Health starts with our cells – they're the fundamental building blocks of every tissue, organ, and system in our body. But in today's fast-paced world, our cells face unprecedented challenges from environmental stressors, poor nutrition, and other lifestyle factors that lead to oxidative stress.
The Antioxidant Paradox: Why Don't Antioxidants Yield Actual Results?

Hobamine (2-HOBA) tackles the "antioxidant paradox" with a unique approach - instead of broadly suppressing oxidation, it specifically targets harmful reactive dicarbonyls before they damage cells. New research shows promising immune and cardiovascular benefits.
While we've long understood that oxidative stress can damage our cells, finding an effective solution has been surprisingly difficult. Traditional antioxidant approaches often fall short, either by not reaching therapeutic levels or by disrupting important cellular processes.
This is well-known as the "antioxidant paradox", the common situation where antioxidants work incredibly in cell studies or in vitro, but fail to generate positive actual outcomes in human health. TSI Group has a compound that flips this paradox on its head:
Hobamine (2-HOBA): TSI Group's Revolutionary Cell Health Compound
Enter Hobamine (2-HOBA), a novel compound from TSI Group that takes a completely different approach to supporting cellular health. Rather than broadly suppressing oxidative processes, Hobamine specifically targets harmful compounds that can damage our cells.
Recent clinical research has shown that Hobamine can positively influence various markers of immune health and inflammation in humans.[1] This study and far more -- including background information, mechanisms of action, and how to try Hobamine -- are covered in this article.
Before diving deeper, sign up for PricePlow's news alerts on Hobamine and TSI Group using the form below, then continue reading to learn how this innovative compound could transform our approach to cellular health:
Subscribe to PricePlow's Newsletter and Alerts on These Topics
What is Hobamine?
Hobamine (2-hydroxybenzylamine acetate, or 2-HOBA) is a naturally-occurring compound first discovered in buckwheat seeds.[2] This unique molecule represents an innovative approach to cellular protection that works differently from traditional antioxidants.
A Natural Compound with Unique Properties
The compound's molecular structure gives it special properties that allow it to rapidly neutralize harmful compounds called reactive dicarbonyl electrophiles, including isolevuglandins (IsoLGs) and other damaging molecules that form during oxidative stress.[3]
Understanding the 2-HOBA Molecule
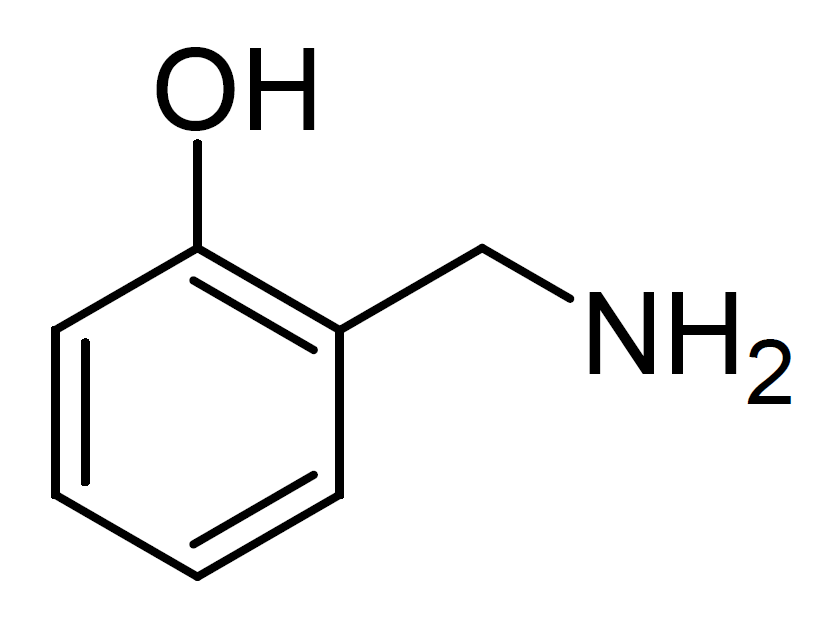
For those interested in the chemistry, 2-HOBA has a simple yet powerful structure that makes it highly reactive with harmful byproducts of oxidative stress. At its core, it consists of a benzene ring -- a stable hexagonal carbon structure -- that's modified with two key functional groups:
- A Hydroxyl Group (-OH): This allows it to interact with and neutralize reactive molecules efficiently.
- An Amine Group (-NH2): This enhances its ability to rapidly bind to and deactivate harmful compounds like isolevuglandins (IsoLGs), which are damaging byproducts of lipid oxidation.
This unique combination makes 2-HOBA a specialized "scavenger" rather than a traditional antioxidant. Instead of broadly neutralizing all oxidative reactions (which can interfere with normal cellular function), it specifically targets highly reactive lipid-derived molecules before they can cause cellular damage.
How Hobamine Works
Unlike traditional antioxidants that try to stop all forms of oxidation (including beneficial ones), Hobamine works by specifically targeting and neutralizing reactive dicarbonyls before they can damage cellular proteins, lipids, and DNA.[4] This selective approach allows normal cellular processes to continue unimpeded while preventing the accumulation of harmful modified proteins that can lead to cellular dysfunction.[3]
What Are Reactive Dicarbonyls and Why Are They Harmful?
Reactive dicarbonyl electophiles are highly reactive compounds that form as byproducts of oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation. These molecules, including isolevuglandins (IsoLGs), malondialdehyde (MDA), and 4-hydroxynonenal (HNE), can rapidly bind to proteins, lipids, and DNA, leading to cellular dysfunction, inflammation, and long-term damage.[3]
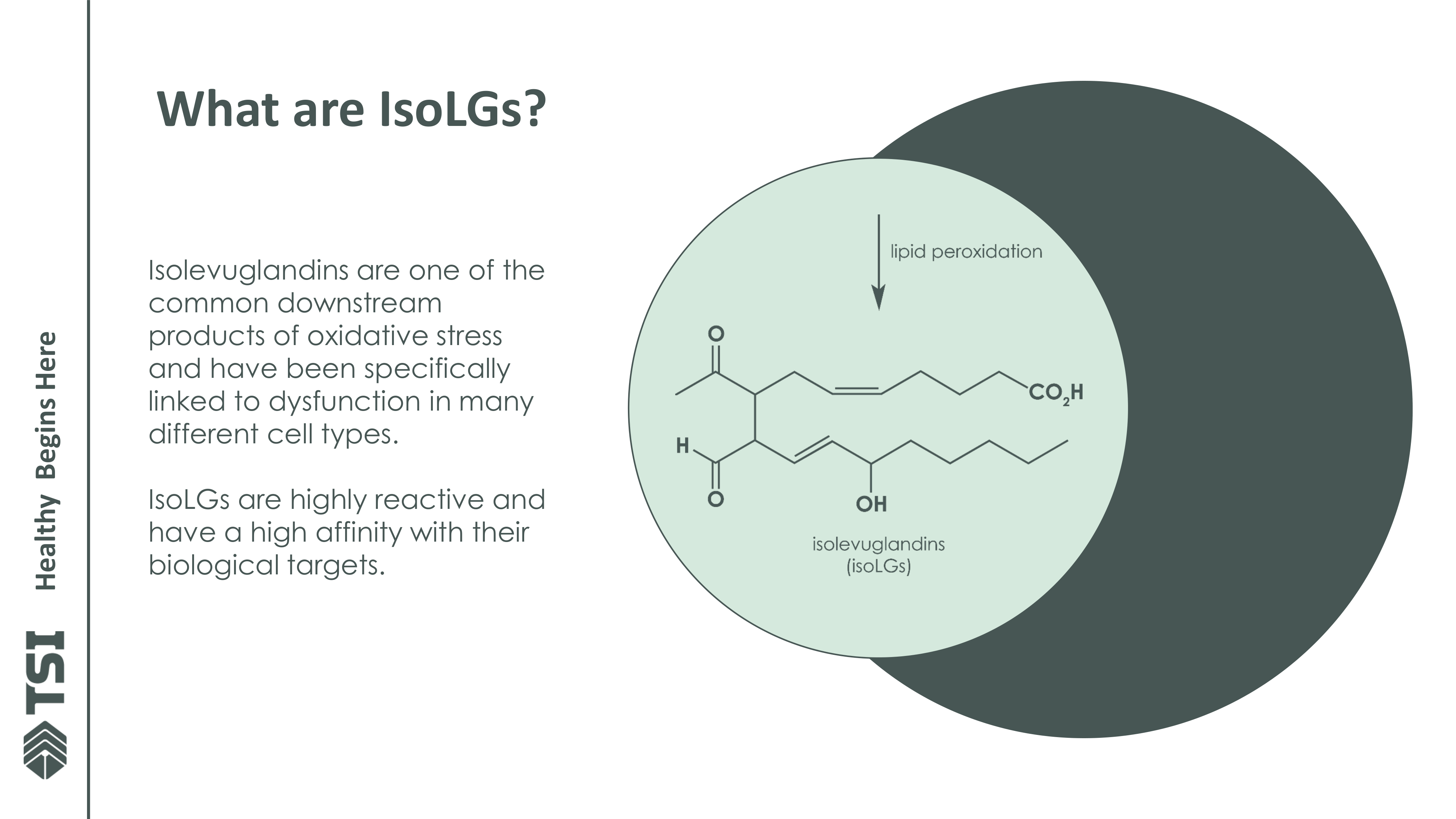
This detailed slide focuses on isolevuglandins (IsoLGs), the harmful reactive compounds that form during oxidative stress. The graphic includes the molecular structure of these dicarbonyl compounds and explains their high reactivity with cellular components. By highlighting how these compounds specifically contribute to cellular damage, the image helps explain why Hobamine's targeted approach to neutralizing IsoLGs is so effective.
Dicarbonyl formation is accelerated by factors like poor diet, stress, pollution, excessive exercise, and aging, making them a major contributor to oxidative stress-related conditions.[5] Hobamine selectively targets these harmful dicarbonyls before they can cause damage, preserving normal cellular function.
Safety and Regulatory Status
While Hobamine can be found naturally in buckwheat,[2] TSI Group produces a bioidentical version as a highly pure acetate salt for supplementation.[6]
Hobamine has undergone extensive safety testing in both animals[7-9] and humans.[6,10] Multiple clinical trials have demonstrated its safety and tolerability.[6,10] The compound achieved self-affirmed GRAS status (Generally Recognized as Safe) in the United States.
Health Canada Status: NPN Given in April 2025!
On April 16th, 2025, TSI Group was proud to announce that Hobamine® received a Natural Product Number (NPN) #80138909 with Health Canada, specifically their Natural and Non-Prescription Health Products Directorate (NNHPD). This is the first time they've issued an NPN issued for a 2-HOBA ingredient, meaning it is now fully approved for sale in Canada.
Dosage: 50-100mg/day
For optimal benefits, the recommended daily dose of Hobamine is 100 milligrams, with a minimum effective intake of 50 milligrams per day. This dosage has been studied in human trials, and is shown to be safe and well-tolerated. Safety research and efficacy studies are both covered in detail lower in this article.
Understanding Cellular Health: The Oxidative Stress Challenge
Our bodies contain trillions of cells, each one serving as a microscopic powerhouse that keeps us alive and functioning. These cells form our tissues, which build our organs, and ultimately create the complex systems that make up our body.
How Cells Power Our Lives
Inside each cell, tiny structures called mitochondria combine the food we eat with the oxygen we breathe to produce energy. This process, known as cellular respiration, powers everything from muscle contractions to brain function.

This informative graphic explains the dual nature of ROS (Reactive Oxygen Species) in cellular function. The balanced quadrant layout illustrates how ROS naturally forms in mitochondria and serves important signaling purposes when balanced, but leads to oxidative stress and cellular damage when levels become excessive – demonstrating why targeted approaches like Hobamine are more effective than broad-spectrum antioxidants.
However, this vital energy production comes with a catch: it generates reactive oxygen species (ROS) as a natural byproduct. While some ROS production is normal and even necessary for proper cell signaling and immune defense, excessive ROS can lead to a state called oxidative stress.[3-5]
The Challenge of Oxidative Stress

This educational slide breaks down the various lifestyle and environmental factors that contribute to cellular damage through oxidative stress. From pollution and radiation to poor nutrition, unhealthy habits, chronic stress, and even excessive exercise, the image provides a comprehensive overview of how everyday stressors can disrupt cellular health and accelerate aging processes at the molecular level.
Think of oxidative stress like rust forming on metal - it's a destructive process that can damage important cellular components. Several factors can trigger excessive ROS production:
- Environmental toxins and pollution
- Poor dietary choices
- Lack of quality sleep
- Physical and emotional stress
- Excessive exercise
- Natural aging processes
When ROS levels become too high, they can damage cellular proteins, lipids, and DNA. This damage triggers a cascade of harmful events, where the byproduct of one ROS-based reaction is another ROS, leading to a long-lasting, negative feedback loop. This includes the formation of highly reactive compounds like isolevuglandins (IsoLGs) that can further modify proteins and compromise cellular function.[3]
This cellular stress and damage can manifest in various ways throughout the body, affecting everything from immune function to cardiovascular health.[1,5] Even worse, many disease processes are also associated with increased ROS production, leading to a vicious negative feedback loop that must be curtailed to reclaim health.
The Antioxidant Paradox: Why Traditional Approaches Fall Short
For decades, the mainstream medical establishment has promoted antioxidants as a solution to oxidative stress. These compounds – like vitamin C, vitamin E, vitamin A (and beta-carotene), along with various polyphenols – show incredible promise in laboratory studies, neutralizing harmful free radicals and protecting cells from oxidative damage.
However, a fascinating phenomenon known as the "antioxidant paradox" emerged when researchers began conducting large-scale human trials: despite working remarkably well in test tubes and cell cultures, traditional antioxidants often fail to deliver meaningful benefits in living, breathing humans.[11-15]
Some interventions, in fact, even lead to significantly increased disease, cancer, and mortality![16-24]
Our understanding of these compounds -- and our prior pushes to use them en masse -- were clearly incomplete and misinformed in decades past. Thankfully, we've continued to learn over the years, and a better generation of dietary ingredients to support cellular health is now here.
Why Most Antioxidants Don't Work As Expected
Several factors contribute to this paradox:
- Antioxidants often can't reach therapeutic concentrations in target tissues
- Many antioxidants are broken down before they can reach their destination
- Broad-spectrum antioxidants can interfere with beneficial oxidative processes
- Some antioxidants become pro-oxidants at higher doses
- The metabolites of some antioxidants are worse than what they're scavenging for
The Problem with Blocking All Oxidation
Here's where things get interesting: while excessive oxidation is harmful, some oxidative processes are actually essential for normal cellular function. These include:
- Cell signaling pathways
- Immune system responses
- Exercise adaptation
- Various metabolic processes
Completely suppressing oxidation with traditional antioxidants is like trying to stop a leaky pipe by turning off water to the entire house – it might fix the immediate problem, but it creates new ones by disrupting normal function. And other times, it simply delays the inevitable until a later time -- when the dam eventually bursts.
This is why we need a more targeted approach – one that can selectively neutralize harmful oxidative byproducts while allowing beneficial oxidative processes to continue normally. This is where Hobamine's unique mechanism of action becomes so important. Before we get there, there's one more critical topic to cover.
Understanding Reactive Dicarbonyls: The IsoLG Challenge
When oxidative stress occurs in our cells, it doesn't just create ROS – it triggers a cascade of reactions that generate even more damaging compounds. Among the most problematic are reactive dicarbonyls, including isolevuglandins (IsoLGs), malondialdehyde (MDA), and 4-hydroxynonenal (HNE), which can rapidly bind to proteins, lipids, and DNA, leading to cellular dysfunction, inflammation, and long-term damage.[3]
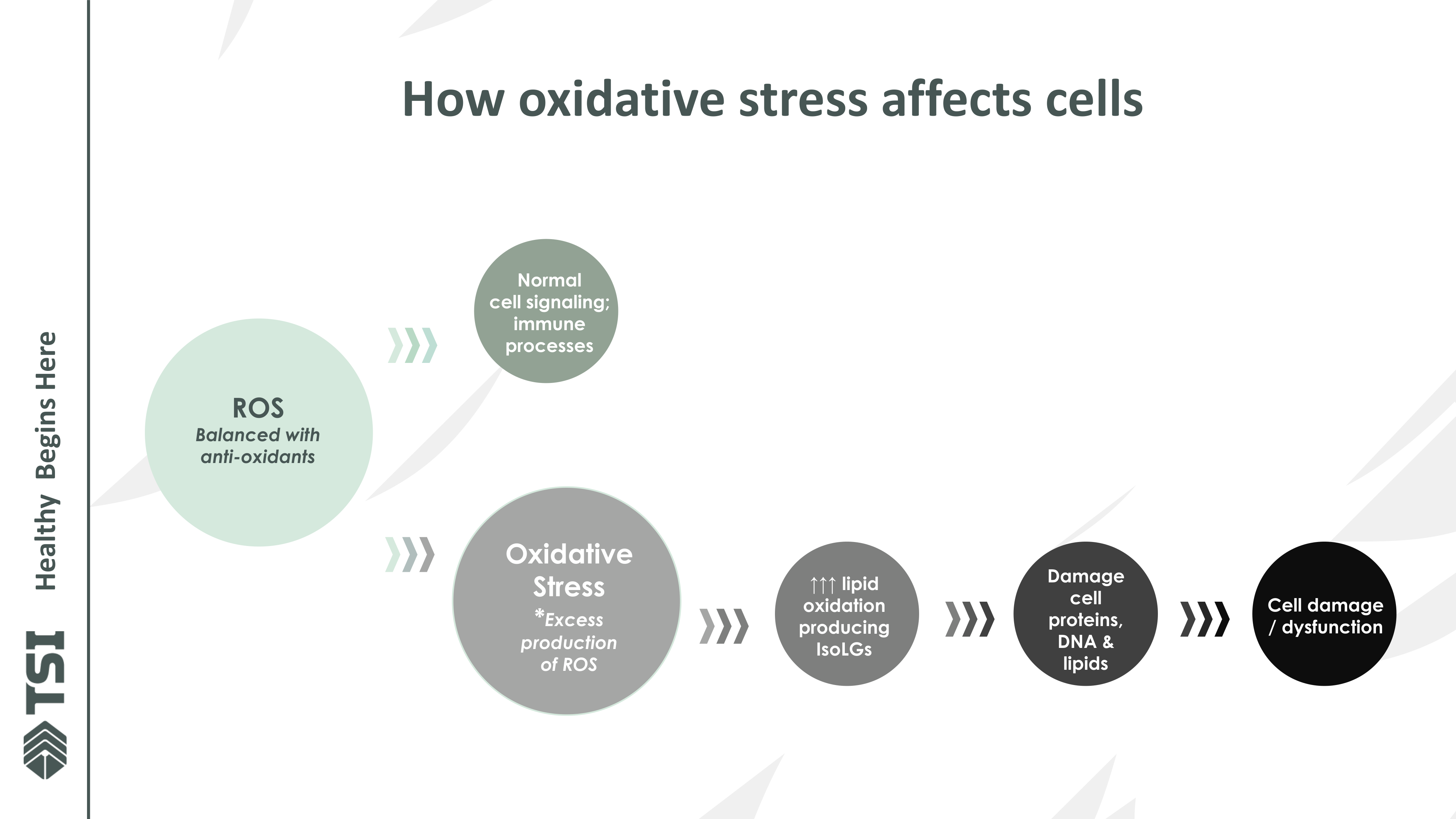
This flow diagram visualizes the progression from balanced ROS to full cellular dysfunction. Beginning with normal ROS levels that support immune function, the chart shows how excessive oxidative stress triggers lipid oxidation and the production of harmful IsoLGs, ultimately leading to protein, DNA, and lipid damage. This pathway demonstrates why intercepting this cascade at the right point is crucial for maintaining cellular health.
What Makes IsoLGs So Dangerous?
IsoLGs are unique among reactive dicarbonyls because of their extreme reactivity with cellular proteins. Once formed, they can:[3,5,25]
- Rapidly modify proteins within seconds
- Create cross-links between proteins
- Alter protein function
- Trigger inflammatory responses
- Generate modified proteins that the immune system may recognize as foreign
Dicarbonyl formation is accelerated by factors like poor diet, stress, pollution, excessive exercise, and aging, making them a major contributor to oxidative stress-related conditions.[5]
A New Approach: Beyond Traditional Antioxidants
Given the limitations of traditional antioxidants and the specific threat posed by reactive dicarbonyls like IsoLGs, a more intelligent approach is needed. Rather than trying to prevent all oxidation – which we now know can be counterproductive – the focus should be on neutralizing these highly reactive compounds before they can damage cellular components.
This is where Hobamine's innovative mechanism sets it apart: instead of broadly suppressing oxidative processes, it specifically neutralizes reactive dicarbonyls before they can cause cellular damage. This selective approach allows normal cellular processes to continue unimpeded while preventing the accumulation of harmful modified proteins that can lead to cellular dysfunction.
How Hobamine Works
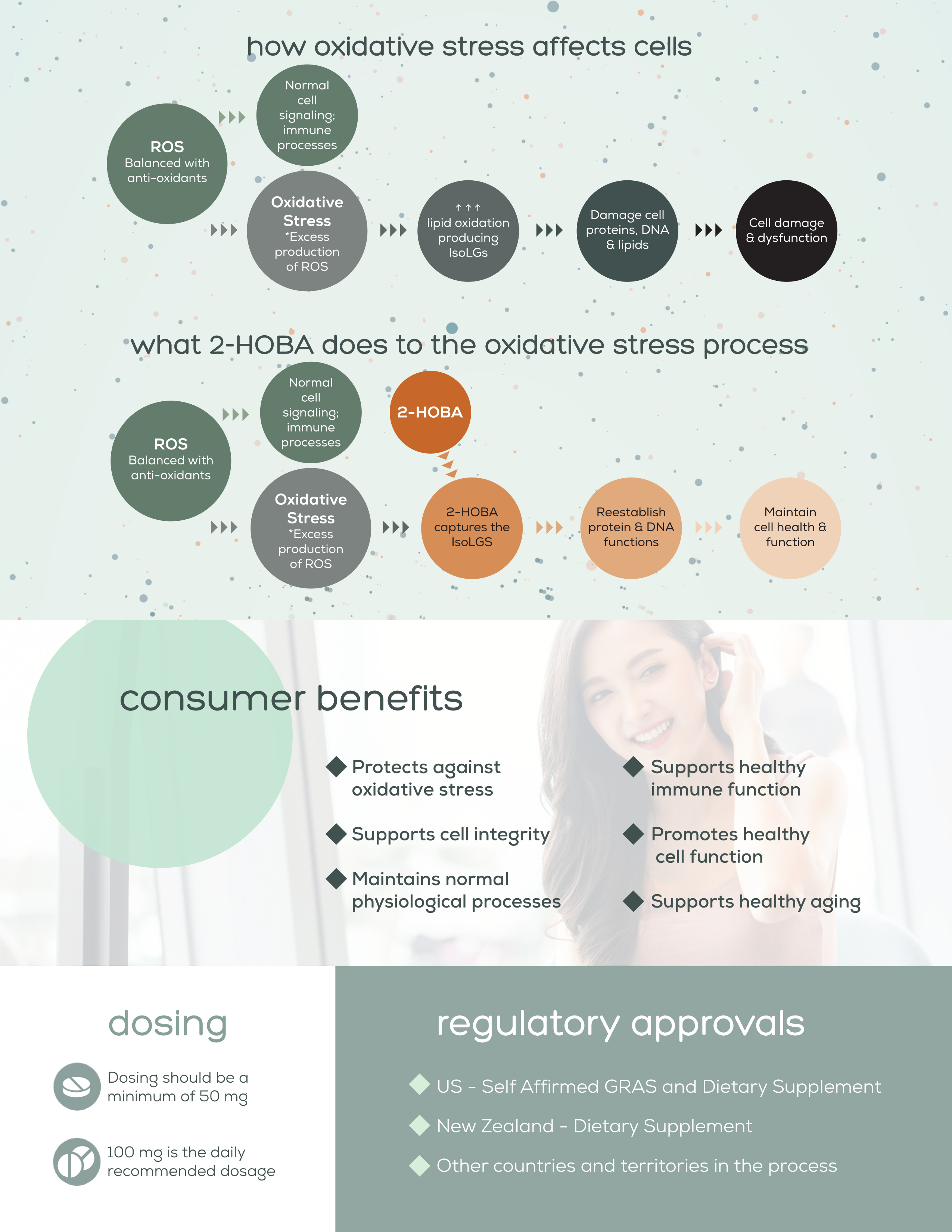
This infographic illustrates how oxidative stress impacts cellular health and how 2-HOBA (Hobamine) uniquely intervenes in this process. While traditional antioxidants work broadly, Hobamine specifically targets reactive dicarbonyls like IsoLGs before they can damage proteins and DNA. The bottom section highlights key consumer benefits, recommended dosing, and regulatory status across different markets.
Hobamine (2-HOBA) represents a breakthrough approach to cellular protection through its unique mechanism targeting isolevuglandins (IsoLGs), the problematic lipid peroxidation byproducts described above.
Here's how this revolutionary compound works to maintain cellular health:
-
The Chemistry Behind 2-HOBA
When it comes to cellular protection, timing and targeting are everything. Researchers have spent years developing strategies to selectively scavenge these problematic compounds before they disrupt proteins.[26] 2-HOBA does just that.
The key lies in Hobamine's chemical structure: it contains a specific molecular arrangement (a 2-aminomethylphenol group) that allows it to rapidly react with and neutralize IsoLGs before they can bind to and damage proteins, DNA, and other cellular components.[3,5]
-
Lightning-Fast Protection
What makes Hobamine particularly special is its reaction speed. Studies have shown that Hobamine reacts with IsoLGs approximately 2,000 times faster than cellular proteins like lysine, effectively intercepting these damaging molecules before they can cause harm.[3]
-
Preserving Normal Cellular Function
One of the most important aspects of Hobamine's mechanism is that it doesn't interfere with normal cellular processes. Unlike traditional antioxidants that can sometimes disrupt beneficial oxidative signaling, Hobamine specifically targets the harmful IsoLGs while allowing normal cellular functions to continue unimpeded.[3,5]
This selective targeting means that:
- Normal cellular signaling remains intact
- Beneficial oxidative processes continue as needed
- Only harmful IsoLGs are neutralized
- Cellular homeostasis is maintained
-
Beyond IsoLGs: Additional Protection
While Hobamine's primary mechanism involves IsoLG scavenging, research has shown it can also neutralize other harmful reactive compounds like malondialdehyde (MDA) and 4-oxo-nonenal (ONE).[3,5]
More specifically:[3]
- Malondialdehyde (MDA): Hobamine prevents MDA from forming toxic protein cross-links, which can drive inflammation.
- 4-Oxo-Nonenal (ONE): Hobamine traps ONE through a multistep reaction, forming a stable adduct before it can damage proteins.
This multi-targeted approach helps provide comprehensive cellular protection while maintaining the specificity that makes Hobamine unique among cellular protective compounds.
So how does it work? This brings us to the clinical research on 2-HOBA:
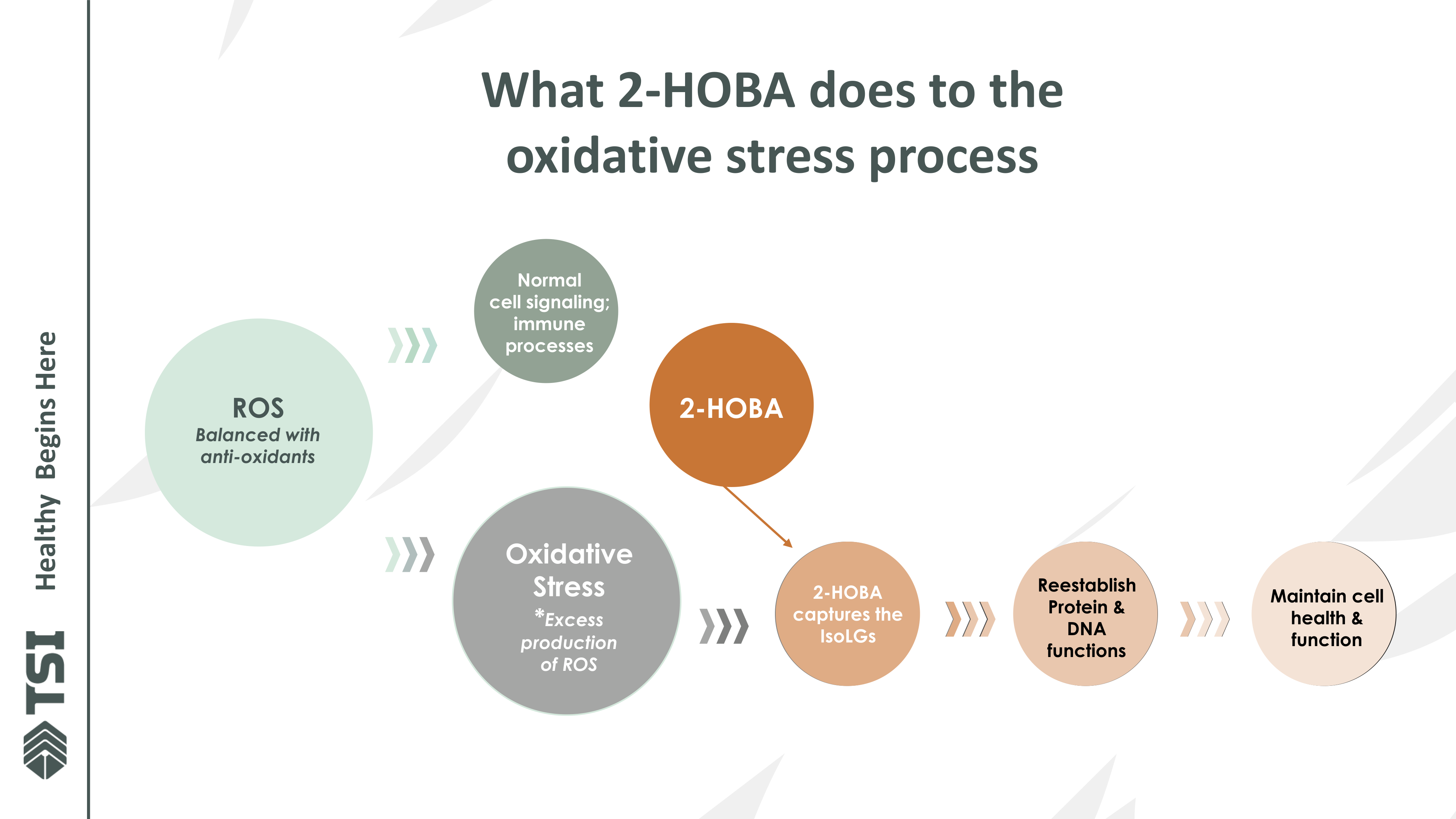
This illustrated workflow diagram shows how 2-HOBA uniquely addresses oxidative stress. The left side depicts normal ROS balance supporting immune function. The central portion shows how oxidative stress leads to excess ROS production. The right side demonstrates 2-HOBA's specific mechanism - rather than broadly suppressing all oxidation, it selectively captures harmful IsoLGs before they can damage cellular components, allowing healthy cellular functions to continue while preventing damage.
Clinical Research Behind Hobamine
Hobamine is supported by three human clinical studies,[1,6,10] which are backed by numerous preclinical animal trials[5,25,27-31] as well as earlier cell/biochemical studies.[3,4] Here are some of the highlights:
-
Safety and Pharmacokinetics of 2-HOBA in Human Clinical Research (Pitchford 2019)
Now that we understand what makes 2-HOBA unique, let's explore how it performs in human research. The first major milestone was a groundbreaking clinical trial that investigated its safety and absorption in humans.[6]
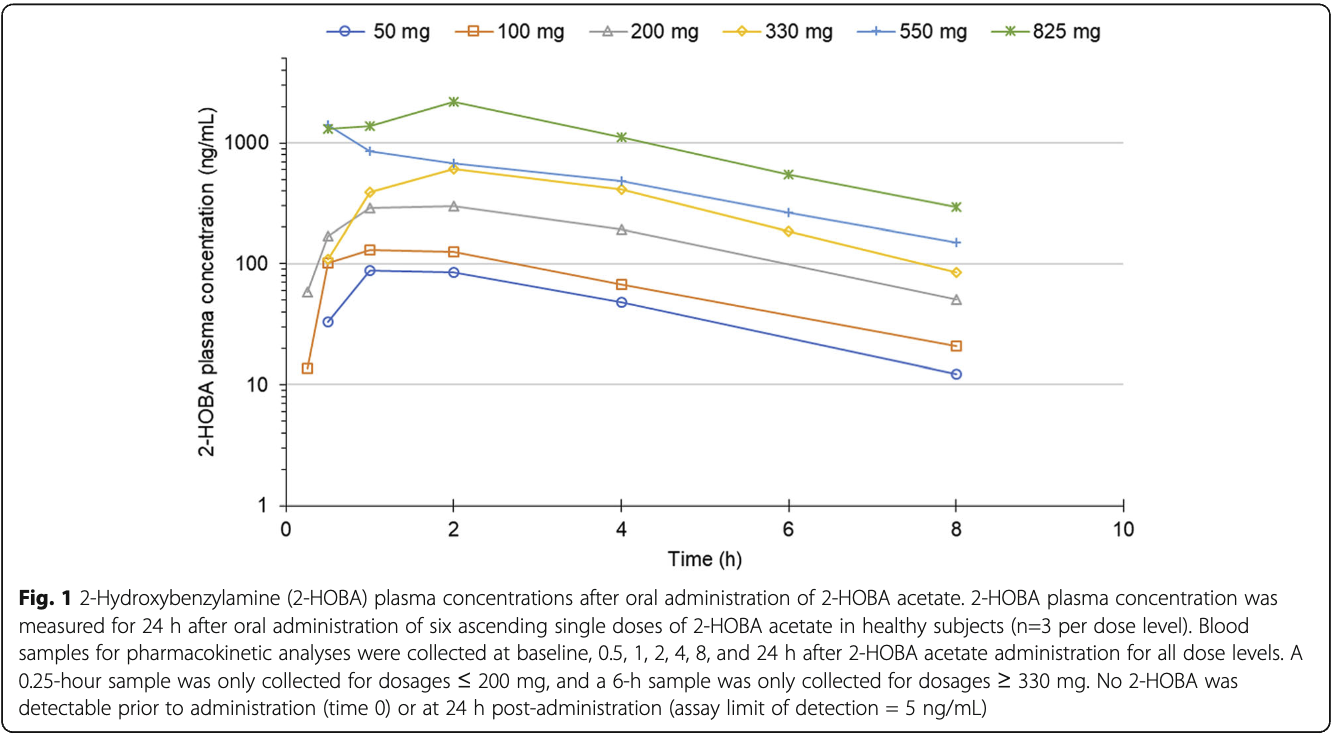
This scientific graph from a clinical trial illustrates how different doses of 2-HOBA (Hobamine) are absorbed and processed in the human body. The chart plots plasma concentrations over an 8-hour period following administration of six different dosages (50mg to 825mg). All doses show rapid absorption within 1-2 hours, followed by a consistent elimination pattern. The dose-dependent response demonstrates predictable pharmacokinetics, with higher doses yielding proportionally higher blood levels, supporting the 50-100mg daily dosing recommendation for supplements.[6]
Study Design and Methods
Researchers conducted an open-label, single ascending dose trial with 18 healthy volunteers. The study tested six different doses of 2-HOBA acetate, starting at 50mg and increasing up to 825mg. Each dose was carefully evaluated for safety before moving to the next level.[6]
Safety Profile and Tolerability
The results were incredibly promising for 2-HOBA's development:[6]
- No serious adverse events were reported
- No clinically significant changes occurred in vital signs, ECG readings, or lab tests
- All reported side effects were mild and considered unlikely to be related to 2-HOBA
- No dose-dependent increases in side effects were observed
Absorption and Processing
The study revealed important details about how our bodies process 2-HOBA:[6]
- Rapid absorption, reaching peak levels in 1-2 hours
- Consistent half-life of approximately 2 hours across all doses
- Predictable dose-dependent increases in blood levels
- Efficient elimination from the body
Research Implications
This first human trial established several crucial points for Hobamine:[6]
- Safety confirmation at single doses up to 825mg
- Predictable absorption and processing by the body
- Well-tolerated across a range of doses
- Foundation for future research into daily supplementation
While this study focused on single doses in healthy adults, it opened the door for further research into long-term use and specific health applications. The researchers noted that these findings support continued development of 2-HOBA as a nutritional supplement.
-
Validating Long-Term Safety Through Multiple Dosing (Pitchford 2020)
Building upon the initial single-dose study, researchers conducted a comprehensive 15-day trial to evaluate how the body handles repeated exposure to 2-HOBA acetate.[10]
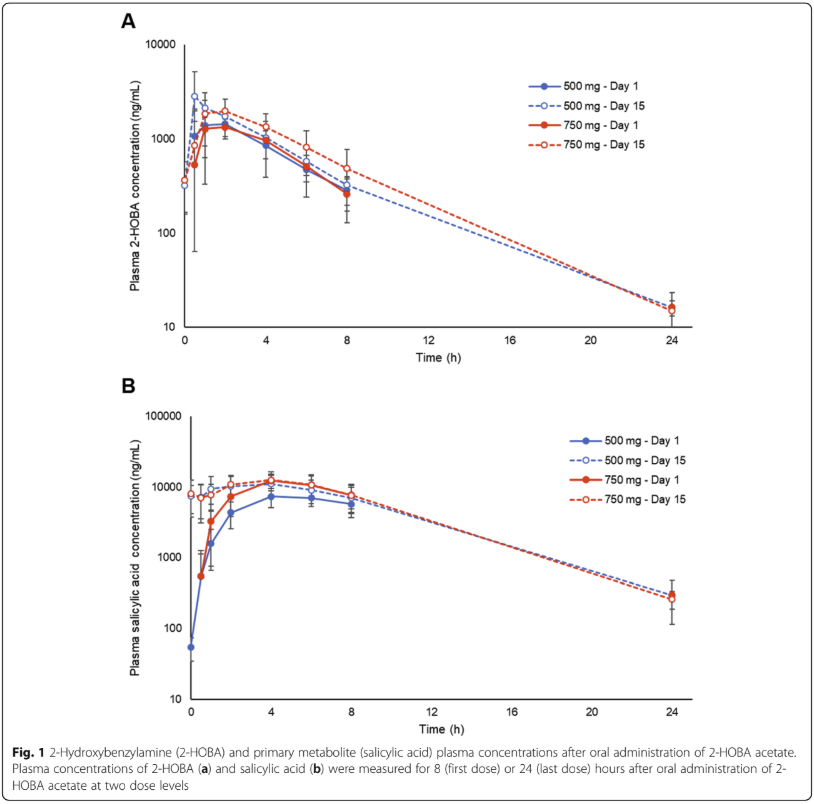
This dual-graph comparison tracks both 2-HOBA (panel A) and its primary metabolite, salicylic acid (panel B), over a 24-hour period. The study measured plasma concentrations after administering either 500mg or 750mg doses on both day 1 and day 15 of treatment. The remarkably similar profiles between first and final doses indicate no concerning accumulation or tolerance development with repeated administration. Both compounds reach peak levels within 1-4 hours and are cleared from the system within 24 hours, supporting a multiple-dose-per-day supplementation strategy for optimal coverage.[10]
Study Design and Methods
The research team designed a rigorous double-blind, placebo-controlled trial once again involving 18 healthy volunteers. Participants received either placebo or 2-HOBA acetate at doses of 500mg or 750mg three times daily over a 15-day period.[10]
Safety Findings and Tolerability
The results strongly supported 2-HOBA's safety profile. Throughout the study, researchers observed:[10]
- No serious adverse events occurred during the trial period. While some participants reported mild effects like headaches (affecting 33% across all groups, including placebo), none were determined to be related to 2-HOBA supplementation.
- No clinically significant changes in vital signs, ECG readings, or laboratory parameters.
Brain Barrier Penetration
In a notable finding, researchers detected 2-HOBA in cerebrospinal fluid samples, with concentrations reaching 34-74% of plasma levels. This discovery suggests that 2-HOBA can cross the blood-brain barrier, opening up possibilities for supporting neurological health.[10]
Anti-Inflammatory Safety Check
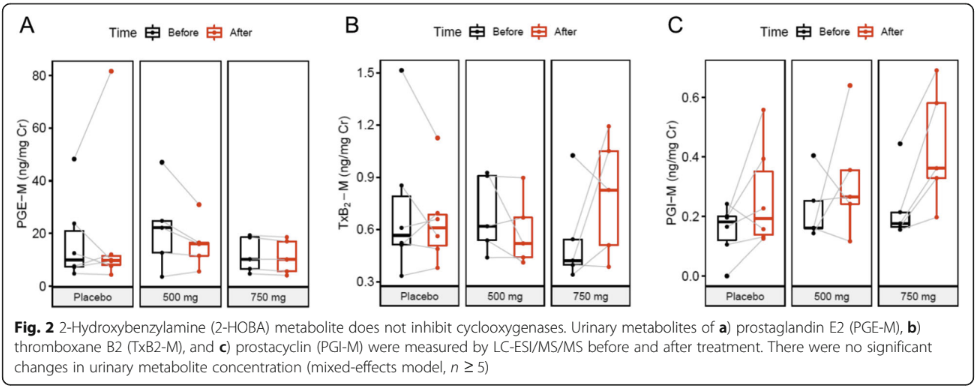
One potential concern with compounds that affect inflammatory pathways is their impact on normal protective inflammation. The research team carefully monitored this by measuring markers of cyclooxygenase function - a crucial enzyme family involved in inflammatory responses. The results showed that 2-HOBA did not interfere with normal cyclooxygenase activity, suggesting it allows beneficial inflammatory processes to continue unimpeded.[10]
This three-panel box plot analysis demonstrates that Hobamine doesn't interfere with normal cyclooxygenase enzyme activity, unlike many anti-inflammatory compounds. The graphs measure urinary metabolites of prostaglandin E2 (PGE-M), thromboxane B2 (TxB2-M), and prostacyclin (PGI-M) before and after treatment with either placebo, 500mg, or 750mg of 2-HOBA. The absence of significant changes confirms that Hobamine selectively targets harmful reactive dicarbonyls without disrupting beneficial inflammatory processes, demonstrating its safety advantage over traditional antioxidant approaches.[10]
This pivotal study strengthened the safety profile of 2-HOBA and paved the way for the next trial, and its development as a dietary supplement. The research demonstrated that even at higher doses taken multiple times daily, 2-HOBA maintains its strong safety profile while showing promising signs of reaching key tissues, including the brain.
-
Efficacy in Humans: The Hobamine Inflammation and Biomarker Study (Rathmacher 2023)
A groundbreaking NIH-funded study published in 2023 has revealed Hobamine's powerful effects on immune system function and inflammatory markers. This research provides the first direct evidence of how 2-HOBA supplementation can positively influence human immune health.[1]
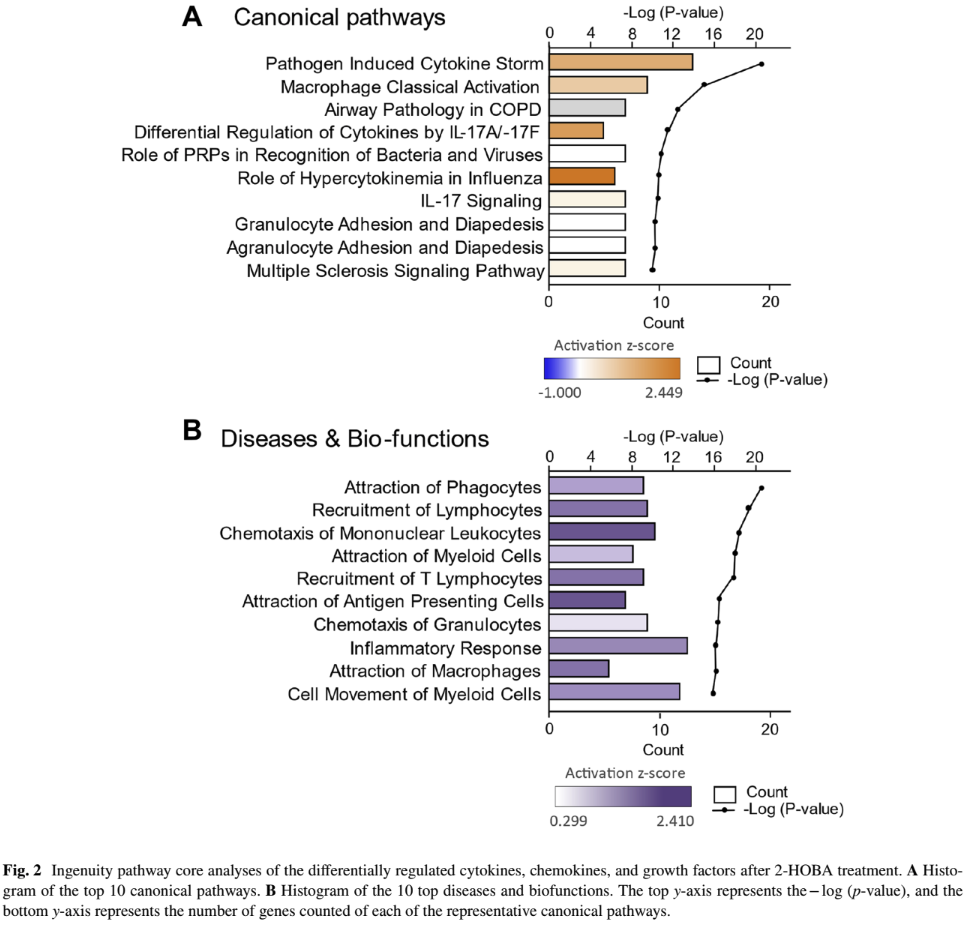
This dual-panel analysis from a 2-HOBA clinical study reveals the compound's significant impact on immune system regulation. Panel A shows how 2-HOBA influences canonical pathways, with notable effects on cytokine signaling and immune cell activation. Panel B illustrates its effects on specific biological functions, particularly enhancing immune cell recruitment, movement, and inflammatory balance. The statistical significance (P-values) and activation scores demonstrate that Hobamine affects multiple aspects of immune function in a coordinated manner, supporting its role as a cellular health protector.[1]
Study Design and Methods
The research team conducted a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial that included both younger and older healthy adults. Participants received either a placebo or 2-HOBA acetate at doses of 500mg or 750mg three times daily over a 15-day period.
Using advanced protein analysis technology, the researchers measured 92 different inflammatory proteins before and after supplementation. Of these, 15 key biomarkers showed significant changes in response to 2-HOBA supplementation.[1]
Key Findings and Impact
The results showed that 2-HOBA supplementation significantly affected several crucial immune system proteins. Most notably, the study found increases in CCL19, IL-12β, and TNFβ[1] - proteins that play essential roles in maintaining healthy immune function and cellular protection.
One of the most striking findings was the dramatic increase in CCL19, a protein that helps regulate immune cell movement and function. This protein showed nearly a 20-fold increase following 2-HOBA supplementation.[1]
This data visualization presents the scientific evidence from human clinical trials showing Hobamine's significant effects on immune system markers. The bar graphs display statistical differences between control and 2-HOBA groups across multiple immune proteins, with clear indicators of statistical significance. This raw data underscores the compound's scientifically-validated benefits for supporting healthy immune function.[1]
The study also revealed a significant decrease in TWEAK, a protein associated with inflammation and cellular stress. This reduction suggests that 2-HOBA may help maintain a balanced inflammatory response.[1]
Pathway Analysis Reveals Broader Benefits
Using sophisticated pathway analysis software, the researchers identified several key biological processes affected by 2-HOBA supplementation. The analysis showed improvements in immune cell recruitment, movement, and function - all critical aspects of a healthy immune system.[1]
This comprehensive grid details five critical biomarkers (CCL19, IL-10, TWEAK, IL-12B, and TNFB) influenced by Hobamine supplementation. Each section explains the biomarker's function in immune health and how 2-HOBA positively impacts it. The most striking finding is the nearly 20-fold increase in CCL19, an important anti-inflammatory protein essential for maintaining healthy T-cell and B-cell functions.
These findings support 2-HOBA's role as a selective scavenger of harmful compounds, showing it can positively influence immune function without disrupting normal cellular processes.
-
Supporting Preclinical Research: Disease Models
Long before Hobamine became available as a supplement, researchers were investigating 2-HOBA's effects in various disease models. Beyond the three toxicology studies performed in animals,[7-9] two early groundbreaking studies helped establish its potential for supporting both cognitive and cardiovascular health, and two more have been recently added.
It is important to note that the following discussion of 2-HOBA research is for educational purposes only and does not pertain to the intended use of Hobamine as a dietary supplement. While these studies provide valuable insights into the biological role of 2-HOBA, dietary supplements containing Hobamine are intended to support overall health and wellness in healthy populations. Any references to disease models or related findings do not imply disease-related applications for dietary supplements. Hobamine, as a dietary ingredient, is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
Cognitive Function & Memory Support (Davies 2011)
In another groundbreaking study, researchers investigated 2-HOBA's effects on cognitive function using a specialized mouse model of cognitive decline.[27]
The research team used mice carrying the human ApoE4 gene - a genetic variant associated with increased cognitive challenges. These mice typically show declining memory performance as they age. However, when given 2-HOBA in their drinking water starting at 4 months of age, the mice maintained significantly better spatial working memory compared to untreated mice.[27]
Importantly, 2-HOBA supplementation:[27]
- Did not affect the animals' growth, strength, or survival
- Specifically protected working memory without impacting other motor functions
- Was well-tolerated over long-term administration
This research suggested that 2-HOBA's ability to protect against isoketal damage may help support healthy cognitive function.
Hypertension & Immune System Support (Kirabo 2014)
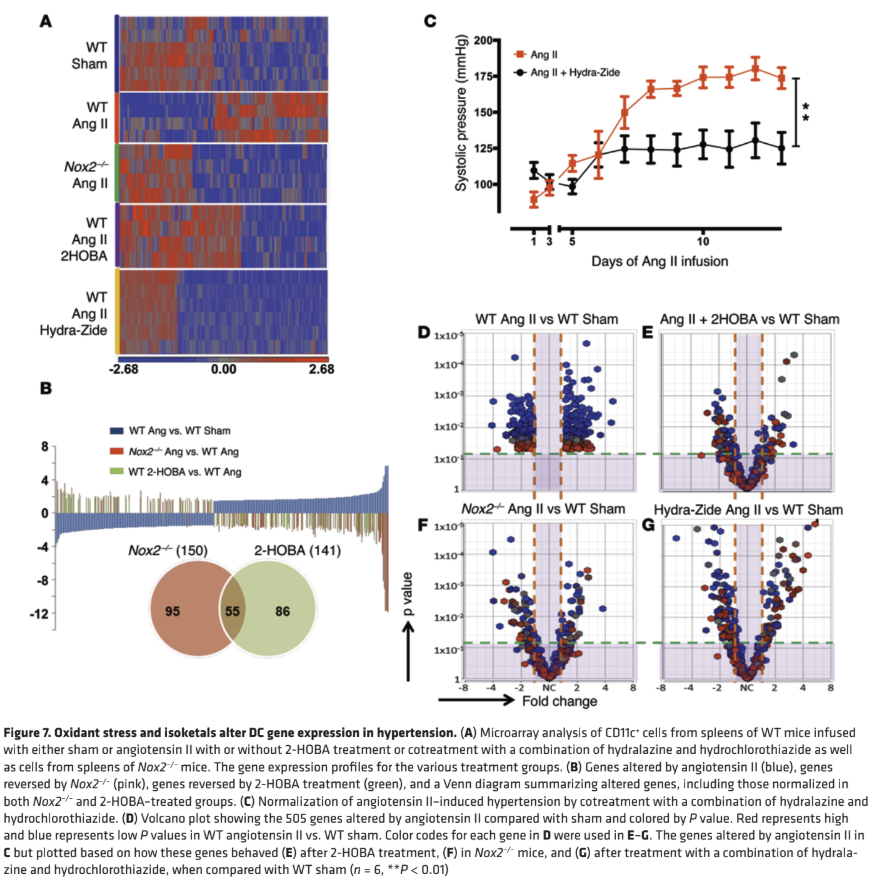
In a pivotal 2014 study published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, researchers found that 2-HOBA could help maintain healthy blood pressure levels by supporting normal immune function.[25]
This multi-panel figure demonstrates how 2-HOBA affects gene expression in a hypertension model. Panel A shows microarray analysis revealing how angiotensin II alters gene expression patterns, which are partially normalized by 2-HOBA treatment. Panel B quantifies these changes, with a Venn diagram showing the 55 genes normalized by both Nox2⁻/⁻ and 2-HOBA treatments. Panel C illustrates the dramatic blood pressure reduction achieved with 2-HOBA plus hydralazine/hydrochlorothiazide. Panels D-G visualize the specific gene expression changes through volcano plots, revealing 2-HOBA's ability to counter angiotensin II-induced alterations similar to Nox2 deletion.[25]
The researchers discovered that during states of high blood pressure, certain immune cells called dendritic cells accumulate high levels of isolevuglandins (IsoLG). When these IsoLGs-modified dendritic cells interact with T cells (another type of immune cell), they trigger a cascade of events that can affect blood pressure regulation.[25]
The study found that treating mice with 2-HOBA prevented this accumulation of IsoLGs in dendritic cells. By doing so, 2-HOBA helped maintain normal immune function and healthy blood pressure levels.
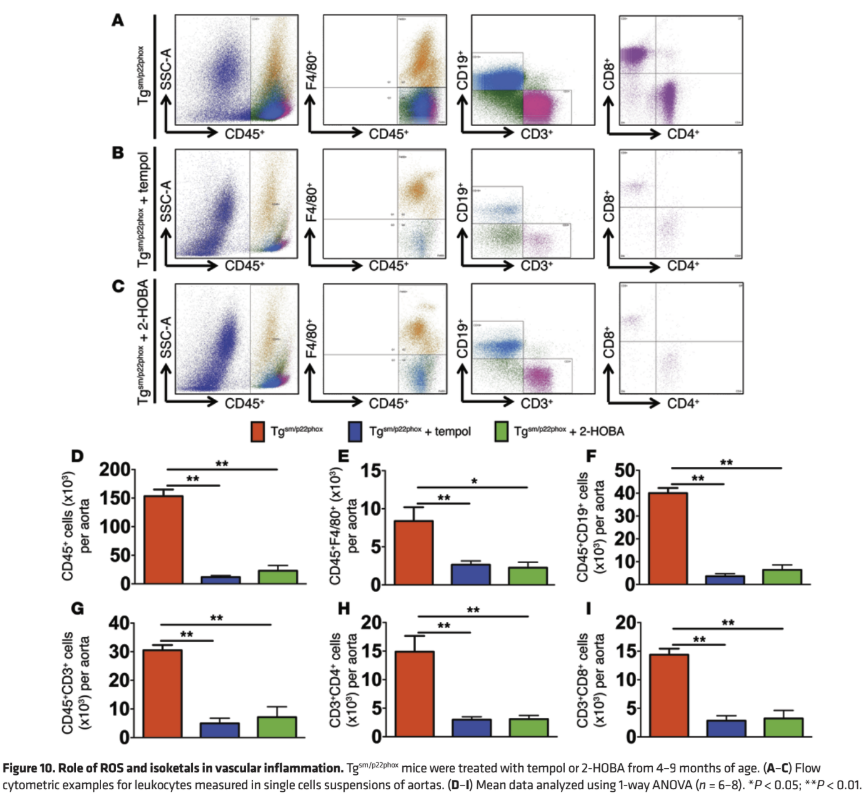
Hypertension & Vascular Inflammation (Wu 2016)
In a landmark 2016 study published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, researchers demonstrated that 2-HOBA prevented vascular inflammation, aortic stiffening, and hypertension in mice with chronic vascular oxidative stress.[29]
This detailed figure demonstrates how 2-HOBA affects vascular inflammation by analyzing immune cell populations in the aortas of mice. Panels A-C show flow cytometry data comparing untreated, tempol-treated, and 2-HOBA-treated mice, revealing how 2-HOBA reduces immune cell infiltration in vascular tissue. Panels D-I quantify these effects across multiple immune cell types, with the orange bars (untreated) showing significantly higher levels of inflammatory cells compared to the green bars (2-HOBA treatment). The data proves that 2-HOBA treatment effectively reduces vascular inflammation similar to the reference compound tempol.[29]
The study found that reactive oxygen species (ROS) trigger the formation of isoketal protein adducts, which accumulate in dendritic cells and promote T cell activation. This leads to infiltration of immune cells into vascular tissues, producing inflammatory cytokines that cause collagen deposition and aortic stiffening. Treatment with 2-HOBA normalized blood pressure and prevented vascular inflammation,[29] further establishing the connection between oxidative stress, inflammation, and hypertension, and confirming 2-HOBA's protective effects.
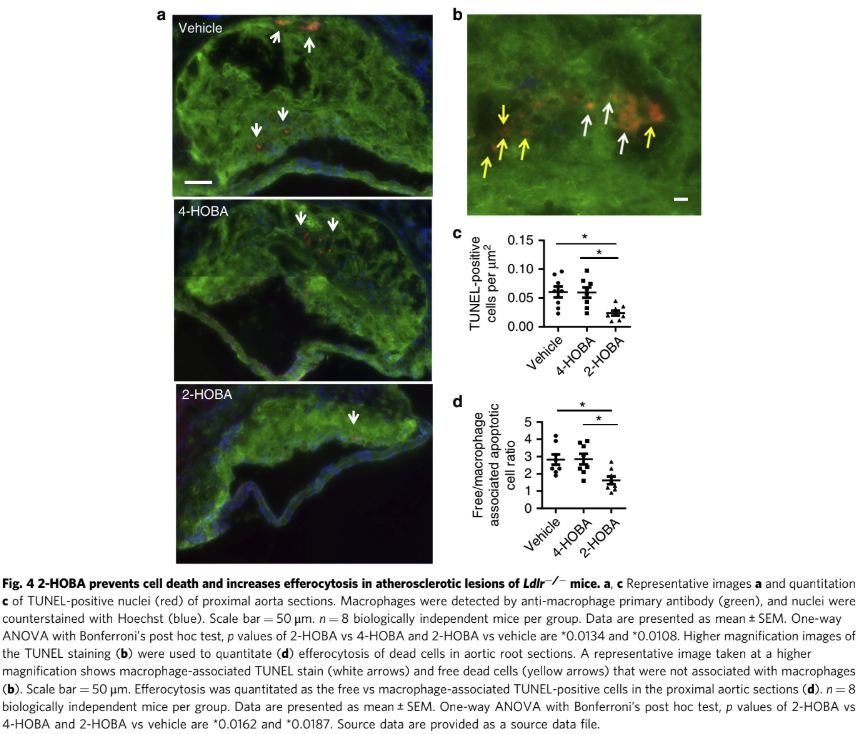
Reduction of Atherosclerosis in Mice (Tao 2020)
In a study published in 2020, researchers discovered that 2-HOBA could significantly reduce atherosclerosis development in mice lacking the LDL receptor (Ldlr−/−).[5] The findings were remarkable - treatment with 2-HOBA decreased atherosclerosis by 60% in these mice without affecting plasma cholesterol levels.
This microscopy figure demonstrates how 2-HOBA protects against cellular damage in atherosclerotic lesions. Panel A shows representative images comparing vehicle, 4-HOBA, and 2-HOBA treatment groups, with 2-HOBA showing significantly fewer TUNEL-positive nuclei (indicating cell death). Panel B highlights the difference between macrophage-associated TUNEL staining (white arrows) and free dead cells (yellow arrows). Panels C and D quantify these observations, confirming that 2-HOBA significantly reduces both TUNEL-positive cells and efferocytosis compared to vehicle and 4-HOBA controls.[5]
More specifically, the study demonstrated that 2-HOBA treatment reduced the formation of harmful MDA and IsoLG adducts in atherosclerotic lesions compared to control mice. This reduction in oxidative damage was accompanied by decreased inflammation and significantly less necrotic plaque formation - key markers of cardiovascular disease progression.[5]
Protection Against Gastric Disease (Gobert 2023)
Building on previous findings, a 2023 study investigated 2-HOBA's effects on gastric cancer development.[28] Using a mouse model of H. pylori infection, researchers found that 2-HOBA treatment significantly reduced both gastric dysplasia and carcinoma development.
The study revealed that mice treated with 2-HOBA showed markedly lower levels of gastric inflammation and DNA damage compared to untreated infected mice. Importantly, this protection occurred without affecting H. pylori colonization levels, suggesting 2-HOBA works by preventing the damaging effects of inflammation rather than through direct antimicrobial action.[28]
This correlation plot demonstrates the relationship between 2-HOBA concentration in gastric tissues and the extent of dysplasia and cancer development. The graph shows a clear negative correlation (r = -0.5524), indicating that higher tissue concentrations of 2-HOBA are associated with lower rates of dysplasia and cancer. This inverse relationship, while just missing traditional statistical significance (P = 0.0615), strongly suggests 2-HOBA's protective effects against gastric disease progression in the study model.[28]
These studies demonstrate how Hobamine can have profound effects across multiple disease models. These promising results in animal studies laid the groundwork for the human trials investigating Hobamine's safety and efficacy in humans. Let's examine what the clinical trials reveal about the safety of using 2-HOBA as a dietary supplement.
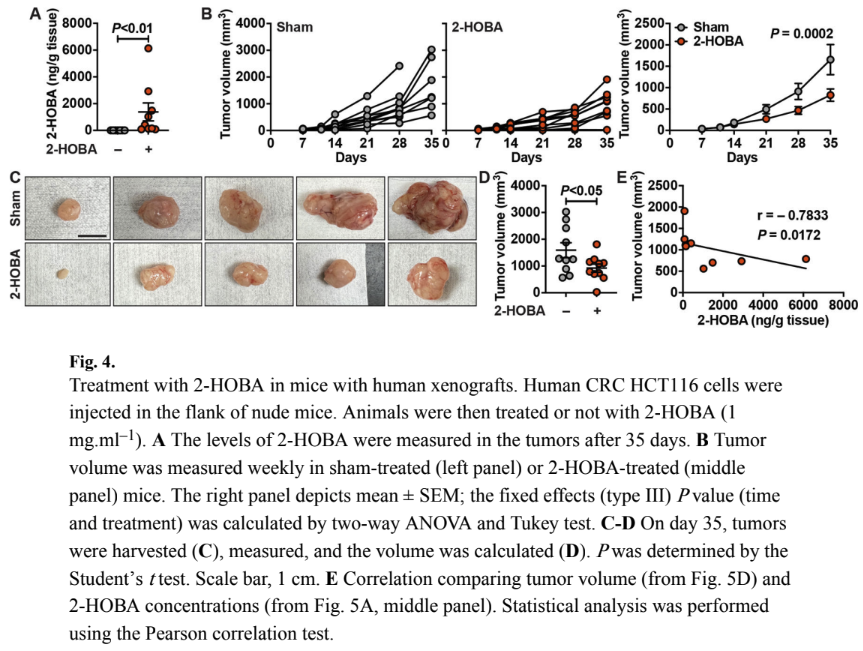
Protection Against Colorectal Cancer (Gobert 2023)
That same year, the above team also demonstrated 2-HOBA's protective effects against colorectal cancer (CRC).[30] The research found that 2-HOBA is bioavailable in the colon after oral administration and reduced tumor growth in multiple CRC models.
Most impressively, 2-HOBA reduced tumorigenesis in both colitis-associated carcinogenesis and sporadic CRC driven by APC gene deletion. The compound also significantly slowed growth of human colorectal cancer cell xenografts, with a tumor growth inhibition rate of 42%.[30]
This multi-panel figure demonstrates 2-HOBA's effects on colorectal cancer xenografts. Panel A confirms that 2-HOBA successfully reaches tumor tissues. Panel B tracks tumor volume over time, showing significantly slower growth in 2-HOBA-treated mice compared to the sham group (P = 0.0002). Panel C provides visual evidence with photographs of harvested tumors, clearly showing smaller tumors in the 2-HOBA group. Panel D quantifies this difference statistically (P < 0.01), while Panel E reveals a strong negative correlation (r = -0.7833) between tumor volume and 2-HOBA concentration in tissues.[30]
Mechanistically, 2-HOBA appears to work by decreasing activation of the NRF2 pathway and reducing dicarbonyl electrophile damage to cellular components. Importantly, 2-HOBA treatment had no negative impact on gut microbiome composition.[30]
The researchers concluded that 2-HOBA represents a promising natural compound for both prevention and treatment of colorectal cancer, potentially extending its benefits beyond cognitive and cardiovascular applications.
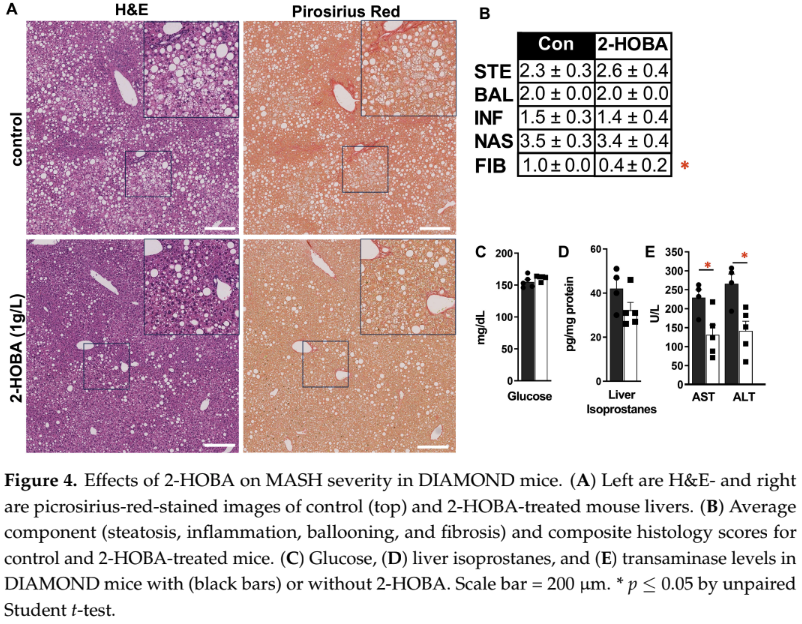
Liver and Metabolic Health (Cheung-Flynn 2025)
A recent 2025 study found that 2-HOBA improved metabolic-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) in two different mouse models.[31]
Researchers discovered that 2-HOBA significantly reduced liver fibrosis scores, lowered liver transaminases (AST and ALT) by over 40%, improved NAFLD activity scores, and decreased inflammatory markers. The treatment also reduced serum F2-isoprostanes by 30%, indicating less oxidative stress. The study identified that 2-HOBA works by scavenging reactive dicarbonyl electrophiles that form during lipid peroxidation, preventing damage to proteins and DNA in liver cells.[31]
This figure shows 2-HOBA's beneficial effects on liver health in the DIAMOND mouse model. Panel A presents liver histology with H&E and picrosirius red staining, comparing control (top) and 2-HOBA-treated (bottom) mice. Panel B quantifies the NASH scoring components, revealing a significant reduction in fibrosis scores with 2-HOBA treatment. Panels C-E show metabolic markers, with 2-HOBA treatment significantly reducing liver isoprostanes (a marker of oxidative stress) and liver enzymes AST and ALT, indicating improved liver function and reduced inflammation.[31]
This suggests 2-HOBA could potentially serve as a therapeutic agent for liver conditions characterized by oxidative stress and inflammation.
Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics
In addition to three animal-based safety studies,[7-9] Hobamine (2-HOBA) has now been studied in humans through three groundbreaking clinical trials described above, demonstrating an excellent safety profile that positions it well for use as a dietary supplement.[1,6,10]
Safety and Tolerability
The safety data from these trials is assuring. In single-dose studies with doses up to 825mg and multiple-dose studies using 500mg or 750mg three times daily for 15 days, Hobamine demonstrated remarkable tolerability. No serious adverse events were reported in any of the trials, and the few mild side effects that occurred were considered unlikely to be related to Hobamine.[6]
The most commonly reported effects across all studies include:
- Mild and transient headaches (affecting about 33% of participants, including those on placebo)
- Occasional gastrointestinal effects like nausea or bloating
- Mild sleepiness in some participants
Importantly, there were no clinically significant changes in vital signs, ECG readings, or laboratory parameters across any of the studies. The safety profile remained consistent even with extended daily use.[10]
Pharmacokinetic Properties
Hobamine demonstrates favorable pharmacokinetic properties that support its use as a dietary supplement. The compound is rapidly absorbed, reaching peak plasma levels within 1-2 hours of ingestion. It has a relatively short half-life of approximately 2-3 hours, suggesting good clearance from the body.[6]
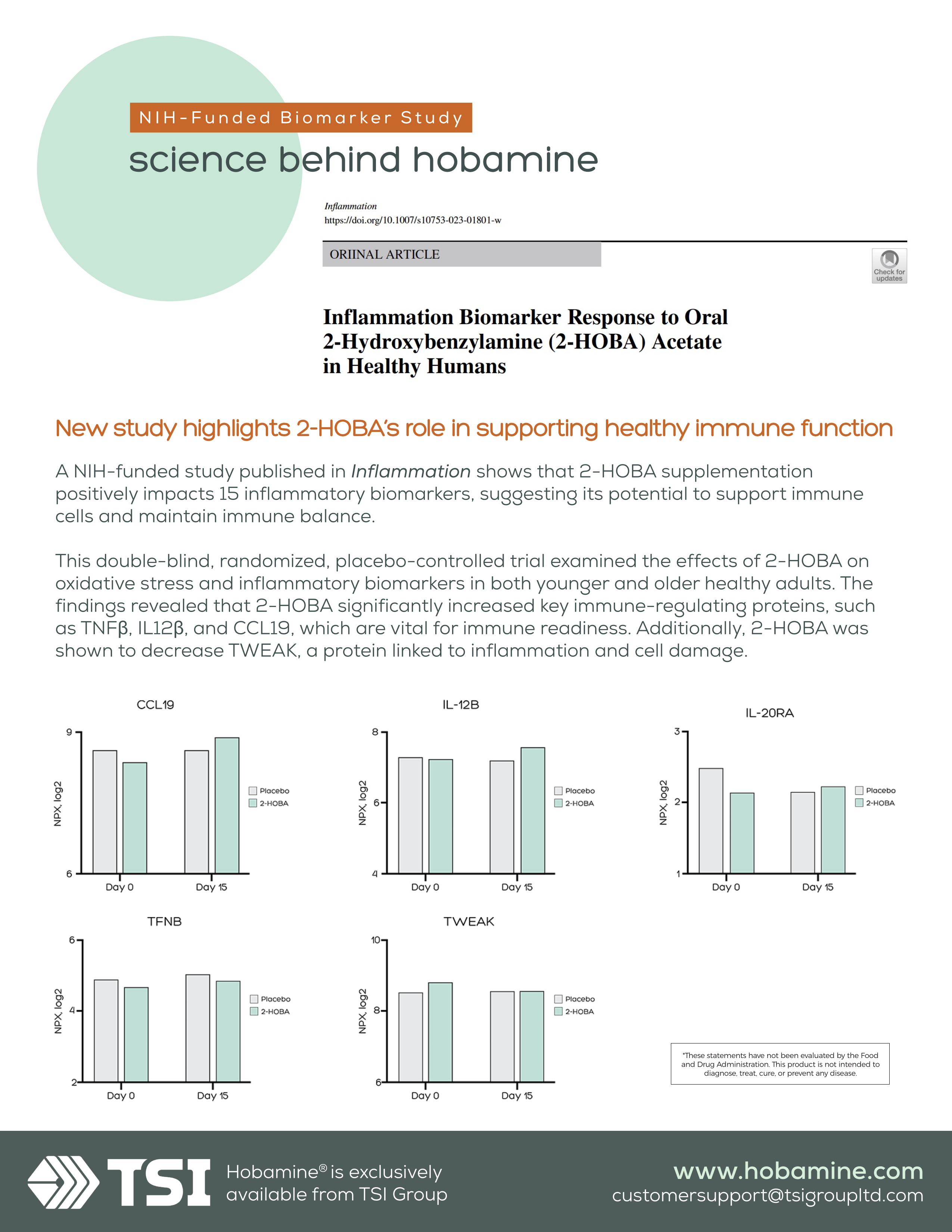
The graphic showcases results from the NIH-funded clinical study published in the journal Inflammation, demonstrating how 2-HOBA positively influences key immune system biomarkers. Bar charts reveal Hobamine's effects on important inflammatory proteins including CCL19, IL-12β, TNFβ, and TWEAK, proving its efficacy in supporting balanced immune function in human subjects through a well-designed, double-blind trial.
When taken multiple times per day, Hobamine shows predictable accumulation patterns, with steady-state levels achieved that maintain therapeutic coverage. The compound also demonstrates the ability to cross the blood-brain barrier, with cerebrospinal fluid levels reaching 34-74% of plasma concentrations.[10]
With several preclinical trials and these three human trials, as well as GRAS affirmation, we're confident in the safety profile of Hobamine as used responsibly in dietary supplements according to TSI Group's guidelines.
Potential Benefits of Hobamine
Hobamine's unique ability to scavenge reactive dicarbonyls opens up several promising applications for human health. Research has demonstrated benefits ranging from cellular protection to cardiovascular support, with the above human clinical trials validating its safety and bioavailability.[1,6,10]
Immune System Support
The human clinical research revealed that Hobamine significantly affects key immune system markers. The compound increases levels of several important proteins that help regulate immune function, including CCL19, IL-12β, and TNFβ.[1] These changes support:
- Healthy immune system signaling
- Balanced inflammatory responses
- Enhanced immune cell communication
As such, it makes perfect sense to formulate it into immune system supplements or add it to fall- and wintertime-immunity supplement stacks.
Cardiovascular Health Benefits
Animal studies have demonstrated impressive cardiovascular benefits from Hobamine supplementation. Research shows it can help maintain healthy blood vessel function and support normal blood pressure levels.[5] The compound has been shown to reduce atherosclerosis by 60% in experimental models without affecting plasma cholesterol levels.[25]
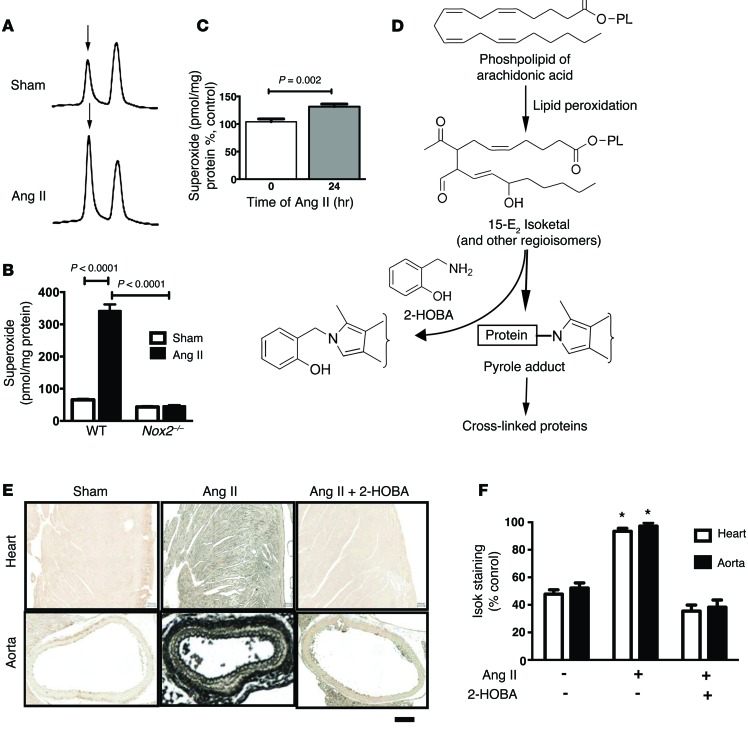
This detailed figure illustrates the mechanism behind 2-HOBA's protective effects. Panels A-C show how angiotensin II increases superoxide production, which leads to isoketal formation. Panel D depicts the chemical pathway from phospholipid oxidation to isoketal formation, and how 2-HOBA interrupts this process by scavenging isoketals before they can modify proteins. Panels E-F provide visual and quantitative evidence that 2-HOBA treatment dramatically reduces isoketal accumulation in heart and aortic tissues compared to angiotensin II alone, demonstrating its mechanism of action in vascular protection.[25]
Cardiovascular-support supplements often focus on blood flow and viscosity, but neglect the targeted antioxidant angle, given the lack of success from such ingredients, as discussed earlier in this article. Hobamine provides an excellent way to improve any cardio-friendly stack.
Cognitive Function Support
One of Hobamine's most promising attributes is its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier, making it potentially valuable for supporting cognitive health.[10] Research has shown that Hobamine can help prevent working memory deficits in experimental models.[27]
There are numerous great nootropic supplements out there, some of which rely on stimulants (enfinity paraxanthine being a popular one). Hobamine adds a new angle not before seen in any cognitive support supplements, and it's one that leads into areas of longevity as well.
Cellular Protection
At its core, Hobamine works by protecting cells from oxidative damage, through the reactive dicarbonyl neutralization as discussed in this article. This fundamental cellular protection mechanism helps to maintain normal protein function and cellular processes, which explain wide-ranging benefits.
When it comes to cell protection and DNA defense,[28,30] we think of one niche specifically: anti-aging. Seeing Hobamine formulated into the growing longevity niche would make perfect sense.
Emerging Research Areas
Scientists continue to explore additional applications for 2-HOBA, with promising preliminary research in several areas:
- Exercise recovery and sports performance
- Metabolic health optimization
- Support for healthy aging processes
- Gut health and the gut-brain axis
- Liver detoxification formulas
Paraxanthine is the primary metabolite of caffeine, providing most of caffeine's beneficial effects. Now you can take it directly with enfinity!
Regarding gut health, recent research has also shown potential benefits for gastrointestinal health, with studies demonstrating that 2-HOBA can reduce inflammation and DNA damage in gastric tissue.[28,30]
Additionally, when we see protection against malondialdehyde (MDA), we think of systemic liver support. This is because MDA is a major marker of lipid peroxidation and oxidative stress and is commonly elevated in liver diseases such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and alcohol-induced liver damage.[31]
The current research is promising, and we look forward to future studies exploring 2-HOBA's additional benefits. Its unique mechanism of action and strong safety profile make it an exciting compound for future research into numerous aspects of human health.
Dosing & Usage
Recommended Dosing
Based on the safety and pharmacokinetic data, the recommended daily dosage of Hobamine acetate is 100mg, with a minimum effective intake of 50mg per day. These doses have been extensively studied and shown to be both safe and well-tolerated while providing optimal benefits.[1]
This comprehensive safety profile, combined with favorable pharmacokinetics and clear dosing guidelines, provides strong support for Hobamine's development as a dietary supplement for maintaining cellular health.
Timing Considerations: AM/PM Setup
Given Hobamine's pharmacokinetic profile showing a half-life of approximately 2 hours,[6] it's best to split the daily dose into multiple servings. For optimal coverage, we suggest taking Hobamine with meals, spread throughout the day. Clinical research demonstrates that taking it with food is well-tolerated.[10]

Hydration is evolving, and Peak ATP is leading the charge. Beyond basic electrolytes, it boosts blood flow, strength, endurance, and cognitive recovery. For premium performance, it’s the ultimate upgrade for next-gen hydration supplements.
Who Should Consider Hobamine?
Since cellular health impacts everyone, Hobamine can benefit a wide range of individuals. Research shows that oxidative stress increases with age, making Hobamine an excellent consideration for those seeking healthy aging support.
The following groups may find Hobamine especially beneficial for their health goals:
- Health-conscious individuals focused on cellular and mitochondrial wellness
- Adults seeking cognitive and cardiovascular support
- Anyone exposed to increased oxidative stress through lifestyle or environmental factors
- Those looking to support healthy inflammatory response
- Athletes and active individuals wanting to support recovery
Supplement Stacking
Hobamine works through a unique mechanism as a selective scavenger of reactive dicarbonyls, making it complementary to many other supplements. Consider stacking Hobamine with:
- Foundational supplements like multivitamins and omega-3s
- Traditional antioxidants for comprehensive oxidative stress support
- Mitochondrial support supplements
- Cognitive enhancement supplements (nootropics)
- Sports nutrition and recovery formulas
Since Hobamine doesn't interfere with normal cellular processes or other supplements, it can be effectively incorporated into most supplement regimens.
Conclusion: The Future of Cellular Health
The emergence of Hobamine (2-HOBA) represents a serious shift in how we approach cellular protection and oxidative stress. Rather than broadly suppressing all oxidative processes like traditional antioxidants, Hobamine's selective targeting of reactive dicarbonyls provides a more intelligent solution for maintaining cellular health.
The research demonstrates that Hobamine operates through multiple mechanisms to support overall health. It protects against oxidative stress by scavenging harmful reactive dicarbonyls before they can damage cellular components, helps maintain proper immune function by supporting healthy inflammatory responses, and may promote cardiovascular health.
On top of it is a demonstrated safety profile in human clinical trials, with no serious adverse events at doses up to 825mg.
Looking Ahead
Current research continues to uncover new applications for 2-HOBA across multiple areas of health, from cognitive function to immune system support. Scientists are exploring its potential role in protecting against age-related cellular decline and supporting healthy aging processes.
As oxidative stress and inflammation become increasingly recognized as key factors in many health challenges, TSI Group's targeted approach to cellular protection positions Hobamine as a promising nutritional compound for supporting long-term health and wellness. Its ability to work at the foundational cellular level, combined with its excellent safety profile, makes it a compelling option for those looking to take a proactive approach to their health.
Stay up to date with the latest developments in Hobamine research and availability by signing up for PricePlow's Hobamine and TSI Group alerts:







Comments and Discussion (Powered by the PricePlow Forum)