Protein powder is one of the most popular supplements in sports nutrition. Customers like them because they're convenient, versatile, and affordable. At the same time, good protein products are low in fats and carbohydrates. Finally, the body needs three macronutrients to survive, including protein (the others are carbohydrates and fats).
Unlike carbs and fats, protein is not typically used as an energy source. Instead, the nutrient supplies the body with numerous amino acids that can be used for a variety of physiological processes ― most notably, the growth, repair, and maintenance of tissue. While you can get all of the protein you need from whole foods, such as steak, Greek yogurt, chicken, eggs, fish, and tofu, having protein powder on hand makes it easier to hit your daily protein intake goals.
There are several types of protein powders on the market. The most common is whey. Whey and casein are the two main proteins naturally found in milk. To formulate a whey supplement or to make whey-based ingredients, you first have to isolate the nutrient. There are two ways to do it: You can separate it from milk or, during the cheese-making process, it can be extracted as a byproduct.
Using whey in protein powder products is ideal because it's easy to flavor; it's rich in all nine essential amino acids; it digests rapidly; it's high in protein; and it contains minimal fat, carbohydrates, and lactose.
Studies have compared whey protein to other sources of protein, including beef, milk, eggs, casein, and soy, and found that it's superior based on the following factors:
- Biological value: a measurement indicating how well the body absorbs and utilizes the protein
- Protein efficiency ratio: determines the effectiveness of a protein by measuring tissue growth
- Net protein utilization: the number of amino acids converted to proteins versus the number of amino acids supplied (similar to biological value)
- Protein digestibility corrected amino acid score (PDCAAS): evaluates the quality of a protein based on an individual's amino acid requirements and their ability to digest it
- Digestible indispensable amino acid score (DIAAS): the ratio of the digestible amino acid content in food to the same amino acid in a reference pattern taken from age-specific amino acid requirements (the current gold standard of protein quality assessment)[1]
Numerous studies have shown that supplementing with whey protein can significantly help enhance recovery, lean body mass, strength, and overall performance.[2-4] So it's no surprise that whey protein powder dominates the sports nutrition industry, but is there a way to make it even better? That's the question Ingredient Optimized (io) asked. What they came up with is ioWhey.
What is ioWhey? Keep reading to find out!
ioWhey Raises the Standard for Whey Protein
By using Ingredient Optimized Technology, io discovered a way to create a whey protein with greater bioavailability than standard whey protein isolate. The company uses a natural atmospheric plasma treatment process to enhance the surface area, solubility, and dispersibility of protein molecules. The technology can be used with various protein sources to improve their absorption, such as whey and pea protein.[5,6]
Unlike other protein processing methods, io doesn't use any harmful chemicals or enzymes to alter the structure of the protein. Instead, io carefully changes the nutrient's tertiary and quaternary structure to expose hydrophobic pockets of the protein molecules.[5,6] This process improves the protein's bioavailability, making it easier for the body to absorb the nutrients and is less likely to cause stomach discomfort.

ioWhey is a more bioavailable form of whey protein that's been shown to outperform whey protein isolate and hydrolyzed whey protein isolate.
According to Ingredient Optimized, here are the key features of ioWhey:
- Proven greater absorption than whey protein isolate
- Taste-neutral. Unlike some processes and enzymes that can leave products tasting bitter and acidic, ioWhey doesn't alter the taste profile
- Easy to use in foods, supplements, and beverages
- Clinically backed by over five years of research & development, along with seven human trials and over five years of research and development
- A scalable process designed to integrate seamlessly into your supply chain
- Safe and compliant, confirmed by the leading FDA legal firm in the U.S. to maintain GRAS (generally recognized as safe) status
- Available as USDA certified organic, NSF certified for sport, halal, kosher, NSF (GMP certificate), and SQF Level 2
- With no third-party ingredients, ioWhey allows for a clean label
- Improves customer engagement and experience[6]
Some ioWhey early adopters include well-respected brands like Performix and Nutrata. The ingredient can be used anywhere you'd see protein powder, including functional foods such as high protein cookies and wafers.
As we reported earlier, Ingredient Optimized Technology is used on and to produce other supplements, including pea protein (ioPEA), branched-chain amino acids (ioBCAA), caffeine, carnitine, and citrulline. So make sure to subscribe below to receive notifications when io releases more cutting-edge trademarked ingredients. And keep reading to learn more about ioWhey.
Subscribe to PricePlow's Newsletter and Ingredient Optimized Alerts
The Science Behind ioWhey
Before launching ioWhey, io conducted several studies to ensure that their ingredient is, in fact, superior to other forms of whey protein. So far, there are seven human clinical trials that support the use of ioWhey. The two main proteins that ioWhey has been compared to are standard whey protein isolate (WPI) and hydrolyzed whey protein (HWP).
Whey protein isolate is considered the purest form of whey protein on the market. It's 90% protein content by weight and contains virtually no carbohydrates or fats. Hydrolyzed whey protein is similar to WPI, but it undergoes additional processing to be "pre-digested." This means that a portion of the protein is broken down into peptides in order to increase the rate of digestion/absorption and bioavailability.
Let's look at the research to see how ioWhey stacks up against WPI and HWP.
-
ioWhey vs. Whey Protein Isolate
In a recent study, researchers from Keiser University used a blinded, randomized clinical trial to assess the effects of ioWhey versus standard whey protein isolate on various measures of body composition in adult athletes.[7]
The researchers recruited 20 healthy men and women volunteers and randomly divided them into two groups:
- Experimental group - received one serving (equated to 28 grams of protein) of ioWhey
- Control group - received one serving (equated to 28 grams of protein) of traditional whey protein isolate[7]
Each day, participants consumed one serving of their assigned supplement after exercising. They also were instructed to maintain their current diet, but discontinue taking any additional supplements for the duration of the eight-week study.[7]
The main outcome measures of the study were collected pre- and post-test, on the same day of the week, and consisted of the following:
- Body mass index (BMI) - measured and calculated by using participants' height and weight
- Fat-free mass (FFM) - measured by a body composition analyzer
- Fat mass (FM) - measured by a body composition analyzer
- Percentage of body fat (PBF) - measured by a body composition analyzer
- Strength - measured by a repetition max on the squat and bench press
- Stomach discomfort and digestion - assessed using psychometric measures of the
protein's taste, impact on stomach distress, and post-training recovery time[7]
After eight weeks, the researchers found that the experimental group experienced:
- Less stomach discomfort
- Faster recovery
- Greater performance improvements for the squat and bench press
- Greater increase in FFM[7]
Based on their findings, the study authors concluded that ioWhey offers numerous advantages over standard whey protein isolate. ioWhey may help users increase lean muscle mass, strength, and recovery. It's also easier on the stomach.[7] The researchers theorize that the difference in results between the two types of protein may be attributed to ioWhey's superior bioavailability.[7]
Another study, this one conducted by researchers from the Applied Science & Performance Institute in Tampa, FL, investigated postprandial plasma amino acid (AA) responses of two different forms of whey protein isolate — WPI (whey protein isolate) and whey protein isolate plus Ingredient Optimized Protein (called WPI + io).[8]
Using a randomized, cross-over design, researchers recruited 12 healthy male volunteers and instructed them to consume 29.6 grams of WPI or WPI + io mixed with 236 milliliters of water.[8] Participants' plasma essential amino acids and branched-chain amino acid concentrations were collected pre-consumption and at five 30-minute intervals post-consumption.[8]
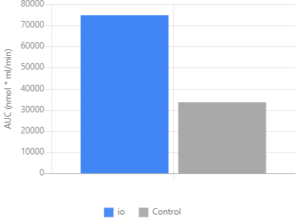
ioWhey increases plasma EAA levels approximately 123% more than standard whey protein isolate. Graph courtesy of Ingredient Optimized.[6]
Here are some of the key findings from the study:
- Plasma levels of total EAA concentration were significantly greater in WPI + io at 30, 60, 90, and 120 minutes post-consumption, compared to WPI
- Plasma levels of total BCAA concentration were significantly greater in WPI + io at 30,60, 90, and 120 minutes post-consumption compared with WPI.
- Only the WPI + io group had elevated leucine levels, compared with pre-test at 90 minutes post-consumption[8]
Although both groups saw significantly elevated EAA, BCAA, and leucine from basal levels, WPI + io raised plasma EAA, BCAA, and leucine to a greater extent compared with untreated WPI.[8] The researchers concluded that ingredient-optimized whey protein may be even more beneficial than traditional whey protein isolate for specific populations (i.e. those who partake in regular exercise, the elderly, and those affected by a reduced sensitivity to amino acids).[8]
A study conducted by researchers at the University of South Florida set out to determine the effects of two different types of whey protein supplements on maximum strength in conjunction with an 8-week resistance-training program — standard WPI versus reduced-volume of a proprietary-processed WPI) (as ioWhey protein). The researchers recruited 32 resistance-trained male volunteers for a randomized, double-blind study.[9]
First, participants were matched according to their fat-free mass (FFM). Then they were randomly assigned to the standard WPI or novel WPI group. The standard WPI group received 27 grams of WPI, whereas the novel WPI group only received 20 grams of ioWhey, plus 7 grams of maltodextrin to match the volume of the standard WPI group.[9]
Participants were instructed to take their assigned supplements immediately following their resistance training session. It's important to note that both groups performed identical training programs and consumed 1.5 to 2.5 grams/kilogram of body weight per day. After eight weeks, to assess changes in maximal strength, the volunteers performed the back squat, deadlift, and bench press.[9]
Despite reduced protein volume, the novel WPI group increased their maximal strength to a similar extent as the standard WPI group.[9] Thus, the researchers concluded that for resistance-trained males, a lower amount (~25% less whey protein isolate) of ioWhey is just as effective as a higher dose of standard WPI for facilitating strength gains.[9] In other words, due to ioWhey's superior bioavailability, the body can absorb more from a smaller amount. The same is not true for standard whey protein isolate.
-
ioWhey vs. Hydrolyzed Whey Protein
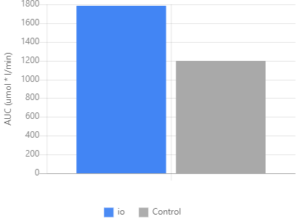
ioWhey increased plasma EAA levels approximately 48% more than hydrolyzed whey protein isolate. Graph courtesy of Ingredient Optimized.[6]
Researchers from the Applied Sciences & Performance Institute examined the postprandial plasma essential amino acid (EAA) and branched-chain amino acid (BCAA) responses of hydrolyzed whey protein isolate (HWPI), compared to plasma-treated, non-hydrolyzed whey protein isolate (PT-NHWPI) (ioWhey).[10]10 volunteers were recruited for the double-blind, randomized, crossover trial. Subjects were instructed to consume 25 grams of either HWPI or PT-NHWPI.[10] The participants' plasma EAA and BCAA concentrations were assessed from pre-supplement-consumption blood samples and again at five 30 minute intervals post-consumption.[9]The results showed that blood plasma levels of both EAA and BCAA concentration were significantly greater in the PT-NHWPI group at each post-consumption time interval.[10] Based on these findings, the researchers concluded that Ingredient Optimized Technology may be an effective method for improving blood plasma amino acid response.[10]
Learn more about ioWhey
Watch this Video to See How ioWhey Protein Works
Where to Find ioWhey
Here are some products that contain ioWhey:
- Performix ioWhey Protein
- Nutrata Plasma ioWhey
ioWhey is Just the Beginning for Ingredient Optimized
Ingredient Optimized prides itself on taking traditional dietary supplements and making them even better through scientific innovation. ioWhey is a prime example of that! Before ioWhey was created, it was widely accepted that whey protein was one of the most optimal sources of protein.
Whey is easily digested, rapidly absorbed, and rich in both essential amino acids and branched-chain amino acids. However, some people have trouble absorbing and utilizing all of the amino acids that whey supplies. So they may not get all of the benefits they could from standard whey protein. Fortunately, Ingredient Optimized created a whey protein with superior bioavailability.
Ingredient Optimized didn't stop there. They used their breakthrough technology on other protein sources and dietary ingredients. For example, Ingredient Optimized recently launched ioPea, a naturally-optimized plant protein that was shown to be just as good as whey protein and superior to standard pea protein.[5]
Learn more about ioPea:
ioPea Protein: A Plant Protein With the Power of Whey
io is working on releasing more cutting-edge ingredients that utilize Ingredient Optimized Technology, including
- ioBeta (beta-alanine)
- ioCaffeine
- ioCitrulline
- ioCarnitine
Needless to say, Ingredient Optimized has a lot to look forward to, so make sure to subscribe below for more information!
Ingredient Optimized – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.






Comments and Discussion (Powered by the PricePlow Forum)