Vegans and vegetarians mainly get protein from legumes, whole grains, nuts, and seeds. But since vegans and vegetarians consume anywhere from zero to a minimal amount of animal products, it can be extremely difficult for that population to intake enough high-quality protein. Therefore, many of them rely on plant-based protein powders.
Over the past few years, the popularity of vegan protein powders has been on the rise, especially in sports nutrition. But there are some potential issues with plant protein products that you should be aware of.
The Potential Downfalls of Plant Protein
Since plants grow in the ground, they're at risk of containing excessive amounts of heavy metal. This is an issue for everyone, not just vegans and vegetarians. But, it's more of a concern for vegans and vegetarians because a larger portion of their diets is comprised of plants. So companies should be careful where they source their plant-protein from.
And also really important is the fact that the majority of plant proteins are classified as incomplete proteins because they lack an adequate amount of one or more of the nine essential amino acids. Essential amino acids (EAAs) must be supplied by the diet and/or supplementation because they cannot be produced by the body.

Some of the major downfalls of plant protein are its bioavailability and amino acid profile. Image courtesy of Ingredient Optimized.
Out of the 20 amino acids in existence, nine are considered essential. They include:
- Leucine
- Isoleucine
- Valine
- Histidine
- Methionine
- Phenylalanine
- Tryptophan
- Lysine
- Threonine
Three of the nine essential amino acids — leucine, isoleucine, and valine — are classified as branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) based on their unique structure. The three BCAAs, especially leucine, play an important role in muscle protein synthesis (the generation of proteins in the body). So if you're looking to maximize your performance, recovery, and health, it's vital to consume enough protein that's rich in EAAs and BCAAs.
Unfortunately, the majority of plants lack sufficient amounts of EAAs and BCAAs, especially leucine, which is the main trigger of muscle protein synthesis (MPS). To solve this problem, manufacturers combine various complimentary plant protein sources. For example, it's common to see a brown rice protein and pea protein blend in vegan protein powders because the amino acids lacking in brown rice protein are in rich supply in pea protein.
This isn't a problem with animal-based protein powders because they're complete protein sources, such as whey or casein. In fact, whey protein is considered the gold standard for protein powder because of its impeccable amino acid profile and bioavailability. Several studies have shown that whey protein increases plasma levels of amino acids significantly more than nearly every other protein source, especially plant proteins.[1-3]
If only there was a way to make plant proteins with the power of whey...
Introducing Ingredient Optimized Technology and ioPea
Up until this point, plant proteins have been considered inferior to whey, but thanks to the masterminds behind Ingredient Optimized Technology that's quickly changing. Ingredient Optimized (io) is an innovative company in the sports nutrition industry that has spent years developing, researching, and testing ways to make a plant protein that performs as well as whey protein.
After years of development, io has finally done it with ioPea protein, the first ingredient in their ioPlant series. ioPea protein is a naturally-optimized plant protein. It's actually been shown, in two human clinical trials, to be just as good as whey protein and better than standard pea protein.[4]
Some key features of ioPea include:
- Nearly 3x more bioavailable than standard pea protein, according to studies
- Tastes neutral
- No third-party ingredients added
- Easy to use in foods, supplements, and beverages
- Clinically backed with over five years of research and development
- Safe and compliant technology that maintains GRAS (generally recognized as safe) status
- Available as USDA Certified Organic, NSF Certified for Sport, Halal, Kosher, NSF (GMP Certificate), and SQF Level 2[5]
ioPea hasn't been around for very long, but it's already gaining traction in sports nutrition. For example, Kaged Muscle, a well-respected supplement brand, was the first company to use ioPea protein — in a product called Plantein, which came out in September 2020. Approximately a month after, another popular brand called Performix designated ioPea as the primary ingredient in ioPlant Protein. Both brands were seeking to innovate vegan protein powders and thanks to ioPea, they were able to do that.
If you want to learn more about the first plant protein to use ioPea, check out this article: Kaged Muscle PLANTEIN: Powered By ioPea Protein
At this point, you may be wondering how io was able to create a superior form of pea protein? Well, keep reading to learn about the science behind Ingredient Optimized Technology and ioPea protein. Make sure to subscribe below for more information on io and their other ingredients!
Subscribe to PricePlow's Newsletter and Alerts on These Topics
Kaged Plantein – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.
Learn about ioPea on Video
Keep reading, or listen to us discuss ioPea's technology in the video below:
Ingredient Optimized Technology: A Natural and Clean Label Process
Ingredient Optimized Technology uses a natural atmospheric plasma treatment process to enhance the surface area, solubility, and dispersibility of protein molecules (i.e. whey or pea protein).[4,5] Unlike other processing methods, io doesn't use any harmful chemicals or enzymes to alter the structure of the protein.
Instead, Ingredient Optimized Technology carefully changes the tertiary and quaternary structure to expose the hydrophobic pockets of the protein molecules.[4,5] This allows for enhanced absorption and bioavailability, as well as reduced stomach discomfort.[5]
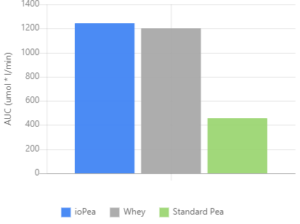
ioPea has significantly increased the bioavailability of all nine essential amino acids. Image courtesy of Ingredient Optimized
Before using Ingredient Optimized Technology with pea protein, io began researching and testing this technology with whey protein nearly five years ago. After several human clinical trials, io discovered that whey protein treated with the Ingredient Optimized Technology was superior to standard whey in terms of enhanced bioavailability for essential amino acids, particularly leucine.[6,7]
Ingredient Optimized even found that compared to standard whey protein, you can use up to 35% less ioWhey and still get a similar amino acid delivery.[6] Furthermore, subjects that consumed the lesser amount of ioWhey experienced similar strength and muscle mass gains as a higher dose standard whey protein.[6]
After discovering their technology has such a profound effect on whey protein, io turned their attention to plant proteins — specifically pea protein.
Pea protein is actually one of the few plants that are classified as a complete protein. In fact, one randomized controlled trial from the Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition found that pea protein isolate performs just as well as whey for increasing muscle mass.[8]
However, pea protein's leucine content and bioavailability still don't come close to whey or casein, and some would argue that pea protein is technically not complete because although it contains all nine EAAs, it's rather low in methionine. Fortunately, by applying Ingredient Optimized Technology to standard pea protein, io is able to overcome all of the downfalls of pea protein. Somehow, they were even able to create a pea protein with an amino-acid profile as comprehensive as whey.
ioPea Protein vs Hydrolyzed Whey
In two double-blind, randomized, crossover trials, researchers from the Applied Science and Performance Institute compared the postprandial plasma essential amino acid (EAA) and branched-chain amino acid (BCAA) responses from various protein sources in 10 resistance-trained men.[4]
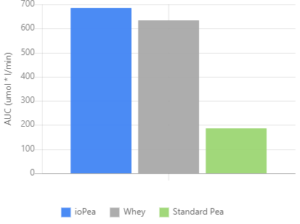
ioPea expresses much higher branch-chained amino acid bioavailability. Image courtesy of Ingredient Optimized.
The five main comparisons of the study were:
- Hydrolyzed whey protein isolate (HWPI) vs. plasma modified non-hydrolyzed whey protein isolate (PM-NHWPI)
- Standard branch-chained amino acids (S-BCAA) vs. plasma-treated branch-chained amino acids (PM-BCAA)
- Standard pea protein (S-PP) vs. plasma modified pea protein (PM-PP)
- Hydrolyzed whey protein isolate (HWPI) vs. plasma modified pea protein (PM-PP)
- Standard leucine (S-Leucine) vs plasma modified leucine (PM-Leucine)[4]
Since we're focusing on ioPea (plasma modified pea protein) in this article, we're only going to discuss the third and fourth group comparisons.
For the S-PP vs. PM-PP comparison, participants were instructed to consume 25 grams of powder of S-PP or PM-PP after an overnight fast. The same conditions were used for the HWPI vs PM-PP comparison.[4]
The two conditions were separated by a seven day washout period. Researchers measured the participants' branch-chained amino acid and essential amino acid plasma concentrations via blood samples at 30, 60, 90, 120, and 180 minutes after ingestion.[4]
The results showed that the PM-PP had a greater bioavailability of leucine, BCAAs, and EAAs, and was up to three times more bioavailable overall compared to S-PP.[4] Furthermore, the PM-PP and HWPI had no significant differences in their ability to elevate plasma levels of BCAAs and EAAs.[4] This means that PM-PP, also known as ioPea, is an adequate alternative to HWPI.
See How Ingredient Optimized Technology Works on Whey!
Key Takeaways
For anyone who wants to get the benefits of a whey protein but consumes a plant-based protein instead, it looks like ioPea protein is the answer! The ability to create a plant protein that performs as well as any form of whey protein, let alone HWPI, is quite remarkable. The future of vegan protein powders is looking bright now thanks to this new technology.
Ingredient Optimized Technology is not limited to just whey or pea protein, it can also be used with other ingredients, including:
- BCAAs
- Leucine
- Citrulline
- Beta-alanine
- Caffeine
Overall, Ingredient Optimized Technology is committed to transforming effective dietary supplements into something even better by enhancing their bioavailability and absorption. Most PricePlow readers understand that the body expels anything it can't absorb, including nutrients and vitamins... So increasing the bioavailability of various ingredients will ultimately boost their effectiveness — and your results.
It's important to note that if you see a product with an ingredient from Ingredient Optimized, it contains the required, efficacious dose shown to be effective in the research. Ingredient Optimized has extremely high standards regarding the brands and manufacturers they work with, so you can rest assured that what's on the label is in fact in your product.
Over the next few months, PricePlow will be covering more innovative ingredients and products from Ingredient Optimized, so make sure to subscribe below - and you can always check out becomeio.com





Comments and Discussion (Powered by the PricePlow Forum)