PEScience's High Volume stimulant-free pre workout pump supplement has been around since 2014 - long before most brands had a stim-free pre workout... hell, long before most of today's supplement brands even existed. With large nitrate doses, the 2014 release was well ahead of its time, but it's also been upgraded a few times along the way. This article covers the formula after those upgrades.

WAY ahead of its time! PEScience High Volume is the original high-nitrate stim-free pre workout pump supplement
The potent pump supplement was originally brought into PEScience through their acquisition of a brand known as Athletix. Like the original version, High Volume is loaded, but has been improved a few times along the way.
The formula has long stood the test of time, with only a minor 2015 tweak to the Performance Pump Matrix, which was upgraded to include Ferula asafoetida root extract (for its ferulic acid), an ingredient we don't see too often in pump pre workouts. We dig into the science behind ferulic acid and everything else in the tub in this article.
PEScience High Volume is a classic, always-underrated, and well-before-its-time stimulant-free pre-workout. You can read all about it below, but first sign up for PricePlow's PEScience news so you don't miss our latest news on the brand:
PEScience High Volume – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.
PEScience High Volume Ingredients
-
L-Citrulline - 4g
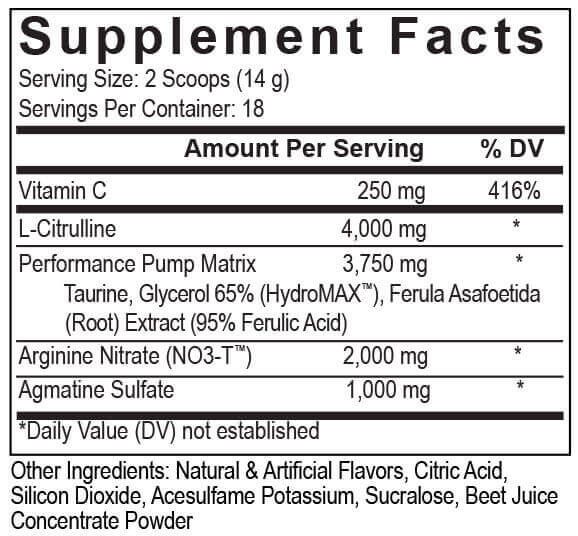
High Volume's Ingredients have mostly been the same since 2014, with a minor tweak in 2015. Check out our discussion on ferulic acid below!
It may seem like a solid, strong dosage now, but back in 2014 when PEScience brought High Volume into their line and reformulated it, this was a game changer. Whenever you see a stimulant-free supplement dosed this well, pay some homage to PES for starting the wave. The same will go for the synergistic nitrate doses as well.
L-Citrulline is an amino acid that increases nitric oxide (NO) levels. It does so by converting to L-arginine,[1-4] and actually generates more NO than direct L-arginine supplementation due to its enhanced bioavailability in the body.[5]
With the increased nitric oxide levels, you get improved circulation and vasodilation,[6] which equates to high volume pumps! The increased nitric oxide (and subsequent blood flow) also means better oxygen and nutrient transport, which assists in prolonged workouts with less soreness and fatigue. Ultimately, citrulline boosts ATP production (ie cellular energy), helping you do more work and at a faster rate with better recovery.[7-9]
4g is a great dose for pumps, and again, PEScience was well ahead of their time. When you combine that with 2g arginine nitrate discussed below, you get mind-blowing pumps that still aren't achieved by most competitors nearly a decade later!
-
Performance Pump Matrix – 3750 mg
-
Taurine
Taurine is the osmolyte ingredient that helps us keep a proper water balance across our cells. It's also a conditional amino acid that the body can create from other molecules. It's easy to develop a taurine deficiency from things like intense exercise, poor diet, and illness. So it's beneficial to supplement the amino acid.[10]
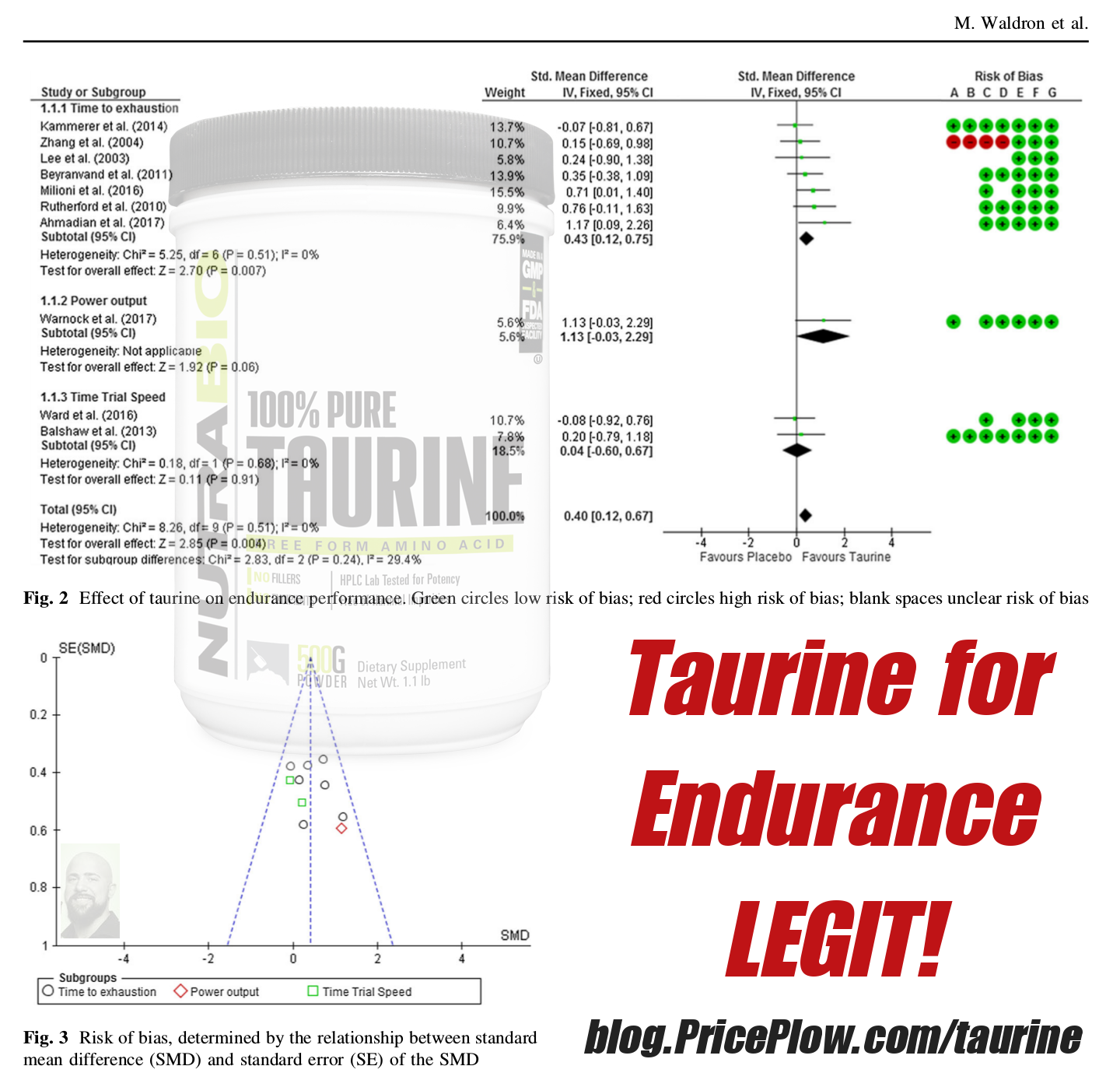
Taurine, long used for a 'filler' amino acid, turns out to be legit for endurance... and after a single use!
Proper taurine supplementation can provide the body with many incredible benefits, including reduced oxidative stress, improved calcium signaling for muscle contractions, a significant increase in endurance (after the first use!), improved cognition, and better bile production for improved fat metabolism.[10-12]
Taurine's incredible endurance effect
If you're interested in reading about taurine's incredible effects on endurance in greater detail,see our blog post titled Taurine: The Underrated Endurance Supplement (New Meta-Analysis). The article is a systematic review published in the journal, Sports Medicine. It looks at several studies and notes improved endurance when using anywhere from 1 to 6 grams of taurine.[12] We're positive that we're getting somewhere in that dose here, since taurine is the first of three ingredients in a 3.75g proprietary blend.
Improved focus
Taurine also has effects on focus and cognition. A 2019 study published in the journal Life Sciences demonstrated a taurine-enhanced cognition boost by restorating taurine and GABA-receptor function. It resulted in decreased neuroinflammation and oxidative stress, activated more physiological pathways, and stimulated mitochondrial and synaptic function.[11]
Get that extra pump from water and nitric oxide
Studies have shown that taurine, alongside L-citrulline, has shown promise in giving greater pumps through water and nitric oxide (NO). A 2020 study published in the journal Nitric Oxide demonstrated that taurine can boost NO levels by activating nitric oxide synthase and also improving nitric oxide bioavailability.[13]
-
Glycerol 65% (HydroMAX)
When it comes to hydration, endurance, cell volumization, and heat tolerance, water is king. And this simple ingredient -- glycerol -- enables you to hold more water for better performance!
Glycerol, a naturally-occuring sugar alcohol, is similarly structured to sugar alcohols in various foods. However, despite ways they're alike, glycerol is quite unique. It's a member of the trihydroxy group, which means that it has three oxygen-hydrogen bonds within its structure.[14] This is sometimes referred to as 1,2,3-Propanetriol or glycerine. HydroMax can take your workouts to the next level when it's part of your pre-workout like it is with High Volume.
Staying hydrated with Glycerol
We know how extremely important it is to stay hydrated during intense exercise. Glycerol puts you in a state of "hyperhydration", which improves your ability to stay hydrated. At high enough doses, it can prolong endurance,[15-17] reduce urination,[18] and protect from heat.[19]
If you'd like to take a more in depth look at Glycerol, see our article titled Glycerol: The Ultimate Guide for Hydration, Heat Protection, and Pumps.
-
Ferula Asafoetida Root Extract (95% Ferulic Acid)
Ferulic acid is a main bioactive ingredient in Ferula asafoetida, and is the most unique ingredient in High Volume. It replaced AmentoMAX (selaginella tamariscina) and evodia rutaecarpa extract sometime around 2018.
Announcing the PEScience Strawberry Kiwi Pre Workout lineup!
There's less research on it, but in 1990, researchers discovered that 30 milligrams of ferulic acid per day taken for eight weeks yielded increased body weight and muscular strength in weightlifters,[20] but a full-text (or even abstract) of this study has proven difficult to find. Further animal research suggested that ferulic acid could enhance endurance capacity and reduce fatigue, likely by elevating antioxidant levels.[21]
A deeper look at ferulates
The background is that ferulates generally come from gamma oryzanol, also known as Rice bran oil, and they are plant phenols with antioxidant properties that interact with neurotransmitters in the hypothalamus since they are structurally similar to normetanephrine,[22] a metabolite of norepinephrine.
When given intravenously to heifers, researchers detect increased somatotropin (growth hormone) levels,[23] so there may be a GH-boosting effect as well. Most effects from gamma oryzanol are attributed to the ferulates inside.[24]
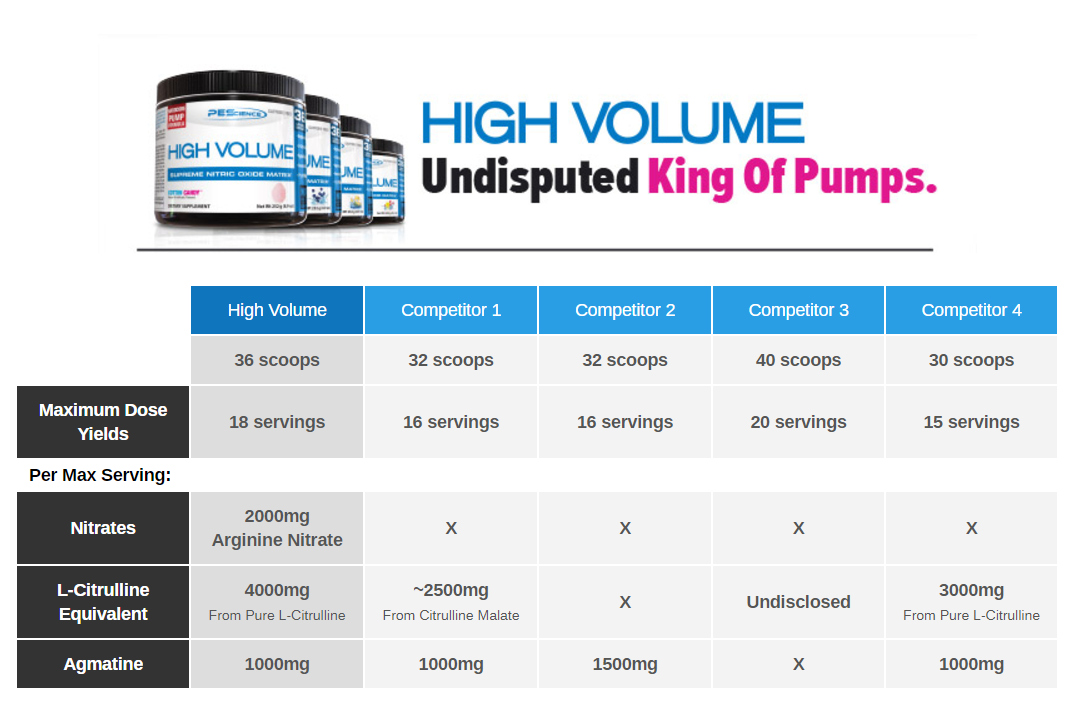
So while there's less research on ferulic acid, there seems to be something there, and it could be the ingredient that still sets High Volume apart from its competitors (many of which are copycats, since High Volume was the original of this nature).
-
-
Arginine Nitrate (NO3-T) - 2g
When the High Volume was released by PEScience in 2014, this was the big deal - a whopping 2g dose of Arginine Nitrate. Still to do this day, supplements don't go much higher than this, as this is near the top of a daily dose. Reason being, nitrates are powerful nitric oxide boosters, and arginine nitrate may be the best of them all, with multiple levels of synergy inside.
We've discussed arginine as a nitric oxide booster above, but nitrates are some of the most powerful ingredients for athletic performance. They provide an enormous number of benefits, including the following:
- Improved blood flow[25]
- Less oxygen cost when exercising / working out[25-28]
- More force and power production (strength!)[29,30]
- Very long-lasting nitric oxide boosts and pumps[29,31]
- Increased athletic endurance[27,28]
- Better recovery and energy at the cellular level[30,32]
Nitrates are strong, but more importantly, they last long. As in, a half-life of 8 hours -- so you can still have pumps half a day later after using them! This means you won't find your pump fading halfway through your workout like other ingredients.
The arginine / nitrate synergy
Remember PEScience's OG branding, back when it was "PES" (Physique Enhancing Science)? Branding may have changed, but because they're so powerful and industry-leading, the formulas haven't!
So why use arginine nitrate specifically? Research indicates that pairing arginine directly with nitrate shows a number of significant improvements -- better and more consistent absorption and uptake, reduced nitrate tolerance, and improved vasodilation.[33,34]
It's the reduced nitrate tolerance that's most important to High Volume's consumers. With other nitrate-based products, you may stop feeling it as much within a week. By bonding arginine in, the reduction of tolerance will make your tub last all the way through.
And finally, to improve the nitrate's effects, PEScience also included a solid dose of Vitamin C, which further prevents nitrate tolerance![35]
-
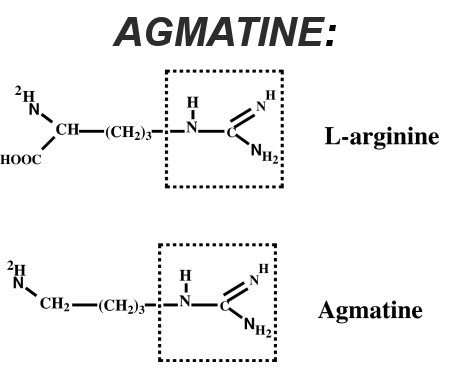
Agmatine Sulfate - 1g
Agmatine sulfate is a metabolite of L-arginine, and is mainly used as an arginase inhibitor, which means it helps prevent the breakdown of arginine.[36] This is a great inclusion, since we have loads of nitric oxide enhancement from the citrulline and arginine nitrate, but now we want to keep it around as long as possible.
Research demonstrates that agmatine sulfate activates the enzyme that produces nitric oxide -- nitric oxide synthase.[37]
Agmatine may even give a slight boost in focus, since it has some neuromodulatory properties and can function as a neurotransmitter.[38] This is similar to taurine - it's not the primary effect, but great to have in the supplement, and some may feel it.
-
Vitamin C - 250mg
The main reason for including Vitamin C in a nitrate-based pre workout supplement is because the popular vitamin antioxidant has been shown to prevent nitrate tolerance,[35] so you'll see synergy with the arginine nitrate.
In addition, high-dose vitamin C may also enhance nitric oxide production.[39] Inversely, those with low vitamin C status have decreased performance and nitric oxide production.[40]
Most nitrate-based pre workout supplements will include Vitamin C for the nitrate tolerance prevention, though.
PEScience High Volume Flavors:
The list of flavors will be kept up to date below:
The OG high-nitrate pump supplement, and still a beast
With some minor tweaks here and there, High Volume is still the same great product and includes an industry-leading nitric oxide pump matrix. The addition of ferulic acid makes it unique, and we're attempting to track down the research showing 30mg/day in weight lifters, because there seems to be something big going on here.

See our PEScience page to compare prices on all of their excellent supplements!
Over time, PEScience added several flavors, such as the ultra-sweet cotton candy, incredibly-blended strawberry kiwi, and our house favorite, melon berry twist.
Whenever you see huge doses of citrulline and nitrate together, know that it was PEScience High Volume who did it first. Everyone needs to try this supplement at least once... and you'll likely use it again after that.
PEScience High Volume – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.







Comments and Discussion (Powered by the PricePlow Forum)