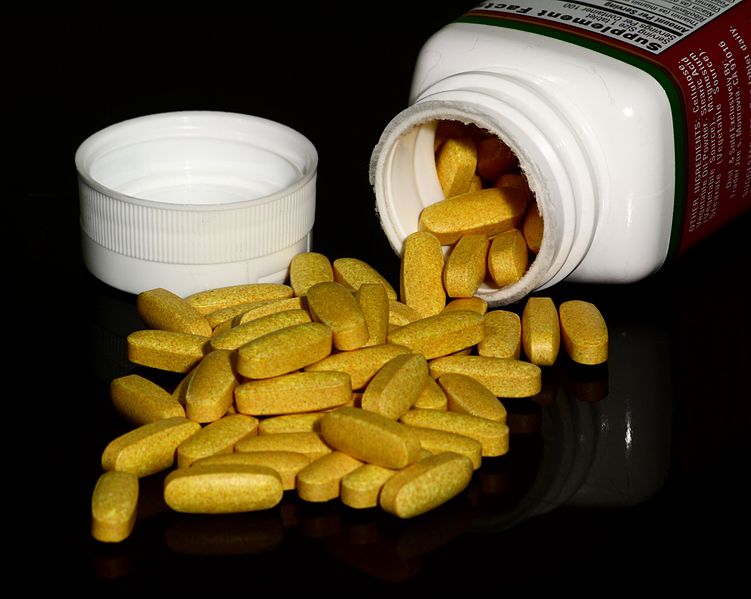
Multivitamins are commonly and appropriately referred to as a "nutritional insurance policy." Unlike a stand-alone vitamin, they contain a broad spectrum of key vitamins and minerals. This ensures you that your bases are covered by providing you with adequate amounts of nutrients that you may be overlooking, or simply having a hard time obtaining through your diet.
Uses
Multivitamins are used to guarantee that you're receiving a regular influx of required nutrients. Keeping your nutrition optimal 100-percent of the time is not easy. Calculating macronutrients (carbs, fats, proteins) is be challenging enough, but keeping track of micronutrients (vitamins and minerals) is a completely different chore and can quickly overwhelm. A properly formulated multivitamin will fill in some of the gaps in your nutrition that would otherwise be easily overlooked.
Common ingredients
Vitamins can be divided into two categories based on their absorption: fat soluble and water soluble. Water soluble vitamins need to be replinished in the body regular because they are easily absorbed in water, therefore they are more rapidly excreted. Fat soluble vitamins, on the other hand, adhere to fat, making them more difficult to excrete. You can go longer without taking certain fat-soluble vitamins because they stay in the body longer. Multivitamins will include both water and fat soluble vitamins. When choosing a product, look for a formula that includes adequate amounts of the following key components:
Vitamin A
Fat soluble, accumulative alcohols that are extraordinarily toxic in excess.
Vitamin C
Also known as ascorbic acid, this water soluble vitamin plays an important role in immune function.[3] It also provides profound antioxidant benefits.[4]
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of two fat soluble compounds, vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) and vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol), that have multiple functions in the body. Most notably it is recognized for it's crucial role in bone health.[5, 6, 7, 8] Leads to calcification and joint stiffness when overdosed.
Vitamin E
Vitamin E is a collective name for a group of eight fat-soluble compounds that share distinct antioxidant qualities. These compounds ward off free radical damage.[9]
- Alpha-tocopherol
- Beta-tocopherol
- Gamma-tocopherol
- Delta-tocopherol
- Alpha-tocotrienol
- Beta-tocotrienol
- Gamma-tocotrienol
- Delta-tocotrienol
Vitamin B complex
There are eight B vitamins known as vitamin B complex, or simply B complex. All of these compounds are water soluble.
Vitamin B1 (thiamine)
Similar to other B vitamins, thiamine is often referred to as an "anti-stress" vitamin because of it's important role in the immune system, nervous system, and brain health. Your body needs thiamine to perform a number a metabolic actions. It's also needed to form adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the source of fuel for every cell in the body.[10]
Vitamin B2 (riboflavin)
Riboflavin helps the body produce energy, provides antioxidant benefits, and helps utilize vitamin B6 and vitamin B9 more efficiently.[11]
Vitamin B3 (niacin)
In addition to improving circulation, niacin helps the body form multiple stress and sex-related hormones.[12]
Vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid)
Pantothenic acid assists in the breakdown of fats and carbohydrates for energy. It is also needed to form sex and stress hormones, synthesize cholesterol, manufacture red blood cells, and maintain a healthy digestive tract. Furthermore, it helps the body utilize vitamin B2 more effectively.[13]
Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine)
Vitamin B6 aids the body in forming neurotransmitters. It's essential for healthy brain development and functionality. Additionally, vitamin B6 helps the body build serotonin and norepinephrine — two hormones that influence mood — and melatonin, a powerful hormone that helps regulate your biological clock. Pyridoxine is needed for the absorption of vitamin B12.[14]
Vitamin B7 (biotin)
Commonly referred to as vitamin H, biotin is used to metabolize carbohydrates, fats, and protein. It's needed for a healthy liver and helps the immune system function properly. It's also beneficial to the skin, hair, and eyes.[15]
Vitamin B9 (folic acid)
Folic acid is critical for proper brain function and essential to mental health. Furthermore, it assists in the production of DNA and RNA. Vitamin B9 also works synergistically with B12 in assisting the body to properly utilize iron and generate red blood cells.[16]
Vitamin B12 (cobalamin)
Cobalamin is a particularly important nutrient in regards to maintaining healthy nerve cells. It also helps with the production of the body's genetic material, DNA and RNA. Vitamin B12 works hand in hand with folic acid to help the body properly utilize iron and form red blood cells.[17]
Minerals
In order to achieve a more well-rounded product, many companies choose to pair their multivitamin formula with a mineral complex. These are the most common minerals used in such products:
Calcium
Calcium is the most abundant mineral in the human body.[18] Among all of its functions, it's most noted for its role in bone health.[19]
Phosphorous
Phosphorous is another mineral that's critical for bone health.[20]
Iodine
This mineral has multiple roles in the body, but is most recognized for its key functions in thyroid health.[21]
Iron
It's one of the most abundant minerals on earth, but in the human body, iron is a key component involved in oxygen transportation. It is also essential for the regulating cell growth.[22]
Magnesium
This is a diverse mineral that helps regulate a multitude of biochemical reactions, including blood glucose control, protein synthesis, blood pressure regulation, muscle and nerve function.[23]
Zinc
Zinc plays a key role in immune function, protein synthesis, DNA synthesis, and cell division. This essential element has also been shown to support normal growth and development during pregnancy, childhood, and adolescence.[24, 25, 26, 27, 28]
Selenium
Selenium plays a critical role in thyroid hormone metabolism, reproduction, DNA synthesis, and protection from oxidative damage and infection.[29]
Chromium
This trace mineral enhances the action of insulin. In turn, the body more effectively metabolizes fats, carbohydrates, and proteins.[30]
Potassium
Potassium is required to ensure the proper functioning of all organs, tissues, and cells. It's particularly crucial for proper heart function and plays a key role in both smooth and skeletal muscle contraction, making it important for healthy muscular and digestive function.[31]
Manganese
Manganese is necessary for healthy nerve and brain function. It's also essential in helping to form bones, connective tissue, and sex hormones. Additionally it's an important factor in fat and carbohydrate metabolism, calcium absorption, and blood sugar regulation.[32]
Copper
Copper assists in iron absorption, energy production, generation of red blood cells, and keeping the immune system and nerve cells healthy. It's also essential in the formation of collagen, making it crucial for healthy bones and connective tissue. The mineral has also been shown to exhibit antioxidant properties, helping to rid the body of free radicals that would otherwise damage cells and DNA.[33]
Stacking
Fish Oil
Not all brands include essential fatty acids (EFA) in their multivitamin formula. If your product of choice doesn't include EFA's, fish oil is an excellent source and will be useful in helping you meet your daily nutritional requirements.
Multi-minerals
While many companies include a mineral complex of some sort in their multivitamin formula, it is wise to check the label. If yours doesn't, you should consider stacking with a multimineral.
Digestive enzymes
Stacking multivitamins with digestive enzymes helps promote proper digestion and optimal nutrient absorption.
Joint support
If your multivitamin is lacking a joint support complex, you should consider stacking it with a product that promotes healthy joint function.
Benefits
Most of the studies proving the benefits of multivitamins are based on their role in disease cure and prevention. While interesting, these studies are highly controversial and constantly disputed. It is true however, that one of the biggest benefits multivitamins provide is the ability to correct vitamin deficiencies and prevent further deficiencies from occurring. They are also particularly beneficial while dieting in a caloric deficit, as you likely won't be getting adequate amounts of micronutrients from whole food sources.
Controversy
Most of the controversy surrounding multivitamins is based on claims regarding their effects on major diseases and illness. There are dozens of conflicting studies that seem to disprove each other.[42, 43] Taking this into consideration, we can only advise supplementation with multivitamins on the basis of ensuring certain daily micronutrient requirements are met.Recommended dosageDifferent formulations contain a multitude of nutrients at varying dosages. Because of this, you should expect dosages to vary from product to product. As a general recommendation, we suggest that you consume an appropriate amount of vitamins to meet your corresponding recommended daily intake (RDI). We always suggest that you follow the directions on the product, and always speak with your healthcare practitioner before starting a new multivitamin regimen.
Forms
Take a multivitamin to guarantee that you're receiving a regular influx of required nutrients.
Multivitamins are available in many forms. Some of the most common are chewable tablets, powders, pills, liquids, and gummies. There are also more exotic forms available, such as transdermal patches, suppositories, and oral sprays. It is worth noting that many companies use vitamin packs (e.g. Animal Pak), in which case one serving will consist of multiple pills, sometimes upwards of ten. Choosing the right formulaMany specialized formulas are available for specific needs and age groups. When choosing a specialized formula you should look for the following basic characteristics:
Children
Children's formulas should have little to no iron. It's also important to choose a product designed specifically for kids, as the nutrient dosages will be adjusted accordingly. Most children's vitamins come in the form of flavored chewables. Products that include calcium and vitamin D are suggested for proper bone health and development.
Teenagers
Parents of teens should look for a formula that includes skin and immune system support. There are also product that include vitamins and/or minerals known for stress management and mood balancing characteristics . — a common concern for man pubescents. To help meet their recommended intake, teens should look for a brand with ample amounts of the B vitamins. Additionally, it is wise to take into consideration that kids between the ages of TK and TK rarely eat a sufficient amount of vegetables. With this in mind, it's smart to choose a product that contains a greens or veggie blend.
Women
Females should choose a product that includes bone, breast, and reproductive support. Pregnant women should consider using prenatal vitamins, but always need to consult with their doctor before using any supplements. It is important for women to make sure their multivitamin includes iron, as they are more prone to become deficient in this mineral.
Men
A proper men's formula will focus on prostate health, including sufficient amounts of selenium and vitamin A for their reproductive health benefits. It is common to see inclusion of additional herbal ingredients because of their alleged benefits regarding prostate health. It is most important for men to choose a multivitamin containing little to no iron since they're more likely to reach iron toxicity.
Athletes
Athletes tend to burn through nutrients at increased rates. Therefore, it is suggested that they look for a product containing higher doses of nutrients close to or at the upper tolerable limit (UL). Athletes need to choose a very well rounded product that includes sufficient amounts of B vitamins for energy production.
Seniors
Seniors should look for a formula that includes vitamin A for vision, potassium for heart health, and B vitamins for immune function, energy, circulation, and brain function. There also needs to be great care taken in choosing a product that does not contain ingredients that could interfere with medications they might currently be taking.
While it is essentially impossible for a company to create a "one size fits all" type of formula, many brands have successfully created unique products that can be useful tools in aiding you to meet your own specific needs and concerns.
Side effects
Side effects from multivitamins will generally occur if you're reaching toxic levels of certain vitamins or minerals.To reduce the chances of toxicity, the Institute of Medicine (IOM) has established recommended daily allowances for vitamins and minerals.
- Vitamin A toxicity can cause reduced bone mineral density, dizziness, nausea, headaches, skin irritation, painful joints and bones, coma, and in extreme cases, even death.[2]
- Vitamin C is considered very safe, with only a small risk for toxicity. It's believed that there are no serious adverse effects at high doses. However, some reports of mild side effects, such as diarrhea, abdominal cramps, nausea, and other gastrointestinal disturbances, do exist.[34]
- Vitamin D toxicity can cause an array of symptoms, like anorexia, weight loss, polyuria, and a heart arrhythmia. It can also raise blood levels of calcium, which can lead to more serious side effects, such as vascular and tissue calcification.[35]
- Studies have shown that increased dosages of vitamin E raises the risk of excessive bleeding because it interrupts the process of blood coagulation.[36, 37]
- Thiamine, also known as vitamin B1, is considered safe and has no established UL. However, there have been reports of upset stomach at high doses.[10]
- Even in large doses, vitamin B2, or riboflavin, is considered safe. There is no established UL. While no serious side effects have been confirmed in association with B2 supplementation, high doses may cause itching, burning, numbness, sensitivity to light, and fluorescent yellow or orange urine.[11]
- High doses of niacin (vitamin B3) have been proven to cause side effects. The most common are burning-tingling sensations in the face and chest, which is often accompanied by reddened skin. This is commonly referred to as the "niacin flush." Very high doses of B3 have been linked to liver damage and stomach ulcers.[12]
- Vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid) is generally considered safe, but at very large doses it has been shown to cause diarrhea. Also, it is noteworthy to mention that numerous companies and publications have stated that pantothenic acid may increase the risk of bleeding. However, it is unclear how to interpret this warning with such inconclusive evidence to back up the claim.[13]
- Vitamin B6, also known as pyridoxine, in extremely high doses can cause temporary neurological problems, such as imbalance and loss of feeling in your legs. Minor side effects can include loss of appetite, sensitivity to sunlight, nausea, and abdominal pain.[14]
- Vitamin B7 (biotin) is non-toxic, even in large doses. No UL has been established.[15]
- Vitamin B9, also known as folic acid, in very high doses has been shown to cause sleep and digestive problems, skin reactions, and seizures.[16]
- The IOM states that vitamin B12 (cobalamin), even in excess, is safe to use and, for the most part, causes no adverse effects. For that reason, there is no established UL for B12.[38] Excessive levels of calcium have been linked to poor kidney function, soft tissue and vascular calcification, constipation, and hypercalciuria (heightened levels of calcium in the urine), which can lead to kidney stones. Some evidence suggests that high calcium intake may also interfere with the absorption of zinc and iron, however this side effect is not well established. Excessive calcium supplementation can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.[18]
- In excess amounts, phosphorus can cause calcification of organs and soft tissue. It has also been linked to diarrhea and can interfere with the body's ability to use iron, magnesium, calcium, and zinc.[39]
- Taking too much iodine can cause similar side effects to iodine deficiency, possibly leading to the formation of goiters, elevated TSH levels, and hypothyroidism.[40]
- Magnesium supplementation at high dosages can often result in diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal cramping. Toxic levels of magnesium can result in ileus (a painful obstruction in part of the intestine), hypotension, vomiting, facial flushing, difficulty urinating, depression, and lethargy. Without intervention, symptoms can progress, causing extreme hypotension, muscle weakness, irregular heartbeat, difficulty breathing, and cardiac arrest.[23]
- Zinc toxicity can result in digestive abnormalities, such as nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, abdominal cramps, and diarrhea. Excessive amounts of the mineral have also been linked to headaches. These effects can be both chronic and/or acute.[41]
- Too much selenium can result in brittle hair and nails, hair and nail loss, skin lesions or rashes, nausea, diarrhea, fatigue, irritability, and nervous system abnormalities. It has also been reported that high levels of selenium can cause your breath to have a garlic-like odor or a metallic taste in your mouth.[29]
- High levels of copper can cause digestive problems, such as nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, and diarrhea. Excess copper intake has also been shown to cause dizziness, headaches, weakness, and a metallic taste in the mouth. At toxic levels it can cause jaundice, heart problems, coma, and even fatality.[33]
- Excess manganese poses a potential threat for nervous system damage. At toxic levels, symptoms may include, hallucinations, irritability, violent outbursts, loss of appetite, headaches, leg cramps, muscle tension, tremors, and convulsions.[32]
- High doses of chromium have not been linked to adverse side effects. As a result, the IOM has not established a UL.[30]
- Potassium, taken at high doses, can result in diarrhea, stomach irritation, and nausea. At toxic doses it can cause muscle weakness, slowed heart rate, and abnormal heart rhythm.[31] This mineral is minimally excreted from the body, causing receptor sites to fill quickly. Excess iron is stored in multiple body tissues and organs, which can be fatally toxic.[22]
Disadvantages
It's possible to accidentally over-supplement vitamins and minerals. In some instances, accumulating too much can result in toxicity. While these occurrences are rare, you should be aware it can happen, especially if you're already meeting many of your daily nutritional requirements through a healthy diet.
Food sources
Vitamins and minerals can be obtained naturally through a diet rich in a variety of foods. You should always strive to eat a well balanced diet. Supplementation is meant solely to optimize nutrition, it's not a substitute for a healthy meal plan.
Warnings
Supplements containing iron should be used with caution and kept out of the reach of children at all times. Pregnant women, seniors, and individuals with pre-existing medical conditions should always consult with a doctor regarding possible contraindications before using a multivitamin.
Considerations
This article is not intended to provide medical advice. It's a compilation of research and opinions. We recommend that you always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplementation.
Where to buy
Shop and compare prices here at PricePlow! Take advantage of our free informational guides and product reviews. We understand the importance of good health and the value of optimal performance, so we made it our mission to help you get the most bang for your buck without sacrificing quality.
References
- Institute of Medicine. Food and Nutrition Board; National Academy Press;Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin A, Vitamin K, Arsenic, Boron, Chromium, Copper, Iodine, Iron, Manganese, Molybdenum, Nickel, Silicon, Vanadium, and Zinc; 2001.
- Office of Dietary Supplements; "Vitamin A"
Strohle A., Hahn A.; Med Monatsschr Pharm; "Vitamin C and immune function;" February 2009 - Jacob RA, Sotoudeh G.; Nutrition in Clinical Care; "Vitamin C function and status in chronic disease;" March-April 2002
- Frei B, et al.; Procedings of the National Academy of Sciences; "Ascorbate is an outstanding antioxidant in human blood plasma;" August 1989
- Institute of Medicine; "Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D;" November 2010
- Cranney A., et. al.; Evidence Report; "Effectiveness and safety of vitamin D in relation to bone health;" August 2007
- Bischoff-Ferrari HA, et. al.; JAMA; "Fracture prevention with vitamin D supplementation: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials;" May 2005
- Bischoff-Ferrari HA, et. al.; BMJ; "Fall prevention with supplemental and active forms of vitamin D: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials;" October 2009
- Sen CK., et. al.; Life Sciences; "Tocotrienols: Vitamin E beyond tocopherols;" March 2006
- University of Maryland Medical Center; "Vitamin B1 (Thiamine);" Reviewed June 2011
- University of Maryland Medical Center; "Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin);" Reviewed June 2011
- University of Maryland Medical Center; "Vitamin B3 (Niacin);" Reviewd August 2011
- University of Maryland Medical Center; "Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic acid);" Reviewed June 2011
- University of Maryland Medical Center; "Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine);" Reviewed June 2022
- University of Maryland Medical Center; "Vitamin H (Biotin);" Reviewed June 2011
- University of Marlyand Medical Center; "Vitamin B9 (Folic acid);" Reviewed June 2011
- University of Maryland Medical Center; "Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin);" Reviewed June 2011
- Office of Dietary Supplements; "Calcium;" Reviewed November 2013
- Straub DA.; Nutrition in Clinical Practice; "Calcium supplementation in clinical practice: a review of forms, doses, and indications;" June 2007
- Heaney RP.; Mayo Clinic Proceedings; "Phosphorus nutrition and the treatment of osteoporosis;" January 2004
- Hess SY.; Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism; "The impact of common micronutrient deficiencies on iodine and thyroid metabolism: the evidence from human studies;" February 2010
- Office of Dietary Supplements; "Iron;" Reviewed August 2007
- Office of Dietary Supplements; "Magnesium;" Reviewed November 2013
- Solomons NW.; Nutrition Reviews;"Mild human zinc deficiency produces an imbalance between cell-mediated and humoral immunity;" January 1998
- Prasad AS.; Nutrition; "Zinc: an overview;" Jan-Feb 1995
- Simmer K. Thomas RP.; Acta paediatrica Scandinavica; "Zinc in the fetus and newborn;" 1995
- Fabris N, Mocchegiani E.; Aging; "Zinc, human diseases and aging;" April 1995
- Rink L, Gabriel P.; The Procedings of the Nutrition Society; "Zinc and the immune system;" November 2000
- Office of Dietary Supplements; "Selenium;" Reviewed July 2013
- Office of Dietary Supplements; "Chromium;" Reviewed November 2013
- University of Maryland Medical Center; "Potassium;" Reviewed July 2011
- University of Maryland Medical Center; "Manganese;" Reviewed July 2011
- University of Maryland Medical Center; "Copper;" Reviewed March 2011
- Office of Dietary Supplements; "Vitamin C;" Reviewed June 2013
- Office of Dietary Supplements; "Vitamin D;" Reviewed June 2011
- University of Maryland Medical Center; "Vitamin E;" Reviewed January 2012
- Office of Dietary Supplements; "Vitamin E;" Reviewed June 2013
- Office of Dietary Supplements; "Vitamin B12;" Reviewed June 2011
- University of Maryland Medical Center; "Phosphorus;" Reviewed June 2011
- Office of Dietary Supplements; "Iodine;" Reviewed June 2011
- Office of Dietary Supplements; "Zinc;" Reviewed June 2013
- Hennekens CH, et. al.; JAMA; Lack of effect of long-term supplementation with beta carotene on the incidence of malignant neoplasms and cardiovascular disease; May 1996
- Huang HY, et. al.; Evidence Report; Multivitamin/mineral supplements and prevention of chronic disease;" May 2006
Multivitamin News on PricePlow
-
Apr 12, 2024 ![]()
Product News
Gorilla Mind Elite Multi-Vitamin was created.
Category: Multivitamins -
Apr 11, 2024 ![]()
Product News
Gaspari Nutrition Anavite has new variations: Category: Multivitamins -
Apr 03, 2024 ![]()
Product News
Natural Factors Super Multi Iron Free was created.
Category: Multivitamins -
Apr 02, 2024 ![]()
YouTube Video
JOCKO WILLINK: Starting Jocko Fuel and Jocko's Supplement Stack | PricePlow 132 -
Apr 02, 2024 ![]()
Blog Post
JOCKO WILLINK | PricePlow Episode #132
Jocko Willink joins PricePlow for Episode 132 to talk about founding Jocko Fuel, doing the right thing, and Jocko's entire stack from start to finish -
Mar 28, 2024 ![]()
Product News
DMoose Fitness Multi Vitamin was created.
Category: Multivitamins -
Mar 27, 2024 ![]()
Product News
PLNT Men's Multivitamin has new variations: Category: Men's Multivitamins -
Mar 25, 2024 ![]()
Product News
PLNT Men's 50+ Multivitamin has new variations: Category: Men's Multivitamins -
Mar 24, 2024 ![]()
Product News
PLNT Men's Multivitamin was created.
Category: Men's Multivitamins -
Mar 24, 2024 ![]()
Product News
PLNT Women's Multivitamin was created.
Category: Women's Multivitamins -
Mar 24, 2024 ![]()
Product News
PLNT Men's 50+ Multivitamin was created.
Category: Men's Multivitamins -
Mar 22, 2024 ![]()
Product News
TrueYou Perfect Ensemble was created.
Category: Women's Multivitamins -
Mar 20, 2024 ![]()
Product News
Huge Supplements Multi was created.
Category: Multivitamins -
Mar 12, 2024 ![]()
Product News
UXO Supplements Daily Essentials was created.
Categories: Multivitamins, Prebiotics, Probiotics -
Mar 12, 2024 ![]()
Product News
Obvi Multi + Collagen was created.
Categories: Collagen, Multivitamins -
Mar 11, 2024 ![]()
Product News
Ayone Nutrition Men’s Multivitamin was created.
Category: Men's Multivitamins -
Mar 07, 2024 ![]()
Blog Post
Animal Brings the CAGE Back: Jason Budsock & Rudy Checo | Episode #128
Animal brings THE CAGE Back to The Arnold Expo, so we record a podcast with Jason Budsock and Rudy Checo to celebrate the start of the weekend. -
Feb 29, 2024 ![]()
Product News
Swanson Multi was created.
Category: Multivitamins -
Feb 27, 2024 ![]()
Product News
MTN OPS Multi-V was created.
Category: Multivitamins -
Feb 26, 2024 ![]()
Product News
The Vitamin Shoppe Vthrive - Bioactive Women's One-Daily Multi was created.
Category: Women's Multivitamins -
Feb 26, 2024 ![]()
Product News
The Vitamin Shoppe Vthrive - Bioactive Men's One-Daily Multi was created.
Category: Men's Multivitamins -
Feb 26, 2024 ![]()
Product News
The Vitamin Shoppe Vthrive - Bioactive Women 50+ One Daily Multi was created.
Category: Women's Multivitamins -
Feb 26, 2024 ![]()
Product News
The Vitamin Shoppe Vthrive - Bioactive Men's 50+ One Daily Multi was created.
Category: Men's Multivitamins -
Feb 26, 2024 ![]()
Product News
The Vitamin Shoppe Chewable Bariatric Multivitamin was created.
Category: Multivitamins -
Feb 26, 2024 ![]()
Product News
The Vitamin Shoppe Prenatal + DHA was created.
Category: Prenatal Vitamins -
Feb 26, 2024 ![]()
Product News
The Vitamin Shoppe One Daily Prenatal Multivitamin with DHA was created.
Category: Prenatal Vitamins -
Feb 25, 2024 ![]()
Product News
The Vitamin Shoppe Multivitamin & Mineral Powder was created.
Categories: Immune System Supplements, Minerals, Multivitamins -
Feb 25, 2024 ![]()
Product News
The Vitamin Shoppe Ultimate Man Gold was created.
Categories: Men's Multivitamins, Minerals -
Feb 25, 2024 ![]()
Product News
The Vitamin Shoppe Ultimate Man was created.
Categories: Men's Multivitamins, Minerals -
Feb 23, 2024 ![]()
Product News
The Vitamin Shoppe Women's Multi Gummies was created.
Categories: Gummy Supplements, Women's Multivitamins -
Feb 18, 2024 ![]()
Product News
Swanson Century Formula without Iron was created.
Category: Multivitamins -
Feb 16, 2024 ![]()
Blog Post
Revive MD Subscription Box: Greens, Vitamin Packs, and More!
Revive MD just released their new Subscription Box, a monthly health kit comprising of Daily Greens, Essential Vitamins Pack, a frother, and a glass bottle. -
Feb 11, 2024 ![]()
Product News
Legion Triumph for Men was created.
Category: Men's Multivitamins -
Feb 07, 2024 ![]()
YouTube Video
Animal Pill Packs – The Full Arsenal of “Paks” Explained -
Feb 07, 2024 ![]()
TikTok Video
Oh, you like this recent pill pack trend? @officialanimalpak did it first!!! Shout out to the OG!! -
Feb 02, 2024 ![]()
Product News
The Vitamin Shoppe Especially for Men has new variations: Categories: Antioxidants, Immune System Supplements, Men's Multivitamins, Prostate Health -
Feb 02, 2024 ![]()
Product News
The Vitamin Shoppe Ultimate Woman has new variations: Category: Women's Multivitamins -
Feb 02, 2024 ![]()
Product News
Healthy Origins Chelated Multi Mineral has new variations: Category: Multivitamins -
Feb 01, 2024 ![]()
Blog Post
Kaged Kickstarts 2024 in The Vitamin Shoppe’s Fit Lifestyle
After a monumental year for Kaged's new era, they don't show any signs of slowing down. Their next step is promoting products beneficial for a Fit Lifestyle. -
Jan 30, 2024 ![]()
Blog Post
Animal Pill Packs – The Full Arsenal of “Paks” Explained
Animal has a wide variety of pill pack supplements tailored to any person's possible needs, whether it's general health, joint care, women's health, or others. -
Jan 30, 2024 ![]()
Product News
The Vitamin Shoppe One Daily Women's 50+ No Iron was created.
Category: Women's Multivitamins -
Jan 30, 2024 ![]()
Product News
The Vitamin Shoppe One Daily Men's 50+ was created.
Categories: Energy & Endurance, Immune System Supplements, Men's Multivitamins, Stress Relief -
Jan 29, 2024 ![]()
Product News
Trace Minerals Men's Multi Gummies was created.
Categories: Gummy Supplements, Men's Multivitamins -
Jan 29, 2024 ![]()
Product News
Trace Minerals Children's Multi Gummies was created.
Categories: Gummy Supplements, Vitamins for Kids -
Jan 29, 2024 ![]()
Product News
Trace Minerals Women's Multi Gummies was created.
Categories: Gummy Supplements, Women's Multivitamins -
Jan 29, 2024 ![]()
Product News
The Vitamin Shoppe Children's Liquid D3 was created.
Categories: Vitamin D3, Vitamins for Kids -
Jan 29, 2024 ![]()
Product News
The Vitamin Shoppe One Daily Women's No Iron was created.
Categories: Energy & Endurance, Immune System Supplements, Women's Multivitamins -
Jan 29, 2024 ![]()
Product News
The Vitamin Shoppe One Daily Women's was created.
Categories: Immune System Supplements, Stress Relief, Women's Multivitamins -
Jan 29, 2024 ![]()
Product News
The Vitamin Shoppe One Daily Men's was created.
Categories: Immune System Supplements, Men's Multivitamins, Stress Relief -
Jan 27, 2024 ![]()
Product News
The Vitamin Shoppe Ultimate Woman Gold was created.
Categories: Antioxidants, Energy & Endurance, Immune System Supplements, Stress Relief, Women's Multivitamins -
Jan 27, 2024 ![]()
Product News
The Vitamin Shoppe Ultimate Woman 50+ was created.
Category: Women's Multivitamins -
Jan 27, 2024 ![]()
Product News
The Vitamin Shoppe Ultimate Woman was created.
Category: Women's Multivitamins -
Jan 23, 2024 ![]()
Product News
MegaFood Men's 40+ Advanced Multivitamin has new variations: Category: Men's Multivitamins -
Jan 23, 2024 ![]()
Product News
Nature's Way Kids Cough Relief + Immune Syrup was created.
Categories: Cough Remedies, Immune System Supplements, Vitamins for Kids -
Jan 23, 2024 ![]()
Product News
Carlson Kid's Black Elderberry Gummies was created.
Categories: Elderberry, Gummy Supplements, Vitamin C, Vitamins for Kids -
Jan 22, 2024 ![]()
Product News
Nutricost Kids Multivitamin was created.
Categories: Gummy Supplements, Vitamins for Kids -
Jan 21, 2024 ![]()
Product News
Centrum Men MultiGummies has new variations: Categories: Gummy Supplements, Men's Multivitamins -
Jan 21, 2024 ![]()
Product News
Centrum Women MultiGummies was created.
Categories: Gummy Supplements, Women's Multivitamins -
Jan 21, 2024 ![]()
Product News
MegaFood Women's Advanced Multivitamin has new variations: Category: Women's Multivitamins -
Jan 21, 2024 ![]()
Product News
MegaFood Men's 55+ Advanced Multivitamin has new variations: Category: Men's Multivitamins -
Jan 17, 2024 ![]()
Product News
New Chapter Prenatal Multivitamin was created.
Categories: Gummy Supplements, Prenatal Vitamins -
Jan 11, 2024 ![]()
Product News
Nutricost Multivitamin has new variations: Category: Multivitamins -
Jan 08, 2024 ![]()
YouTube Video
Daily Health Pack with Nootropics! Core Nutritionals Multivitamin Pack -
Jan 08, 2024 ![]()
Product News
Nutricost Multivitamin For Men was created.
Category: Men's Multivitamins -
Jan 08, 2024 ![]()
Product News
Nutricost Multivitamin was created.
Category: Multivitamins -
Jan 08, 2024 ![]()
Blog Post
Core Nutritionals Daily Health Pack: A Modern Spin on Vitamin Packs
Core Nutritionals Daily Health Pack is here with 9 capsules full of vitamins, minerals, feel-good nootropics, greens, omegas, and more! -
Jan 08, 2024 ![]()
Product News
Core Nutritionals Daily Health Pack was created.
Category: Vitamin Packs -
Jan 08, 2024 ![]()
TikTok Video
Would tou difch your stack and use @CoreNutritionals daily packs? -
Dec 30, 2023 ![]()
Product News
MTN OPS Multi-V for Women;s was created.
Category: Women's Multivitamins -
Dec 30, 2023 ![]()
Product News
MTN OPS Multi-V - Men's was created.
Category: Men's Multivitamins -
Dec 27, 2023 ![]()
Product News
FNX Men's Multi was created.
Category: Men's Multivitamins -
Dec 27, 2023 ![]()
Product News
FNX Women's Multi was created.
Category: Women's Multivitamins -
Dec 26, 2023 ![]()
Product News
MegaFood Men's Advanced Multivitamin has new variations: Category: Men's Multivitamins -
Dec 26, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Swolverine Multivitamin was created.
Category: Multivitamins -
Dec 13, 2023 ![]()
YouTube Video
Revive MD Essentials Vitamin Pack: Cover Nutrient Basics -
Dec 10, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Cheap Supplements Multivitamin was created.
Category: Multivitamins -
Nov 28, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Centrum Women 50+ MultiGummies was created.
Categories: Gummy Supplements, Women's Multivitamins -
Nov 21, 2023 ![]()
YouTube Video
Bare Performance Nutrition Strong Multivitamin: With Cognizin® Citicoline -
Nov 16, 2023 ![]()
Blog Post
Bare Performance Nutrition Strong Multivitamin: With Cognizin® Citicoline
Bare Performance Nutrition's Strong Multivitamin is a perfect way to start your day – with a clinically-backed 250mg dose of Cognizin® Citicoline! -
Nov 12, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Centrum MultiGummies Women was created.
Category: Women's Multivitamins -
Nov 12, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Centrum Men MultiGummies was created.
Categories: Gummy Supplements, Men's Multivitamins -
Nov 11, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Centrum Men 50+ MultiGummies was created.
Categories: Gummy Supplements, Men's Multivitamins -
Nov 01, 2023 ![]()
Blog Post
Revive MD Essential Vitamins Pack: Your Daily Nutrient Insurance
Revive MD Essential Vitamins Pack consists of 6 targeted health benefits: immune, organ, inflammation, free radical, heart health, and antioxidant support. -
Oct 27, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Revive MD Essential Vitamins Pack was created.
Category: Vitamin Packs -
Sep 28, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Universal Animal Pak has new variations: Category: Vitamin Packs -
Sep 24, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Healthy Origins Chelated Multi Mineral was created.
Category: Multivitamins -
Aug 15, 2023 ![]()
Product News
MegaFood Men's 55+ Advanced Multivitamin was created.
Category: Men's Multivitamins -
Aug 15, 2023 ![]()
Product News
MegaFood Women 40+ Advanced Multivitamin was created.
Category: Women's Multivitamins -
Aug 15, 2023 ![]()
Product News
MegaFood Men's 40+ Advanced Multivitamin was created.
Category: Men's Multivitamins -
Aug 15, 2023 ![]()
Product News
MegaFood Men's Advanced Multivitamin was created.
Category: Men's Multivitamins -
Aug 15, 2023 ![]()
Product News
MegaFood Women's Advanced Multivitamin was created.
Category: Women's Multivitamins -
Aug 07, 2023 ![]()
YouTube Video
Revive MD Vitamin B-Complex: Improve Brain Function & Fatigue -
Aug 03, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Natural Factors WellBetX - Complete Multi was created.
Category: Multivitamins -
Aug 03, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Natural Factors Big Friends - Multi Vitamins was created.
Category: Vitamins for Kids -
Aug 03, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Natural Factors Women's Plus MultiStart was created.
Category: Women's Multivitamins -
Jul 22, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Nutrex Vitadapt Complete was created.
Category: Multivitamins -
Jul 03, 2023 ![]()
Product News
EndurElite Vitamin Elite was created.
Category: Multivitamins -
Jul 03, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Swanson Multi with Iron was created.
Categories: Iron, Multivitamins -
Jul 02, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Swanson Chewable Multi for Children was created.
Category: Vitamins for Kids -
Jun 25, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Swanson Multi Adults 50+ was created.
Category: Senior Multivitamins -
Jun 21, 2023 ![]()
YouTube Video
NEW ANIMAL PAK POWDER -
Jun 16, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Swanson Kids Multivitamin was created.
Categories: Gummy Supplements, Vitamins for Kids -
Jun 13, 2023 ![]()
Product News
BodyTech Elite Modern Man Multi was created.
Category: Men's Multivitamins -
Jun 12, 2023 ![]()
Product News
BodyTech Men's Sports Pack was created.
Category: Vitamin Packs -
Jun 12, 2023 ![]()
Product News
BodyTech Men's Sport One Daily was created.
Category: Men's Multivitamins -
Jun 12, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Swanson Just One Complete Multi was created.
Category: Multivitamins -
Jun 04, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Optitune by MuscleSport Synergy was created.
Category: Multivitamins -
Jun 04, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Optitune by MuscleSport Synergy for Him was created.
Category: Men's Multivitamins -
May 25, 2023 ![]()
Blog Post
AstroFlav Multivitamin: Boosted with Spectra, Shilajit, CoQ10, and More!
AstroFlav Multivitamin is out and uses high-quality vitamins, minerals, and is boosted with shilajit, CoQ10, turmeric, Spectra, and more! -
May 18, 2023 ![]()
Blog Post
Animal Pak POWDER: Multivitamin Powder with Upgraded Flavor and No Pills!
Animal Pak Powder now comes in a new and improved version with 30 full servings, better flavors, no artificial colors, and a new Fruit Punch flavor! -
May 18, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Universal Animal Pak has new variations: Category: Vitamin Packs -
May 12, 2023 ![]()
Product News
EHP Labs EHP Labs Enhanced Womens Performance Vitamins was created.
Category: Women's Multivitamins -
May 07, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Swanson Mini Cap Multi was created.
Category: Multivitamins -
May 02, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Swanson MULTI Plus Immune Support (with Iron) was created.
Categories: Immune System Supplements, Multivitamins -
Apr 30, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Swanson Multi without Iron was created.
Category: Multivitamins -
Apr 19, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Swanson Adult Multivitamin was created.
Categories: Gummy Supplements, Multivitamins -
Apr 19, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Swanson Men's Multi Plus Prostate Support was created.
Categories: Men's Multivitamins, Prostate Health -
Apr 19, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Swanson Multi Plus Energy was created.
Categories: Energy & Endurance, Multivitamins -
Apr 19, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Swanson Women's Multi Plus Hormone Support was created.
Categories: Hormone Supplements, Women's Multivitamins -
Apr 14, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Swanson Daily Essential Multi was created.
Category: Multivitamins -
Apr 03, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Nature's Way Alive! Max3 Potency - Women’s Multivitamin was created.
Category: Women's Multivitamins -
Mar 31, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Rainbow Light Kid's Sunny Gummies Vitamin D3 was created.
Categories: Gummy Supplements, Vitamin D3, Vitamins for Kids -
Mar 15, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Solaray Focus for Children was created.
Category: Vitamins for Kids -
Mar 10, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Revive MD Multi Vitamin was created.
Category: Multivitamins -
Mar 08, 2023 ![]()
Blog Post
Animal Pak: The Product That Created a Brand (2023 Updates)
Universal Nutrition created the original Animal Pak nearly 30 years ago, but they continue to improve the existing formula - now in just 8 pills! -
Mar 05, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Swanson Whole Food Formula Multi Vitamin & Mineral was created.
Categories: Minerals, Multivitamins -
Mar 03, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Swanson MULTI and Mineral without Iron was created.
Category: Multivitamins -
Feb 28, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Nature's Way Alive! Men's 50+ Premium Gummy Multivitamin was created.
Categories: Gummy Supplements, Men's Multivitamins -
Feb 27, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Nature Made Multi For Her 50+ was created.
Category: Women's Multivitamins -
Feb 17, 2023 ![]()
YouTube Video
New Animal Pak: Now with Spectra and AstraGin! -
Feb 01, 2023 ![]()
YouTube Video
A Multivitamin with MitoPrime, SAMe, & Boron! Glaxon Multi+ -
Feb 01, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Nature's Way Alive! KIDS Complete Multivitamin Gummy was created.
Categories: Gummy Supplements, Vitamins for Kids -
Jan 31, 2023 ![]()
Product News
GNC Earth Genius - Men's Multivitamin was created.
Category: Men's Multivitamins -
Jan 29, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Nature's Way Alive! Max3 Potency - Multivitamin was created.
Category: Multivitamins -
Jan 24, 2023 ![]()
YouTube Video
ANIMAL FORMULATOR TELLS ALL | Universal Nutrition | Jason Budsock | Episode 080 -
Jan 24, 2023 ![]()
Blog Post
Jason Budsock – Animal at Universal Nutrition | Episode #080
Jason Budsock, a 20-year employee at Animal / Universal USA, joins the PricePlow Podcast to reminisce on the past and get fired up for Animal's future -
Jan 21, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Solaray Once Daily Active Man was created.
Category: Men's Multivitamins -
Jan 21, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Solaray Once Daily Woman Multivitamin was created.
Category: Women's Multivitamins -
Jan 15, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Solaray kids Focus was created.
Category: Vitamins for Kids -
Jan 15, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Natural Vitality Calm Kids (Magnesium Supplement) was created.
Categories: Magnesium, Vitamins for Kids -
Jan 10, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Nature's Way Alive! Men's 50+ Complete Multivitamin was created.
Category: Men's Multivitamins -
Jan 10, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Nature's Way Alive! Women's Gummy Complete Multivitamin was created.
Categories: Gummy Supplements, Women's Multivitamins -
Jan 10, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Nature's Way Alive! Men's Gummy Multivitamins was created.
Categories: Gummy Supplements, Men's Multivitamins -
Jan 10, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Garden of Life baby - multi-vitamin was created.
Category: Vitamins for Kids -
Jan 05, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Nature's Way Alive! Women's 50+ Gummy Complete Multivitamin was created.
Categories: Gummy Supplements, Women's Multivitamins -
Jan 05, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Nature's Way Alive! Women's 50+ Gummy Multivitamin was created.
Categories: Gummy Supplements, Women's Multivitamins -
Jan 05, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Super Nutrition SimplyOne Women Multivitamin was created.
Category: Women's Multivitamins -
Jan 03, 2023 ![]()
Blog Post
Glaxon Multi+ Mood + Metabolism: Supercharged Health
The Glaxon Multivitamin is finally here, and it's as unique as expected! Glaxon Multi + Mood + Metabolism includes MitoBurn, SAMe, and Boron inside! -
Jan 01, 2023 ![]()
Product News
New Chapter Women's 50+ Multivitamin was created.
Categories: Gummy Supplements, Women's Multivitamins -
Jan 01, 2023 ![]()
Product News
Nature's Way Alive! Women's Gummy Multivitamin was created.
Categories: Gummy Supplements, Women's Multivitamins -
Dec 31, 2022 ![]()
Product News
New Chapter Every Man's One Daily Multivitamin 40+ was created.
Category: Men's Multivitamins -
Dec 31, 2022 ![]()
Product News
New Chapter One Daily Prenatal Multivitamin 35+ was created.
Category: Prenatal Vitamins -
Dec 28, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Gaia Herbs Kids Sniffle Support Herbal Drops was created.
Categories: Sinus Relief, Vitamins for Kids -
Dec 28, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Gaia Herbs Kids Bronchial Wellness Syrup was created.
Categories: Cough Remedies, Immune System Supplements, Vitamins for Kids -
Dec 28, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Gaia Herbs Kids Echinacea Supreme Herbal Drops was created.
Categories: Echinacea, Vitamins for Kids -
Dec 28, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Gaia Herbs Kids Echinacea Goldenseal Herbal Drops was created.
Categories: Echinacea, Goldenseal, Vitamins for Kids -
Dec 24, 2022 ![]()
Product News
NatureCity TrueMulti was created.
Category: Multivitamins -
Dec 22, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Glaxon Multi+ Mood +Metabolism was created.
Category: Multivitamins -
Dec 21, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Nature's Way Alive! Max3 Potency - Men's Multivitamin was created.
Category: Men's Multivitamins -
Dec 19, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Twinlab Daily One Caps For Women was created.
Category: Women's Multivitamins -
Dec 18, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Source Naturals Wellness Multiple was created.
Category: Multivitamins -
Dec 18, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Rainbow Light 35+ Mom and Baby Multivitamin was created.
Category: Women's Multivitamins -
Dec 18, 2022 ![]()
Product News
One A Day Kids Complete Multivitamin was created.
Categories: Gummy Supplements, Vitamins for Kids -
Dec 18, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Carlson Kid's Vitamin C was created.
Categories: Gummy Supplements, Vitamins for Kids -
Dec 17, 2022 ![]()
Product News
GNC Earth Genius - Women's Multivitamin was created.
Category: Women's Multivitamins -
Dec 12, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Natural Factors Whole Earth & Sea - Men's Multivitamin & Mineral was created.
Category: Men's Multivitamins -
Dec 12, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Natural Factors Whole Earth & Sea - Women's 50+ Multivitamin & Mineral was created.
Category: Women's Multivitamins -
Dec 12, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Natural Factors Whole Earth & Sea - Men's 50+ Multivitamin & Mineral was created.
Category: Men's Multivitamins -
Dec 12, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Natural Factors Whole Earth & Sea - Women's Multivitamin & Mineral was created.
Category: Women's Multivitamins -
Dec 11, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Nature Made Kids First Multivitamin with Omega-3 was created.
Categories: Gummy Supplements, Vitamins for Kids -
Dec 04, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Goli Nutrition Complete Kids Multi Gummies was created.
Categories: Gummy Supplements, Vitamins for Kids -
Nov 30, 2022 ![]()
Product News
First Endurance MultiV was created.
Category: Multivitamins -
Nov 28, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Rainbow Light Men's One 50+ Daily Multivitamin was created.
Category: Men's Multivitamins -
Nov 23, 2022 ![]()
YouTube Video
The Animal DOUBLE STACK: Primal Pre-Workout and Animal Pak -
Nov 03, 2022 ![]()
Product News
NOW Liquid Berry Vits was created.
Category: Liquid Multivitamins -
Oct 31, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Thorne Research Kids Multi + was created.
Category: Vitamins for Kids -
Oct 24, 2022 ![]()
Product News
One A Day Women's Complete Multivitamin was created.
Category: Women's Multivitamins -
Oct 21, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Evogen Evovite naturals was created.
Categories: Fat Burners, Multivitamins -
Oct 17, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Nature's Way Alive! Adult Premium Gummies Multivitamin was created.
Categories: Gummy Supplements, Multivitamins -
Oct 08, 2022 ![]()
Blog Post
The Animal Double Stack: Primal Pre-Workout and Animal Pak Stacked to Save
With the Animal Double Stack, the classic meets the novel - get the legendary Animal Pak and Animal Primal pre-workout together for a discount! -
Sep 25, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Paradise Herbs Earth's Blend Superfood Multi-Vitamin was created.
Category: Multivitamins -
Sep 16, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Nature Made Multi + Omega-3 For Her was created.
Categories: Gummy Supplements, Omega-3, Women's Multivitamins -
Sep 16, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Nature Made Multi For Her + Omega-3s was created.
Categories: Gummy Supplements, Omega-3, Women's Multivitamins -
Sep 16, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Nature Made Maximin Pack was created.
Category: Multivitamins -
Sep 16, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Nature Made Postnatal Multi + DHA was created.
Categories: DHA, Postnatal Vitamins -
Sep 16, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Nature Made Multi + Omega-3 was created.
Categories: Multivitamins, Omega-3 -
Sep 05, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Universal Animal Double Stack was created.
Categories: Pre Workout Supplements, Vitamin Packs -
Sep 03, 2022 ![]()
Product News
New Chapter Perfect Postnatal Whole-Food Multivitamin was created.
Category: Postnatal Vitamins -
Aug 28, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Rainbow Light Postnatal Multivitamin was created.
Category: Women's Multivitamins -
Jul 23, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Nature's Way Kids - Cool Calm & Collected was created.
Category: Vitamins for Kids -
Jul 17, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Garden of Life mykind Organics - Kids Elderberry & Sleep was created.
Categories: Elderberry, Vitamins for Kids -
Jul 17, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Garden of Life kids vitamin D3 was created.
Categories: Gummy Supplements, Vitamin D3, Vitamins for Kids -
Jul 17, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Garden of Life kids multivitamin powder was created.
Category: Vitamins for Kids -
Jul 10, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Nature's Way Alive! Once Daily Men's was created.
Category: Men's Multivitamins -
Jul 10, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Nature's Way Alive! Once Daily Women's 50+ was created.
Category: Women's Multivitamins -
Jul 05, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Real Ketones Keto Essentials was created.
Category: Multivitamins -
Jun 24, 2022 ![]()
Product News
KAL Vitality for Women was created.
Category: Women's Multivitamins -
Jun 21, 2022 ![]()
Product News
KAL Dinosaurs Jurassic Elderberry was created.
Category: Vitamins for Kids -
Jun 18, 2022 ![]()
Product News
KAL Dinosaurs Dino Colostrum was created.
Categories: Colostrum, Vitamins for Kids -
Jun 17, 2022 ![]()
Product News
KAL Dinosaurs Vitamin D-Rex was created.
Categories: Gummy Supplements, Vitamins for Kids -
Jun 17, 2022 ![]()
Product News
KAL Dinosours Jurassic Elderberry was created.
Category: Vitamins for Kids -
Jun 16, 2022 ![]()
Product News
KAL Dinosaurs MultiSaurus Vitamins & Minerals was created.
Category: Vitamins for Kids -
Jun 15, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Performix SST Multi+ was created.
Category: Multivitamins -
Jun 09, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Natural Factors Women's MultiStart was created.
Category: Women's Multivitamins -
Jun 09, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Natural Factors Men's MultiStart was created.
Category: Men's Multivitamins -
Jun 08, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Solaray Women's Golden Multivitamin was created.
Category: Women's Multivitamins -
Jun 08, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Solaray Men's Golden Multivitamin was created.
Category: Men's Multivitamins -
Jun 07, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Super Nutrition SimplyOne Men Multivitamin was created.
Category: Men's Multivitamins -
Jun 05, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Goli Nutrition Multi Bites was created.
Category: Multivitamins -
Jun 01, 2022 ![]()
Product News
New Chapter Organics 40+ Every Man II was created.
Category: Men's Multivitamins -
Jun 01, 2022 ![]()
Product News
GNC Mega Men Essentials was created.
Category: Men's Multivitamins -
Jun 01, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Nature's Way Alive! Men's 50+ Ultra Potency Multivitamin was created.
Category: Men's Multivitamins -
Jun 01, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Nature's Way Alive! Men's 50+ Gummy MultiVitamins was created.
Categories: Gummy Supplements, Men's Multivitamins -
May 22, 2022 ![]()
Product News
Pioneer Chewable Vitamin Mineral (Iron Free) was created.
Category: Multivitamins -
May 19, 2022 ![]()
Product News
New Chapter One Daily Prenatal Multivitamin was created.
Category: Prenatal Vitamins -
May 14, 2022 ![]()
Product News
New Chapter Every Woman Multivitamin was created.
Category: Women's Multivitamins -
May 11, 2022 ![]()
Product News
New Chapter Women's Multivitamin was created.
Category: Women's Multivitamins -
May 11, 2022 ![]()
Product News
New Chapter Men's Multivitamin was created.
Category: Men's Multivitamins -
May 08, 2022 ![]()
Product News
GNC Men's Extreme Training was created.
Category: Men's Multivitamins -
May 08, 2022 ![]()
Product News
GNC Men's Ripped Vitapak Program was created.
Category: Men's Multivitamins -
May 08, 2022 ![]()
Product News
GNC Women's Ripped Vitapak Program was created.
Category: Women's Multivitamins -
May 01, 2022 ![]()
Product News
GNC Women's One Daily Multivitamin was created.
Category: Women's Multivitamins -
May 01, 2022 ![]()
Product News
GNC Women's One Daily Multivitamin 50 Plus was created.
Category: Women's Multivitamins -
May 01, 2022 ![]()
Product News
GNC Women's Multivitamin Diabetic Support was created.
Categories: Blood Sugar Supplements, Women's Multivitamins -
Apr 30, 2022 ![]()
Product News
GNC Women's Multivitamin Soft Chew was created.
Category: Women's Multivitamins -
Apr 29, 2022 ![]()
Product News
GNC Women's Multivitamin Prenatal was created.
Category: Prenatal Vitamins -
Mar 16, 2022 ![]()
Blog Post
Crush It Kids Multi: Core Nutritionals Gummy Multivitamins
Core Nutritionals Crush It Kids Multi is here to help parents fill nutritional gaps for their children. Naturally flavored and colored gummies! -
Mar 15, 2022 ![]()
TikTok Video -
Feb 18, 2022 ![]()
Blog Post
Ghost Multi is Back! Level Up Your Micronutrient Intake
Ghost Multi is here to level up your micronutrient intake with 21 vitamins and minerals, along with several trademarked ingredients, such as PhytoServ! -
Jan 21, 2022 ![]()
Blog Post
Ghost Lifestyle Updates for Early 2022: Building The Brand S8:E13
In Ghost Lifestyle's Building the Brand Season 8, Episode 13 titled "Back for Good", the brand made big announcements, including the return of Ghost Multi! -
Sep 27, 2021 ![]()
YouTube Video
I ATE THEM ALL: Myprotein Multivitamin Gummies -
Jul 30, 2021 ![]()
YouTube Video
WHAT I TAKE FROM REVIVE MD | Health Supplement Stack Overview -
Jul 29, 2021 ![]()
Blog Post
Revive MD Starter Stack: Step 1 in Reviving Your Health
Revive MD makes excellent supplements, but where to start? The simple answer is their STARTER Stack, which has CALM+, Daily Greens, and Immune Multi! -
May 19, 2021 ![]()
YouTube Video
KIDS Gummies Multivitamin from Revive MD! (Discontinued) -
May 17, 2021 ![]()
Blog Post
Revive MD Kids Gummies Multivitamin: Supplementing a Healthy Children’s Diet
Revive MD Kids' Gummies Multivitamin provides a delicious source of essential vitamins and minerals to help kids reach reach daily micronutrient needs -
Apr 27, 2021 ![]()
YouTube Video
Dieter's Multivitamin | TruMulti by PEScience! (Men's & Women's) -
Apr 26, 2021 ![]()
Blog Post
PEScience TruMulti: A Dieter’s Multivitamin for Men and Women
PEScience TruMulti are multivitamins with dieters in mind. Cortisol control from KSM-66 and insulin sensitivity from Chromax Chromium Picolinate! -
Apr 26, 2021 ![]()
Giveaway Contest
Giveaway! Who wants to WIN and get PUMPED?! We're giving away a stack of @PEScience TruMulti and... -
Apr 07, 2021 ![]()
Blog Post
Chromax Chromium Picolinate: 25+ Years of Insulin Sensitivity Improvement
Chromax Chromium Picolinate from Nutrition21 has been improving insulin sensitivity for over 25 years. This article recaps the research behind Chromax -
Feb 05, 2021 ![]()
Blog Post
Myprotein Women’s Multivitamin: Cover Your Daily Needs at a Value
Myprotein's Women's Daily Multivitamin is a great "insurance plan" for Myprotein's health-conscious customers - it's affordable and full-spectrum. -
Feb 02, 2021 ![]()
Blog Post
Bob Levi Named CEO of Universal Nutrition
Universal Nutrition, creators of the legendary Animal Pak, have always been family-owned and operated. In 2021, they brought their first CEO, Bob Levi -
Jan 05, 2021 ![]()
YouTube Video
Meet The New and Improved Animal Pak | The Product That Started A Brand -
Oct 13, 2020 ![]()
YouTube Video
Kaged Muscle Multivitamin Breakdown | A Whole-Food Based Vitamin and Mineral! -
Oct 08, 2020 ![]()
Blog Post
Kaged Multivitamin: A Whole Food Vitamin and Mineral Blend
The second product to join Kaged Naturals is a comprehensive multivitamin called Kaged Multivitamin, which is derived from whole-foods! -
Sep 24, 2020 ![]()
YouTube Video
GHOST MULTI IS HERE | Best Multivitamin 2020?! -
Aug 11, 2020 ![]()
Blog Post
American Made Nutrition Supplements: It All Starts Here
American Made Nutrition is from the creators of Axe & Sledge Supplements, but with a focus is on health and wellness and a bit of sports performance! -
Apr 27, 2020 ![]()
Blog Post
The WARRIOR Series From Nutrex Research: Your Legacy Starts Here
Nutrex Research has been working on a major project for nearly a year and they are finally able to reveal it! The Warrior Series has finally arrived! -
Apr 02, 2020 ![]()
Blog Post
NutraBio EpiCor: The “Multi-Vitamin” For Your Immune System
NutraBio EpiCor is an immune system boosting supplement. EpiCor (dried yeast fermentate) stands out with a far different way of approaching immunity! -
Feb 05, 2020 ![]()
Blog Post
Nutrex Vitadapt: Multivitamin for Comprehensive, Year-Long Health!
Nutrex Vitadapt is our favorite multivitamin, and is one of the most comprehensive ones on the market! See all it has to offer, including adaptogens! -
Dec 23, 2019 ![]()
Blog Post
NutraBio MultiSport Men’s Formula Revitalized with Better B Vitamins!
The NutraBio MultiSport Men's and Women's multivitamins have been upgarded for 2020, with more bioavailable forms of B Vitamins (such as P5P!) -
Oct 30, 2019 ![]()
Blog Post
NutraBio Introduces UpSorb Starter Kits for Retailers
NutraBio UpSorb is taking over countertops, and for great reason - it works with SO many supplements. Now retailers can get an UpSorb Starter Kit! -
Sep 11, 2019 ![]()
YouTube Video
SteelFit Multi-V Flavor Review! -
Jun 26, 2019 ![]()
YouTube Video
SteelFit Multi-V Multivitamin Powder: MORE Than Just a Multi! -
Jun 17, 2019 ![]()
Giveaway Contest
Let's start this week off RIGHT! Win yourself a tub of SteelFit USA's Steel Multi-V on the... -
Jun 06, 2019 ![]()
Blog Post
Live Relentless: Tim Kennedy’s Supplement Brand
Meet the Alpha Sheep Dog, Tim Kennedy at the new Relentless Nutrition Launch Event in Austin, TX on April 13, 2019! -
May 01, 2019 ![]()
YouTube Video
Relentless Daily Wellness: Night/Day Multivitamins, Nootropics, & Sleep Aids! -
Apr 21, 2019 ![]()
YouTube Video
Tim Kennedy (Army Green Beret, MMA) Brings RELENTLESS Supplements -
Apr 20, 2019 ![]()
YouTube Video
Introducing RELENTLESS Nutrition with CEO Charlie Hartwig -
Apr 09, 2019 ![]()
Blog Post
Primeval Labs Glory MV: Multivitamin / Minerals for the Masses
Primeval Labs Glory MV is a basic multivitamin / multimineral to cover your dietary bases, and includes some awesome mineral support thanks to TRAACS! -
Jul 11, 2018 ![]()
YouTube Video
Mike Loves This Multi Vitamin! | Nutrex Vitadapt -
May 15, 2018 ![]()
Blog Post
USPlabs Vitamer PRO – A “Less is More” Multivitamin!
USPlabs is bringing a "less is more" approach to its newest supplement, Vitamer PRO, which is a multivitamin for men and women. -
Mar 07, 2018 ![]()
YouTube Video
Drug-Tested Athlete Safe Multi Vitamin | Nutrex VITADAPT -
Nov 02, 2017 ![]()
YouTube Video
Had a Baby! Fertility Supplements, Prenatal Vitamins, Gestational Diabetes, C-Section, & Cats -
Aug 17, 2016 ![]()
Blog Post
Advanced Molecular Labs (AML) Supplements: Return of the King
Advanced Molecular Labs is an up and coming supplement brand developing products led by one of the industry longest tenured gurus, Steve Blechman. -
Oct 12, 2015 ![]()
Blog Post
Magnum PRIMER – Peak Performance Vitamin Pack
Magnum Primer is a comprehensive multivitamin / multimineral that covers all the bases you need plus omega 3 and digestive support. -
Sep 23, 2014 ![]()
Blog Post
Vita JYM: The PhD’s Take on Multivitamins
Vita JYM is Jim Stoppani's answer to multivitamins. Keep reading to find out what makes it so different: good ingredients in, bad ingredients out!
Sign up for future Multivitamin news!
Click the button below to sign up for future Multivitamin news, deals, coupons, and reviews!
Multivitamin Price Alerts
The following price alerts are still active:
- Apr 22, 2024Controlled Labs Orange Triad 180 Tablets dropped by 24.8% to $19.99 at Muscle and Strength
- Apr 22, 2024Controlled Labs Orange Triad 270 Tablets dropped by 16.7% to $24.99 at Muscle and Strength
- Apr 16, 2024Universal Animal Pak 44 Packs dropped by 6.8% to $33.59 at Vitamin Shoppe
- Feb 02, 2024Optimum Nutrition Opti-Women 60 Capsules dropped by 7.2% to $12.99 at Walmart
- Dec 20, 2023GHOST Multi 90 Vcaps dropped by 20% to $29.60 at Ghost Lifestyle
- Sep 27, 2023Universal Animal Pak 30 Servings (only Orange Crushed) dropped by 6.5% to $39.95 at A1 Supplements
Sign up for future Multivitamin deals and coupons!
Click the button below to sign up for future Multivitamin deals, news, and coupons!
Multivitamin Reviews & Videos
-
Apr 02, 2024JOCKO WILLINK: Starting Jocko Fuel and Jocko's Supplement Stack | PricePlow 132
-
Feb 07, 2024Animal Pill Packs – The Full Arsenal of “Paks” Explained
-
Feb 07, 2024Oh, you like this recent pill pack trend? @officialanimalpak did it first!!! Shout out to the OG!!
-
Jan 08, 2024Daily Health Pack with Nootropics! Core Nutritionals Multivitamin Pack
-
Jan 08, 2024Would tou difch your stack and use @CoreNutritionals daily packs?
-
Dec 13, 2023Revive MD Essentials Vitamin Pack: Cover Nutrient Basics
-
Nov 21, 2023Bare Performance Nutrition Strong Multivitamin: With Cognizin® Citicoline
-
Aug 07, 2023Revive MD Vitamin B-Complex: Improve Brain Function & Fatigue
-
Jun 21, 2023NEW ANIMAL PAK POWDER
-
Feb 17, 2023New Animal Pak: Now with Spectra and AstraGin!
-
Feb 01, 2023A Multivitamin with MitoPrime, SAMe, & Boron! Glaxon Multi+
-
Jan 24, 2023ANIMAL FORMULATOR TELLS ALL | Universal Nutrition | Jason Budsock | Episode 080
-
Nov 23, 2022The Animal DOUBLE STACK: Primal Pre-Workout and Animal Pak
-
Mar 15, 2022
-
Sep 27, 2021I ATE THEM ALL: Myprotein Multivitamin Gummies
-
Jul 30, 2021WHAT I TAKE FROM REVIVE MD | Health Supplement Stack Overview
-
May 19, 2021KIDS Gummies Multivitamin from Revive MD! (Discontinued)
-
Apr 27, 2021Dieter's Multivitamin | TruMulti by PEScience! (Men's & Women's)
-
Jan 05, 2021Meet The New and Improved Animal Pak | The Product That Started A Brand
-
Oct 13, 2020Kaged Muscle Multivitamin Breakdown | A Whole-Food Based Vitamin and Mineral!
-
Sep 24, 2020GHOST MULTI IS HERE | Best Multivitamin 2020?!
-
Sep 11, 2019SteelFit Multi-V Flavor Review!
-
Jun 26, 2019SteelFit Multi-V Multivitamin Powder: MORE Than Just a Multi!
-
May 01, 2019Relentless Daily Wellness: Night/Day Multivitamins, Nootropics, & Sleep Aids!
-
Apr 21, 2019Tim Kennedy (Army Green Beret, MMA) Brings RELENTLESS Supplements
-
Apr 20, 2019Introducing RELENTLESS Nutrition with CEO Charlie Hartwig
-
Jul 11, 2018Mike Loves This Multi Vitamin! | Nutrex Vitadapt
-
Mar 07, 2018Drug-Tested Athlete Safe Multi Vitamin | Nutrex VITADAPT
-
Nov 02, 2017Had a Baby! Fertility Supplements, Prenatal Vitamins, Gestational Diabetes, C-Section, & Cats
Subscribe for more Multivitamin news and alerts!
Subscribe to PricePlow on YouTube, follow PricePlow on Instagram or click the button below to sign up for our latest Multivitamin news and reviews!