The supplement industry is an industry of rivalry and competition — which is why we love it. This competition even extends to the corner of the industry that focuses on amino acid supplementation. Products that deliver just the branched chain amino acids or the full spectrum of essential amino acids have been at war for years with no end in sight to the conflict… until now.
But today, InnovaPharm is dropping the hammer with monstrous doses of both in their new supplement, Recover EAA.
We’re in love with this formula from a dosage standpoint alone, and are happy that InnovaPharm was the one to do it. Remember, this is the brand that put out the ridiculously strong stimulant-free pre workout supplement in NovaPump, with a similar strategy.
We're going to get into the backstory of the whole "BCAA vs. EAA" battle that Recover-EAA is 'alpha-ing' today, but first sign up for PricePlow's InnovaPharm news alerts since we have a lot more content and giveaways coming from the aggressive brand:
InnovaPharm Recover EAA – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.
My Recover EAA Review
This is a no-fuss, no-nonsense, no-hype-needed essential amino acid supplement that has nothing but a monster dose of EAAs and fantastic flavoring. In the review below, I literally said "OMG" to the OMG flavor... kinda embarrassing but the stuff is awesome, especially given the excellent dose!
Recover-EAA: The Premise and Some Science
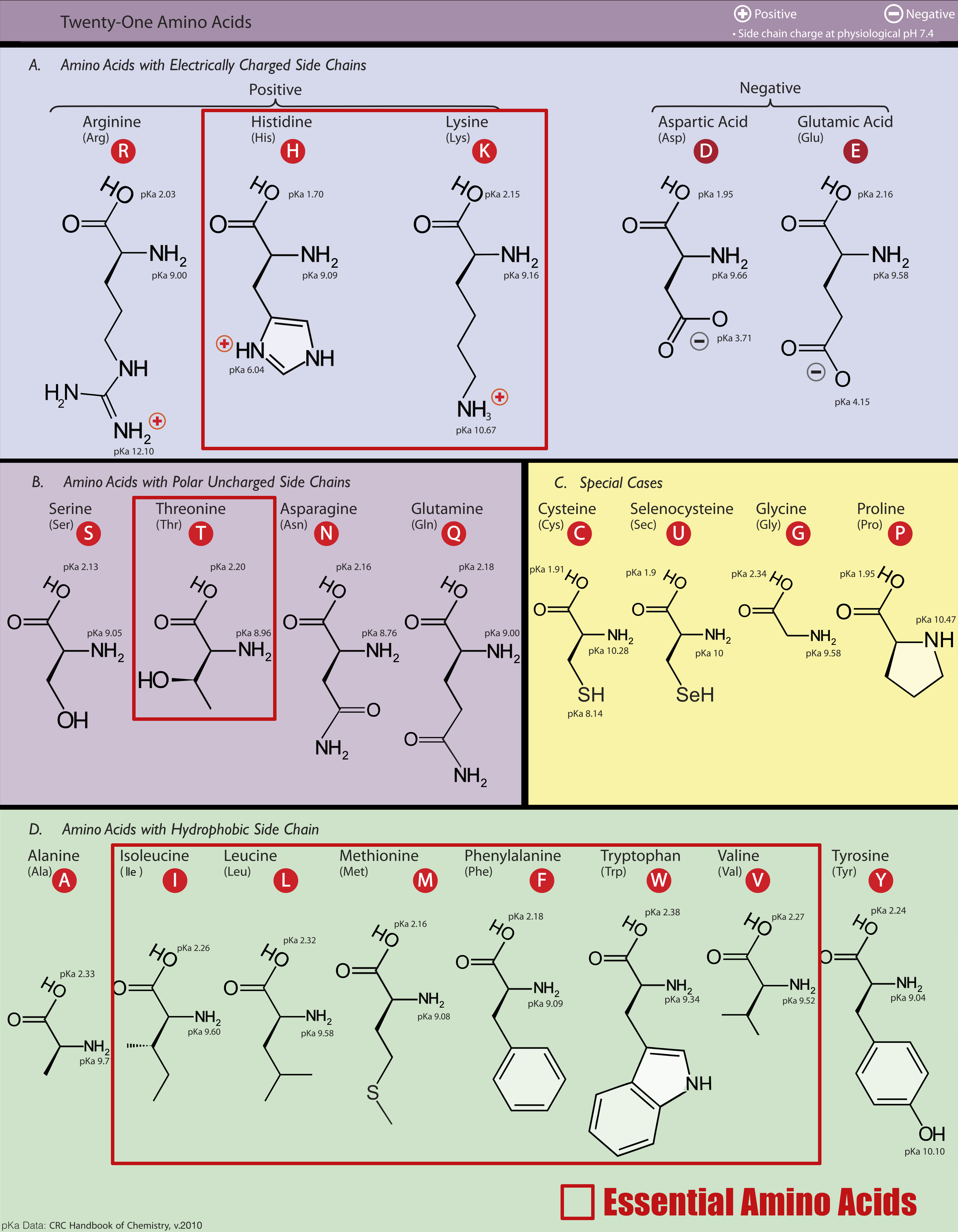
Amongst these primary amino acids, the essential amino acids are in red. Leucine, Valine, and Isoleucine are the three Branched-Chain Amino Acids.
Branched chain amino acid products, or BCAAs, are three of the nine essential amino acids found in proteins that have held a cornerstone in the supplement market for over a decade. If you go to any commercial gym by you, we promise you’ll see at least one bro drinking a neon-colored beverage from a large jug. While the benefits of such products have been debated, the influence of BCAAs on consumer behavior is massive. More recently, companies have produced products containing complete essential amino acid matrices - likely to target the demographic that had come to know and love BCAA products.
Some background is helpful in understanding the difference between these similar-sounding products. The first order of business is to understand what essential means in terms of biochemistry. Essential refers to anything that the body must extract from food or liquid sources. The essential amino acids, therefore, are protein precursors the body must get from food in order to function. The branched chain amino acids, leucine, isoleucine, and valine are a subset of the essential amino acids. Early supplement research showed that these three amino acids, leucine especially, are important in the body’s muscle building process when compared to other EAAs.[1]
Are your meal portions 5g of protein?
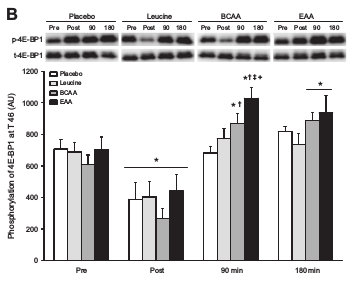
”In summary, oral supplementation with BCAA following resistance exercise stimulates mTORC1 signaling more potently than ingestion of leucine alone, but not as effectively as EAA.”
However, there has been more recent research showing that the branched chain amino acids are important for muscle protein synthesis but may only build new muscle when combined with other essential amino acids — like the amount you would find in steak or a scoop of whey protein, for example.[2] Considering this research, companies produced essential amino acid products that include the full spectrum of amino acids the body cannot produce.
InnovaPharm saw this happening, but the doses are often too small to get them excited. Consider that steak you eat for dinner. Does it only have 5g amino acids in it? Hell no! So InnovaPharm decided to combine both product concepts. Recover EAA delivers a massive dose of the branched chain amino acids alongside the complete spectrum of essential amino acids, which is also well-dosed - right when you want it - during training!
Now that we have the background and premise out of the way, we can hit the science behind this product.
Recover-EAA Ingredients
-
The BCAA’s in a 2:1:1 Ratio (10g)
If you’ve followed PricePlow for any amount of time — you know leucine is the star of the branched chain aminos. For those new to these products, leucine earned its fame as it may have an ability to light the embers of protein synthesis through its interaction with the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR - sometimes also known as mammalian target of rapamycin).[3]
The mTOR pathway, for reference, plays a substantial role in cellular metabolism, growth, cell division, and even survival of the cell itself.[4] While there are two mTOR pathways, the one we care about is mTORC1 as it is responsible for the muscle building process.[4] Beyond its role in getting muscle building underway, leucine may help prevent muscle protein breakdown.
Isoleucine is very similar in structure to leucine and can also help stroke the embers of protein synthesis. However, it’s not as potent. Isoleucine may help enhance glucose uptake during exercise.[5] Valine is the least-researched amongst the triplet BCAAs. However, it is essential for normal body functioning. For example, valine plays an irreplaceable role in creating glycogen,[6] which is needed by everyone - and thus valine is needed by everyone's diet, as we can't generate it ourselves.
Other BCAA benefits: Endurance and Reduction of Soreness
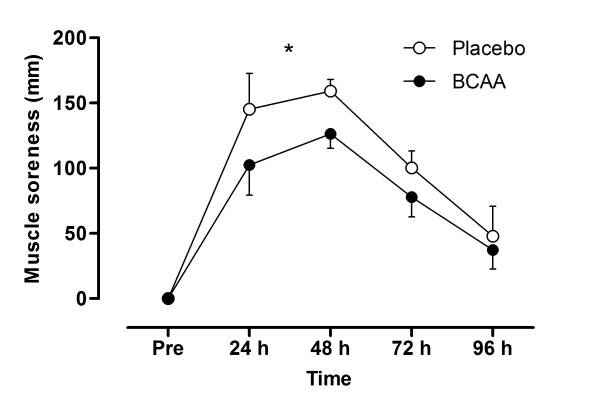
BCAAs may help boost endurance and stamina during training.[2] BCAA’s also may help lifters experience less DOMs by enhancing the recovery process. While these benefits may be subtle, more recovery means more potential training volume... which also means more gains, if you achieve that extra volume.[7] BCAAs may also help with fat breakdown, which is good news for dieters,[8] so long as they don't put you in a caloric surplus (remember, BCAAs have calories)!
BCAAs can do wonders for muscle soreness according to some research, but more aminos are needed to build muscle.
The 2:1:1 leucine:isoleucine:valine ratio that InnovaPharm used is our preferred dosing relationship. Most of the research done on the BCAAs uses a 2:1:1 ratio and other ratios have not gone through the same scientific rigor. Beyond the ratio being ideal — the dose present in InnovaPharm EAA is massive. Many BCAAs products deliver 5g per scoop — InnovaPharm included 10g per scoop.
If you're smaller or on a budget, right off the bat you could probably split this dose in half... but let's not forget, we're writing this post for steak-eaters today!
-
The Other Essential Amino Acids
-
Lysine (2g)
Lysine is an essential amino acid that supports protein synthesis, so a high dose here makes sense. Beyond its role in protein synthesis, lysine helps immune function, collagen production, wound healing, and even the formation of new red blood cells.[9-11] Lysine is also an essential aspect of the carnitine shuttle — an essential step in fatty acid breakdown.
There are products on the market that list their entire essential amino acid matrix at 2g. This dose is absolutely absurd.
Alongside leucine, lysine is the other 100% ketogenic amino acid, which means that it cannot be converted to glucose in the body. This is useful for those who are on low-carb / ketogenic diets or are simply scared of such a massive supplement spiking blood sugar too much: Two of the most well-dosed ingredients here aren't going to cause a rise in blood sugar at all.
-
Threonine (2g)
Threonine is interesting as it acts as a precursor for two non-essential amino acids: glycine and serine. Glycine and serine both play a role in muscle synthesis — so having more of their substrate is a good idea. Threonine, like lysine, also plays a role in immune function and collagen synthesis. Threonine also helps methionine and aspartic acid in the digestion of fats, so it may provide GI benefits. InnovaPharm went nuts with the dose here — and we’re all for it!
-
Histidine (100mg)
Histidine is an amino acid that serves as an important precursor in anabolic pathways. Beyond its role in producing histamine, histidine can be converted to carnosine. Think of carnosine as a sponge inside muscle cells that helps your muscle tissue work harder and longer by sucking up excess protons. Remember, beta alanine supplementation works by producing carnosine, so supplementation of histidine may help you “feel” the benefits of beta alanine if you were deficient in histidine.[12]
Histidine also plays important roles in maintaining neural, immune, and vascular health.[13-14] While the dose here may feel lower than the previous two — this is more than enough histidine per serving and is where we're seeing the other EAAs dose.
-
Methionine (100mg)
InnovaPharm shows off their cajones and flavoring prowess with this dose!
Methionine is the bane of supplement companies as its flavor is impossible to mask, due to the sulfur atom that resides inside. It tastes quite awful, due to that sulfur 'rotten egg' smell. This is why we sometimes see scrawny doses as low as 25mg, but InnovaPharm wanted to show their skills here.
Why do we care so much, beyond its issue with flavoring? Methionine is the first amino acid of any peptide chain in eukaryotes — as the start codon in genetics instructs ribosomes to use methionine first. Methionine is also the methyl donor in methylation — a process that changes DNA in response to environmental triggers. Methionine can become cysteine, which is an amino acid involved in immune function.[15]
Our diets are typically deficient in sulfur, which can lead to joint problems and all kinds of other biological issues due to the fact that the processes discussed above cannot happen without it. We'll take methionine and its sulfur atom when and where we can get it - but hopefully tastefully!
-
Phenylalanine (100mg)
More BCAA, more EAA, more recovery and more muscle protein synthesis. Train hard and train with purpose!
Phenylalanine helps produce neurotransmitters and catecholamines. It converts into phenethylamine (PEA) — a compound that PricePlow loves and writes about ad nauseum. It is also a building block of dopamine, epinephrine, and norepinephrine — all compounds that help us both feel good and perform well - especially in those "flight or fight" modes we induce at the gym in order to mobilize and burn fat. So the feel good effect of phenylalanine may combat mood disorders while extra epinephrine and norepinephrine may boost fat breakdown.[16-17]
-
Tryptophan (100mg)
Tryptophan is infamous as everyone and their mom thinks it’s making them tired after Thanksgiving dinner. While science has debunked this effect, there is truth that tryptophan is a precursor for serotonin. Serotonin is a multifaceted neurotransmitter that impacts well-being, executive functioning, and sleep. The body can also convert serotonin to melatonin, a hormone supplemented for its sleep onset effects. Tryptophan plays a role in memory and learning. Supplementation may have a feel-good, nootropic effect.[18,19]
-
Flavors
InnovaPharm went bold with the flavors for their EAA. Foremost is the first “OMG!” flavor — Orange Mango Grapefruit. If the OMG! Flavor doesn’t suit your palate, EAA also comes in momma’s sweet tea and pink lemonade, a flavor released in NovaPump as well. The flavor matrix is a mix of natural and artificial sweeteners (which includes erythritol, sucralose, and ace-k) and also includes a bitterness blocker — likely to help out with methionine. We‘re happy to report that InnovaPharm lists no artificial colors on the formula, just like in NovaPump!
Worth noting as a benefit is the himalayan sea salt that's providing additional sodium, and there's 4% RDA of potassium as well, so your sodium-to-potassium ratio doesn't get knocked out of whack!
Conclusion: Recover EAA may be for more than recovery!
It's a big, massively-dosed BCAA/EAA supplement with tons of leucine, lysine, and threonine. What's to hate?!
InnovaPharm Recover EAA is the next big threat on amino acid market. It is also the second atomic bomb InnovaPharm dropped on its competition this year after their incredible pump product, NovaPump. While it may not offer vegan-sourced amino acids (remember, we're writing this one for the steak-eaters anyway), it makes up for it with a transparent label, interesting flavors, and massive doses. If have no diet restrictions and want a ton of EAA’s — InnovaPharm’s new offering is the way to go. Hydrate with it during training after you've taken NovaPump and there's no way you're not going to have a good time with this stack.
InnovaPharm Recover EAA – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.









Comments and Discussion (Powered by the PricePlow Forum)