In the last couple years — but particularly in 2023 — we've seen a lot of premium supplement manufacturers compete in an industry-wide reinvention of the protein supplement. A number of revolutionary high-tech designer ingredients with different synergistic effects on dietary protein are angling to dominate this staple category. Interestingly, it seems like each formulation team is backing a different horse.
The Podium Nutrition x Hard Work Pays Off (HWPO) Whey

Powered by Nutrition21's Velositol, Podium Nutrition's HWPO Whey Isolate Protein makes hard work pay off even more!
To enhance their specialty whey protein isolate, Velositol is the horse that Podium Nutrition is betting on, and it's a bet many of the best formulators have been making this decade.
This whey protein isolate goes beyond the brand's traditional whey protein powder, adding Nutrition21's patented blend of chromium and amylopectin to boost muscle protein synthesis. We covered Velositol all the way back in 2018 and have enjoyed watching it grow into an industry-defining force.
For this enhanced protein supplement, Podium Nutrition collaborated with Hard Work Pays Off (HWPO) to create the premium whey protein isolate that we're covering today. While the best part of this formula is the inclusion of Velositol, the second best part, in our opinion, is the tasty chocolate peanut butter flavor.
You may recognize HWPO Training: This is the training system of Mat Fraser (5x Fittest Man on Earth), a sponsored athlete of Podium Nutrition. If there's a protein powder collaboration that deserves some Velositol-based fortification, it's this one.
Let's get into how Podium's HWPO Whey works, but first, check the PricePlow news and deals:
Podium Nutrition HWPO Isolate Whey Protein – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.
This area is reserved for Team PricePlow's upcoming videos.
Subscribe to our channel and sign up for notifications so you catch it when it goes live!
The Podium x HWPO Macros
While HWPO contains a little cocoa powder and peanut flour, there's no emulsifying oil. Thanks to this and the use of whey isolate, the macros on Podium x HWPO are exceptionally good:
-
Calories: 105
-
Protein: 20 g
-
Total Carbs: 3 g
-
Total Sugars: <1 g
-
Added Sugar: 0g
-
-
-
Total Fat: 1 g
-
Saturated Fat: <1 g
-
Podium Nutrition HWPO Isolate Whey Protein Ingredients
In a single 28.8-gram serving (1 scoop) of Podium x HWPO Whey Isolate, you get the following:
-
Whey Protein Isolate 87% (21.75 grams, supplying 18.7 grams protein)
Whey protein is the industry's favored choice for supplemental protein for several reasons:
To begin with, whey boasts exceptional bioavailability. Compared to other protein sources, the body efficiently absorbs and utilizes a higher percentage of ingested whey.[1]
Whey also acts rapidly, reaching its peak concentration in the bloodstream merely one hour after consumption (as opposed to roughly three hours for mixed-macro meals).[2] This swift absorption makes whey well-suited for supporting speedy post-workout recovery.
Compared to plant-based proteins, whey contains more essential amino acids, the indispensable molecular building blocks that we must acquire through diet.[3] A wealth of research shows that, when combined with a nutritionally dense whole-foods diet, whey supplements contribute to enhancing body composition and strength, benefiting both men and women.[4-7]
Whey Isolate vs. Whey Concentrate
You may have observed that whey isolate isn't the sole form of whey – it's also frequently marketed as whey concentrate.
Our preference leans toward the isolate form of whey because, compared to whey concentrate, it undergoes a more rigorous filtration process designed to remove as many naturally-occurring carbohydrates and fats as possible from the whey fraction.
Generally speaking, this translates to more favorable macronutrient ratios, especially for those eating a high-protein diet. Anecdotally, some (not all!) individuals with dairy sensitivities find whey isolate easier to tolerate than whey concentrate.
-
VELOSITOL (Amylopectin Chromium Complex) – 1,000 mg
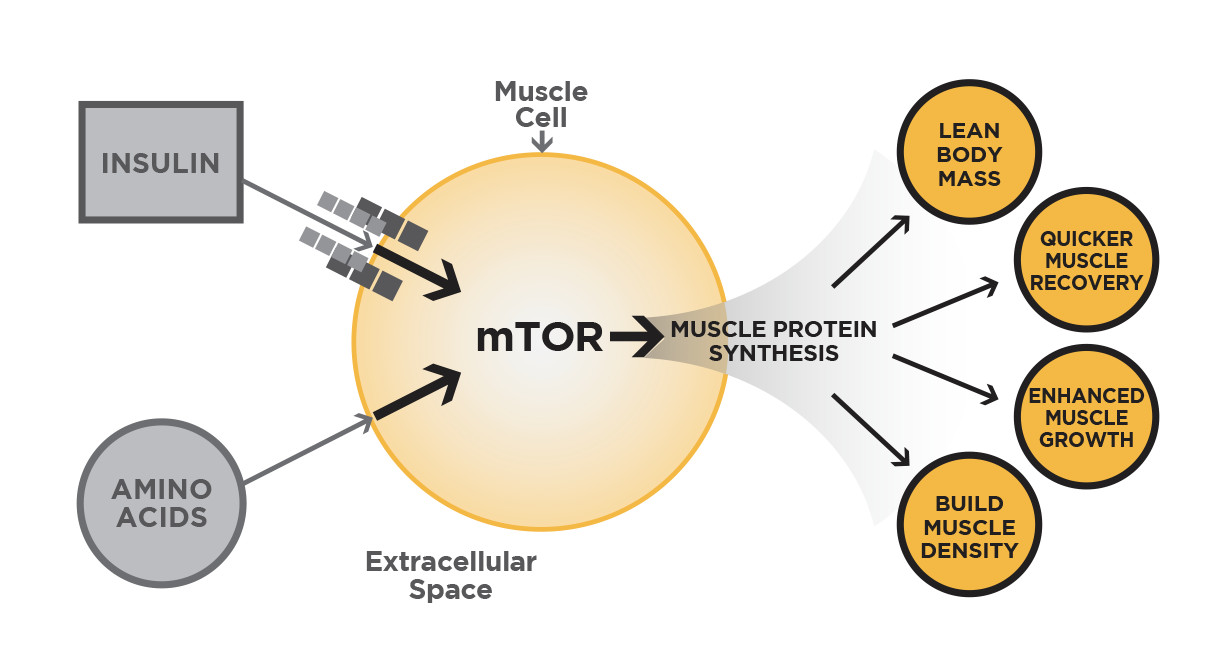
Velositol, developed by Nutrition21, is a patented complex consisting of the mineral chromium and amylopectin starch.[8,9] When these molecules are combined, they can enhance the body's anabolic response through synergistic effects related to insulin. More specifically, while amylopectin causes the body to stimulate the production of insulin, chromium simultaneously heightens muscle cell sensitivity to that insulin.[10]
Velositol: An Overview
Velositol is a muscle growth activator, meaning it's most effective when used alongside protein to enhance strength and power outcomes by increasing the body's rate of muscle protein synthesis (MPS). MPS plays a crucial role in promoting effective muscle growth, acquiring lean mass, and facilitating muscle recovery. Velositol does this by enhancing amino acid uptake, the end result of its dual effect on insulin signaling.
Made by Nutrition 21, the experts in Chromium and Insulin management, Velositol can boost Muscle Protein Synthesis by using chromium and a 'tickle' of insulin-spike from amylopectin!
It's only natural that Nutrition21 was the company to come out with Velositol. Their Chromax ingredient – a trademarked form of chromium picolinate backed by more than 32 studies on the ingredient itself (in addition to 48 peer-reviewed scientific studies on the ingredient in general, making for a whopping total of 80 studies)[11] – long ago established Nutrition21 as the supplement industry's leader on chromium and chromium science.
Although Velositol is a newer dietary ingredient, it already has plenty of scientific support:
The Research on Velositol
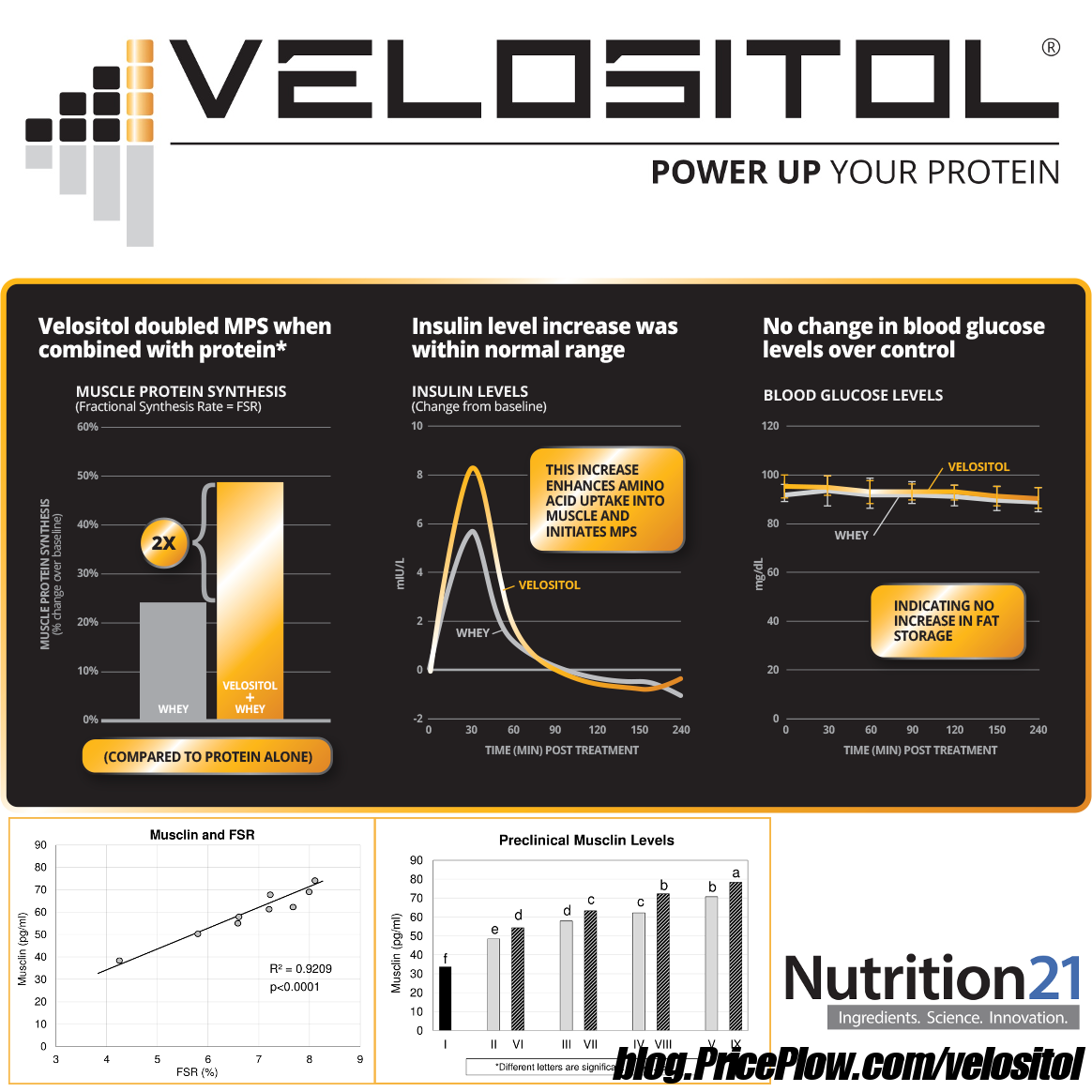
A 2017 study demonstrated that the combination of 2 grams of Velositol used with suboptimal amounts of whey protein (6 grams) significantly enhances muscle protein synthesis compared to the same amount of whey protein alone. Four hours after ingestion, the Velositol+whey group showed significantly greater fractional synthesis rate (as obtained through muscle biopsy - an incredibly strong indicator) than the whey-only group.[12]
Remarkably, Velositol optimizes the insulin spike shortly after ingestion without causing an increase in blood glucose levels:
It's worth noting that the 6 grams of whey used in this study is considerably smaller than the 20 grams available in one serving of Podium x HWPO Whey. Therefore, it's reasonable to expect an even more pronounced effect from the protein in this product.
It's also worth noting that both the above and below studies used 2 grams of Velositol, but HWPO Whey Isolate has 1 gram. This means that best results will be seen when using two servings per day.
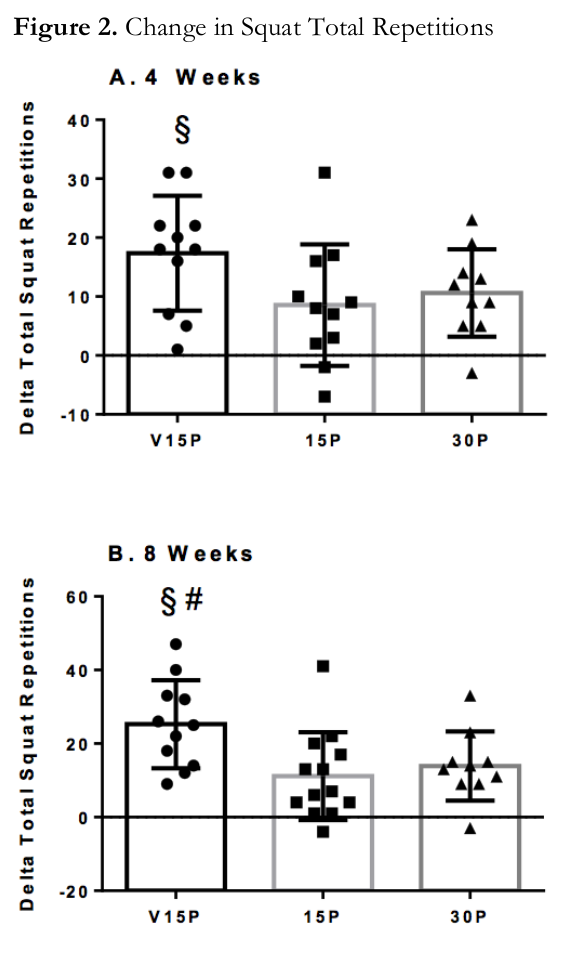
Continuing along their line of inquiry, researchers sought additional data with larger protein doses, culminating in a study published in 2021 detailing real-world athletic outcomes. The study involved three distinct treatment groups:[13]
- 15 grams of whey protein + 2 grams of Velositol (V15P)
- 15 grams of whey protein alone (15P)
- 30 grams of whey protein alone (30P)
Here's what the numbers looked like:
Changes versus baseline:[13]
Squat reps to failure Vertical jump power (Watts/kg body weight) Vertical jump height (cm) V15P +25.3 +2.1 +8.7 15P +12.0 +0.4 +1.6 cm 30P +13.9 +0.3 +0.9 cm Following 8 weeks of intake coupled with resistance training, the V15P group outperformed the 15P group, which is not entirely surprising. However, what is truly remarkable is that the V15P group also outperformed the 30P group. In other words, a mere 2 grams of Velositol added to 15 grams of whey protein – again, 5 grams less than the whey dose in Podium x HWPO Whey – had a more significant positive impact than twice that amount of protein without Velositol.[13]
Award-winning research
The velositol group had significantly better squat performance, and over time they out-performed both other groups![13]
Thanks to the above research, Velositol was named NutraIngredients-USA's 2023 'Hector Lopez Excellence in Sports Nutrition Science Award',[14] which is an incredibly high honor, given the namesake of one of the industry's greatest minds.
We've long been big fans of chromium supplementation -- see our main article on chromium picolinate for more information. And thanks to the above research on Velositol, we're especially fond of it when combined with protein powder.
You can read more about the athletic endpoint study in our 2021 article titled "Velositol Increases Exercise Performance: New University Study Published". And for a greater overview of Velositol itself, see our article titled "Velositol: Enhancing Muscle Protein Synthesis with Science" -- again, realize that the clinically-verified results were seen with 2 grams of Velositol, so keep that in mind when using HWPO Whey Isolate.
-
Flavor system extras (cocoa and peanut flour)
While not the primary ingredient in Podium x HWPO Whey, we always appreciate the use of cocoa powder.
Cocoa is rich in epicatechin and other polyphenol antioxidants,[15] consumption of which has been linked to reduced inflammation, improved circulation, decreased blood pressure and cholesterol, and better blood glucose management.[15]
Cocoa's capacity to improve blood pressure can be attributed, in part, to the nitric oxide (NO)-boosting effect of these antioxidants.[16,17] The improvements in circulation linked to NO can benefit both physical and cognitive function.
In keeping with the chocolate peanut butter flavor, there's also a bit of peanut flour. In terms of flavor, a little peanut goes a long way, so there doesn't seem to be very much of it in Podium x HWPO Whey. It's still worth mentioning, though, that peanuts are an excellent source of resveratrol, phenolic acids, flavonoids, and phytosterols.[18] Little nutritional advantages like these are one of the reasons why we love seeing flavor systems use real whole foods instead of artificial agents.
-
Other Ingredients
Podium x HWPO is sweetened with sucralose and contains a bit of salt to complement that sweetness.
Finally, at the end of the label, Podium x HWPO has a gum blend of guar gum, gum acacia, and xanthan gum. We've found that using multiple gums instead of just one provides better product dispersion, especially in whey isolates.
Also included is the patented DigeZyme complex, which consists of the enzymes amylase, protease, lactase, cellulase, and lipase. Since these enzymes help the body break down dietary protein, they are in Podium x HWPO Whey to maximize the bioavailability of the whey isolate.
Informed Sport Certified!
The HWPO lineup at Podium Nutrition is also Informed Sport Certified, meaning it's batch-tested and shown to be free of banned substances. Informed Sport's mantra is "We Test. You Trust."
If you're a drug-tested athlete, make sure you use only supplements with this type of certification (NSF Certified for Sport and BSCG are two other trusted certifications). After all, Hard Work Pays Off, and we'd hate for you to get kicked out of competition over a banned substance.
Why Eat a High-Protein Diet?
If you've spent a significant time at the gym, you're likely well-acquainted with the post-workout protein shake ritual. Most serious weightlifters and athletes strive to consume protein shortly after exercising.
One reason for this practice is to leverage the "anabolic window," a 1-2 hour period following a workout when metabolism is optimized to make the most of ingested protein and carbohydrates. It's believed that consuming food within this window leads to more efficient muscle building per calorie.
In recent years, researchers have raised questions about the existence of the anabolic window. That debate is ongoing. Still, eating inside the anabolic window doesn't hurt, so there's no reason not to if you want to be absolutely sure you aren't leaving any gains on the table.
Beyond the Anabolic Window: Daily Total Protein Intake
No matter what you believe about the anabolic window, there's a more fundamental reason for eating supplemental protein: the total amount of protein you consume significantly influences muscle growth in response to exercise.[19]
The key question, as always, concerns appropriate dosage. How much protein should we eat?
The latest research suggests that additional protein intake yields diminishing returns at around 0.75 grams of protein per pound of body weight per day.[20]
Taking this figure as the basis for a 95% double confidence interval – adding two standard deviations of protein intake to ensure comprehensive coverage, just to be absolutely sure we're not leaving any potential muscle growth unrealized – gets us about 0.82 grams per pound of body weight per day.[21]
This figure is quite a bit higher than the United States Department of Agriculture's Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for dietary protein, which stands at 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight —equivalent to a meager 0.36 grams per pound.[21]
It's not that the RDA is not inherently wrong. Rather, it's calibrated for a certain type of person — namely, sedentary individuals whose primary goal is to maintain nitrogen balance and prevent muscle loss. Athletes, bodybuilders, and highly active individuals interested in building additional muscle require significantly more protein than prescribed by the RDA. For individuals in these categories, figures like 0.75 grams, or 0.82 grams per pound of body weight per day, come into play.
According to a comprehensive study by Dr. Guoyao Wu of Texas A&M University, individual protein recommendations vary according to activity level:
Based on short-term nitrogen balance studies, the Recommended Dietary Allowance of protein for a healthy adult with minimal physical activity is currently 0.8 g protein per kg body weight (BW) per day. To meet the functional needs such as promoting skeletal-muscle protein accretion and physical strength, dietary intake of 1.0, 1.3, and 1.6 g protein per kg BW per day is recommended for individuals with minimal, moderate, and intense physical activity, respectively."[22]
The most active individuals benefit the most from consuming 1.6 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day, which equates to approximately 0.71 grams of protein per pound of body weight per day.
Example body weights and protein intakes
The average daily protein intake for the typical American adult is around 88 grams. Applying our 95% double confidence interval protein target of 0.82 grams of protein per pound of body weight per day, this amount of protein is sufficient for an athlete weighing roughly 107 pounds. However, most athletes and weightlifters, particularly males, exceed this weight by quite a bit.

For over 25 years, Chromax chromium picolinate has been improving insulin sensitivity. We argue that it's only gotten better, as dietary deficiencies have gotten worse over this time period.
By comparison, sedentary individuals can weigh up to 244 pounds before requiring more than 88 grams of protein per day. This illustrates how exercise significantly increases protein requirements.
Suppose you lift three times a week, with cardio on the days in between. In that case, we say a protein intake ranging from 0.71 to 0.82 grams per pound of body weight is prudent.
For instance, a highly active individual weighing 175 pounds needs roughly 125-143 grams of protein per day to optimize recovery and muscle growth from exercise. This amount surpasses what the Standard American Diet (SAD) typically provides, making it challenging to obtain enough protein through meals alone. Fortunately, protein powders like IsoMix can help.
The Thermic Effect of Protein Adds to Caloric Deficit
In addition to enhancing muscle gains, a high-protein diet can help achieve and maintain a lean physique.
One reason for this is that protein has the highest thermic effect of any macronutrient.[23]
Thermic effect refers to the energy your body expends while digesting food. Each calorie spent on digestion contributes to your total daily energy expenditure (TDEE), increasing your calorie deficit and, potentially, accelerating fat loss.

Podium Nutrition PUMP is a non-stim pre-workout for hybrid athletes, powered primarily by a combination of Nitrosigine and L-citrulline
This phenomenon has been observed by direct measurement. In one study, researchers provided subjects with isocaloric diets of varying composition — that is, these diets contained the same number of daily calories, but different macronutrient ratios. The study demonstrated that individuals on a high-protein diet had a higher resting metabolic rate (RMR) than those consuming more carbohydrates or fat.[24]
Protein Enhances Satiety and Naturally Reduces Food Intake
Another study revealed that participants who ate 30% of their daily calories as protein spontaneously ate 441 fewer calories per day.[25]
A 441-calorie/day reduction adds up to a weekly deficit of 3,087 calories. Based on the widely accepted model that 1 pound of body fat contains 3,500 calories, this implies a potential weekly fat loss of nearly 1 pound, solely through increased protein intake!
Why Choose Protein Powder
Whole foods can provide protein. So, naturally, the question arises: why bother with a protein powder supplement?
Consuming substantial amounts of protein can be challenging. Because whole-food dietary protein typically comes bundled with significant quantities of carbohydrates and fat, individuals may struggle to consume 130-140 grams of protein even on a maintenance calorie diet — let alone when reducing calories to induce fat loss.
This is where high-quality protein powders like Podium x HWPO come into play – they can dramatically simplify the process of hitting a high-protein macronutrient target.
Podium x HWPO, being based on whey isolate, provides roughly 76% of its calories from protein (80 calories out of 105 calories per serving). It's nearly impossible to find whole foods with such a high proportion of calories from protein— except perhaps for the bodybuilder's infamous staple, chicken breast.
Consuming an exceptionally high-protein food source like Podium x HWPO helps skew your macronutrient ratio toward protein, thus helping you meet your protein target while adhering to calorie restrictions.
Convenience and Accessibility
Preparing protein-rich meals is generally time consuming and requires access to a kitchen and fresh ingredients. While it's possible to dine out and find protein-rich options like burgers, uncertainty surrounding the precise quantity of protein in restaurant dishes may not suit the most disciplined and meticulous food trackers.
Protein powder offers unparalleled convenience by eliminating the guesswork. It can be taken anywhere, requiring only liquid (water or milk) to create a quick and hassle-free protein source.
Conclusion
This formula is simple, but elegant and effective. Velositol just makes protein work better. It's a no-brainer for inclusion in a whey isolate product like HWPO.
Between this and Podium Pump, we think Podium's doing a great job of catering to their demographic of hybrid athletes. Expect this to be an area of growth -- and for Podium to grow along with it!
Podium Nutrition HWPO Isolate Whey Protein – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.











Comments and Discussion (Powered by the PricePlow Forum)