
Women respond differently to creatine, and research shows it works exceptionally well. Benefits span muscle growth, bone density, brain health, and mood across every life stage. No bloating or unwanted weight gain. Animal breaks down the science and provides options for every goal.
For decades, creatine research focused almost exclusively on male athletes, creating a knowledge gap that left women's unique responses largely unexplored. That oversight has finally been corrected. Recent science reveals women don't just respond differently to creatine because of lower body mass or different training patterns. They experience fundamentally distinct hormonal, metabolic, and cellular interactions that make creatine supplementation uniquely beneficial across the entire female lifespan.
Creatine for Women: The Full Scientific Scoop
The concerns that kept many women from trying creatine lack scientific support. Creatine doesn't cause unwanted bloating, excessive water retention, or fat gain. It doesn't make you bulky. What it does do is provide cellular energy that supports muscle growth and preservation, enhances cognitive function, and potentially protects bone density during menopause. It may even help combat low mood states in women at nearly twice the rate of men!
Whether you're a competitive athlete seeking performance gains, a woman navigating the hormonal shifts of perimenopause and menopause, or someone focused on maintaining strength and independence through aging, the research demonstrates clear benefits. From young female soccer players improving sprint performance to postmenopausal women preserving bone density and functional capacity, creatine supplementation works across every life stage when combined with resistance training.
And this article explores the science demonstrating all of that.
Animal's creatine lineup provides options for every preference and goal, from advanced synergistic formulas to pure, flexible powders. Check PricePlow's coupon-powered prices and availability below, and sign up for our Animal alerts to stay informed about new products and deals - they are the sponsor of this article, but the research below is from decades of independent studies.
Universal – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.
This area is reserved for Team PricePlow's upcoming Research Study video.
Subscribe to our channel and sign up for notifications so you catch it when it goes live!
The Science: Creatine for Women
First, a background. It turns out, creatine isn't just for muscle. It's really all about cellular energy.
Reason being, creatine rapidly regenerates ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the molecule powering all cellular energy from muscle contractions to brain function. This universal energy system explains why creatine's benefits extend well beyond the weight room.
So rather than first covering muscle, let's get into the hormonal influences first:
-
Hormonal Influences on Creatine Kinetics
First, let's prove that creatine has a special place for women. It begins with the hormones, and can be seen during special situations like pregnancy.
Estrogen and progesterone directly influence creatine synthesis, transport, and creatine kinase activity throughout the female reproductive cycle.[1] Creatine kinase levels peak during menstruation and decline throughout the menstrual cycle, during pregnancy, and with age.[2] These hormone-driven changes alter creatine bioavailability across menses, pregnancy, post-partum, perimenopause, and postmenopause, highlighting critical windows where supplementation may provide the most value.[1]
Interestingly, the lowest creatine kinase values occur during early pregnancy (20 weeks or less), dropping to approximately half the concentration found at peak levels in teenage girls.[3] Metabolic demand from the placenta during gestation further depletes maternal creatine pools, potentially contributing to low birth weight and pre-term birth.[4] This hormonal modulation of creatine metabolism has been largely overlooked in performance-based studies, yet it suggests women may benefit from creatine supplementation in ways that extend far beyond the gym.
So it's not just for guys and muscle. But what has the research done for women over the years?
-
Performance Benefits in Young Women
Despite common misconceptions that creatine only benefits male athletes, controlled research demonstrates clear performance enhancements in women across multiple domains. The landmark Vandenberghe study showed that young women (19-22 years) taking 20 g/day for 4 days followed by 5 g/day during 10 weeks of resistance training significantly increased intramuscular creatine concentrations, muscle mass, and strength compared to placebo.[5]
Research shows creatine + HMB work better together than apart. Studies demonstrate 67% greater muscle growth and 680% improvement in testosterone-to-cortisol ratio when combined. Animal Creatine HMB+ leverages this synergy with clinical doses of both.
Sport-specific benefits appear equally robust. Elite female soccer players (22 ± 5 years) supplementing with 20 g/day for 6 days improved sprint and agility performance compared to placebo during a field test simulating match play.[6] The improvements manifested in specific agility runs during testing blocks, suggesting creatine enhances the repeated high-intensity efforts characteristic of competitive soccer.[6]
Upper-body performance responds equally well. Hamilton and colleagues demonstrated that 25 g for 7 days augmented upper-body exercise capacity in strength-trained women (21-33 years) compared to placebo.[7] The enhancement occurred in work capacity during fatiguing elbow flexion exercises, suggesting creatine extends performance during the high-repetition training that many women prefer.[7]
Even short-term protocols show benefits. College-aged women (20 years) taking 0.5 g/kg of fat-free mass for 5 days improved maximum quadriceps contraction performance compared to placebo.[8] The improvements in peak torque during isokinetic testing demonstrate that creatine enhances maximal force production in women, not merely endurance during submaximal efforts.
But not every woman cares about extreme athletic performance. Lately, creatine's surging because of the brain health and longevity benefits:
-
Brain Health and Cognitive Benefits
Women face unique vulnerabilities in brain health. Mood disorder rates run approximately twice as high among women throughout the reproductive years and accelerate around pubertal hormonal changes. Females also have lower baseline creatine levels in the brain's frontal lobe compared to males.[9]
Creatine supplementation significantly augments cerebral phosphocreatine and inorganic phosphate in women.[10] In adolescent females with SSRI-resistant mood disorder states, 10 grams of creatine supplementation increased cerebral phosphocreatine inversely correlated with depression symptoms.[11] This suggests creatine may provide great mood benefits, likely through improved brain bioenergetics and mitochondrial function.[1]
Animal Creatine HMB+ combines 5g creatine monohydrate with 3g myHMB for superior results. Research shows this duo delivers 67% more muscle growth and 38% more strength than creatine alone. Plus vitamin D3 and electrolytes for complete performance support.
A pilot study in females in addictive states found that creatine supplementation reduced low mood symptoms, providing preliminary evidence for broader mental health applications.[12] Altered brain bioenergetics and mitochondrial dysfunction have been linked with depression, involving creatine kinase, ATP, and inorganic phosphate.[1]
The cognitive benefits extend beyond clinical populations. Meta-analyses show that creatine supplementation improves short-term memory and intelligence/reasoning in healthy individuals, with effects more robust in older adults.[13] Given women's lower baseline brain creatine levels, they may experience enhanced cognitive responses to supplementation, though this hypothesis requires direct testing.
-
Benefits for Postmenopausal Women
The intersection of aging and declining estrogen creates a critical period where creatine supplementation provides multifaceted benefits. Accumulating research over the past decade demonstrates that creatine supplementation during resistance training improves muscle mass, upper- and lower-body strength, and functional tasks in postmenopausal women.[1]
Muscle Mass and Strength
Aguiar and colleagues examined 12 weeks of creatine supplementation (5 g/day) combined with resistance training in postmenopausal women (mean age 64.9 years).[14] The creatine group achieved greater training volume throughout the program and demonstrated superior improvements in 1RM bench press, biceps curl, and knee extension performance compared to placebo.[14] Beyond raw strength, creatine improved functional capacity in real-world tasks like the 30-second chair stand, arm curl test, and getting up from lying on the floor, measurements that directly predict independence in daily living.[14]
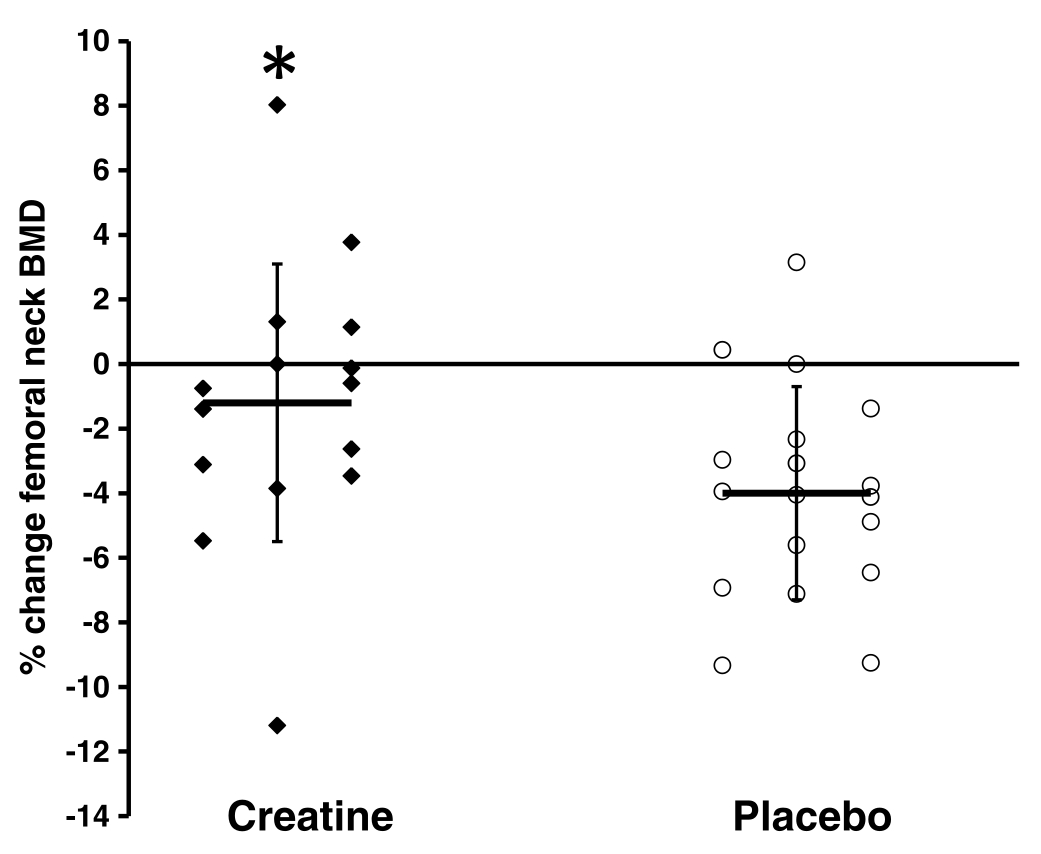
Research data comparing creatine supplementation versus placebo in postmenopausal women during resistance training. The creatine group experienced significantly better preservation of bone mineral density at the femoral neck (hip area) over 52 weeks, supporting healthy bone structure during this critical life stage.[15]
The mechanisms involve more than water retention. The creatine group increased fat-free mass and muscle mass beyond what training alone provided, suggesting genuine hypertrophy rather than merely fluid accumulation. The enhanced training capacity likely drives superior muscle protein synthesis, satellite cell activation, and growth factor expression that amplify resistance training adaptations.[14]
Yet without resistance training, creatine shows limited benefits for muscle mass in postmenopausal women. A 2-year supplementation protocol (3 g/day) without exercise failed to increase lean mass or prevent sarcopenia, confirming that creatine amplifies training stimulus rather than replacing it.[1]
Animal drops FIVE new flavors this April! Blood Orange Primal, Strawberry Whey, Candy'd Crush'd Creatine Chews, Rainbow Candy Cuts, and Kiwi Lime Fury.
Bone Health
Beyond muscle, creatine may help preserve bone mineral density when combined with resistance training. Postmenopausal women supplementing daily with 0.1 g/kg/day during 52 weeks of supervised whole-body resistance training experienced attenuated bone mineral loss at the femoral neck (hip) compared to placebo.[15] The femoral neck carries significant clinical importance as a primary site of osteoporotic fractures.[15]
The mechanisms remain under investigation but likely involve the close metabolic coupling between muscle and bone. Greater muscle forces during resistance training stimulate bone formation, and creatine's enhancement of training capacity may translate to stronger osteogenic signals.[15] However, creatine supplementation without resistance training shows no bone benefits, emphasizing the requirement for mechanical loading.[1]
-
Pregnancy and Reproductive Health
Animal studies reveal neuroprotective effects of maternal creatine supplementation during pregnancy. Pre-clinical research demonstrates protective effects against fetal death and organ damage associated with intrapartum hypoxia.[16] Creatine supplementation during pregnancy enhanced neuronal cell uptake of creatine and supported mitochondrial integrity in animal offspring, reducing brain injury induced by intrapartum asphyxia.[17]
Reduced creatine levels in late pregnancy have been associated with low fetal growth.[16] The metabolic demand from the placenta during gestation depletes maternal creatine pools, potentially contributing to low birth weight and pre-term birth.[4]
Although human studies evaluating creatine supplementation during pregnancy remain limited, creatine could provide a safe, low-cost nutritional intervention for reducing intra- and post-partum complications associated with cellular energy depletion.[1] This may hold great importance for vegetarian women or those unable to consume meat due to nausea or taste preferences, as meat contains approximately 0.7 g of creatine per 6 oz serving.[1]
Animal Creatine Chews bring a fun and simple way to get creatine in - and they've got us hooked!
Prospective cohort studies in low-risk pregnant women are underway to evaluate creatine's effects on pregnancy outcomes in humans.[18] Until more human data emerges, pregnant women should consult healthcare providers before supplementing with creatine, though animal evidence suggests substantial potential benefits.
-
Body Composition Effects
Concerns that creatine causes unwanted water retention or fat gain in women lack scientific support. Meta-analyses show that creatine supplementation does not increase fat mass across various populations.[1] In fact, participants supplementing with creatine had greater reductions in body fat percentage, with the creatine group losing approximately 0.5 kg more fat mass compared to placebo.[1]
Recent meta-analysis confirms that creatine enhances resistance training's body composition adaptations, promoting hypertrophy and reduced body fat mass without requiring concurrent dietary interventions.[19] Women generally represent about 20-25% of subjects in performance supplement literature, and emerging evidence suggests unique impacts in female subjects, including changes to hydration status across the menstrual cycle.
Initial weight gain from creatine typically reflects increased intracellular water content rather than extracellular bloating. This fluid retention serves functional purposes, facilitating greater training volume and enhanced protein synthesis. Over longer supplementation periods, any initial water weight becomes overshadowed by genuine lean mass gains from improved training capacity.
-
Safety and Dosing Considerations
Extensive research confirms creatine's safety profile in women. Multiple studies examining acute creatine loading (20-25 g/day for 5-7 days) reported no adverse effects on hemodynamics, blood chemistry, liver function, or kidney function in women.[20][21]
Creatine Gummies were recently discovered to fail NOW Foods' testing - 46% failed testing! But Animal Creatine Chews are built different.. and better
Standard dosing protocols work effectively in women:
- Loading Phase (Optional / Not Necessary): 20-25 g/day split into 4-5 doses for 5-7 days, or calculated as 0.3 g/kg body weight per day. This rapidly saturates muscle creatine stores within one week.[1]
- Maintenance Phase: 3-5 g/day maintains elevated muscle creatine stores after loading.[1]
- Alternative Protocol: 3-5 g/day from the start achieves similar muscle saturation as loading protocols, though it requires 3-4 weeks rather than one week.[1]
Women can use body weight-adjusted dosing (0.1 g/kg/day for maintenance) when precise individualization matters, though the 3-5 g/day range works effectively for most.[15]
The studies reviewed reported minimal side effects distributed equally between creatine and placebo groups. When side effects occurred, they were rated as minimal in severity.[22] Creatine monohydrate remains the most studied form with the strongest safety and efficacy evidence in women.[1]
-
Practical Implications for Female Athletes
The evidence collectively positions creatine as a multifactorial supplement across the female lifespan with minimal safety concerns. Young female athletes gain performance benefits in strength, power, and sport-specific capacities comparable to males. Postmenopausal women experience enhanced training adaptations, improved functional capacity, and potential bone-protective effects when combining creatine with resistance training. Emerging evidence suggests cognitive and mood benefits that may address women's higher depression rates and support brain health during vulnerable periods.
Animal's creatine monohydrate provides the most researched form, available in several formats discussed above, including powders and capsules that come without unnecessary additives. Whether you're competing at elite levels, training to maintain strength and independence through menopause, or simply optimizing health and performance, creatine supplementation offers evidence-based benefits specifically validated in women.
The historical exclusion of women from creatine research created a knowledge gap that recent science continues to fill. Current evidence makes clear: creatine works for women, and it works well.
Animal’s Creatine Options
Animal offers four distinct creatine products, each designed for specific needs and preferences. For women seeking maximum benefits from creatine supplementation, these options provide flexibility across training goals, life stages, and lifestyle demands.
-
Animal Creatine HMB+: The Premium Choice for Muscle and Bone Health
For women concerned about muscle preservation, bone density, and overall body composition, Animal Creatine HMB+ stands out as the most comprehensive option in Animal's lineup.
This formula combines 5g of creatine monohydrate with 3g of myHMB, a combination that delivers 67% greater muscle growth and 38% more strength than creatine alone. The synergy between these ingredients amplifies the muscle-building and muscle-preserving effects critical for women at every life stage.
Beyond the core ingredients, Creatine HMB+ includes vitamin D3 and an electrolyte complex with sodium, potassium, and magnesium. Vitamin D plays a crucial role in bone health, making this formula relevant for postmenopausal women facing accelerated bone mineral loss. The electrolyte blend supports hydration and cellular function without added sugars or unnecessary carbohydrates.
With zero stimulants and zero sugar, Creatine HMB+ fits seamlessly into any eating pattern, including intermittent fasting protocols. The formula provides clinical doses of scientifically validated ingredients without compromising macros or meal timing flexibility. For women training consistently and seeking to maximize strength, preserve muscle mass during fat loss, or maintain bone health through perimenopause and beyond, this represents Animal's most advanced creatine solution.
Universal Animal Creatine HMB+ – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.
-
Animal Creatine Chews: Convenience with Carbohydrate Considerations
Animal Creatine Chews deliver 5g of creatine monohydrate in delicious chewable tablets with multiple flavor options. The convenience factor makes them appealing for busy schedules, travel, or anyone who prefers not to mix powders.
Each serving includes 25mg of AstraGin for enhanced absorption and 4g of carbohydrates from sugar and dextrose. These carbohydrates serve dual purposes: they improve taste and support post-workout glycogen replenishment. Research shows glucose and dextrose effectively restore muscle glycogen after training, and creatine enhances this glycogen-loading effect.[23]
However, women managing carbohydrate intake for body composition goals should account for these 4g of sugar per serving. The chews work well around training when carbohydrate timing matters, but they may not fit every dietary approach. Unlike creatine gummies that often fail quality testing, Animal uses a dry tablet pressing process that maintains creatine stability without degradation into creatinine.
For women who want grab-and-go convenience and can accommodate the carbohydrate content, Creatine Chews provide an enjoyable alternative to powders. Available flavors include Grape, Fruit Punch, Green Apple, Lemon Ice, and Candy'd Crush'd.
Universal Animal Creatine Chews – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.
-
Animal 100% Pure Creatine Monohydrate: The Flexible Foundation
Animal 100% Pure Creatine Monohydrate provides exactly what the name promises: pure, micronized creatine monohydrate without additives, flavors, or extras.
This unflavored powder offers maximum versatility for women who prefer controlling every aspect of their supplementation. Add it to pre-workout formulas, protein shakes, coffee, or any beverage without altering flavor profiles. The micronized form breaks down creatine particles by a factor of 20, improving solubility and absorption without changing the molecular structure.
Cost-effectiveness makes pure creatine monohydrate ideal for higher-dose protocols. Women using creatine for cognitive benefits often consume 10-20g daily, doses that become expensive with flavored or enhanced formulas. Loading phases for rapid muscle saturation (20-25g daily for 5-7 days) also benefit from the economical pricing of bulk creatine powder.
The research supporting creatine's benefits in women uses creatine monohydrate almost exclusively. This makes Animal's pure version the most evidence-based choice for those who want the exact form tested in clinical trials. Whether you're stacking it with Animal Creatine HMB+ for higher total creatine intake, following cognitive enhancement protocols, or simply want flexibility in how you consume creatine, the pure powder delivers.
Universal Animal 100% Pure Creatine Monohydrate – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.
-
Animal Ready-to-Go Creatine Capsules
For ultimate convenience without any preparation, Animal offers creatine monohydrate in capsule form. These provide precise dosing with zero taste considerations and work well for travel or maintaining consistent intake away from home.
Universal Animal Ready-to-Go Creatine – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.
For detailed guidance on combining these products strategically or choosing the right option for specific goals, see our complete guide: Animal's Complete Creatine Lineup: Finding Your Perfect Match.
Conclusion: Creatine is For Women!
The historical exclusion of women from creatine research created decades of missed opportunities. The science now makes clear what should have been studied from the beginning: creatine works exceptionally well for women, delivering benefits that extend far beyond the weight room.

Animal covers every creatine need with 4 distinct products: convenient chews with glycogen support, synergistic HMB+ combinations, pure micronized powder for loading, and travel-ready capsules. Each targets specific goals from muscle growth to cognitive enhancement.
Young women gain strength, power, and sport-specific performance enhancements. Women navigating perimenopause and menopause experience improved training adaptations, enhanced functional capacity, and potential bone-protective effects when combining creatine with resistance training. Cognitive benefits may address women's elevated depression rates and support brain health during hormonal transitions. These aren't theoretical advantages. They're documented outcomes from controlled research.
Animal's four creatine options ensure you'll find a format matching your needs, whether you prioritize the muscle-preserving synergy of Creatine HMB+, the flexibility of pure powder, the convenience of capsules, or the grab-and-go simplicity of chewable tablets. Each product delivers clinically effective doses using the creatine monohydrate form validated in research.
The question isn't whether creatine works for women. The evidence settled that debate. The question is which format and approach best support your specific goals across your unique life stage and training demands. With Animal's comprehensive lineup and over four decades of quality manufacturing behind every product, you have options backed by both science and practical real-world results.
Universal Animal 100% Pure Creatine Monohydrate – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.











Comments and Discussion (Powered by the PricePlow Forum)