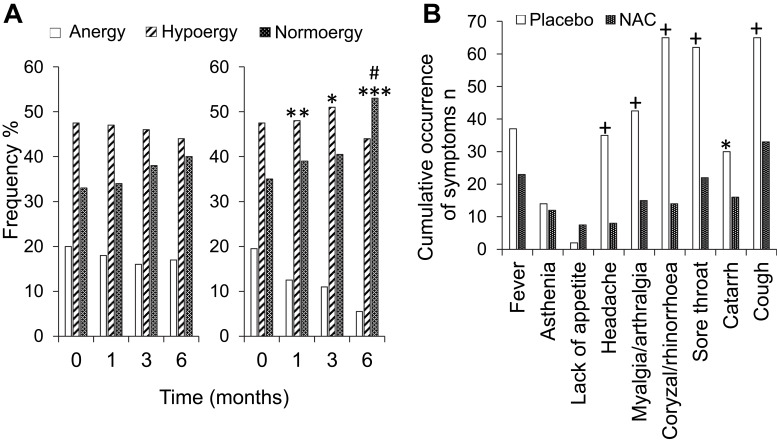
Effect of Bacognize Bacopa monnieri (300 mg/day) on neuropsychological tests (mean scores ± SD).[4] Notice the massive imrovement in the bacopa group vs placebo.
Bacopa monnieri brings serious brain power to Organ Defender with a powerful 300mg dose standardized to 50% bacosides, which are the plant's primary bioactive compounds. This ancient Ayurvedic herb has been used for over 3,000 years to enhance memory and cognitive function, but modern research reveals it's also a neuroprotective agent.
The 300mg dose is right in line with what's shown to be effective in clinical research. Multiple randomized, placebo-controlled studies using doses of 300mg have demonstrated significant improvements in various aspects of cognitive function after 12 weeks of supplementation.[18]
How Bacopa Works
Bacopa's cognitive benefits stem from several key mechanisms:
- Antioxidant Powerhouse: Bacopa contains powerful flavonoids and bacosides that scavenge free radicals and reduce oxidative damage in brain tissue.[19]
- Anti-inflammatory Brain Support: Bacopa significantly reduces inflammatory markers in the brain, including TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, protecting neurons from inflammation-driven damage.[20]
- Enhanced Blood Flow: Research shows Bacopa increases cerebral blood flow independent of blood pressure changes, improving oxygen and nutrient delivery to brain cells.[21]
- Neurotransmitter Support: Bacopa modulates key neurotransmitters like acetylcholine, serotonin, and dopamine, supporting mood balance and cognitive function.[22] By the way, if you like those neurotransmitters, Merica Labz has plenty of pre-workouts to help boost them further!
- Beta-Amyloid Protection: Studies show Bacopa can inhibit beta-amyloid protein aggregation, which is a major factor in age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases.[23]
The cognitive benefits of Bacopa aren't just theoretical: Human clinical trials consistently show improvements in memory acquisition, retention, and verbal learning after supplementation.[24]
While many focus on Bacopa's memory-enhancing effects, its neuroprotective properties make it a perfect addition to Organ Defender's comprehensive support formula. Your brain is arguably your most important organ, and Bacopa ensures it gets the protection it deserves.
So kudos to 'Merica Labz for including this. These "whole body / liver / kidney health" supplements never touch the brain, but they definitely didn't neglect it here! But on the note of the liver, another rockstar ingredient for it is next:
-
Milk Thistle Extract (Silybum marianum) (seed) (std. 80% silymarin) – 300mg
Another core of Organ Defender's formula is a solid 300mg dose of Milk Thistle Extract standardized to 80% silymarin. As with NAC, this isn't your garden-variety dose -- it's a clinical-strength serving that means business for your liver health.
Milk thistle (Silybum marianum) has been used for liver protection since the 4th century B.C. and remains one of the most thoroughly researched plant-based hepatoprotective agents.[25] The active component, silymarin, is a complex mixture of flavonolignans that includes silybin (the most active component), isosilybin, silydianin, and silychristin.
Silymarin works through multiple mechanisms:
- Antioxidant protection: Silymarin neutralizes harmful free radicals and reduces oxidative stress that can damage liver cells.[26]
- Membrane stabilization: It helps maintain the integrity of liver cell membranes, preventing toxins from entering cells.[27]
- Regenerative support: Silymarin stimulates protein synthesis in liver cells, helping them repair and regenerate after damage.[25]
- Anti-inflammatory action: It inhibits inflammatory pathways, reducing liver inflammation that can lead to long-term damage.[28]
Research shows that silymarin can help normalize elevated liver enzymes (ALT, AST) and improve liver function parameters.[29]
Whether your liver's working overtime from intense training, dietary choices, or weekend indulgences, this silymarin-packed extract acts as your organ's personal defense system.
-
Grape Seed Extract (95% proanthocyanidins) – 250mg
Grape Seed Extract (GSE) brings powerful antioxidant support to this organ protection formula thanks to its rich concentration of polyphenolic compounds, especially the proanthocyanidins. These naturally occurring compounds pack a serious punch when it comes to neutralizing free radicals and reducing oxidative stress throughout the body.[30]
GSE plays a major role in cardiovascular health. These potent compounds help maintain healthy endothelial function.[31]
The benefits don't stop there. GSE promotes healthy blood pressure levels by activating nitric oxide production, supporting vasodilation and enhanced blood flow throughout the body.[32] This improved circulation means better nutrient delivery and waste removal – exactly what your hardworking organs need.
For athletes and active individuals, GSE offers another significant advantage: improved recovery and exercise performance. Research shows that GSE supplementation can increase time to exhaustion during intense physical activity and reduce markers of exercise-induced muscle damage.[33]
Grape seed proanthocyanidins also help support healthy hepatic function by reducing oxidative damage and improving antioxidant defense systems.[34]
At 250mg standardized to 95% proanthocyanidins, Organ Defender provides an effective and clinically-backed dose of this multi-faceted ingredient, offering incredible protection to your most vital freedom-fighting organs while supporting optimal performance and recovery.
-
Marigold Extract (Flower) (5% Lutein) - 200mg
Marigold Extract brings powerful eye and brain protection to Organ Defender's formula through its star component - lutein. At 200mg standardized to 5% lutein, you're getting a solid 10mg dose of this critical carotenoid that works overtime to protect your vision and cognitive function. And don't worry, Organ Defender also includes zeaxanthin (which we'll cover below) to complement lutein's protective effects.
Lutein belongs to the xanthophyll family of carotenoids and, along with its isomer zeaxanthin, selectively accumulates in the retina and brain.[35] While humans consume approximately 50 carotenoids in their diet, lutein constitutes a whopping 60% of total carotenoids in the brain despite making up only 12% of carotenoid consumption.[36] Food for thought!
Visual Protection
In the eyes, lutein and zeaxanthin form macular pigment, which acts as a natural blue light filter and powerful antioxidant.[37] This matters because:
- It filters short-wavelength blue light that can cause oxidative damage
- It neutralizes free radicals that would otherwise harm delicate eye tissues
- It helps maintain the structural integrity of the macula
Multiple meta-analyses have found that higher blood levels of lutein are associated with a significant reduction in nuclear cataract risk (27% lower risk).[37] (Wait until you see how well zeaxanthin did in that study, too!) Additionally, supplementation with lutein has been shown to improve visual function parameters in adults with age-related macular degeneration.[38]
Brain Protection
Lutein doesn't just look after your eyes, it's also a key player in cognitive health. As mentioned above, it accumulates in brain regions responsible for learning and memory, where it provides antioxidant protection and supports neural efficiency.[39]
Research indicates lutein supplementation can:
- Support working memory and processing speed
- Improve neural efficiency during cognitive tasks
- Help maintain cognitive function with aging
The 10mg dose provided in Organ Defender falls right in the range shown to produce meaningful increases in both serum lutein and macular pigment optical density - the two key markers of lutein status.[40]
-
Saw Palmetto Berry Powder – 160mg
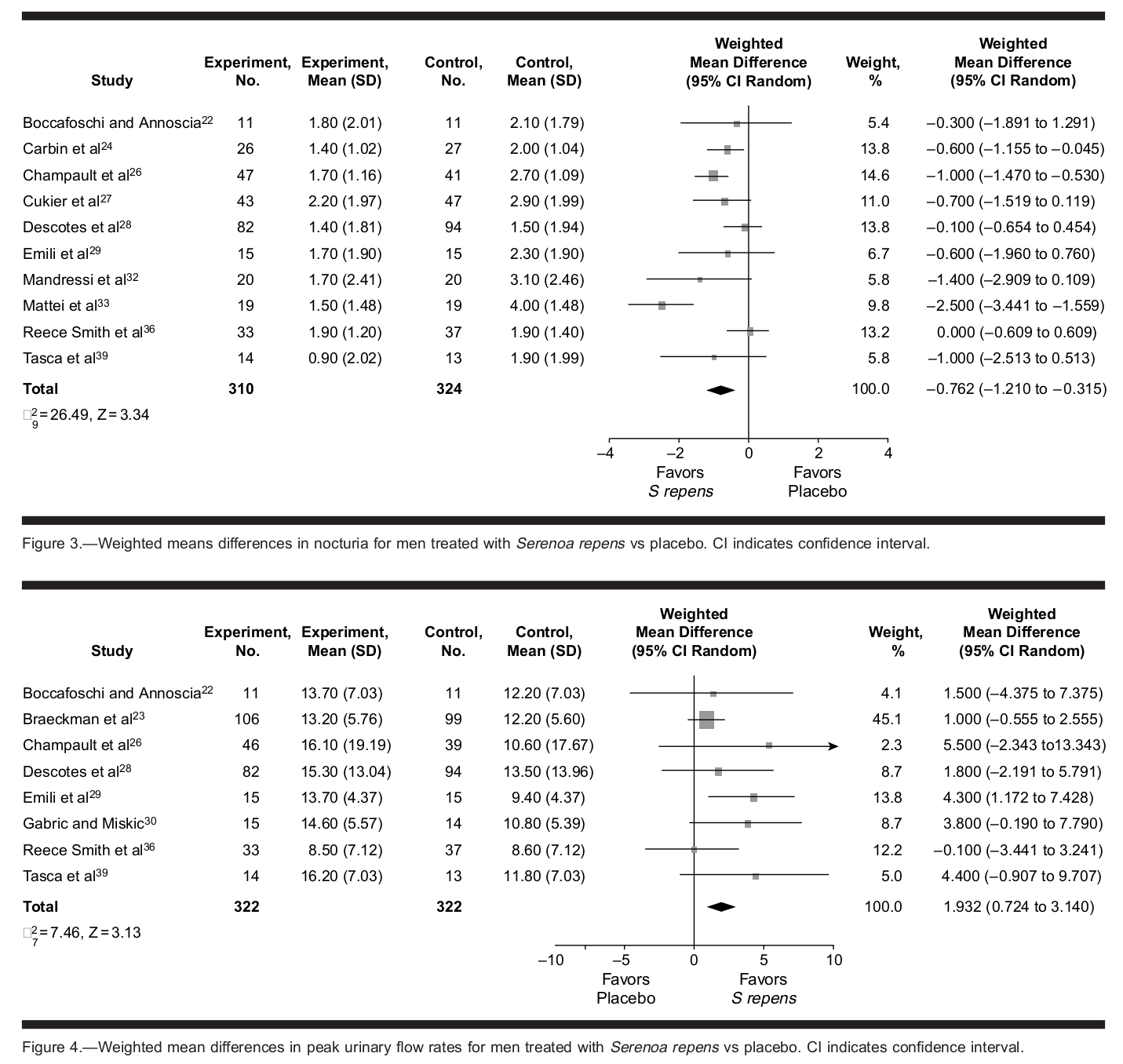
Saw palmetto (Serenoa repens) isn't just for your grandfather's medicine cabinet anymore. This powerful berry extract has earned its place in Organ Defender with good reason: it's one of the most well-researched natural compounds for supporting prostate health and overall male wellness.
Prostate Support When You Need It
Your prostate works overtime as you age, and saw palmetto works to keep it functioning properly. Research shows that the extract of saw palmetto berries can significantly improve lower urinary tract symptoms common in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).[41]
Discussed below, saw palmetto has enough evidence across multiple studies showing improved symptoms of BPH, and that's what was known in 1998.[42]
How It Works
Saw palmetto operates through multiple pathways to keep your prostate in check:
- Anti-androgenic effects: It inhibits 5α-reductase, the enzyme that converts testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which can contribute to prostate enlargement.[43]
- Anti-inflammatory action: Chronic inflammation plays a key role in prostate issues, and saw palmetto extract has demonstrated significant anti-inflammatory properties by reducing inflammatory markers in prostate tissue.[44]
- Pro-apoptotic effects: Research indicates saw palmetto can help regulate cellular growth in the prostate by promoting natural cell death (apoptosis) of unwanted cells.[41]
Beyond the Prostate
While prostate support is its claim to fame, saw palmetto offers additional benefits for men's health. Its fatty acid content from lauric acid and phytosterols like β-sitosterol help its overall effectiveness.[43]
The 160mg dose in Organ Defender provides clinically relevant support without going overboard -- it's the sweet spot for daily maintenance and protection of one of your body's most critical but overlooked organs.
Saw palmetto works without the common side effects that impact hormonal balance or sexual function.[45]
-
Coenzyme Q10 (Ubiquinone) – 100mg
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is the ultimate cellular energy supporter that works overtime inside your mitochondria, which keep your organs functioning. This naturally-occurring compound serves a dual role as both an essential component in energy production and a powerful antioxidant.
CoQ10 is found in virtually every cell in your body, but with the highest concentrations in high-energy-demanding organs like your heart, kidneys, and liver[46]... exactly the organs 'Merica Labz is targeting with Organ Defender. This isn't just coincidence -- these organs need CoQ10's support the most.
What makes CoQ10 so crucial? It acts as an electron carrier in the mitochondrial respiratory chain. This basically means it helps convert the food you eat into ATP, the energy currency your cells spend to function. But its benefits go beyond just keeping the lights on:
- As a powerful lipid-soluble antioxidant, CoQ10 protects cell membranes from oxidative damage, helping maintain organ integrity and function.[47]
- CoQ10 levels naturally decline with age and can be depleted by certain medications like statins, making supplementation increasingly important as you get older.[48]
- For cardiovascular health, CoQ10 has been shown to support healthy blood pressure levels and improve endothelial function.[49]
- Multiple studies suggest CoQ10 helps support optimal heart function, with one key trial showing it can improve symptoms and reduce major adverse cardiovascular events.[50]
- Your liver, which works overtime to process toxins, nutrients, and metabolic waste, also benefits from CoQ10's protective effects against oxidative stress.[51]
By including an incredible 100mg of CoQ10 in each serving, Organ Defender provides meaningful support for your hardest-working organs, ensuring they have the energy production support and antioxidant protection needed to function at their freedom-loving best.
-
Zeaxanthin 10% - 20mg
Zeaxanthin takes organ protection to the next level in Organ Defender -- this is an ingredient we sadly rarely see in "liver protector" type supplements like this. But 'Merica Labz knows that there's more to the body than just the liver and heart, right? At a potent 20mg of 10% zeaxanthin extract, you're getting a solid 2mg dose of this powerful carotenoid that works in perfect synergy with lutein to safeguard your vital organs from oxidative damage.
While lutein gets much of the spotlight, zeaxanthin deserves equal billing in the antioxidant hall of fame. This xanthophyll carotenoid is structurally similar to lutein (they're isomers) but displays unique protective properties that make it essential for comprehensive organ defense.
Superior Antioxidant Protection
Zeaxanthin is a heavy hitter in the antioxidant world with a unique molecular structure that makes it effective at neutralizing harmful free radicals. Research shows zeaxanthin may be an even more potent singlet oxygen scavenger than lutein, and this is critical to protect cells from oxidative damage.[52]
Enhanced Eye Protection
In the retina, zeaxanthin concentrates in a different pattern than lutein, with zeaxanthin dominating the central macula while lutein is more prevalent in the peripheral regions.[53]
Meta-analyses have found that higher blood zeaxanthin levels are associated with a 37% reduced risk of nuclear cataracts, which was even more protective than lutein's 27% risk reduction![37]
Liver and Metabolic Support
Beyond eye health, zeaxanthin offers potent hepatoprotective benefits. Research demonstrates that it can significantly improve hepatic function by enhancing antioxidant defenses (by activating Nrf2), reduce liver inflammation, and prevent liver mitochondria dysfunction.[54]
One study found that a form of zeaxanthin significantly improved liver function tests and reduced inflammatory markers in subjects with alcoholic liver damage, showing its powerful organ-protective capabilities.[54]
Cognitive Function Support
Like lutein, zeaxanthin accumulates in brain tissue where it provides neuroprotection by combating oxidative stress and supporting healthy inflammatory responses there as well. Studies show that higher blood levels of zeaxanthin are associated with improved cognitive performance across multiple domains, particularly executive function.[36]
The 2mg dose of zeaxanthin in Organ Defender works synergistically with lutein to create a comprehensive protection system for your most vital organs, exactly what you need when pushing your body to its limits.
These supplements often neglect the eyes, but not 'Merica! After all, the anthem does start with "Oh say can you see", does it not?
-
Probiotic Blend - 5 Billion CFU
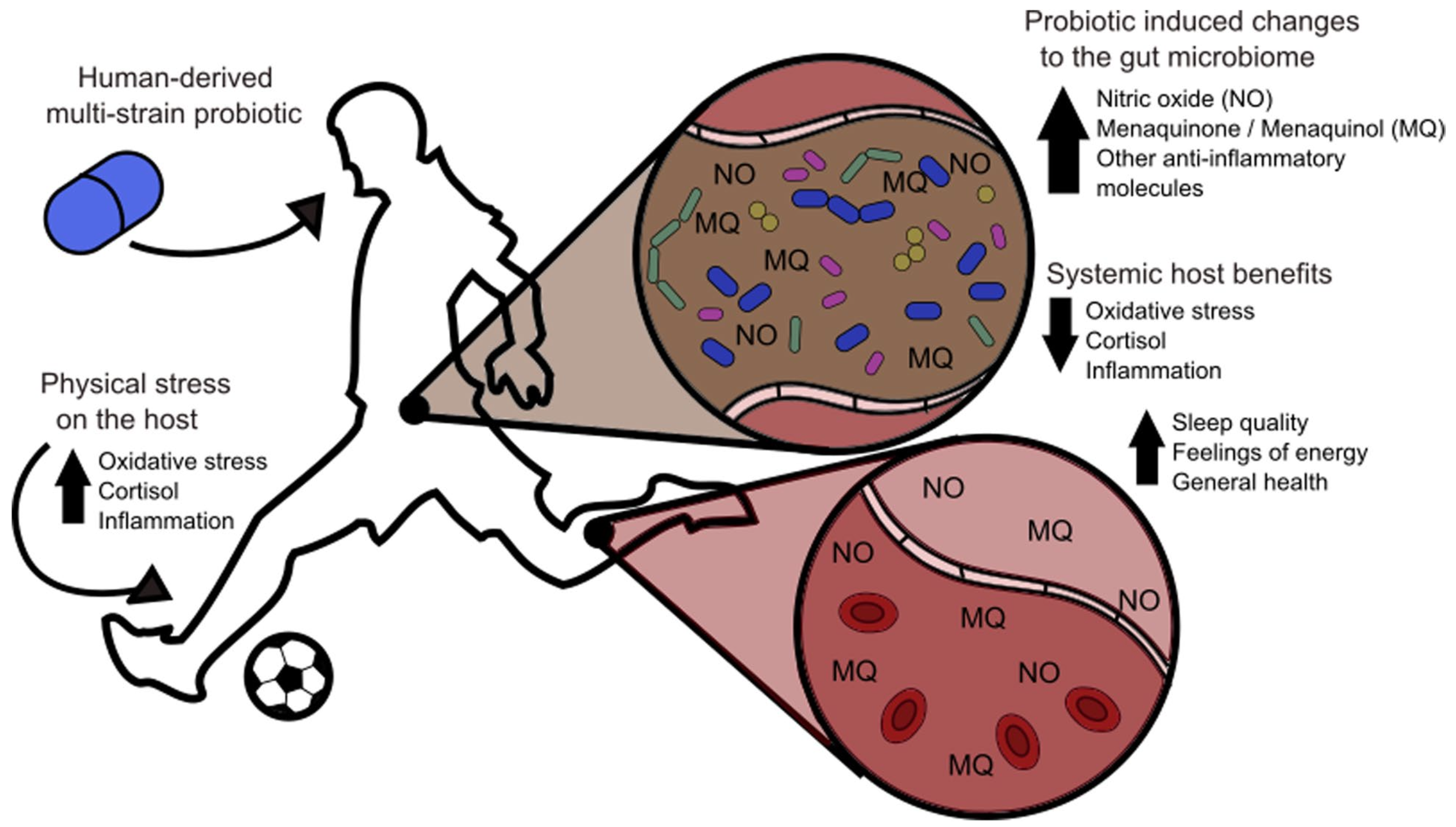
Illustration of probiotic-induced changes in the gut microbiome and their effects on oxidative stress, inflammation, and systemic host benefits.[55]
'Merica Labz rounds out Organ Defender with a comprehensive multi-strain Probiotic Blend delivering 5 billion CFU of beneficial bacteria, taking the "support" concept beyond just your major organs to include your gut microbiome, which, after the liver, is the foundation of whole-body health.
This isn't a basic single-strain probiotic, but is instead a strategic blend of ten different bacterial strains including multiple species from the Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, and Streptococcus genera. This diversity matters because different probiotic strains have unique effects and colonize different parts of your digestive tract.[56]
Why Multiple Strains Matter
Research suggests multi-strain probiotics may provide broader benefits than single-strain products for several reasons:
- Complementary mechanisms: Different strains work through distinct pathways, potentially offering more comprehensive support.[57]
- Survival advantage: Different strains have varying strengths in surviving stomach acid, bile salts, and other digestive challenges, increasing the likelihood that beneficial bacteria reach their target sites.[58]
- Enhanced colonization: The diverse strains can establish beneficial populations throughout different regions of your GI tract.[59]
Point being - there's more to this than just taking lactobacillus! 'Merica Labz knows this.
Beyond Digestion
While gut health is a primary benefit, the effects of probiotics extend far beyond digestion. We're learning more about this every year, but so far, here's what we know your probiotic population influences:
- Liver function: Probiotics help process and eliminate toxins, reducing the workload on your liver.[60]
- Immune system regulation: Approximately 70% of your immune system resides in your gut, and these beneficial bacteria help train and regulate immune responses.[61]
- Nutrient absorption: Probiotics enhance the breakdown and absorption of nutrients from food and supplements, meaning better utilization of everything else you're taking.[61]
- Inflammation control: Many probiotic strains help regulate inflammatory processes throughout the body.[61]
The inclusion of this robust probiotic complex shows 'Merica Labz' commitment to comprehensive organ support. They've recognized that true internal health doesn't just mean supporting individual organs, but fostering the symbiotic relationship between your gut microbiome and vital body systems. This truly holistic approach is made to keep your freedom-fighting internal machinery running at peak capacity.
-
Added Vitamins and Minerals
You may have noticed these three at the top of the label, and they're nothing to sneeze at:
-
Vitamin C (as Ascorbic Acid) - 200mg (222% DV)
Vitamin C is the classic powerful antioxidant that serves as a frontline defender for virtually every organ in your body. This water-soluble vitamin plays a critical role in maintaining your internal defenses against oxidative damage and environmental stressors.
The famous vitamin serves a dual action here, as both a direct antioxidant and a "recycler" of other antioxidants. It works synergistically with glutathione (which NAC above and selenium below helps boost) to enhance your body's overall antioxidant capacity.[62]
For liver health, vitamin C has been shown to decrease oxidative stress markers and improve glutathione status.[63] This becomes especially important during periods of increased physical stress, when your body's antioxidant reserves can become depleted.
Patrick Mabe (@mr.patrick.mabe) of Core Nutritionals, Merica Labz, and Merica Energy joins the PricePlow Podcast Episode #073 to discuss his competition in the Tactical Games, fatherhood, and living the Crush It Lifestyle at Core Nutritionals in North Carolina!
The 200mg dose (222% DV) provided in Organ Defender is enough to saturate plasma levels and ensure your organs have the antioxidant protection they need.[64]
Beyond antioxidant protection, vitamin C also supports:
- Collagen synthesis for blood vessel integrity and wound healing
- Immune function through enhanced white blood cell activity
- Iron absorption for optimal oxygen transport to organs
- Neurotransmitter production for brain and nervous system health
When combined with the other organ-supporting ingredients in this formula, vitamin C promotes system-wide defense for your hardest-working internal components.
-
Iodine (as Kelp Extract) - 200mcg (133% DV)
Iodine is an essential mineral that doesn't get nearly enough attention in the fitness world, yet it's absolutely critical for optimal hormonal function and metabolic health. At 200mcg (133% DV), Organ Defender provides a meaningful dose from natural kelp extract.
This trace mineral serves as the cornerstone of thyroid hormone production, where it's incorporated directly into both T3 and T4 hormones.[65] Without adequate iodine, your thyroid can't produce the hormones that regulate virtually everything from your metabolism and body temperature to heart rate and protein synthesis.
Avoid iodine deficiency, which is coming back lately!
When iodine intake is insufficient, your body struggles with:
- Reduced metabolic rate - making fat loss much harder
- Decreased energy production - limiting your training intensity
- Impaired cognitive function - affecting focus and recovery
- Compromised recovery - hampering your gains
What's often overlooked is that iodine also functions as an antioxidant and supports breast health, with research showing its role in maintaining healthy breast tissue.[66] Merica Labz is often built for men, but this is worth knowing about.
The 200mcg dose in Organ Defender hits the sweet spot - sufficient to support optimal thyroid function without risking excess, which can actually cause similar problems as deficiency![67]
For those pushing their limits in the gym, ensuring proper iodine status isn't just beneficial, it's smart and essential for maintaining the metabolic fire that powers your freedom gains.
-
Selenium (as Selenium Glycinate) - 200mcg (364% DV)
Selenium isn't just another mineral, it's your body's antioxidant insurance policy, coming in at a powerful 200mcg dose (364% of the Daily Value) in Organ Defender. This highly-underrated, essential trace element functions as a cornerstone of your body's antioxidant defense system when converted into selenoproteins, which protect your cells from the daily assault of oxidative stress.[68]
Here's why selenium matters for your organ health:
- Master antioxidant support: Selenium is a critical component of glutathione peroxidase, an enzyme that works alongside glutathione (your body's primary antioxidant, as discussed earlier) to neutralize harmful free radicals that would otherwise damage your organs.[69] This will synergize with the NAC and vitamin C in Organ Defender, since NAC provides cysteine as a glutathione building block.
- Liver protection: Your liver takes the brunt of toxin processing, and selenium helps keep it functioning properly. Studies show selenium decreases the risk of liver cancer and supports healthy liver function.[70]
- Immune system regulation: Selenium enhances immune function by influencing both innate and adaptive immunity, helping your body's defense systems work more efficiently.[71]
- Thyroid hormone metabolism: Selenium is crucial for the production and regulation of thyroid hormones through selenoenzymes called deiodinases, maintaining proper metabolic function throughout your body.[72]
The 200mcg dose in Organ Defender is substantial enough to correct deficiencies and provide optimal support for your hardworking organs without approaching levels that might raise concerns about excess selenium intake.
What a great way to finish the supplement off, from top to bottom, we have three ingredients (NAC, vitamin C, and selenium) helping you to create more glutathione!
-
How to Use Organ Defender
Using Organ Defender is as straightforward as exercising your right to bear arms (but with fewer range fees). 'Merica Labz recommends taking 3 capsules daily with a meal to maximize absorption. For best results, stay consistent with daily use. Your organs don't take days off, and neither should your support system.
This product works best as part of a wide-scale approach to health, including proper hydration, nutrition, and adequate recovery. Whether you're a hardcore athlete, a weekend warrior, or someone who just wants their insides running as smoothly as a well-oiled AR-15, Organ Defender provides support where it matters most.
Who Should Use Organ Defender?
Organ Defender is ideal for:
- Fitness enthusiasts following intense training regimens
- Those using performance-enhancing supplements
- Individuals concerned about environmental toxin exposure
- Anyone looking for whole-body or preventative organ support
The beauty of Organ Defender's formula is that it's beneficial for almost anyone interested in maintaining their long-term internal health. Unlike some supplements designed for specific short-term goals, Organ Defender offers benefits that accumulate over time with consistent use.
Conclusion: Patriotic Protection for Your Vital Organs
'Merica Labz doesn't do anything halfway, and Organ Defender is no exception. This massive formula brings together research-backed ingredients in effective doses to support your body's most important systems. In a world where we're focused on what you can see in the mirror (or on Instagram), Organ Defender stands out by addressing what you can't see... but what ultimately matters most.
Your organs work tirelessly to keep you functioning at your best, even when you push them to their limits. Organ Defender is the backup they deserve -- think of it as an insurance policy for your internal freedom fighters.
By combining traditional botanicals with modern nutritional science, 'Merica Labz has created a product that's as sensible as it is powerful. And with their signature patriotic flair and unmistakable branding, they've done it in a way only 'Merica Labz could.
So whether you're looking to support recovery, maintain peak performance, or simply invest in your long-term health, Organ Defender deserves a spot in your supplement arsenal. Because true freedom starts with a healthy foundation.
Get your Organ Defender today and give your body's command centers the support they've earned:
Merica Labz Organ Defender – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.

















Comments and Discussion (Powered by the PricePlow Forum)