
The ultimate guide to saffron supplementation. Clinical trials show saffron extract (28-30mg daily) supports mood, cognitive function, and eye health with effects comparable to pharmaceuticals but superior safety profiles. Quality matters -- standardization to crocins and safranals is essential.
Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) has transformed from the world's most expensive culinary spice into one of the most clinically validated botanical supplements available today. Derived from the hand-harvested stigmas of saffron crocus flowers, this golden-red extract delivers powerful bioactive compounds that have demonstrated remarkable benefits across multiple areas of human health.
The Saffron Story: Finding a Superior Source
Over two decades of clinical research has established saffron's efficacy for mood enhancement, with randomized controlled trials demonstrating significant improvements in mood scores and emotional well-being. Further, saffron has shown to support eye health, cognitive enhancement in both healthy adults and aging populations, appetite control for weight management, and specialized applications for women's health, and overall quality of life.
The active compounds lies in saffron's unique standardized profile of crocins (carotenoid compounds responsible for mood and cognitive benefits) and safranals (volatile compounds that modulate serotonin pathways). Research consistently demonstrates optimal effects at doses of 28-30mg daily of standardized extract, which is a smaller total amount than you'd use in cooking, but concentrated and calibrated for maximum beneficial impact.
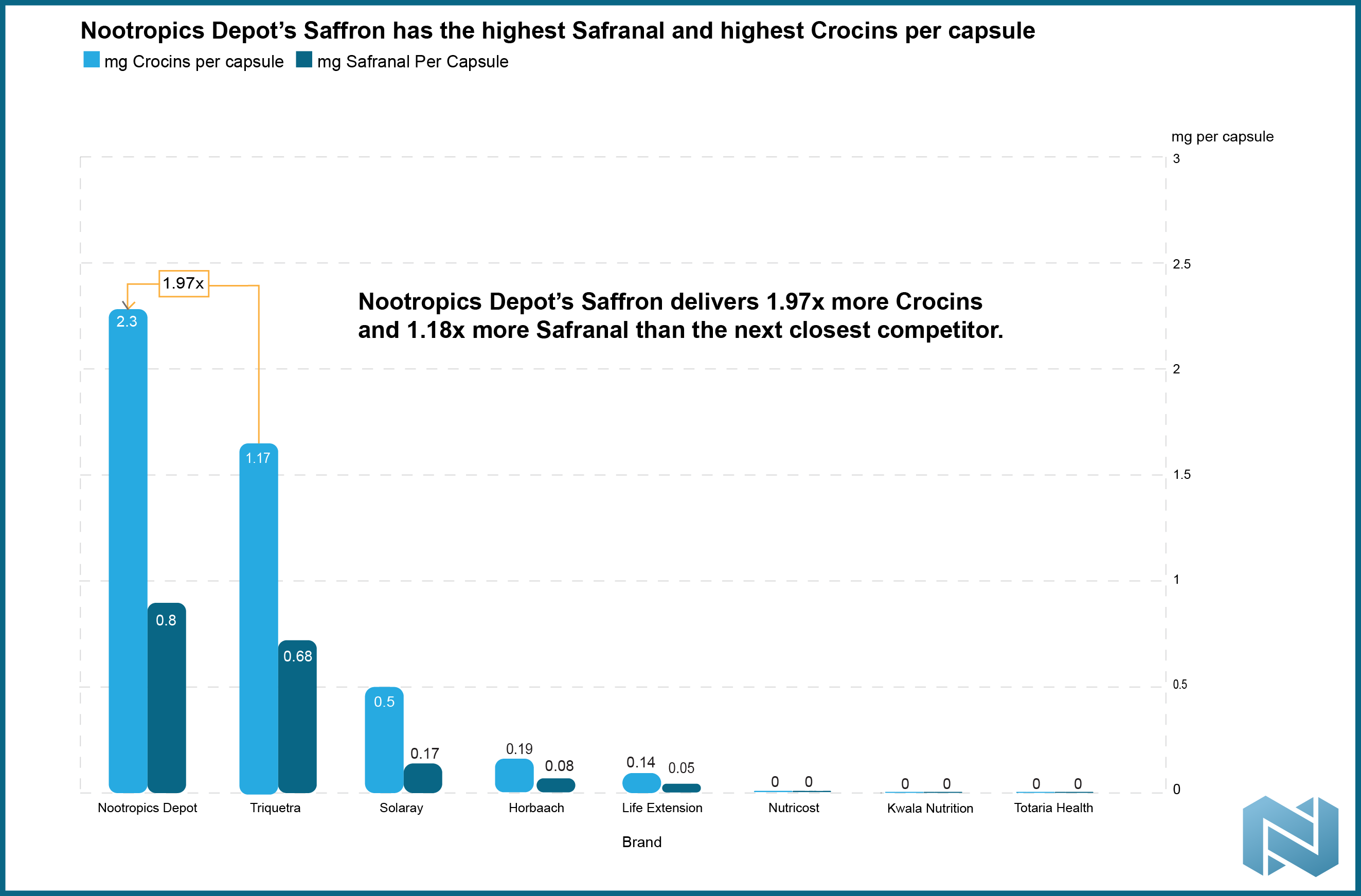
What sets premium saffron supplements apart is dual standardization to both crocins and safranals, ensuring consistent potency. Nootropics Depot's High Potency Saffron Extract delivers industry-leading standardization with 7.5% crocins and 1% safranals, which is significantly higher than competitors who often standardize to only one compound or just provide lower concentrations. Each batch undergoes third-party testing in GMP-certified facilities, providing the transparency and quality assurance that clinical research demands.
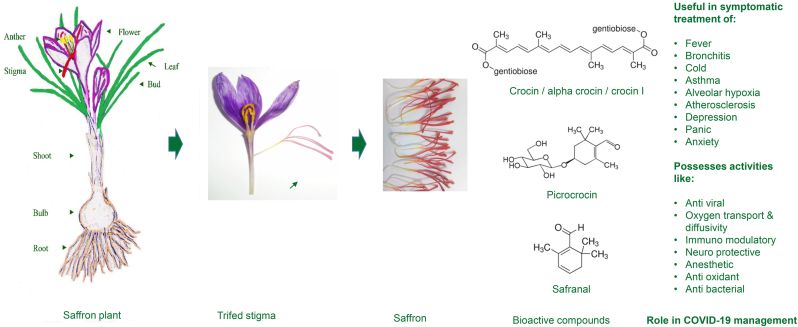
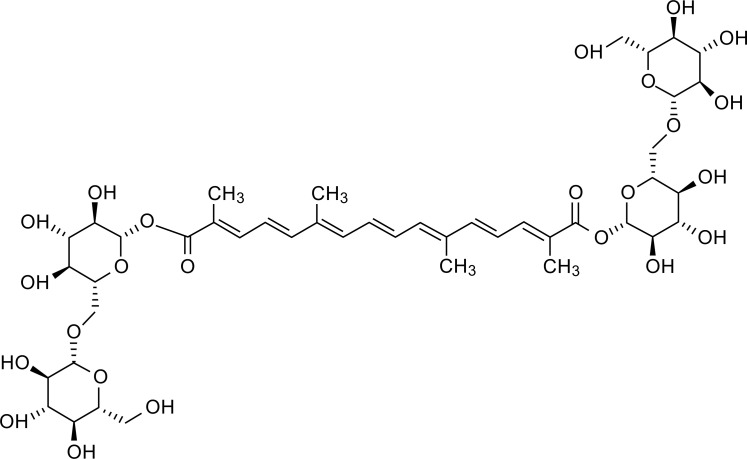
Complete overview from crocus flower to extracted bioactive compounds (crocin, safranal, picrocrocin) with their established therapeutic applications across multiple health conditions.[1]
Nootropics Depot High Potency Saffron – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.
What Is Saffron?
Saffron is derived from the dried stigmas of Crocus sativus L., a small perennial flowering plant belonging to the iris family. Known as "red gold" for its extraordinary value, saffron holds the distinction of being the world's most expensive spice by weight, and for good reason.[2]
The World's Most Labor-Intensive Harvest
Each saffron flower produces just three delicate crimson stigmas, which must be hand-picked during a narrow harvest window in autumn. The production of one kilogram of saffron requires an astounding 150,000 to 200,000 flowers and approximately 400 hours of painstaking manual labor.[3] This intensive process explains why saffron commands prices up to $20,000 per kilogram, making it more valuable than gold by weight.[4]
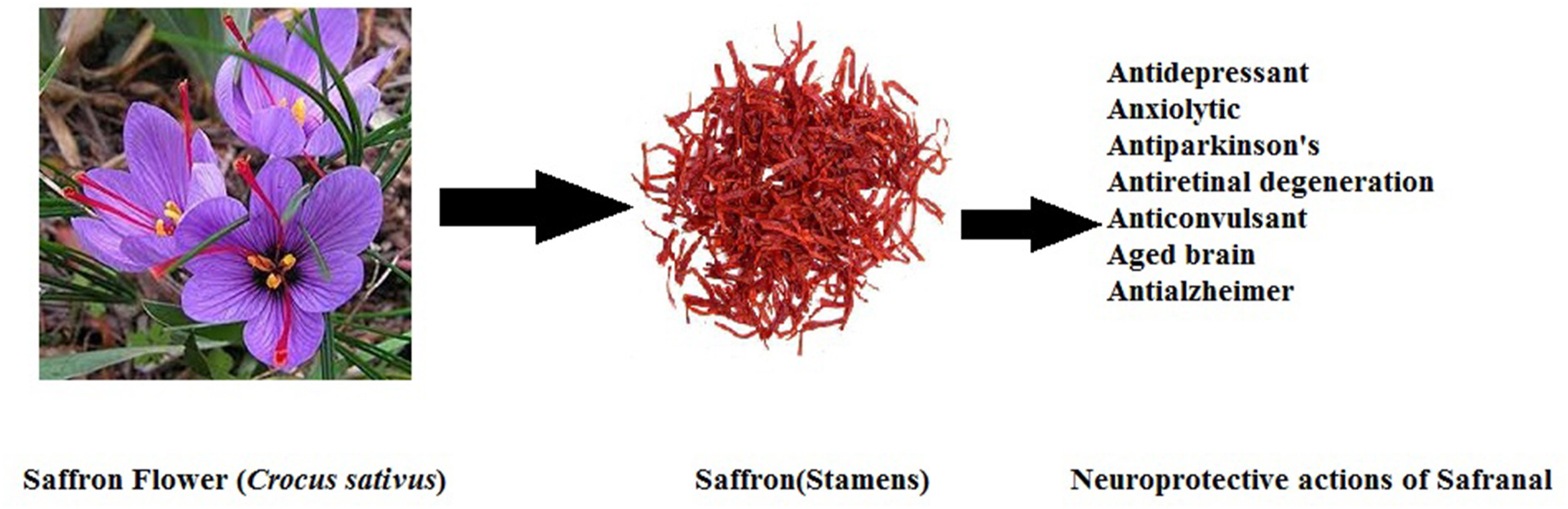
Simple extraction pathway illustrating how saffron crocus flowers yield stamens that provide safranal with documented brain-protective properties.[2]
Ancient Wisdom Meets Modern Science
Saffron's history spans over 4,000 years, with the earliest depictions dating to 1600-1700 BC.[3] Traditional Persian medicine systems valued saffron for supporting mood balance, women's health concerns, and eye comfort. Ancient practitioners in Ayurveda and Traditional Chinese Medicine incorporated saffron into formulations for emotional well-being and cognitive support.[2]
From Spice to Supplement: Why Modern Extracts Matter
While culinary saffron has been treasured for millennia, modern supplement science has unlocked saffron's true potential through standardized extraction and concentration. Clinical research has revealed that saffron's beneficial effects stem from specific bioactive compounds: crocins, safranal, crocetin, and picrocrocin.
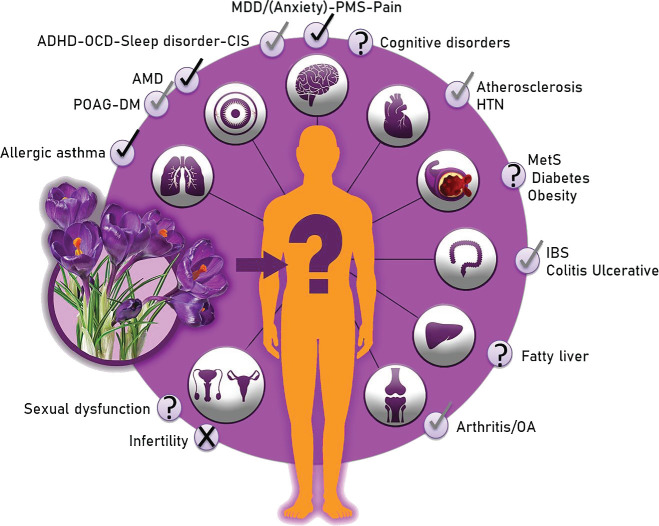
Comprehensive health applications diagram showing saffron's established effects (checkmarks) and areas under investigation (question marks) across neurological, metabolic, and systemic disorders.[5]
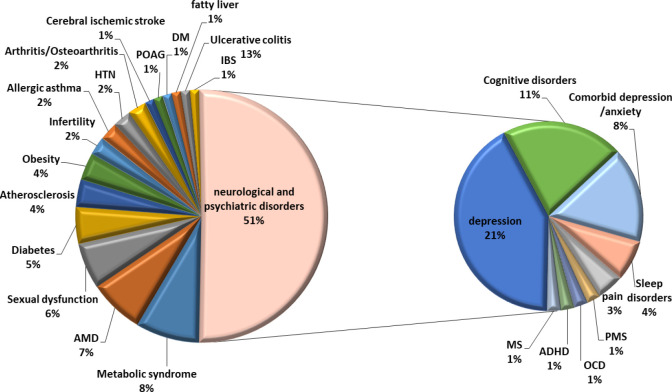
Research allocation showing neurological and psychiatric disorders comprise 51% of saffron studies, with depression trials representing the largest single category at 21%.[5]
Active Compounds & Standardization
Saffron's impressive effects stem from a sophisticated array of bioactive compounds that work synergistically to deliver its clinically-validated benefits. Understanding these compounds is essential for selecting premium saffron supplements that deliver consistent results.
-
Crocins: The Water-Soluble Carotenoid Powerhouse
Crocins are the crown jewel of saffron's health-supporting arsenal. These unusual water-soluble carotenoids make up approximately 25-35% of saffron's total dry matter, giving the spice its characteristic golden-red color.[7] What makes crocins unique among carotenoids is their glycosylated structure: they're structured in such a way that they're highly soluble in water, unlike most carotenoids (which are generally fat soluble).[8]
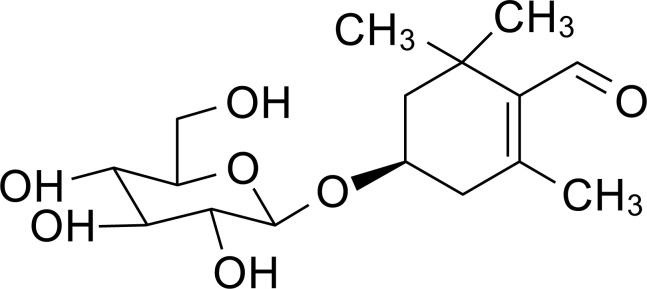
Digging deeper, the crocin family includes several variants, with crocin-1 (or α-crocin) being the most abundant.[7] These compounds demonstrate impressive health-supporting activities, including antioxidant and memory enhancement effects.[9]Molecular structure of crocin showing the water-soluble carotenoid backbone with glucose attachments that enable superior bioavailability compared to other carotenoids.[7]
Crocins serve as the primary drivers of saffron's mood and cognitive benefits, making their concentration a critical factor in supplement standardization.
-
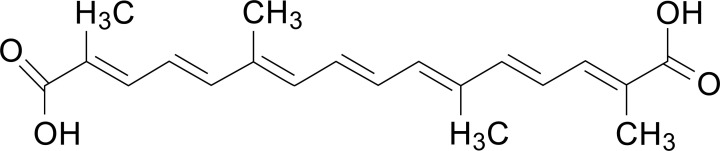
Crocetin: The Bioavailable Active Metabolite
While crocins provide the most well-known benefits, crocetin is the key to saffron's bioactivity. This unique apocarotenoid with a short carbon chain length (C20) and dicarboxylic acid structure is what actually reaches target tissues after oral consumption.[10]
Once ingested, crocins are rapidly hydrolyzed by intestinal enzymes and microbiota to release crocetin.[7] What makes crocetin remarkable is its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier -- a feat that sets it apart from other carotenoids that are larger and hydrophobic.[7]
Pharmacokinetic studies reveal that crocetin is also absorbed more rapidly than other carotenoids, reaching peak plasma concentrations within 4-8 hours (compared to 15-33 hours for β-carotene, lutein, and lycopene).[10] This rapid absorption and brain penetration makes crocetin the active metabolite responsible for saffron's neuroprotective and mood-enhancing effects.[11] -
Safranal: The Aromatic Mood Modulator
Safranal is the volatile monoterpene aldehyde responsible for saffron's distinctive aroma, comprising about 0.001% to 0.006% of the spice's dry matter.[7] While present in small quantities, safranal plays a crucial role in saffron's mood-enhancing effects through its interaction with serotonin pathways.
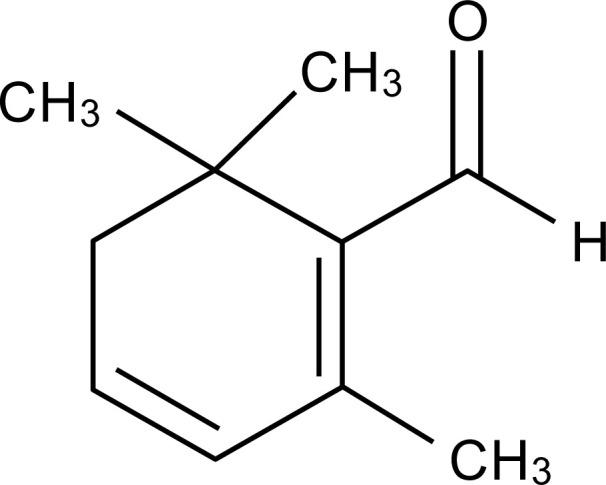
Research detailed below demonstrates that safranal exhibits anxiolytic and hypnotic effects, increasing total sleep time in a dose-dependent manner while showing anti-stress activity in maze tests.[2] The compound also demonstrates mood-enhancement activity in forced swimming tests, likely through modulation of GABA receptors.[2]Chemical structure of safranal, the monoterpene aldehyde responsible for saffron's distinctive aroma and GABA pathway modulation effects.[7]
Safranal is formed through the breakdown of picrocrocin during saffron processing and storage, making it a critical component to monitor in standardized extracts.
-
Picrocrocin: The Bitter Taste Marker of Authenticity
Picrocrocin constitutes approximately 26% of saffron's dry matter and serves as the compound responsible for the spice's characteristic bitter taste.[7] More importantly for supplement consumers, picrocrocin functions as a molecular marker of saffron authenticity.
This monoterpene glycoside has been identified exclusively in the genus Crocus, with Crocus sativus L. being the only edible species in this genus.[8] This makes picrocrocin an invaluable tool for detecting adulteration and verifying genuine saffron content in supplements.Molecular structure of picrocrocin, the glycosylated compound that provides saffron's bitter taste and serves as an authenticity marker unique to genuine saffron.[7]
Picrocrocin also serves as the precursor to safranal. Under appropriate conditions, it degrades to release safranal, contributing to the aromatic profile that indicates quality saffron processing.[9]
Why Proper Standardization Matters
The difference between effective saffron supplements and disappointing ones often comes down to standardization, which is the process of ensuring consistent, measurable levels of active compounds in each dose.
The Limitations of Traditional ISO 3632 Standards
The ISO 3632 standard,[12] established for culinary saffron grading, uses UV-visible spectrophotometry to measure "coloring power" (crocin content at 440 nm), "bittering power" (picrocrocin at 270 nm), and "odorous power" (safranal at 330 nm).[4] While useful for culinary applications, this method has significant limitations for supplement standardization, and can be gamed.
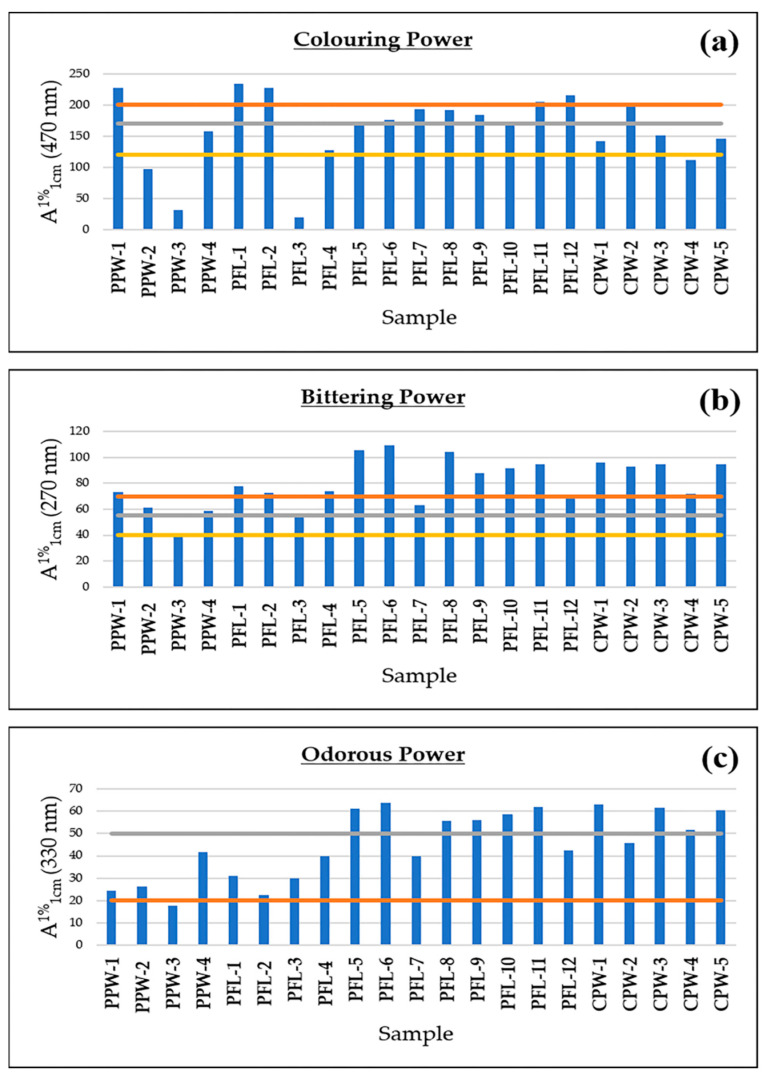
Traditional saffron grading measurements showing coloring power, bittering power, and odorous power across different commercial samples with quality grade thresholds.[4]
The Gold Standard: HPLC Analysis with Dual Standardization
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis is the superior method for saffron supplement testing. This technique provides precise quantification of individual crocin compounds and safranal concentrations, offering far greater accuracy than UV-visible spectrophotometry alone.[4]
Premium saffron supplements employ dual standardization, to both crocins and safranal percentages, ensuring consistent delivery of the compounds responsible for clinical benefits. This approach recognizes that both compound classes contribute to saffron's effects through different but complementary mechanisms.
The Adulteration Problem
Saffron's extraordinary value makes it a prime target for adulteration. Common adulterants include turmeric, marigold petals, safflower, corn silk, and even synthetic colorants designed to mimic saffron's appearance.[4] These adulterants may provide color, but lack the specific bioactive compounds responsible for saffron's health benefits.
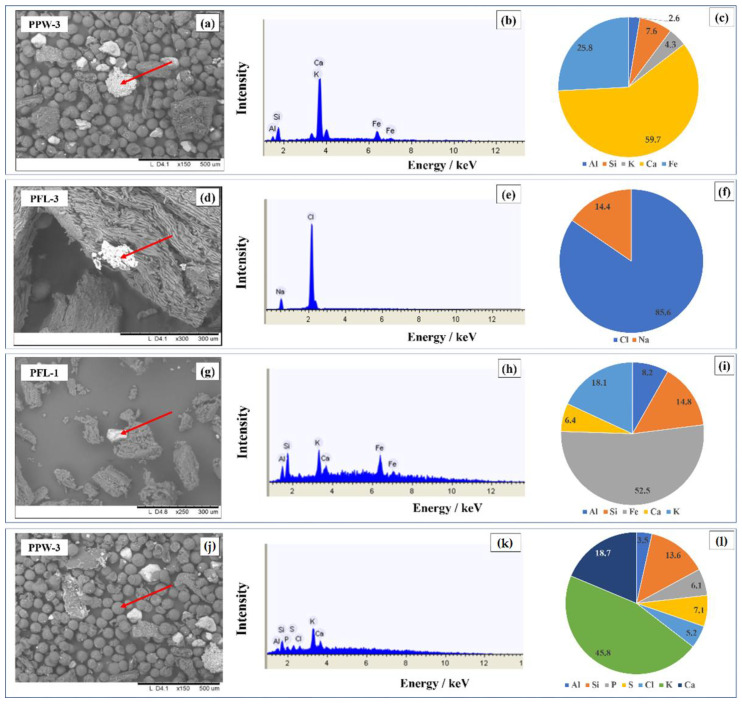
Scanning electron microscopy revealing particle composition and elemental analysis used to identify adulterants and verify authentic saffron material quality.[4]
Ultimately, expensive ingredients get adulterated most frequently, positioning saffron as a spice that needs thorough testing from trusted companies. This necessitates standardization to specific percentages of crocins and safranal, verified through advanced analytical methods, which is what Nootropics Depot has done for saffron as well as numerous other botanical ingredients.
Before talking about products, however, we need to get into the mechanisms of action and then the actual clinical studies:
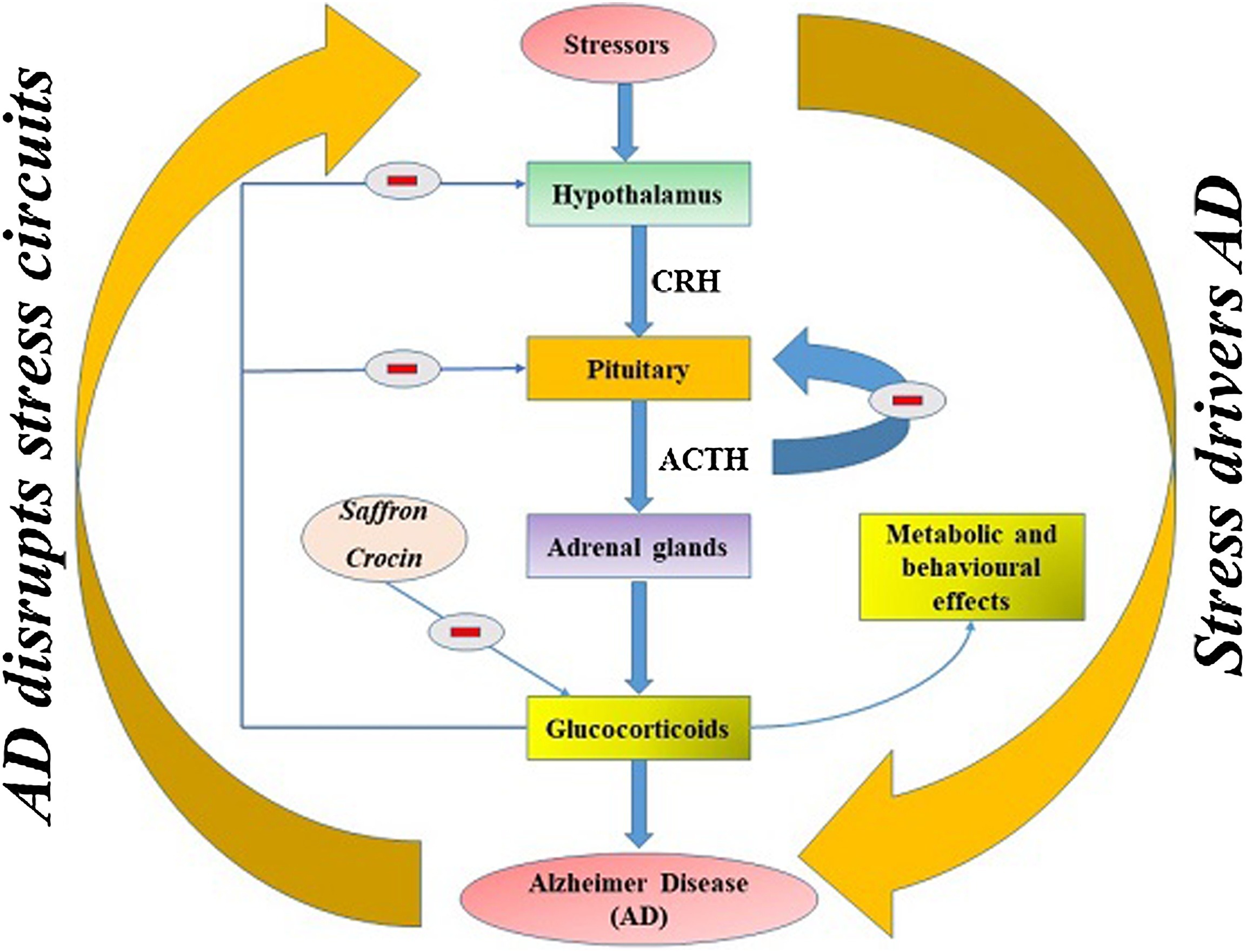
Mechanisms of Action
Understanding how saffron works at the molecular level reveals why this ancient spice has been shown to be so effective across diverse health applications. The above bioactive compounds (crocins, crocetin, safranal, and picrocrocin) engage multiple pathways simultaneously, creating a synergistic network of beneficial effects that extends far beyond simple antioxidant activity.
-
Serotonin & Mood Pathways
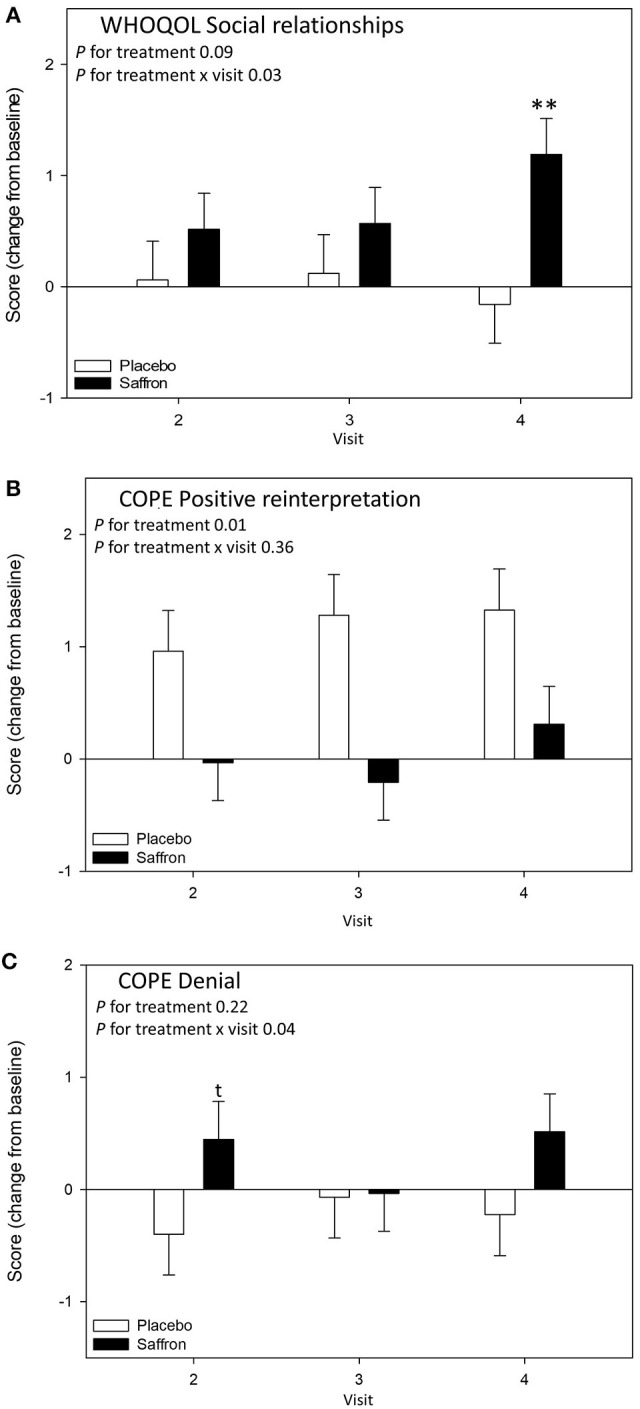
Saffron's mood-enhancing effects stem from its modulation of neurotransmitter systems, with mechanisms that mirror and complement those of pharmaceutical compounds. Clinical research has revealed that saffron demonstrates SSRI-like activity through inhibition of the serotonin transporter (SERT), effectively increasing synaptic serotonin availability.[14]WHO Quality of Life social relationship scores and COPE coping strategy measurements showing enhanced positive reinterpretation and social functioning with saffron versus placebo over 4-week treatment.[13]
However, saffron's neurochemical actions extend beyond serotonin modulation. Research demonstrates that crocin and safranal can inhibit the reuptake of dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin, making for a triple-action mechanism that provides broader neurotransmitter support than single-target compounds.[15] This multi-neurotransmitter approach may explain saffron's effectiveness across different cognitive situations shown in the clinical research below.
Safranal contributes additional mood-stabilizing effects through modulation of GABA(A)-benzodiazepine receptor complexes, demonstrating anxiolytic and hypnotic properties in preclinical studies.[2] This GABAergic activity provides a calming counterbalance to serotonergic activation, potentially explaining saffron's ability to improve mood without causing the activation or restlessness sometimes seen with conventional interventions.
The interaction between saffron compounds and monoamine oxidase (MAO) enzymes adds another layer of complexity. Derivatives of safranal have demonstrated potent MAO-B inhibition, which could contribute to dopaminergic support and neuroprotection.[1] This multi-target approach (combining reuptake inhibition with enzymatic modulation) creates a broader yet gentler intervention than single-mechanism ingredients.
-
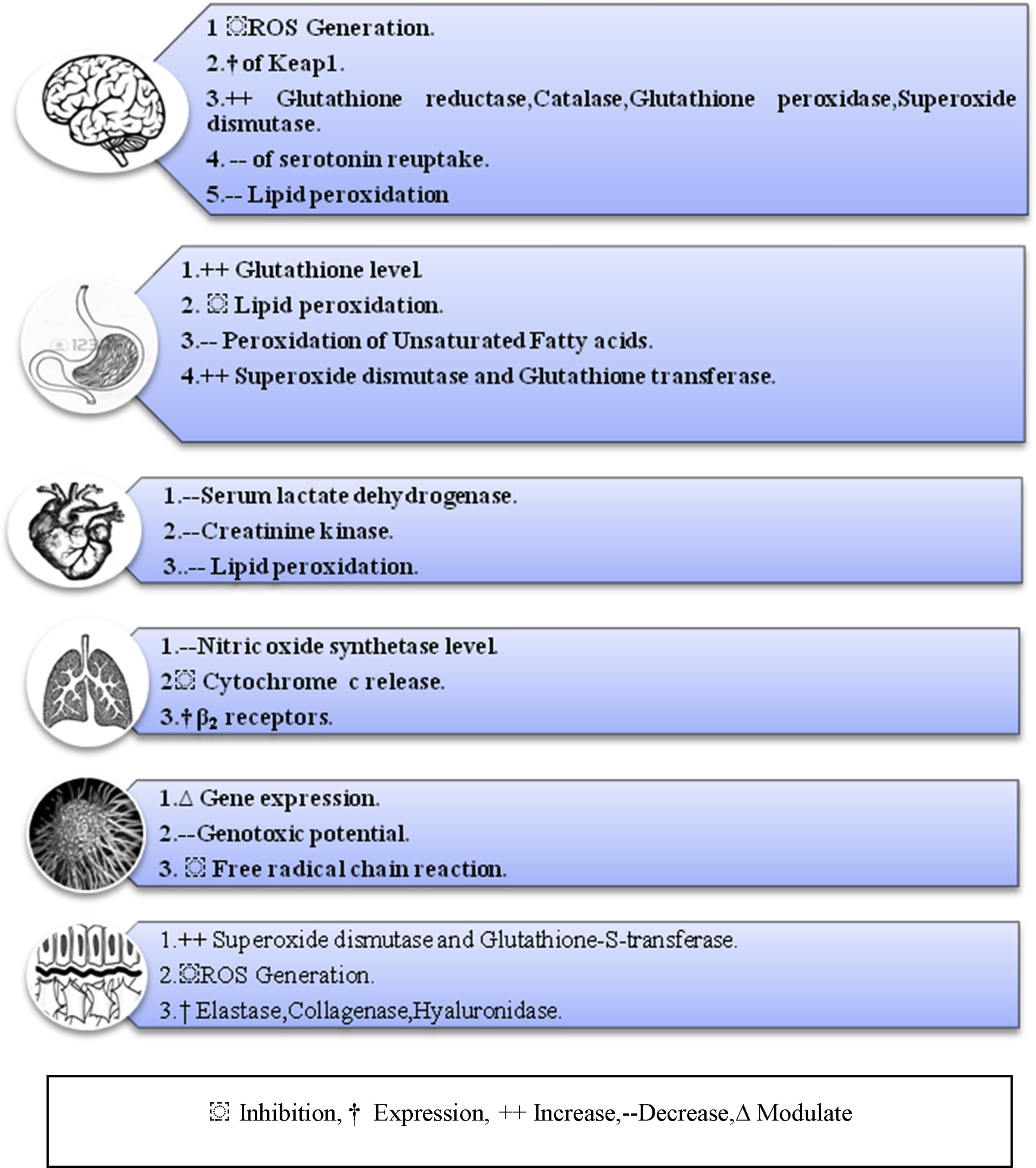
Antioxidant & Anti-inflammatory Effects
Saffron's antioxidant activity operates through multiple pathways that go well beyond simple free radical scavenging. Meta-analyses reveal significant reductions in key inflammatory markers including C-reactive protein (CRP), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and interleukin-6 (IL-6), alongside improvements in total antioxidant capacity (TAC).[16]
Educational overview explaining saffron's crocus flower origin, neurotransmitter enhancement mechanisms, and mood-brightening properties.
At the transcriptional level, crocin activates the Nrf2 pathway, a master regulator of cellular antioxidant defense. This activation enhances the expression of endogenous antioxidant enzymes including superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and glutathione peroxidase (GPx), providing sustained protection against oxidative damage.[16]
Simultaneously, saffron compounds suppress pro-inflammatory signaling through nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) inhibition. Crocin effectively blocks the activation of NF-κB, a key transcription factor that drives inflammatory gene expression.[16] This suppression reduces the production of inflammatory cytokines that contribute to chronic disease states.
More specifically, saffron compounds inhibit key enzymes in the inflammatory cascade like cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and phospholipase A2.[17] This multi-enzyme inhibition helps break the cycle of inflammation that underlies many chronic health conditions.
Safranal demonstrates direct anti-inflammatory activity in respiratory tissues, reducing nitric iNOS levels in bronchial epithelial cells while promoting β2-adrenoceptor activation for bronchodilation.[2] These effects may explain saffron's traditional use in respiratory conditions and its potential relevance for inflammatory lung diseases.
-
Neuroprotective & Retinal Effects
Saffron's neuroprotective mechanisms converge on mitochondrial support and cellular energy metabolism. Crocetin's unique ability to cross the blood-brain barrier enables direct neuroprotection through multiple pathways, including mitochondrial stabilization and reduction of neuroinflammation.[18]
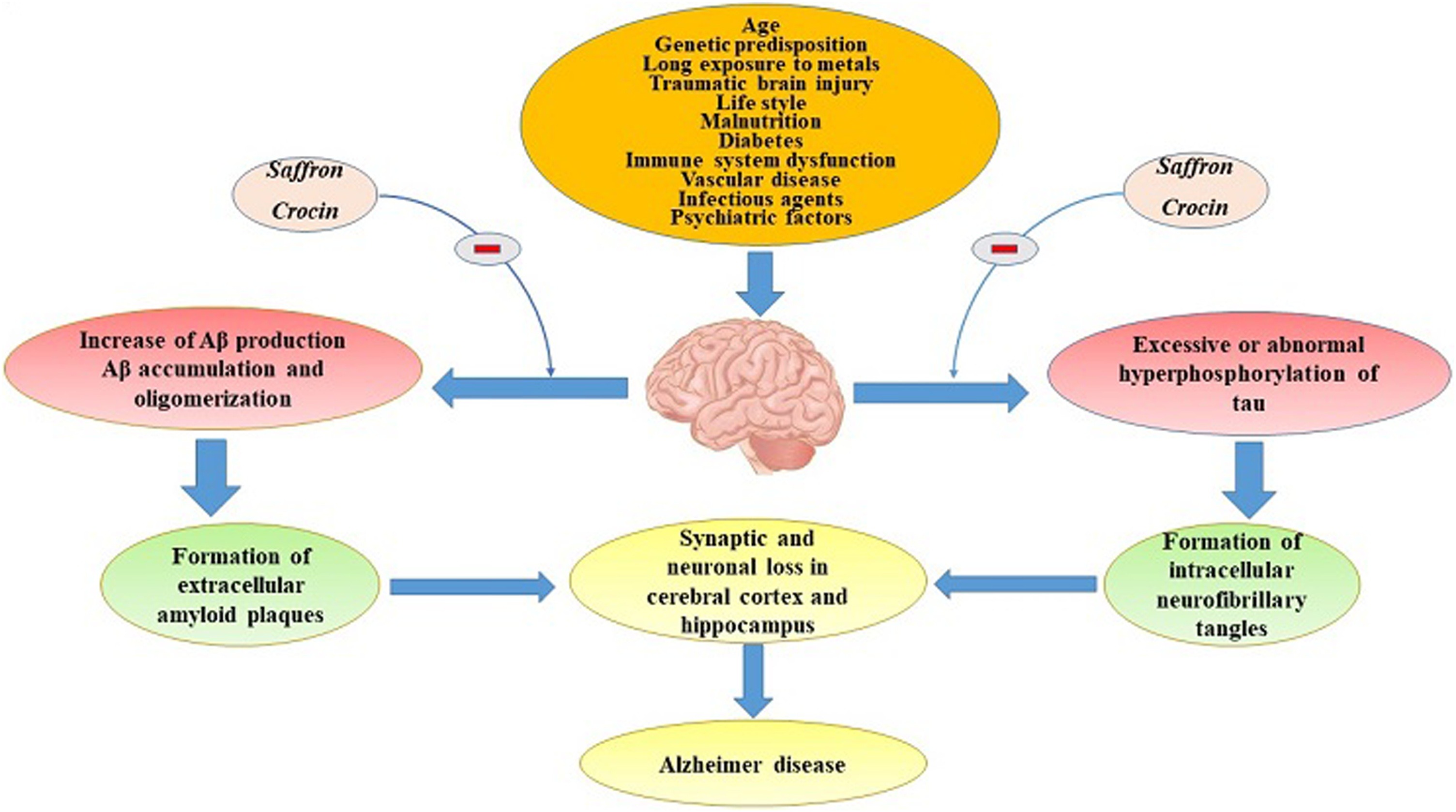
In age-related macular degeneration (AMD), saffron supplementation significantly improves retinal function through photoreceptor protection and inflammatory modulation.[19] Saffron compounds protect retinal ganglion cells from excitotoxicity, reduce ATP-induced cytotoxicity, and maintain photoreceptor morphology under oxidative stress.[20] The protection involves regulation of programmed cell death pathways and maintenance of retinal blood flow, addressing multiple pathological mechanisms simultaneously. In neurodegenerative situations, saffron's neuroprotection operates through amyloid-beta modulation, tau protein stabilization, and synaptic protection. Crocetin shows the ability to prevent amyloid-beta aggregation while supporting cholinergic neurotransmission, which is directly relevant to cognitive preservation.[18] These effects, combined with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities, create a multi-pronged approach to neurological support that addresses both symptoms and underlying pathology.
Saffron's mechanisms reveal a sophisticated botanical that works through coordinated pathways rather than isolated targets. This multi-system approach -- affecting neurotransmitters, inflammation, oxidative stress, and cellular protection simultaneously -- explains both saffron's broad clinical applications and its fantastic safety profile. Unlike single-target ingredients, saffron's networked mechanisms provide gentle yet effective modulation that supports the body's natural healing processes.
Clinical Research by Outcome
Saffron boasts one of the most robust clinical portfolios of any botanical compound. The following sections examine the peer-reviewed research that has established its efficacy across multiple health domains, demonstrating that ancient wisdom can indeed meet modern scientific standards:
-
-
Mood Support in Adults
Saffron's mood-supporting effects have been rigorously validated through multiple randomized controlled trials, with research demonstrating efficacy comparable to other well-known interventions but with superior tolerability. The clinical evidence spans from direct comparisons with established ingredients to meta-analyses confirming consistent benefits across diverse populations.
Comprehensive protection profile showing saffron's documented effects across brain, digestive, cardiovascular, respiratory, hepatic, and dermal systems with specific biomarker improvements.[2]
Head-to-Head Ingredient Comparisons
The strongest evidence for saffron's mood-supporting effects comes from direct comparisons with established products. Akhondzadeh and colleagues conducted landmark randomized controlled trials comparing the effects of saffron with both fluoxetine and imipramine.[21][14]
- In the imipramine comparison trial, 30 participants received either 30mg daily saffron extract or 100mg daily imipramine for six weeks. Both treatments produced statistically equivalent improvements in Hamilton Rating Scale (HAM-D) scores, with saffron demonstrating similar efficacy to the tricyclic compound.[21] Importantly, the saffron group experienced significantly fewer anticholinergic side effects, notably reduced dry mouth and sedation compared to imipramine.
- The fluoxetine comparison study enrolled 40 participants who received either 30mg daily saffron or 20mg daily fluoxetine for six weeks. Analysis revealed no significant differences between treatments on HAM-D scores, with both groups showing substantial improvements from baseline.[22]
Meta-Analysis Confirmation
Hausenblas and colleagues conducted a meta-analysis that included five randomized controlled trials involving adults with low mood states.[6] The analysis revealed large effect sizes for saffron versus placebo (ES = 1.62) and demonstrated that saffron performed equivalently to prescription interventions with no significant differences in efficacy.
The meta-analysis confirmed that saffron supplementation at 30mg daily consistently outperformed placebo across multiple mood rating scales while showing comparable effectiveness to clinical interventions. These findings established saffron as a legitimate alternative for mood support.
Healthy Adult Populations
Saffron also demonstrates mood-enhancing effects in healthy adults experiencing subclinical symptoms. Kell and colleagues conducted a four-week randomized controlled trial in healthy adults, finding that 28mg daily standardized saffron extract significantly improved multiple mood parameters including reductions in tension, low mood state, confusion, and fatigue on the Profile of Mood States (POMS) scale.[23]
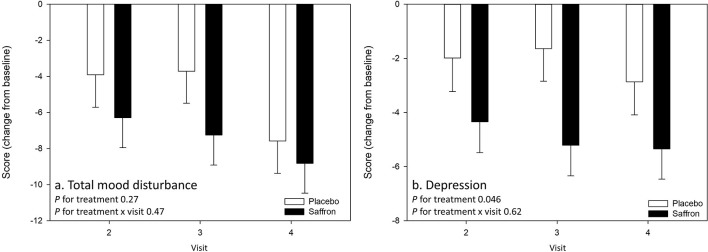
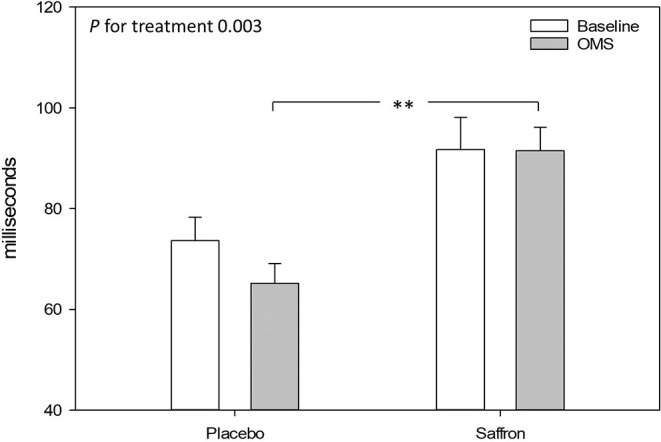
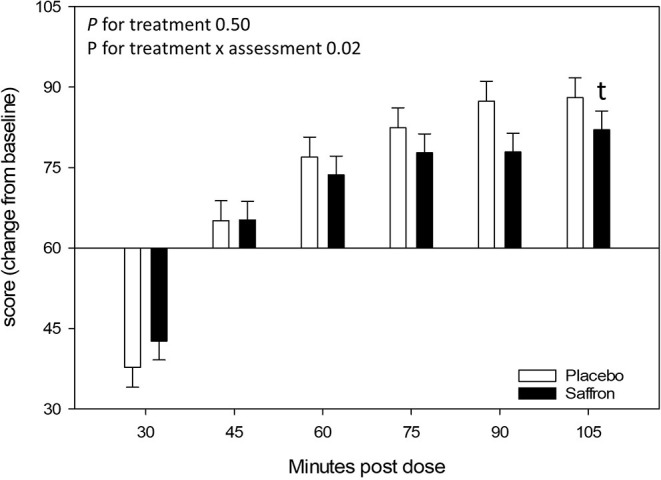
Jackson and colleagues expanded this research with an eight-week trial examining saffron's effects on mood and stress response in 56 healthy adults with subclinical low mood.[13] While the primary outcome (total mood disturbance) did not reach statistical significance, significant improvements were observed in other mood state subscales. Additionally, saffron demonstrated stress-protective effects: participants maintained heart rate variability during laboratory stress testing, while the placebo group showed decreased cardiac resilience. Biomarker correlations strengthened the clinical findings. Urinary crocetin levels showed significant negative correlation with poor mood scores, providing biological validation that saffron's active metabolites directly correspond to mood improvements.[13] Altogether, this evidence establishes saffron as a versatile mood-supporting intervention suitable for diverse populations seeking natural alternatives to conventional antidepressants.Profile of Mood States scores demonstrating saffron's significant effects on depression subscales compared to placebo over 4-week treatment period.[13]
-
Postpartum Mood Effects
Postpartum mood alterations affect approximately 14.5% of new mothers globally, creating significant challenges for maternal well-being and infant development. The situation is quite resistant to conventional treatment, with many mothers unable to tolerate pharmaceutical side effects or are justifiably concerned about medication transfer through breast milk. Two groundbreaking clinical trials have demonstrated saffron's potential as a safer alternative for this vulnerable population.
Tabeshpour Study: Saffron vs Placebo
Tabeshpour and colleagues conducted the first placebo-controlled trial examining saffron's effects on women's postpartum mood states, enrolling 60 breastfeeding mothers with mild-to-moderate symptoms.[24] The eight-week trial compared 30mg daily saffron extract against placebo using the Beck Inventory-II (BDI-II) as the primary outcome measure.
Traditional applications spanning Assyrian cuisine, ancient Greek medicine, and Ayurvedic practices, showing saffron's centuries-long therapeutic heritage.
Results demonstrated significant profound effects with saffron-treated mothers showing meaningful improvements in mood scores compared to placebo. The study confirmed saffron's safety profile in breastfeeding women, with no significant differences in adverse events between groups and no reported concerns regarding infant safety through breast milk exposure.[24]
Kashani Study: Saffron vs Fluoxetine
Kashani and colleagues directly compared saffron with fluoxetine in a six-week randomized controlled trial involving 60 women with mild-to-moderate postpartum mood symptoms.[25] Participants received either 15mg twice daily saffron extract or 20mg daily fluoxetine.
Both treatments produced equivalent improvements in Hamilton Rating Scale (HDRS) scores, with no statistically significant differences between groups at endpoint. Importantly, saffron demonstrated superior tolerability with fewer reported side effects compared to the fluoxetine group. The equivalent efficacy combined with improved safety profile positioned saffron as a compelling alternative for postpartum management.
-
Pre Menstrual Syndrome & PMDD
Premenstrual syndrome (PMS) affects 20-40% of reproductive-age women, while premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD, a severe subtype) impacts 3-8% of women with debilitating mood and behavioral changes. Both conditions are linked to serotonergic dysfunction during the luteal phase, making saffron's multi-neurotransmitter mechanisms highly relevant for these cyclical disorders.
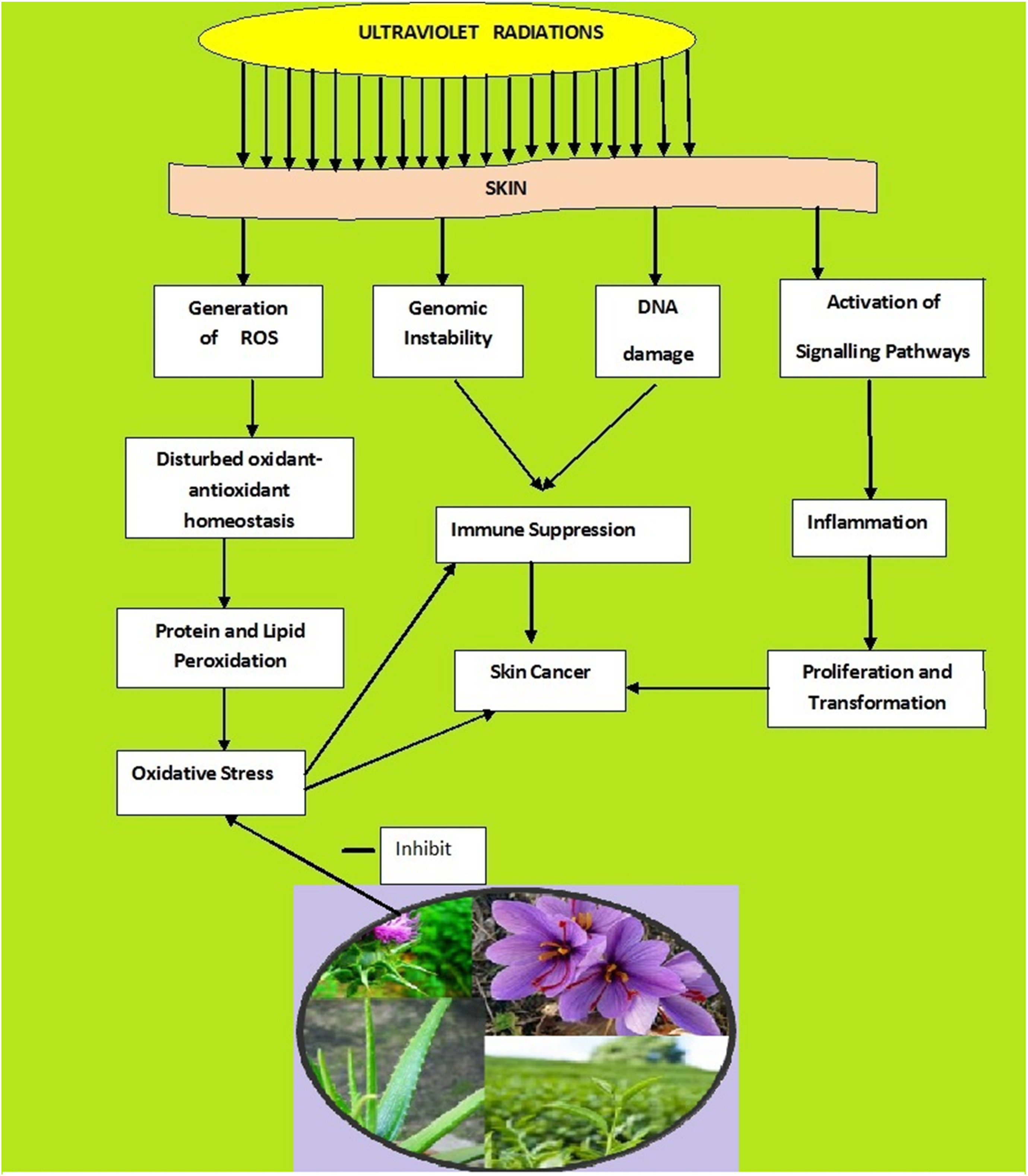
Protective pathway diagram demonstrating how safranal from saffron inhibits UV-induced oxidative stress, preventing skin cancer and inflammatory cascade activation.[2]
PMS Clinical Evidence
Agha-Hosseini and colleagues conducted a pivotal double-blind, placebo-controlled trial involving 50 women aged 20-45 years with regular menstrual cycles and at least six months of PMS symptoms.[26] Participants received either 30mg daily saffron (15mg twice daily) or placebo for two complete menstrual cycles.
Saffron demonstrated significant superiority over placebo in reducing total premenstrual daily symptoms and Hamilton Rating Scale scores during both treatment cycles. The improvements encompassed both physical symptoms (bloating, breast tenderness, fatigue) and psychological symptoms (mood swings, irritability, stress), establishing saffron's comprehensive efficacy for PMS management.
PMDD Clinical Evidence
Rajabi and colleagues advanced this research with a three-arm trial comparing saffron directly against fluoxetine in 120 women with diagnosed PMDD.[15] Participants received either 15mg twice daily saffron, 20mg twice daily fluoxetine, or placebo for two weeks during the luteal phase of two menstrual cycles.
Results revealed saffron's significant superiority over placebo on the Daily Record of Severity of Problems (DRSP) scale, while showing no significant differences compared to fluoxetine in efficacy. However, fluoxetine produced significantly more adverse effects than either saffron or placebo, highlighting saffron's superior tolerability profile for this sensitive population.
The mechanism underlying these benefits likely involves saffron's serotonin transporter inhibition and GABA modulation. These are the same pathways that make SSRIs effective for PMDD, but without the harsh side effect profile that often leads to treatment discontinuation.
-
Cognitive Focus in Youth
Two clinical trials have examined saffron in children and adolescents, exploring whether the same neurotransmitter mechanisms that support mood in adults may also play a role in attention, focus, and self-regulation in younger populations.
Baziar Study: Saffron vs Methylphenidate
Baziar and colleagues conducted a six-week randomized, double-blind pilot study comparing saffron directly with methylphenidate in 50 children aged 6-17 years in the context of attention and behavioral research.[27] Participants received either saffron extract (20-30mg daily based on weight) or methylphenidate (0.3-1mg/kg daily).
Both treatments produced significant improvements in parent-reported rating scores from baseline, with no significant differences between groups at endpoint. The response rate was comparable between saffron (96%) and methylphenidate (84%) groups, suggesting equivalent clinical efficacy. Importantly, no significant differences in adverse events were observed between treatments, indicating saffron's safety profile in younger populations.
Blasco-Fontecilla Study: Clinical Effectiveness
Blasco-Fontecilla and colleagues conducted a non-randomized clinical effectiveness study comparing standardized saffron extract with methylphenidate in 63 children and adolescents aged 7-17 years.[28] The study used objective computerized attention tests alongside traditional rating scales.
Results showed comparable overall efficacy between treatments, but with interesting differential effects. Saffron was more effective for hyperactivity symptoms, while methylphenidate showed superior effects on inattention symptoms. Both treatments demonstrated significant improvements from baseline, supporting saffron's potential as an alternative intervention.
These studies suggest that saffron's dopamine and norepinephrine reuptake inhibition may provide clinically relevant benefits for youth and adolescents, offering parents a natural alternative to stimulant medications with potentially fewer side effects.
-
Drug-Associated Sexual Dysfunction
Sexual side effects rank among the most common reasons people discontinue SSRI medications, affecting 7-70% of users and impacting all phases of sexual function including desire, arousal, and satisfaction.[29] While several pharmaceutical options exist for managing these effects, many carry their own side effects or may interfere with mood improvements. Two clinical trials have demonstrated saffron's potential as a natural solution that addresses sexual dysfunction without compromising mood support.
Clinical Evidence in Men
Modabbernia and colleagues conducted a four-week randomized controlled trial in 36 married men whose mood symptoms had stabilized on fluoxetine but who experienced sexual difficulties.[29] Participants received either 30mg daily saffron (15mg twice daily) or placebo while continuing their established fluoxetine regimen.
Results showed significant improvements in sexual function compared to placebo. By week 4, saffron produced meaningful improvements in erectile function and intercourse satisfaction domains, with 60% of saffron-treated men achieving normal erectile function scores compared to only 7% in the placebo group.[29] Importantly, these sexual improvements occurred without any changes in mood scores, confirming that benefits stemmed from direct sexual effects rather than general mood enhancement.
Clinical Evidence in Women
Kashani and colleagues extended this research to females in a similar four-week trial involving 38 women whose mood symptoms had stabilized on fluoxetine.[30] Participants received 30mg daily saffron or placebo while maintaining their fluoxetine regimen.
-
Saffron again demonstrated significant improvements in multiple domains of female sexual function. Women treated with saffron showed meaningful improvements in arousal, lubrication, and pain reduction compared to placebo, though effects on desire, satisfaction, and climax did not reach statistical significance.[30] The improvements occurred without affecting mood stabilization achieved through fluoxetine treatment.
Both studies confirmed saffron's excellent safety profile, with side effect frequencies similar to placebo and no interference with antidepressant efficacy. This combination of sexual benefits without mood compromise makes saffron an attractive adjunctive option for individuals experiencing pharma-related sexual difficulties.
-
Appetite & Weight Management
The global obesity epidemic has sparked intense interest in natural alternatives to pharmaceutical appetite suppressants, many of which carry significant side effects and safety concerns. Saffron has emerged as an option for gentle appetite regulation, with clinical evidence demonstrating meaningful effects on snacking behavior and weight management through mood-mediated pathways rather than harsh metabolic stimulation.
The 2010 Proof of Concept
Gout and colleagues conducted the landmark placebo-controlled trial that established saffron's appetite-regulating potential in 60 mildly overweight women (BMI 25-28 kg/m²).[31] The eight-week study used a patented saffron stigma extract, administered as 176.5mg daily (divided into two doses) without any dietary restrictions.
Results revealed striking anti-snacking effects that progressively intensified over the treatment period. By study endpoint, saffron-treated participants showed a 2-fold reduction in spontaneous snacking frequency compared to baseline, while the placebo group experienced only modest decreases.[31] This effect correlated with subjective reports of increased satiety, with significantly more saffron users reporting reduced hunger before meals (68.8% vs 54.0%) and decreased need for between-meal snacking (69.6% vs 50.0%).
The behavioral changes translated into measurable weight loss. Despite unrestricted food intake, the saffron group achieved approximately 1kg greater weight reduction over eight weeks compared to placebo, which is a modest but statistically significant difference that occurred without dietary intervention or exercise modifications.[31]
Mechanisms: Beyond Simple Appetite Suppression
The appetite-regulating effects appear to stem from saffron's mood-stabilizing properties rather than direct metabolic stimulation. Research suggests that emotional eating and stress-induced snacking drive much of the inappropriate food consumption that leads to weight gain, especially in women.[31]
Mashmoul and colleagues identified four potential mechanisms through which saffron compounds could support weight management:[32]
- Decreasing calorie intake through pancreatic lipase inhibition
- Providing antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects that combat obesity-related inflammation
- Suppressing food intake by increasing satiety through neurotransmitter modulation
- Enhancing glucose and lipid metabolism.
Saffron is a gentle but effective appetite regulator that addresses emotional eating through mood stabilization rather than harsh metabolic stimulation. While weight loss effects are modest, the anti-snacking benefits and excellent safety profile make saffron a valuable tool for individuals seeking natural support for healthy eating behaviors and sustainable weight management approaches.
-
Eye Health & Age-Related Macular Degeneration
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) affects millions of older adults worldwide, with limited treatment options available for the early-to-moderate stages where intervention could prevent vision loss. While AREDS supplements remain the standard of care, saffron has emerged as a promising complementary approach, with three clinical trials demonstrating measurable improvements in retinal function and visual parameters.
Falsini Study: Initial Proof of Concept
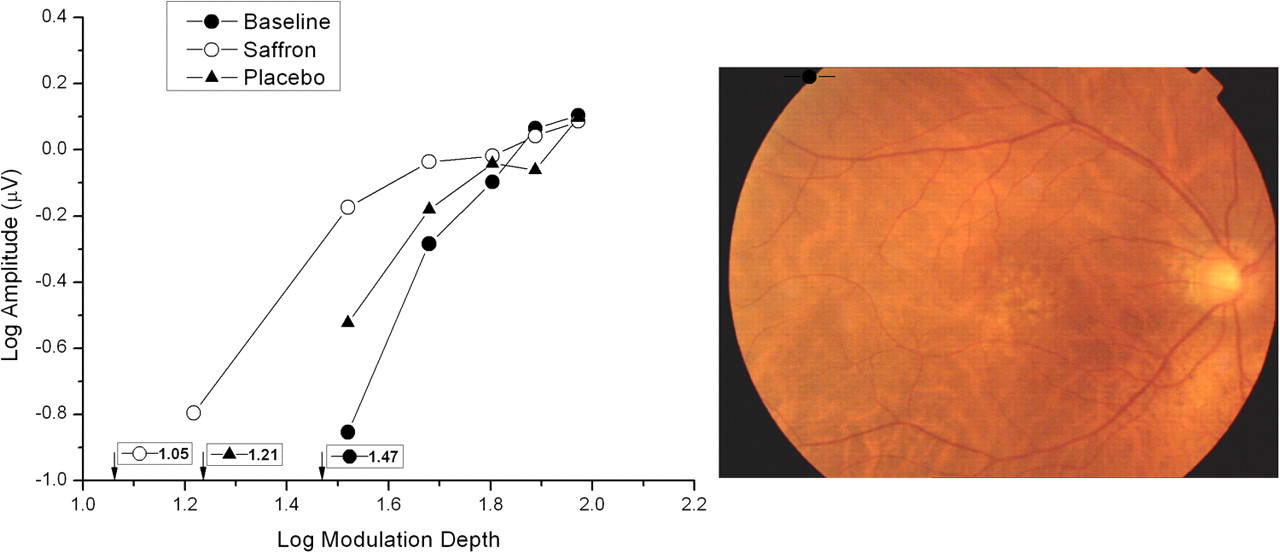
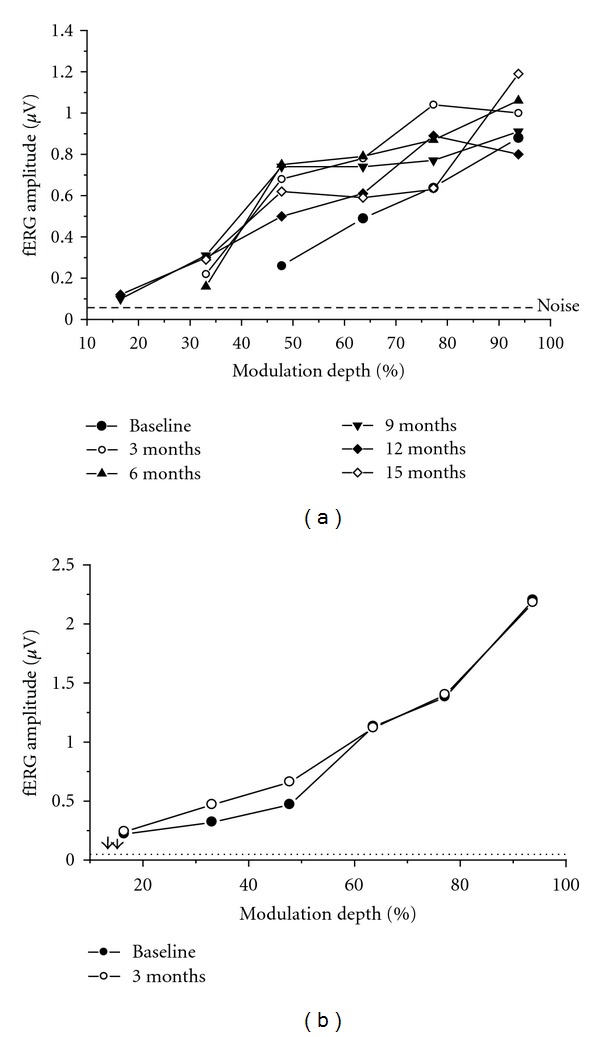
Falsini and colleagues conducted the first randomized controlled trial examining saffron's effects on retinal function in 25 participants with early AMD.[19] The three-month crossover study used 20mg daily saffron supplementation with focal electroretinogram (fERG) testing to measure macular function objectively.Focal electroretinogram measurements showing enhanced retinal response amplitudes in AMD patient after 90 days of saffron versus placebo, with corresponding fundus photograph displaying macular changes.[19]
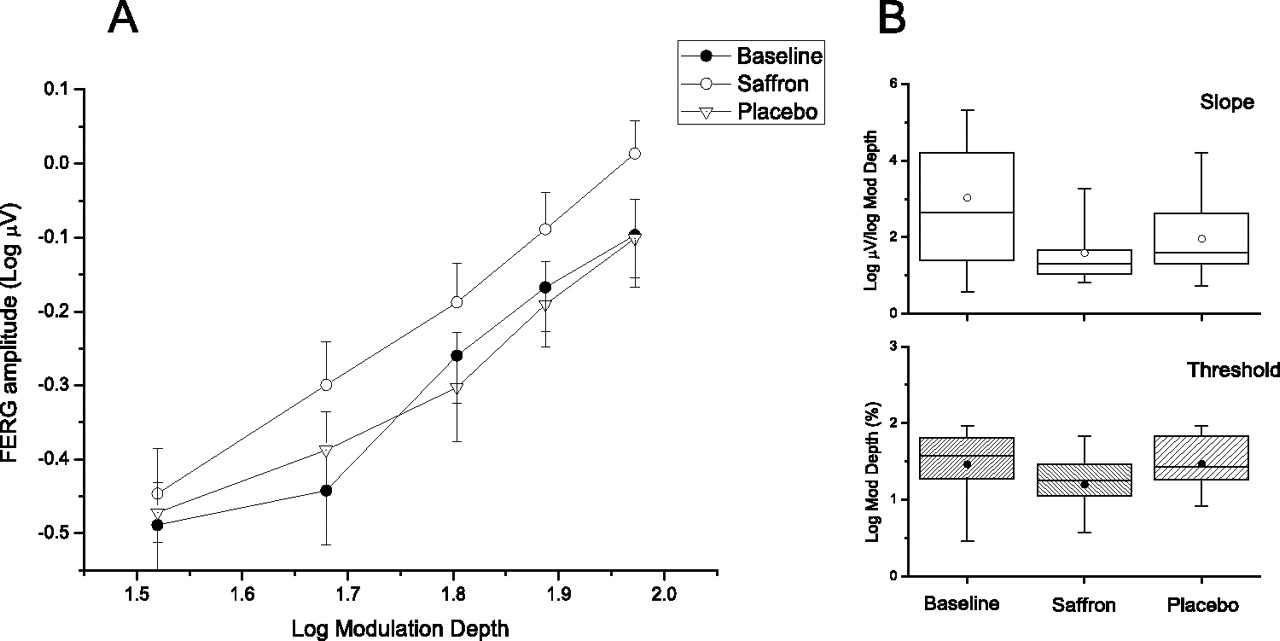
Results demonstrated significant functional improvements in retinal sensitivity. After saffron supplementation, patients showed increased fERG amplitudes compared to both baseline and placebo phases.[19] Additionally, fERG thresholds decreased after saffron treatment, indicating improved retinal sensitivity to light stimulation.Statistical distribution of retinal function measurements demonstrating improved sensitivity slopes and thresholds in saffron-treated AMD patients compared to baseline and placebo groups.[19]
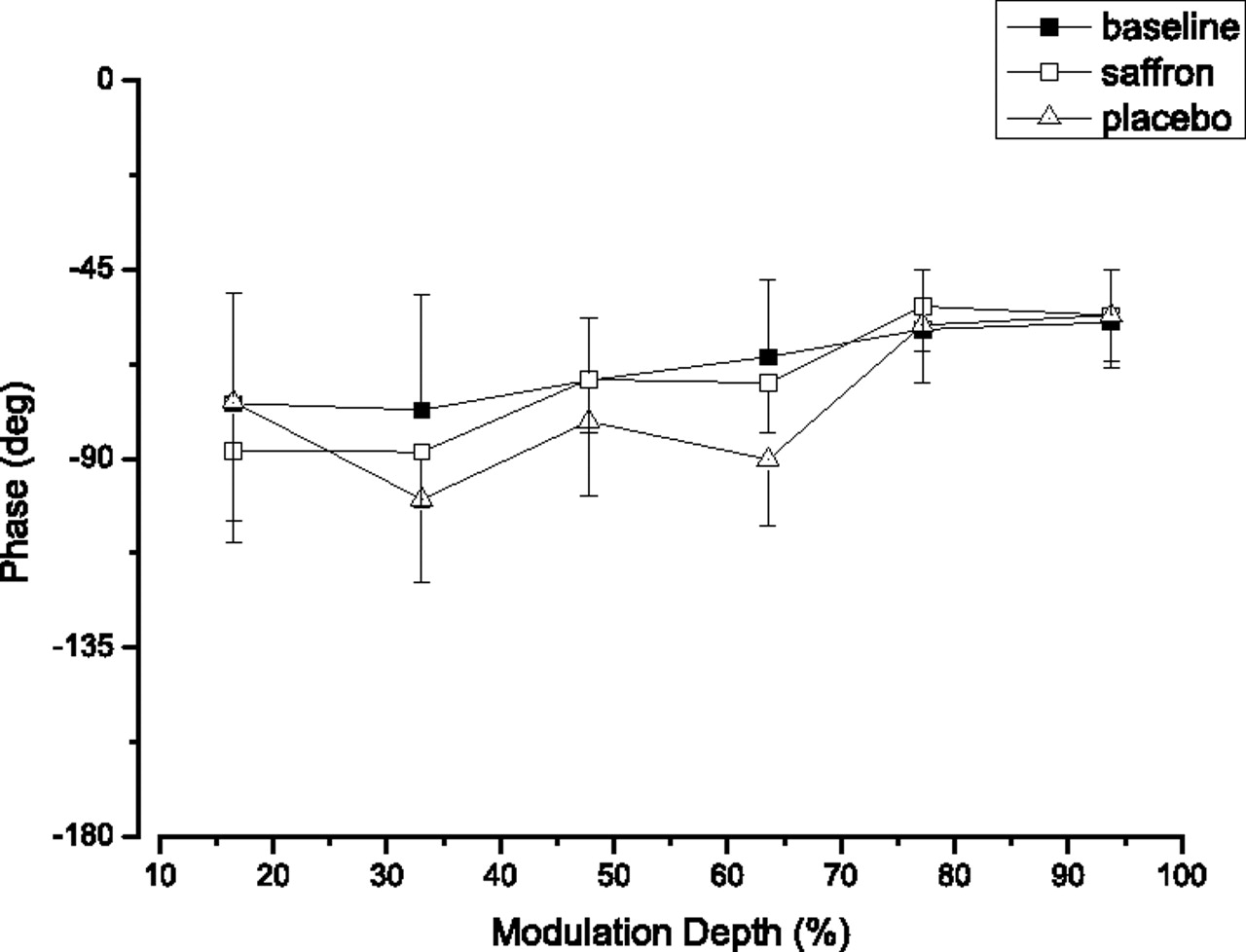
Phase measurements across different modulation depths showing maintained retinal timing responses in AMD patients during saffron treatment versus placebo conditions.[19]
Piccardi Study: Long-Term Benefits
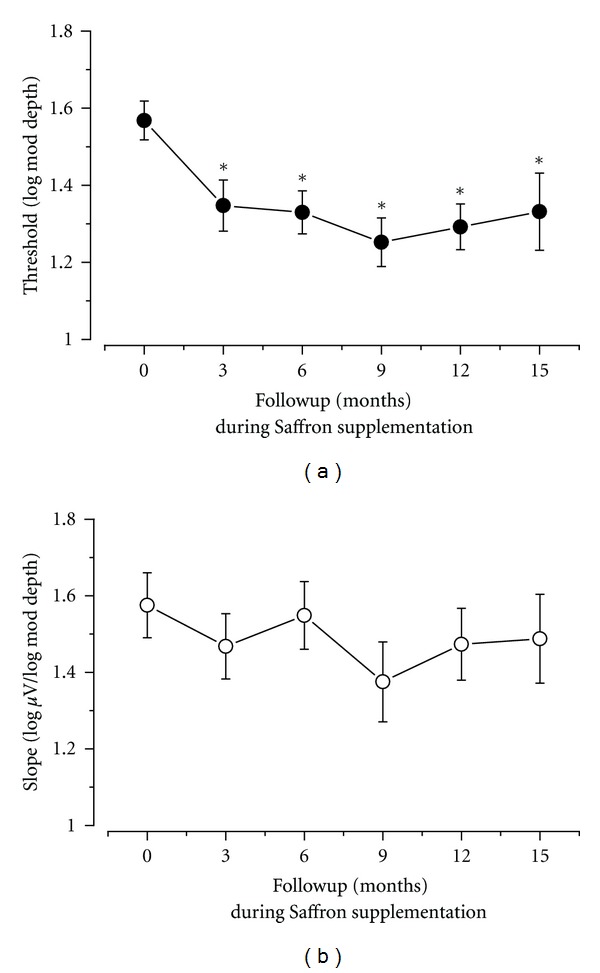
Piccardi and colleagues extended this research with a 14-month longitudinal follow-up study in 29 early AMD patients receiving continuous 20mg daily saffron supplementation.[20] This open-label trial examined whether the functional improvements observed in the short-term study could be maintained over extended treatment periods.
The results confirmed sustained retinal benefits throughout the entire follow-up period. After three months of supplementation, mean fERG sensitivity and visual acuity significantly improved compared to baseline.[20] Importantly, these improvements remained stable over the entire 14-month treatment period, suggesting that longer-term supplementation maintains functional benefits without tolerance development.Progressive improvements in retinal sensitivity measured by focal electroretinogram in early AMD patients taking 20mg daily saffron, with sustained benefits throughout 15-month treatment period.[20]
Broadhead Study: Real-World Effectiveness
Broadhead and colleagues conducted the most comprehensive AMD trial to date: a 12-month open-label extension study involving 93 adults with mild-to-moderate AMD who had previously completed the initial crossover trial.[33] This study was designed to assess long-term effectiveness in real-world conditions, including participants already taking AREDS supplements.
Results demonstrated continued retinal function improvements at 12 months. Mean multifocal electroretinogram (mfERG) response density was significantly higher compared to baseline, indicating preserved or improved macular function.[33] Importantly, saffron benefits were observed even in participants already taking AREDS supplements, suggesting additive protective effects when combined with standard nutritional support.
-
Cognitive Decline & Neurodegenerative Conditions
Cognitive decline affects millions of aging adults worldwide, with limited beneficial options that provide only modest symptomatic relief, and even fewer that don't carry significant side effects. Saffron has emerged as a promising natural alternative, with clinical trials demonstrating cognitive benefits comparable to established interventions but with superior tolerability profiles.
Akhondzadeh Study: Head-to-Head Pharmaceutical Comparison
Akhondzadeh and colleagues conducted a landmark 22-week randomized controlled trial directly comparing saffron with donepezil in 54 patients with mild-to-moderate cognitive decline.[34] Participants received either 30mg daily saffron extract or 10mg daily donepezil in this head-to-head comparison.
Results demonstrated equivalent cognitive benefits between treatments. Both groups showed statistically significant improvements on the Cognitive Assessment Scale (ADAS-cog) and Clinical Rating Scale-Sums of Boxes (CDR-SB), with no meaningful differences in efficacy between saffron and donepezil.[34] Importantly, saffron once again demonstrated superior tolerability, with significantly less vomiting compared to the donepezil group while maintaining equivalent cognitive support.Retinal threshold and slope measurements showing enhanced light sensitivity in AMD patients during extended saffron supplementation, with improvements stabilizing after 3 months.[20]
Meta-Analysis Confirmation
Since then, there have been additional studies, and Ayati and colleagues provided systematic validation in a meta-analysis of four randomized controlled trials involving patients with mild cognitive impairment and neurodegenerative conditions.[35] The analysis examined trials comparing saffron with both placebo and active pharmaceutical controls including donepezil and memantine.
Results confirmed saffron's cognitive benefits across multiple standardized assessment tools. The meta-analysis revealed that saffron significantly improved cognitive function compared to placebo groups, while showing no significant differences in efficacy compared to conventional measures on tests including ADAS-cog and CDR-SB scales.[35] Crucially, no serious adverse events were reported across the included studies, confirming saffron's excellent safety profile in older adult populations.
Mechanistic Understanding
D'Onofrio and colleagues reviewed preclinical evidence, and highlighted that crocin demonstrates multifunctional brain cell protection through regulation of glutamate levels, reduction of oxidative stress, and modulation of protein aggregation pathways. The neuroprotective mechanisms include acetylcholinesterase inhibition, anti-amyloid aggregation effects, and tau protein stabilization, addressing multiple pathological targets simultaneously.[7]
-
Cardiometabolic & Emerging Areas
Beyond saffron's established benefits for mood and cognitive health, emerging clinical research has revealed promising applications across diverse health domains. From metabolic support to inflammatory conditions and neuroprotection, these studies demonstrate saffron's versatility as a multi-target botanical intervention with broad clinical potential.
-
Blood Sugar Control & Metabolic Health
Tajaddini and colleagues conducted an eight-week randomized controlled trial examining saffron's effects on glycemic control and metabolic markers in 70 adults with type 2 diabetes.[36] Participants received 100mg daily saffron powder or placebo while maintaining their standard medications.
Results demonstrated significant metabolic improvements across multiple parameters. Saffron supplementation reduced fasting blood glucose by 7.57% compared to placebo, alongside meaningful improvements in lipid profiles and liver enzyme function.[36] Additionally, saffron enhanced antioxidant status with notable reductions in oxidative stress markers including malondialdehyde with 16.35% reduction.
Karim and colleagues provided systematic validation through comprehensive meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials involving 869 participants with early and ongoing blood sugar issues.[36] The analysis revealed significant improvements in fasting blood glucose, HbA1c, triglycerides, and systolic blood pressure compared to placebo groups, establishing saffron's potential as a complementary approach for metabolic syndrome management.
-
Inflammatory Bowel Conditions
Tahvilian and colleagues investigated saffron's anti-inflammatory potential in a randomized controlled trial involving 80 patients with mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis.[37] The eight-week study used 100mg daily saffron supplementation alongside conventional treatments.
Results showed significant improvements in both symptom severity and antioxidant status. The Simple Clinical Colitis Activity Index scores improved significantly, indicating reduced inflammatory activity.[37] Simultaneously, key antioxidant enzymes increased substantially: total antioxidant capacity, superoxide dismutase, and glutathione peroxidase all showed meaningful improvements compared to placebo.
-
Neurological Recovery
Asadollahi and colleagues explored saffron's neuroprotective effects in acute ischemic stroke through a randomized clinical trial involving 50 patients.[38] Participants received either standard stroke care or standard care plus 200mg daily saffron extract for three months following hospitalization.
Saffron demonstrated significant neuroprotective benefits in both short-term and long-term recovery measures. The National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) scores improved significantly in the saffron group compared to controls after just four days of treatment.[38] At three-month follow-up, functional independence scores were substantially higher in saffron-treated patients, suggesting enhanced recovery and reduced long-term disability.
Biomarker analysis revealed the mechanistic basis for these functional improvements. Saffron treatment significantly increased brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) concentrations that support neuronal repair and plasticity while reducing neuron-specific enolase and S100 protein levels (established markers of brain injury).[38]
These emerging applications highlight saffron's potential as a versatile botanical medicine that extends well beyond its established mood and cognitive benefits. The consistent anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and neuroprotective mechanisms appear to translate into meaningful clinical benefits across diverse health conditions, positioning saffron as a valuable addition to integrative health approaches.
-
Dosing & Timing
The clinical research consistently points to 28-30mg daily as the optimal saffron dose for most applications, with this range demonstrating efficacy across mood enhancement, cognitive support, eye health, and metabolic benefits.
-
Standard Clinical Dosing
Most successful trials employed 30mg daily saffron extract, typically administered as 15mg twice daily to maintain consistent blood levels throughout the day. The landmark mood studies by Akhondzadeh and colleagues used this split dosing approach, while the eye health trials by Falsini and Piccardi demonstrated sustained benefits with 20mg once daily.[14][20]
Recent research has also validated 28mg daily as effective. Kell and colleagues demonstrated significant mood improvements with 28mg standardized extract, while Jackson and colleagues confirmed stress-protective benefits at the same dose.[23] This convergence around 30mg reflects the dose range that consistently delivers clinical benefits without unnecessary excess.
-
Onset & Duration Expectations
Users typically experience subtle mood enhancements within days, but greater effects require 2-3 weeks of consistent supplementation. This timeline mirrors the adaptation period seen with conventional antidepressants, suggesting that saffron's neurotransmitter modulation requires time to achieve stable effects.
Trial durations varied by application, providing guidance for realistic expectations. Mood and appetite studies typically lasted 4-8 weeks and demonstrated peak benefits by endpoint, while cognitive and eye health trials extended 3-14 months to capture the slower-developing neuroprotective effects.
-
Timing Considerations
Most studies used twice-daily dosing (morning and evening) to maintain consistent plasma levels of active compounds. Pharmacokinetic research reveals that crocetin reaches peak concentrations within 4-8 hours and has a relatively short half-life, supporting divided dosing for optimal bioavailability.[10]
Saffron can be taken with or without food, as clinical trials employed both approaches successfully. The Jackson study administered doses at least 30 minutes after meals to optimize absorption,[13] while other trials showed efficacy regardless of food timing. For individuals sensitive to gastric irritation, taking saffron with food may improve tolerance without compromising effectiveness.
The clinical evidence establishes 30mg daily as the evidence-based dose range that consistently delivers benefits across saffron's diverse applications. This standardized approach ensures users receive the same compound concentrations that demonstrated efficacy in peer-reviewed research, transforming ancient botanical wisdom into modern, precision wellness support.
Safety Profile & Considerations
Clinical Safety Data
The clinical trials described above consistently demonstrate excellent tolerability for saffron at doses of 28-100mg daily. Comprehensive analysis of randomized controlled trials reveals that 30mg daily saffron for periods ranging from one month to 12 months produces no significant adverse effects in most participants.[5]
When side effects do occur, they are typically mild and transient. The most commonly reported effects across clinical studies include gastrointestinal discomfort, fatigue, dizziness, headache, and dry mouth, occurring in small percentages of participants.[5] Meta-analysis of adverse events from three studies involving 156 participants found no statistically significant differences between saffron and placebo groups for any reported side effects.[35]
Safety studies at higher doses confirm saffron's wide dosing window. Controlled trials examining 200-400mg daily for one week in healthy volunteers showed that even these elevated doses produced only minor, clinically insignificant changes in blood parameters that remained within normal ranges.[39] Research indicates that doses up to 1.5g daily are generally safe, with toxicological concerns emerging only at doses exceeding 5g daily, which is well above suggested supplemental ranges.[5]
Drug Interactions
Clinical studies examining saffron alongside conventional medications reveal minimal interaction concerns at standard supplemental doses. The sexual dysfunction trials demonstrated that 30mg daily saffron can be safely combined with fluoxetine without affecting efficacy or increasing adverse events.[29][30]
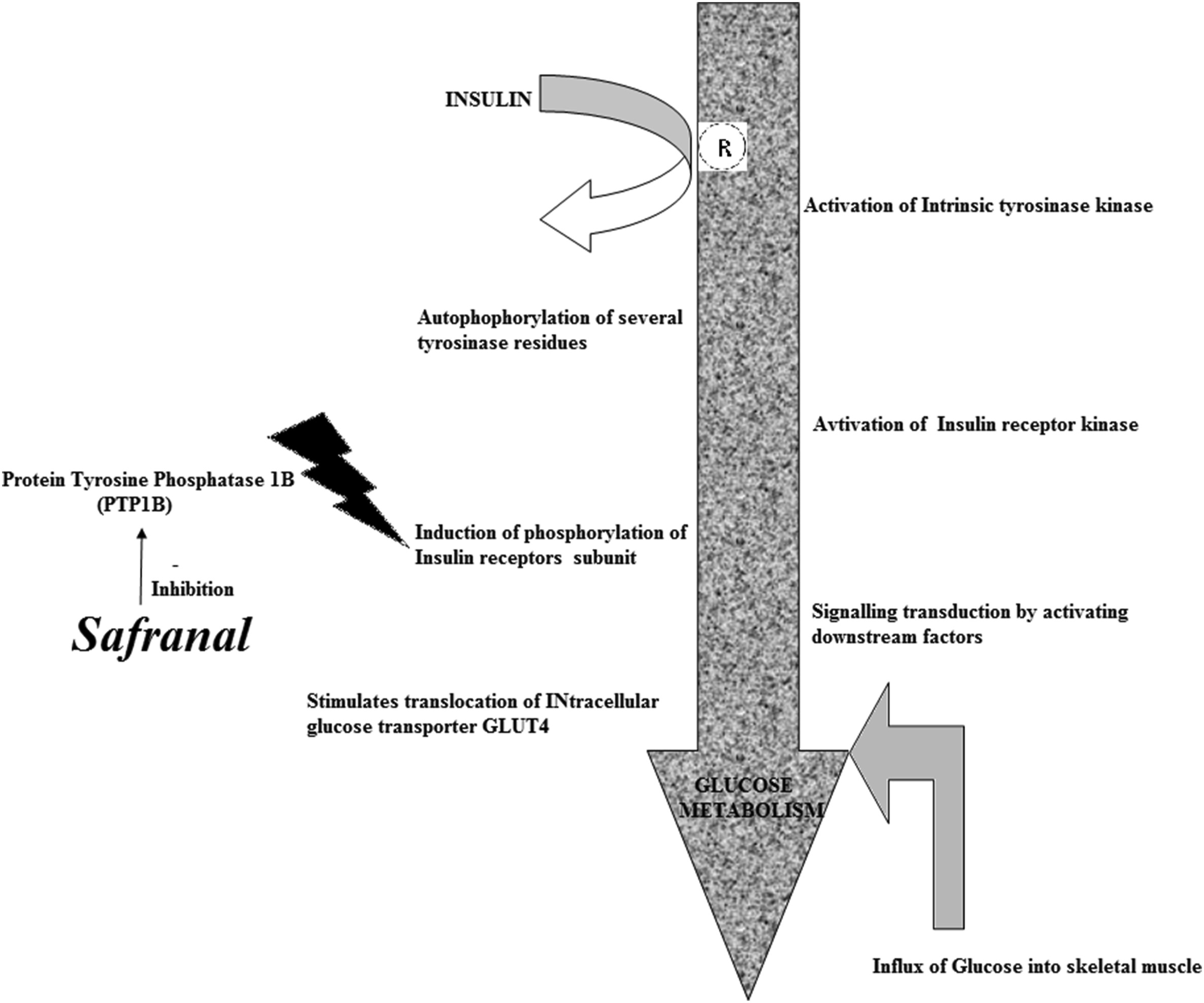
Molecular pathway showing safranal's inhibition of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B, enhancing insulin receptor signaling and glucose metabolism in skeletal muscle.[2]
Special Populations
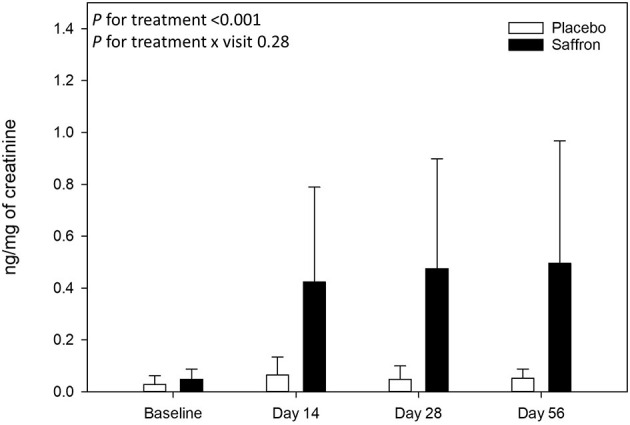
As always, pregnancy and lactation require caution, though clinical data is limited. While traditional culinary use suggests general safety, supplemental doses during pregnancy have not been systematically studied. Animal research indicates potential concerns at very high doses, and case reports suggest possible effects on uterine contractions.[39] In lactation, one study noted two mothers discontinuing saffron due to reduced milk supply, though other participants in the same trial did not experience this effect.[24]
Pediatric use shows promising safety data from cognitive trials, where children received weight-based saffron dosing (20-30mg daily) with no significant differences in adverse events compared to placebo groups.[27] However, long-term pediatric safety data remains limited.
For all special populations, consultation with qualified healthcare providers is recommended before initiating saffron supplementation, particularly for individuals with existing medical conditions or those taking prescription medications.
Choosing a High-Quality Saffron Extract
The difference between effective saffron supplementation and disappointing results often comes down to standardization quality, yet most consumers lack the technical knowledge to evaluate what makes one saffron extract superior to another. With saffron commanding prices up to $20,000 per kilogram and widespread adulteration plaguing the market, choosing a high-quality extract requires understanding both the science of standardization and the red flags that signal inferior products.
Why Crocin and Safranal Percentages Matter
The clinical research we've examined throughout this guide consistently used saffron extracts standardized to specific percentages of active compounds, not random, unverified saffron powder or whole stigma preparations. The trials that demonstrated antidepressant effects equivalent to fluoxetine used extracts with defined crocin content, while the eye health studies employed standardized preparations with quantified bioactive levels.[14][19]
Crocins serve as the primary drivers of saffron's mood and cognitive benefits, making their concentration the most critical factor in supplement selection.[7] Without verified crocin content, there's no guarantee that a saffron supplement contains adequate levels of the compounds responsible for clinical benefits.
Safranal concentration proves equally important for comprehensive saffron effects. This volatile compound contributes to mood stabilization through GABA pathway modulation and provides the aromatic indicators of proper saffron processing.[2] Many saffron supplements list only crocin percentages while ignoring safranal content, creating an incomplete (and unknown) profile that fails to capture saffron's full benefits.
The synergy between these compounds matters as much as individual concentrations. Clinical trials demonstrate that whole saffron extracts often outperform isolated crocin or safranal supplementation on their own, suggesting that the natural ratios found in quality stigmas provide optimal effects.[5]
HPLC Analysis: The Gold Standard vs Outdated Methods
The analytical method used to verify saffron quality directly impacts supplement reliability and consumer safety. While the food industry continues to rely on outdated ISO 3632 standards that use UV-visible spectrophotometry, supplement science demands the precision of High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) analysis for accurate bioactive quantification.
Traditional UV-Vis methods suffer from critical limitations that compromise supplement standardization. ISO 3632 methodology struggles with accurate safranal quantification and fails to detect adulterations that could fool basic spectrophotometric analysis.[4] The method measures "coloring power", "bittering power", and "odorous power" through broad absorbance readings rather than identifying and quantifying specific bioactive compounds.
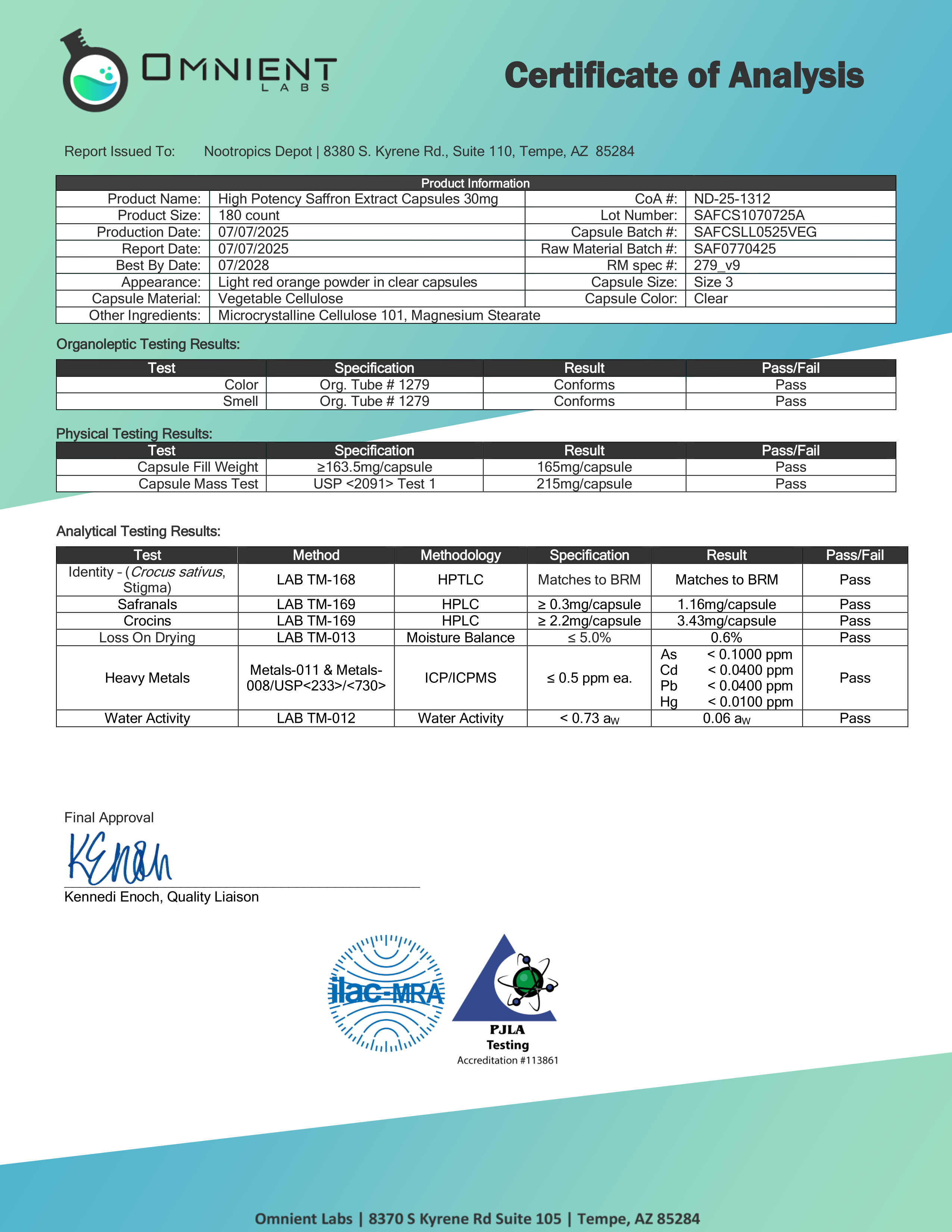
Official testing document from ISO-accredited Omnient Labs confirming 1.16mg safranals and 3.43mg crocins per capsule via HPLC analysis, exceeding minimum specifications with full heavy metals and purity verification.
HPLC analysis provides compound-specific identification and quantification that enables true standardization. This technique separates individual crocin variants (crocin-1, crocin-2, etc.) and precisely measures safranal concentrations, providing the accuracy needed for consistent effects.[4] Advanced HPLC-MS methods can even confirm compound identity through mass spectrometry detection, eliminating uncertainty about what's actually present in the extract.
The practical difference affects your results. Supplements verified through HPLC analysis ensure that each capsule contains the same bioactive concentrations that produced benefits in clinical trials. UV-Vis standardized products may contain adequate color compounds but lack the specific crocin and safranal ratios needed for mood, cognitive, and eye health benefits.
The Adulteration Crisis
Saffron's extraordinary value makes it the most adulterated spice in global commerce, with studies revealing that first-grade, unadulterated saffron is increasingly rare in international markets.[4] Common adulterants include turmeric powder, marigold petals, safflower, corn silk, and synthetic colorants designed to mimic saffron's golden-red appearance while providing none of its beneficial compounds.
Curcumin-based adulterants pose the most sophisticated challenge for consumers and even some testing laboratories. Turmeric powder and synthetic curcumin can replicate saffron's color profile while completely lacking crocins and safranals. These adulterants may pass basic visual inspection and even some spectrophotometric tests, but provide very little of saffron's expected benefits, despite appearing legitimate.[4]
Marigold petal contamination affects even supposedly premium saffron. This adulteration adds carotenoid compounds that can enhance color readings on basic tests while diluting the specific crocin content needed for clinical benefits. Advanced analytical techniques including DNA barcoding and targeted compound analysis are required to detect these sophisticated adulterations that can fool traditional quality control methods.
Nootropics Depot: Setting the Quality Standard
As we've learned through our previous guides such as ecklonia cava, tongkat ali, cistanche, and lion's mane, the above issues are the perfect problem for Nootropics Depot to solve.
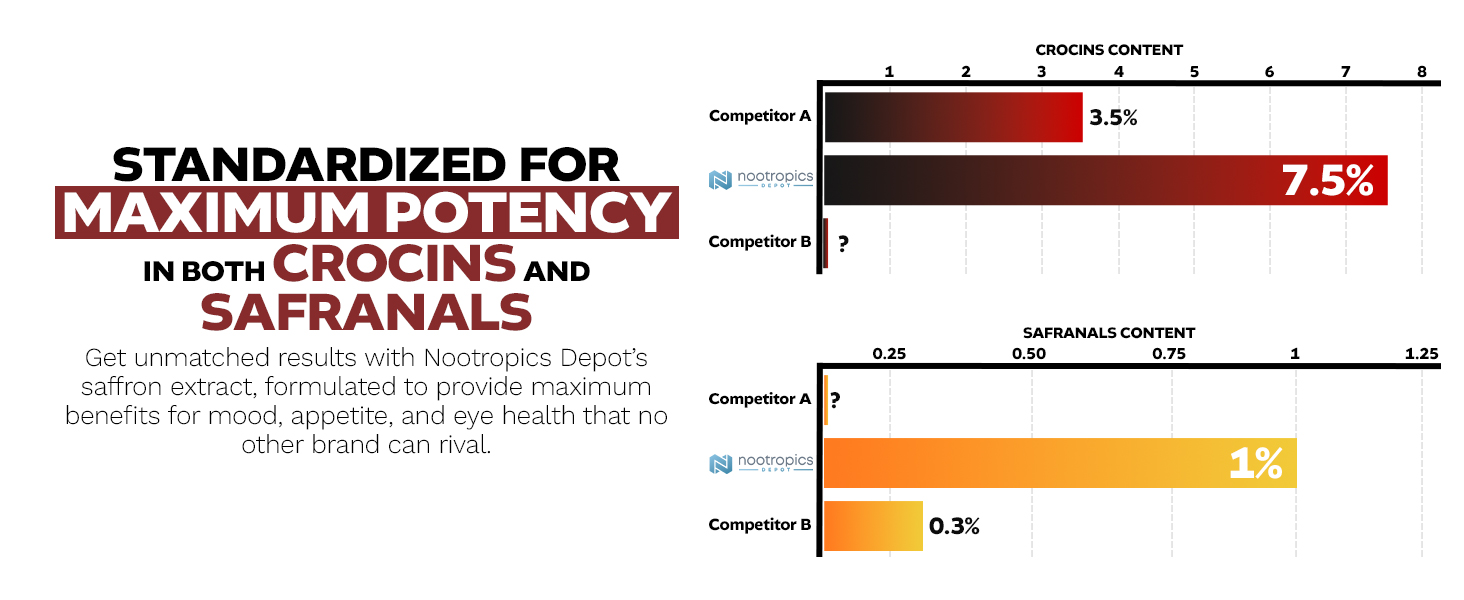
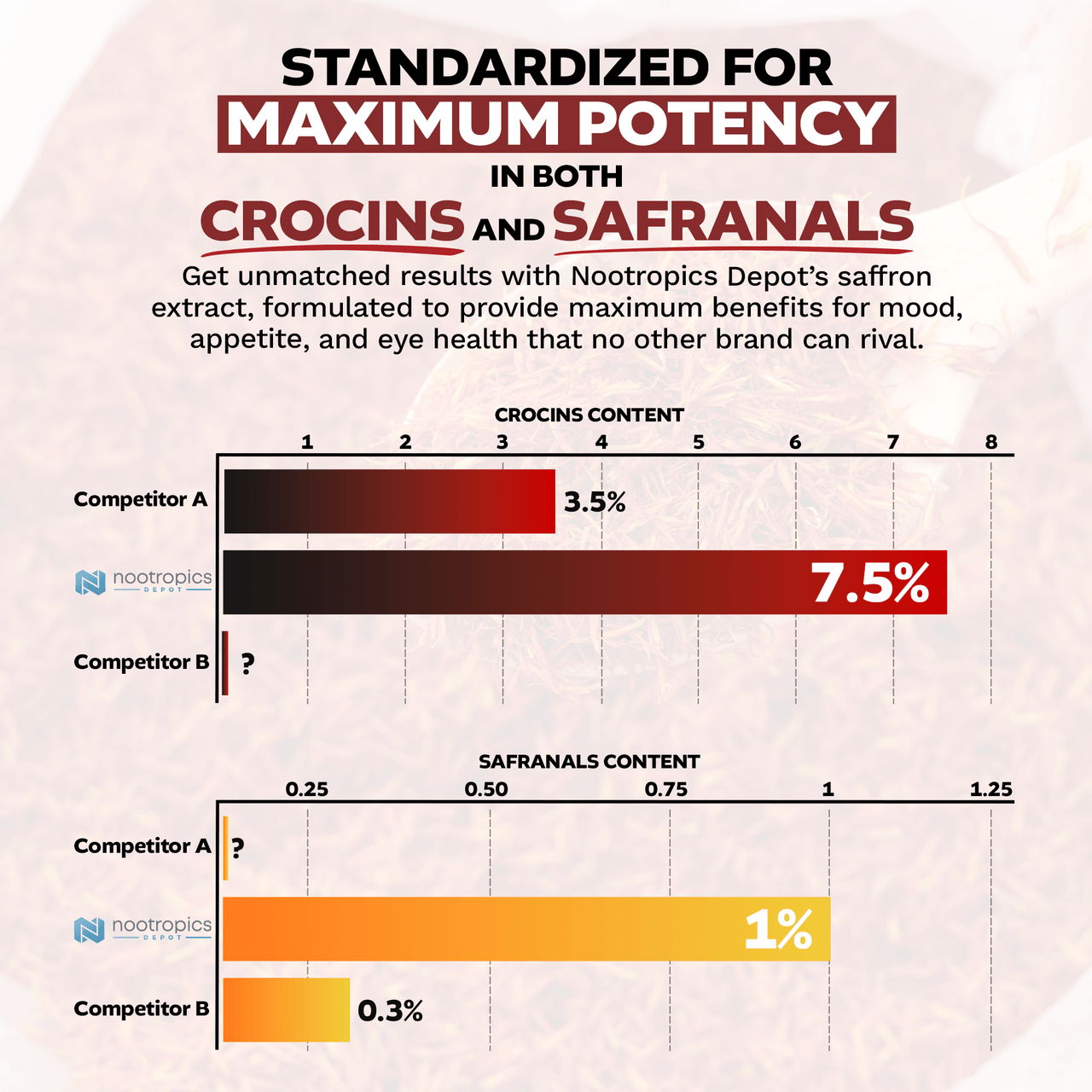
Nootropics Depot's High Potency Saffron Extract delivers industry-leading standardization that addresses every quality concern raised in this analysis. Each 30mg capsule provides 7.5% crocins and 1% safranals, concentrations that dwarf competitor products and ensure delivery of the bioactive levels used in successful clinical trials.
The potency advantage becomes clear when compared to typical market offerings. While many competitors provide saffron extracts with 3.5% crocins and unspecified safranal content, Nootropics Depot delivers more than double the crocin alongside meaningful safranal standardization. This dual standardization approach recognizes that both compound classes contribute essential effects: crocins for mood and cognitive benefits, safranals for stress reduction and aromatic authenticity markers.
Every batch undergoes comprehensive HPLC analysis in third-party ISO-accredited laboratories, providing the analytical precision that clinical research demands. This testing verifies both identity and potency of active compounds while screening for adulterants that could compromise its effects. The certificates of analysis are made publicly available, demonstrating the "Transparency You Can See" commitment that sets apart legitimate supplement companies from marketing-focused brands.
Manufacturing in GMP-certified, FDA-registered facilities in Arizona ensures that each capsule meets pharmaceutical-grade quality standards. This domestic production provides supply chain transparency and quality control that's often lacking in imported saffron products where origins and processing methods remain opaque.
The 60-count and 180-count sizing options reflect practical considerations for different supplement users. New users can start with the 60-count bottle to assess individual response, while experienced users can choose the 180-count option for better value during extended supplementation periods. The standardized 30mg dosing aligns perfectly with the clinical research that established saffron's effects.
Third-party testing extends beyond active compound verification to include screening for heavy metals, pesticides, microbiological contaminants, and other adulterants that could compromise safety or efficacy. This comprehensive testing approach addresses the full spectrum of quality concerns that affect imported botanical supplements, providing consumers with confidence that they're receiving pure, potent saffron extract rather than adulterated material.
The Bottom Line: Effective saffron supplementation requires products that match the standardization used in successful clinical trials. Specifically, we need to see verified percentages of both crocins and safranals confirmed through HPLC analysis. Nootropics Depot's High Potency Saffron Extract delivers these requirements alongside industry-leading quality control that ensures each capsule contains the same compounds that demonstrated benefits in peer-reviewed research.
When choosing saffron supplements, prioritize dual standardization, analytical verification, and transparent quality documentation over marketing claims and low prices that often signal compromised quality.
Nootropics Depot High Potency Saffron – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.
Stacking & Synergies
Saffron's multi-target mechanisms make it an excellent foundation for targeted supplement stacks that address specific health goals. The key to successful stacking lies in combining complementary pathways rather than overlapping mechanisms, allowing each ingredient to contribute unique benefits while avoiding redundancy or potential interactions.

Lion's Mane isn't just another mushroom supplement. Clinical studies show it supports memory, focus, and mood through NGF stimulation. But most products lack active compounds. Nootropics Depot Erinamax breakthrough changes everything with verified erinacine A content.
Mood & Stress Support Stacks
For mood support, saffron pairs excellently with calming minerals and adaptogenic compounds:
- Magnesium glycinate (200-400mg) provides GABA pathway support that complements saffron's serotonin modulation, creating a balanced approach to mood stabilization and sleep support.
- L-theanine (100-200mg) offers synergistic stress protection through alpha-wave promotion and glutamate modulation, working alongside saffron's GABA receptor activity to provide calm focus without sedation. This combination proves particularly valuable for individuals experiencing both mood concerns and stress-related cognitive difficulties.
- Bacopa monnieri (300-600mg standardized extract) can enhance the neuroprotective aspects of saffron supplementation. While saffron provides immediate mood support through neurotransmitter modulation, bacopa contributes long-term neuroplasticity benefits through BDNF enhancement and synaptic strengthening. This pairing creates both acute mood benefits and sustained cognitive resilience.
Cognitive Enhancement Stacks
For cognitive optimization, saffron combines well with cholinergic and neuroplasticity-supporting compounds.
- Cognizin® Citicoline supports the cholinergic and dopamine systems, and is the most well-studied form of choline on the market.
- Bacopa monnieri provides complementary cognitive enhancement through different pathways, as described above.
- Sabroxy® (oroxylin A, 100-200mg) offers promising synergy through GABAergic modulation and neuroplasticity promotion. The combination may provide comprehensive cognitive benefits that address both performance and resilience aspects of brain function.
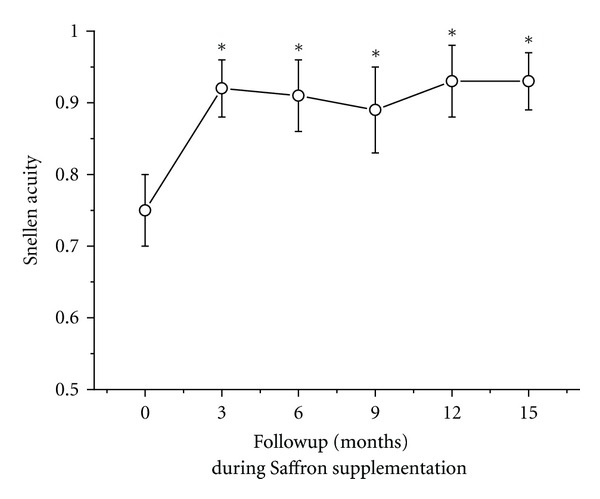
Visual acuity scores demonstrating significant improvements within 3 months of saffron treatment, maintaining enhanced vision throughout the study period.[20]
Eye Health & Vision Protection
Saffron demonstrates additive benefits when combined with AREDS nutrients. The optimal eye health stack combines saffron (20-30mg) with lutein/zeaxanthin (10/2mg) and zinc (25mg) at the very least. This approach provides both the macular pigment support of traditional AREDS nutrients and the unique retinal function benefits demonstrated in saffron clinical trials.
Combinations to Avoid
Avoid combining saffron with other serotonergic herbs, particularly St. John's Wort, which could theoretically lead to excessive serotonin activity. While no clinical trials have documented interactions, the overlapping mechanisms suggest potential for additive effects that could become problematic.
Exercise caution with multiple mood-supporting botanicals that work through similar pathways. Combining saffron with rhodiola, ashwagandha, or other adaptogens requires careful attention to individual response, as the combined effects may be more pronounced than expected.
Successful saffron stacking focuses on complementary mechanisms that enhance rather than duplicate saffron's diverse benefits, creating synergistic combinations tailored to specific health goals.
Conclusion: From Ancient Spice to Modern Nootropic
What began as the world's most expensive spice -- worth more than gold by weight -- has emerged as one of the most thoroughly validated natural compounds available today. The clinical evidence spanning mood enhancement, cognitive protection, eye health, and metabolic support positions saffron as a genuine alternative to stronger interventions, but with safety profiles that conventional medications simply cannot match.

Cistanche tubulosa, the "desert ginseng" that saved Genghis Khan's army, naturally supports testosterone through enhanced enzyme production. Modern research validates 2,000+ years of use for hormonal health, cognitive function & vitality.
Over two decades of rigorous clinical trials have demonstrated that 30mg daily saffron extract provides clinically significant mood-supporting effects, cognitive benefits, and retinal protection, comparable to current standards of care. While other medications typically target single pathways, saffron's crocins and safranals work across neurotransmitter systems simultaneously. This networked activity explains both saffron's broad clinical applications and its exceptional tolerability.
However, the clinical benefits depend entirely on standardization quality. The saffron extracts that demonstrated mood benefits equivalent to antidepressants contained verified percentages of crocins and safranals, not random saffron powder or adulterated material. The eye health and cognitive studies used standardized extracts with quantified bioactive levels. Quality matters, and most saffron supplements don't deliver it.
Nootropics Depot's High Potency Saffron Extract provides the standardization that clinical research demands. With 7.5% crocins and 1% safranals, each 30mg capsule delivers more than double the bioactive concentration of typical market offerings. This isn't just marketing, it's the result of HPLC analysis in ISO-accredited laboratories that verify every batch meets the same standards used in successful clinical trials. The dual standardization ensures users receive both the mood-supporting crocins and the stress-modulating safranals that work together to create saffron's comprehensive effects.

Tongkat Ali research shows impressive results for testosterone support, sexual health, stress reduction, and athletic performance. This comprehensive guide covers the science, proper dosing, and how to choose quality standardized extracts like Nootropics Depot's lab-tested options.
The manufacturing standards match the analytical precision. GMP-certified, FDA-registered facilities in Arizona provide pharmaceutical-grade quality control, bringing a stark contrast to imported saffron products where origins and processing methods remain mysterious. Comprehensive third-party testing screens for heavy metals, pesticides, and adulterants while confirming bioactive potency, delivering the "Transparency You Can See" that separates legitimate supplement science from marketing-driven brands.
As consumers increasingly seek natural alternatives to pharmaceutical interventions, saffron provides validated efficacy without the side effects that plague conventional medications. The growing body of research continues to reveal new applications, from neuroprotection in stroke recovery to anti-inflammatory benefits in metabolic disorders.
The journey with saffron starts with quality. Nootropics Depot's High Potency Saffron Extract brings clinical-grade quality with the convenience of modern supplementation. When it comes to natural mood and cognitive support, ancient wisdom enhanced by modern science delivers results that traditional remedies alone simply cannot match.
Nootropics Depot High Potency Saffron – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.












Comments and Discussion (Powered by the PricePlow Forum)