You may have read our mega-guide about nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) supplements. This article will focus on our preferred nucleotide supplement on the market — BioNMN by NNB Nutrition.
The Basics
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) is a precursor to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+). NAD+ plays a crucial role in the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) — which fuels most of the cells in our body. NAD+ levels decline as we age, which may cause health problems. Humans cannot absorb NAD directly, but can process NMN precursors into NAD+.
The issue with NAD+ supplements is that high quality, lab-tested products are hard to find. This is where NNB Nutrition comes in. BioNMN is NNB Nutrition's patented take on NMN that emphasizes bioavailability and quality through their mastery of "Ingredientology". NNB Nutrition backs BioNMN via third party high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). HPLC is a gold standard form of analytic chemistry that tells us exactly what is inside a product down to the molecule — so you know what you're getting with BioNMN.
Most NAD enhancement supplements on the market use untraceable ingredients from no-name companies, but NNB put their entire philosophy into BioNMN, and any brand can use it. While ingredient quality is good, you may be wondering why NMN is worth taking.
Subscribe to PricePlow's Newsletter and Alerts on These Topics
The Science Behind BioNMN
-
Potential Brain and Heart Benefits
NAD+ supplementation appears to stimulate SIRTUIN, a family of genes that geriatric researchers implicate in the aging process. By stimulation of SIRTUIN, NAD+ may mitigate the cellular damage that occurs from physiologic stress.
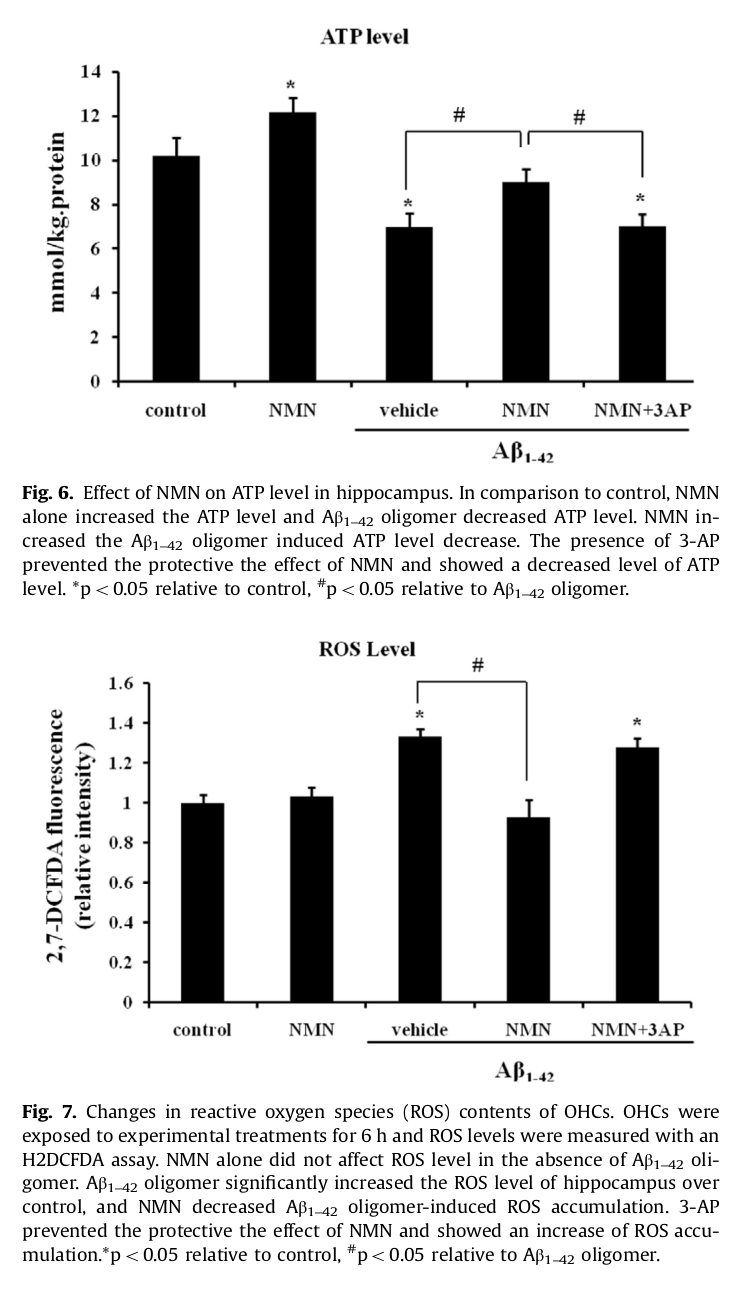
NMN helped the brain generate more ATP and less ROS (reactive oxygen species),[1] which alone makes it of major interest
A study in 2014 by Rutgers Medical School and Tokai University shows that NMN supplementation maintains tissue perfusion (circulation of blood, providing oxygenation) even in the face of ischemia.[2,3] The researchers linked this protective effect to a dose-dependent stimulation of SIRT3, a gene within the SIRTUIN family.[3]
Another investigation shows that NMN supplementation confers cardioprotective effects through a combination of improved ATP synthesis and induction of a relative acidosis.[4]
Neuroprotection
NMN acts as a neuroprotective agent through similar mechanisms — and may even benefit those suffering from neurodegenerative disorders! A trial on mice with Alzheimer's Disease suggests that NMN use increases mitochondrial oxygen utilization, reduces mitochondrial damage, and even strengthens mitochondrial integrity within neural tissue.[1] A separate trial showed that NMN combats amyloid plaque accumulation — a pathognomonic feature of Alzheimer's Disease implicated in the neural degenerative aspects of the disease.[5]
For those that want the brass tax — BioNMN supplementation may protect cells against low oxygen states and may improve mitochondrial health. Which is exactly what NNB Nutrition strives for, as told in our articles detailing The NNB Nutrition Story: Supplement Ingredient Solutions for the New Decade.
-
Hormonal Health
NNB Nutrition's BioNMN takes NMN bioavailability to a new level, and is backed by an incredibly innovative novel ingredient development team
NMN supplementation may also improve insulin sensitivity.[6]
Researchers at the University of Washington found that mice with diabetes have lower amounts of NAD+ within their fat and liver tissue compared to healthy mice.[7] When these diabetic mice were given NMN for 7-10 days, their insulin sensitivity improved. The researchers believe low levels of NAD+ may suppress genes responsible for insulin sensitivity. Due to the improvement in insulin sensitivity after supplementation, this study illustrates that glucose-control gene activity may improve when NAD+ deficiency is corrected.[8,9]
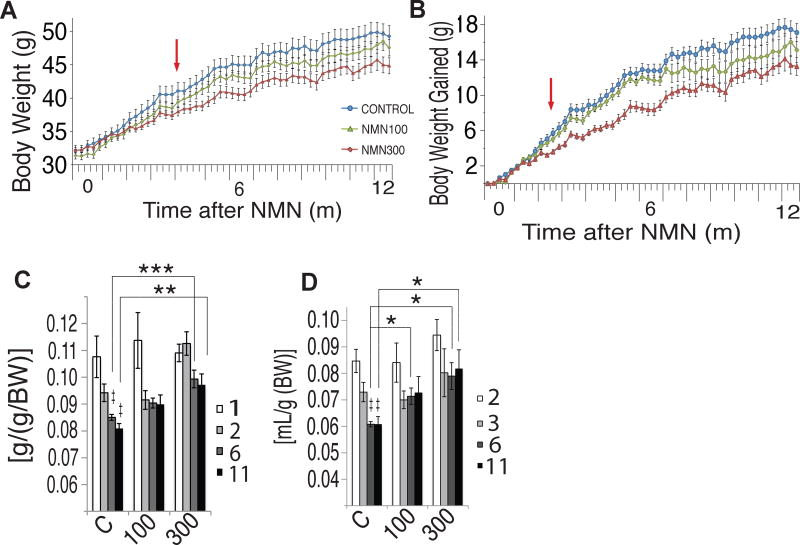
More NMN, more food, less age-related weight gain in mice.[10] It seems that improved insulin sensitivity is a huge benefit of this mitochondrial-boosting ingredient
This improvement in insulin sensitivity could help combat obesity. A trial published in Cell Metabolism shows that a daily-dose of NMN led to lower body weights in mice that ate more food than a control group. While this appears to be an obvious violation of the "calories in vs calories out'' manifesto, it makes sense as NMN-treated mice showed more oxygen consumption and energy expenditure than the control group,[10] likely demonstrating even greater "calories out" than the amount from increased food consumption!
Another trial done on exercising mice concluded that NMN supplementation may combat obesity in a mechanism similar to regular exercise.[11] Since exercise also tends to increase oxygen consumption and energy expenditure — this conclusion did not surprise us. Interestingly, this reminds us of another exercise-induced "signal" that can be supplemented, NNB Nutrition's MitoBurn, which is their branded form of L-BAIBA.
While we are optimistic about NMN's future as a diabetic health supplement, we want to see more results in humans (the existing ones are quite promising) before giving our full endorsement. As NNB ran human trials for NucleoPrime, we expect more research to develop as BioNMN matures as a product.
-
The Longevity Angle
To go even deeper, click on our main article about NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide), a fascinating molecule that can be supplemented for improved energy
Neurologic health, mitochondrial functionality, and metabolic efficiency decrease with age.[12,13] As NMN provides a protective role throughout the body, BioNMN truly shines as an anti-aging supplement. For those that want direct research of NMN's benefits in geriatrics patients, the animal study below is quite promising.
A trial in Aging Cell sought to reverse vascular dysfunction in older mice through NMN supplementation. The researchers compared the carotid artery functionality of these older mice against a younger control group. Prior to supplementation, the older mice had worse vascular function than the control group. By the end of this trial, the older mice given NMN had vascular function that was nearly indistinguishable from the younger mice.[13] While we want this finding replicated, it certainly created a serious amount of hype in the anti-aging space.
NMN supplementation also may improve optic health, bone health, and myeloid-lymphoid composition.[10]
-
Human Trials: In progress and succeeding (2021 update)
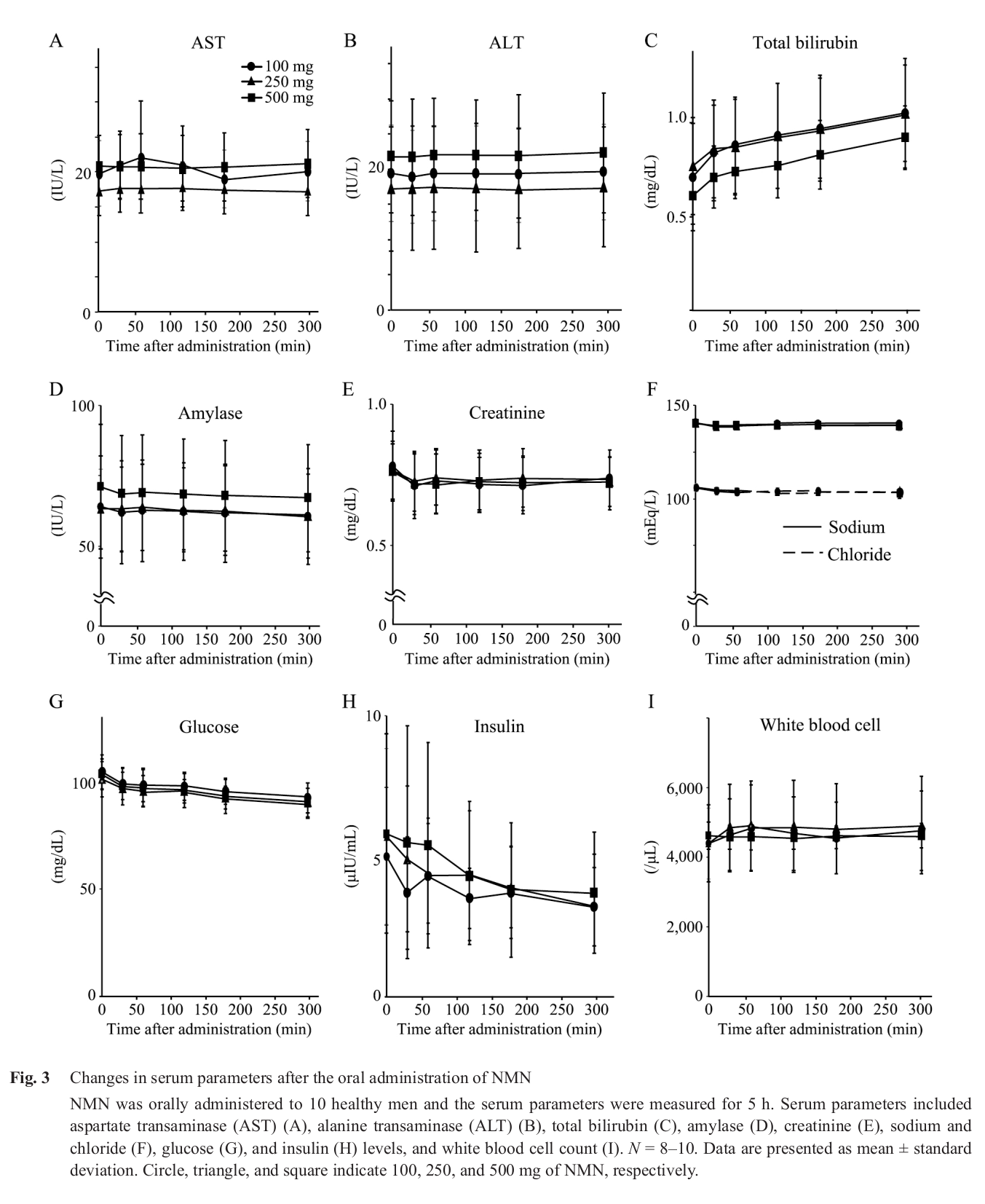
The human safety data is great news, but even more compelling is the reduction in insulin alongside a drop in glucose.[14]
The keen-eyed readers of PricePlow may be curious about human-based trials. While such research is still young, it is promising. A trial by the Keio University School of Medicine suggests that NMN is well-tolerated in humans. While the subject size was small at 10 subjects, no adverse effects were noted. The trial also shows that NMN supplementation may reduce insulin concentration and blood glucose levels[14] — a finding that supports the insulin sensitivity improvements shown in mice.
Phase II of this study, utilizing a larger subject pool is currently underway. The National Institute of Health is also conducting a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study on NMN in humans. This study is expected to finish in 2021[15] — so stay tuned and subscribe to our NMN alerts below for updates.
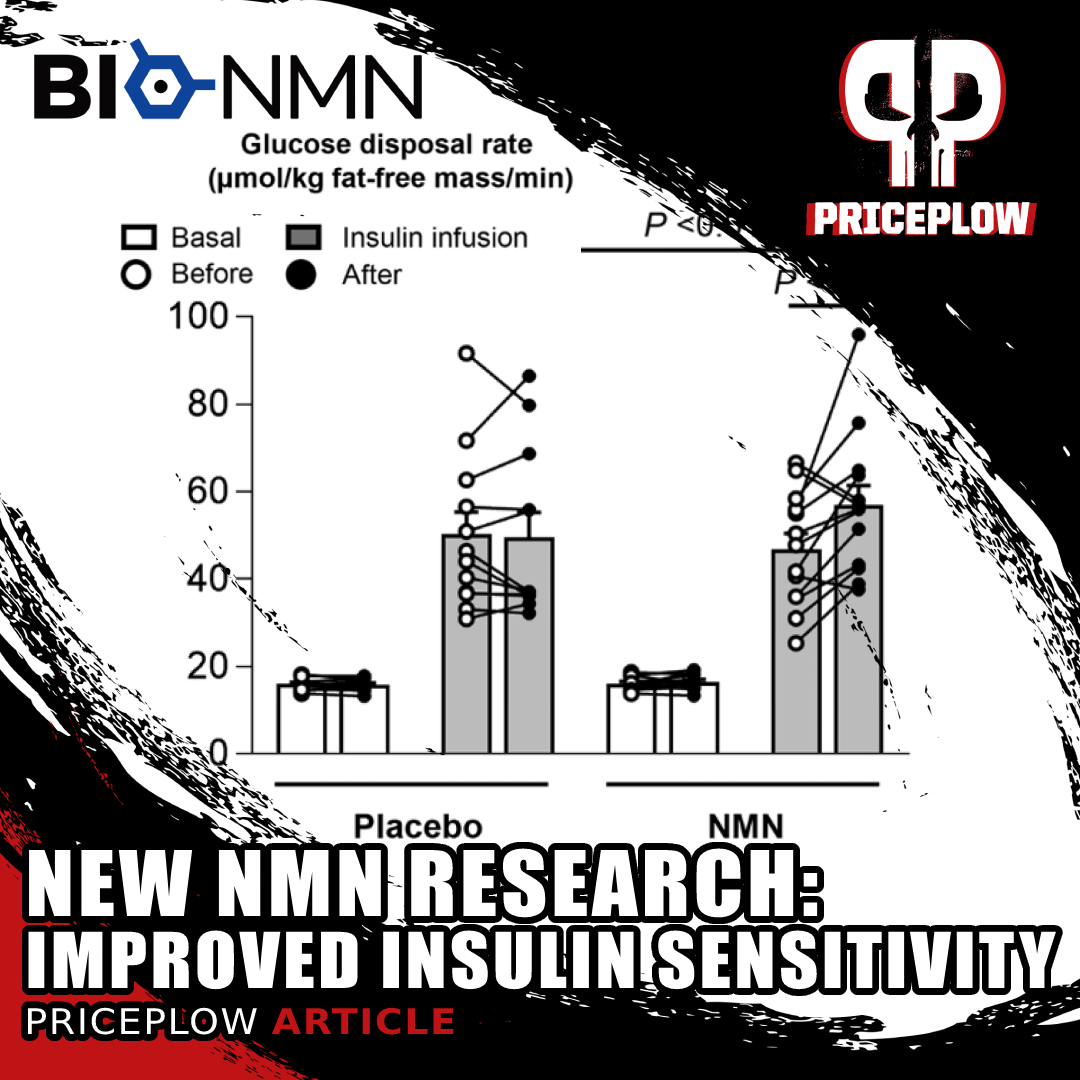
2021 Update: Increased Muscle Insulin Sensitivity in Overweight Women
A new research study on overweight, insulin-resistant women has shown that NMN supplements improve muscle insulin sensitivity. What does this mean for us?
A 2021 human double-blinded, placebo-controlled study out of Washington University has been published showing NMN improve muscle insulin sensitivity in overweight women![16]
The study is covered in our article titled New NMN Study: Improved Muscle Insulin Sensitivity in Women, but essentially, 13 women in the NMN group (taking 250mg twice daily) averaged a 20% improvement in muscle insulin sensitivity compared to no change in the control group of 12 women.
In addition, NMN also improved expression of genes involved in muscle structure and remodeling.
This leads us to believe that the dosing suggested below (250mg twice daily) is on the right path, and also leads us to wonder if we have a new glucose disposal agent ingredient here for athletes as well as metabolically unfit individuals!
Dosing and Recommended Products
We look forward to seeing anti-aging and mitochondrial booster supplements with a dose of 250-500mg BioNMN.. but what about GDA supplements too?
As a newer supplement, there is no agreed upon clinical dosing for NMN supplementation. Much of the trials relied on intramuscular dosing as well — making an effective oral dose an open question. The Keio University study suggests doses of 500mg at one time are well-tolerated.[14] For those new to BioNMN products, we suggest taking 250mg twice per day and titrating up to 500mg twice per day.
Other nicotinamide products are generally recognized as safe (GRAS),[17-19] which bodes well for BioNMN achieving GRAS status soon as well. For those that are formulating, or want to give NAD+ supplements a shot, we suggest looking towards NNB Nutrition's BioNMN. As we saw with other anti-aging / cellular energy supplements such as NucleoPrime, MitoBurn, and GlucoVantage, NNB backs their ingredients with actual top-of-the-line HPLC lab tests - not just COAs.

How does the best glucose disposal ingredient in berberine get any better? It's known as dihydroberberine, and sold as NNB Nutrition's GlucoVantage, and if there's one anti-aging ingredient we suggest, it's this one!
The Ultimate Anti Aging Stack
Anti-aging supplements seem to have "stalled" in the past couple of years, with a lot of emphasis shifted to immunity and stress. Getting back to forward progress, you can stack BioNMN with NucleoPrime (mixed nucleotides) and GlucoVantage (dihydroberberine, a more bioavailable form of berberine) as an effective all-inclusive anti-aging combination. MitoBurn L-BAIBA could make great sense as a mitochondrial booster as well. We suspect that such an offering will eventually be available as an official product that brings cellular energy and blood sugar support back to give a breath of fresh air to your mitochondria. On top of the NNB Nutrition Story linked above, you can also learn more about this philosophy in our article titled The Power of "Mito": Optimizing the Mitochondria to Unlock Clean Energy.
Conclusion: BioNMN is the next major NAD Booster

NNB Nutrition is an innovative ingredient development company with an elite team of over 100 scientists from over 10 countries.
NAD+ supplements are an exciting innovation in an all-too-stale category of the industry. They appear to provide cardiovascular and neurologic benefits while also improving insulin sensitivity. As these three domains of health worsen with age, NAD+ products may be a potent inclusion to an antiaging regimen. BioNMN by NNB Nutrition appears to be on the cutting edge of the industry because of NNB's emphasis on ingredient quality, bioavailability, and safety. For those looking to improve their preventative health measures, keep an eye out for BioNMN as it makes its way into products.
To learn more about the biochemistry behind this molecule, see our in-depth article on NMN.


Comments and Discussion (Powered by the PricePlow Forum)