Black Magic Supply made their entry into the supplement arena with the phenomenal pre-workout, BZRK. A monster of a formula with huge doses of psychoactive stimulants, BZRK offers consumers a bracing look into the mentality steering this radical company whose powers are summoned from "the other side."

Made of whey, casein, and egg protein, Multi-Source Protein is a phenomenal and powerful protein blend - and it now comes in Honey Grahams flavor!
We just discussed the new Orange Cooler flavor of BZRK, and as promised, Black Magic Supply also released a new flavor for their Multi-Source Protein powder. Just like BZRK will get people wondering what possessed your workout, Multi-Source Protein is designed to get you thinking that your taste buds are similarly possessed with dark magic deliciousness.
Black Magic Multi-Source Protein: Magical deliciousness
You don't have to eat boiled toad with wormwood to reap the benefits of this nutritional witchcraft – Multi-Source Protein comes in a range of delicious flavors, the newest being Honey Grahams. We've all had Honey Graham crackers before and, suffice it to say, most of us are going to love this flavor.
Since we've never covered Multi-Source Protein here on the blog yet, we do a full deep dive and explain why casein and whey together is a superior protein blend. But first, check availability of the new Honey Grahams flavor and see our tasting review:
Black Magic Protein Multi-Source – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.
Black Magic Multi-Source Protein Nutrition Facts
The nutrition may vary a bit from flavor to flavor, but here's what the new Honey Grahams flavor provides:
-
Calories: 140
-
Protein: 24g
-
Fat: 1.5g
-
Total Carbohydrates: 6g
-
Sugar: 4g
-
This is a bit more than a few of the other flavors, but in the case of Honey Grahams, it's made with real graham crackers!
Next, let's take a look at the main ingredients in Multi-Source Protein and how they will help you sculpt your berserker body:
Black Magic Multi-Source Protein Ingredients
In a single 1-scoop serving of Black Magic Supply Multi-Source Protein, you get the following:
-
Whey Protein (Concentrate and Isolate)
Whey protein is the most common protein supplement on the market today, and we'll tell you why.
For one thing, the particular amino acids that constitute whey are highly bioavailable,[1] meaning that a large proportion of what you ingest is actually absorbed and used by your body. By contrast, something with poor bioavailability mostly passws through your body without being digested (dietary fiber is a good example). Compared to whey, plant-sourced protein has poor bioavailability.[2]
Whey is also very insulinogenic,[3] which in the context of recovery from exercise is actually a good thing. Insulin can increase muscle protein synthesis provided you take in a sufficient amount of protein[4], which is the whole point of a protein supplement!
And in fact, although whey stimulates the release of large quantities of insulin, whey supplementation has been shown to increase insulin sensitivity (i.e., decreasing insulin resistance) because of its effect on the body's antioxidant capacity.[5] That's because whey is high in cysteine, an amino acid that'sa precursor to glutathione, the body's master antioxidant.[6]
Whey is high in essential amino acids, defined as amino acids that your body cannot synthesize on its own and must obtain in their complete form from external sources.[7]
Research on whey has repeatedly shown that whey supplementation can accelerate strength and muscle gains.[7-10]
But what is whey concentrate?
There are two main forms of whey on the market today: whey isolate and whey concentrate.
The difference between the two is the degree of filtration. Whey isolate is pure whey and whey concentrate varies in purity, from 25% to 89% protein. The remainder of the whey concentrate consists of, as you might have guessed, carbs and fat from milk.
Using whey concentrate is not necessarily worse than using whey isolate, but people with dairy sensitivities should take note as whey concentrate is more likely to cause gastrointestinal issues compared to whey isolate.
Multi-Source Protein has both forms of whey!
If you already scanned the ingredients panel, you'll notice f that Multi-Source Protein from Black Magic Supply contains both forms of whey.
-
Micellar Casein
Between the two whey proteins on the label, we have micellar casein protein second on the list, meaning there's a solid dose of it. Casein is one of two groups of proteins in mammalian milk[11] – whey is the other.
Perhaps unsurprisingly, there is some research that shows the combination of whey and casein performs better as a supplement than either form alone.
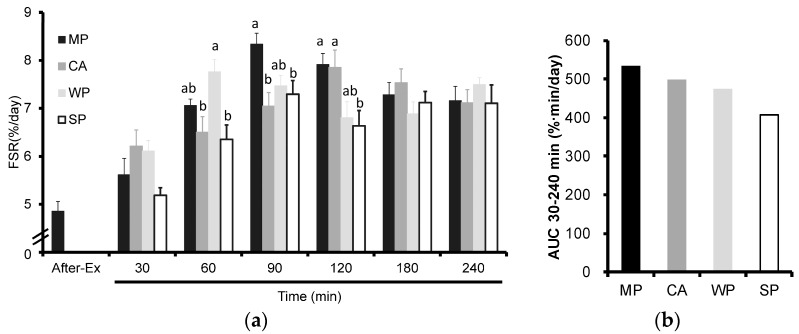
You wouldn't be the first to wonder how that's possible. An animal study from 2016 set out to answer this question by randomizing rats to either whey, casein, or milk protein supplementation following exercise. The researchers then measured the rate at which the rats synthesized new muscle protein and calculated the total effect of each protein supplement (measured as area under the curve) on muscle protein synthesis.[12]
They found that milk protein, which naturally contains both casein and whey – increased muscle synthesis to a greater extent than either on their own.[12]
Whey is fast, casein is slow, but what brings more muscle protein synthesis overall when looking at the total area under the curve in rats?! It was the milk protein blend.[12]
Why is whey+casein better than whey or casein alone?
One reason why the combination works better is that whey and casein cause muscle synthesis to peak at different times.[12] So taking both at once gives you the best of both worlds: whey acts more quickly for rapid recovery and casein acts over a longer period of time to extend the anabolic response. Human research has demonstrated great effects on strength and body composition as well.[13]
Whey and casein work on different growth factors
Muscle protein synthesis is mediated by a number of different messengers and hormones. Insulin, as we discussed above, is one of them, and is stimulated by whey. Casein, on the other hand, causes your body to produce more insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1).[14]
Insulin and IGF-1 are anabolic in different ways, and may synergize with each other for a stronger anabolic response. There's at least one study showing that suppressing insulin or IGF-1 levels in mice significantly decreased the amount of muscle synthesized from food.[15]
-
Egg Albumin Protein
Egg albumin protein is derived from albumen, a fancy term for egg white. In other words, this is egg white protein.
Egg whites are popular with supplement manufacturers and consumers because the protein they contain has an extremely high rate of net protein utilization (NPU),[16] meaning that it's highly bioavailable.
Egg white protein also has a high protein efficiency ratio (PER), which is a measure of a protein's ability to induce weight gain.[17] If you're looking to get jacked, you can't do much better than adding egg white protein to your regimen.
Additionally, egg whites have a low phosphorus-to-protein ratio,[18-20] which is great since high phosphorus intake can disrupt your body's ability to metabolize calcium.[21]
-
Medium-Chain Triglyceride (MCT) Powder
Just in time for the HOT Summer of 2022, it's a new Orange Cooler flavor of BZRK
Medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) are a type of dietary fat that contains fatty acids between six and 12 carbon atoms in length.[22-25]
Naturally, short-chain fatty acids have fewer than six carbon atoms, and long-chain fatty acids have more than 12 carbon atoms.
After being ingested, MCTs are transported to the liver where they're rapidly metabolized and made available to cells as usable energy in the form of ketones.[26] Importantly, this conversion — MCTs to ketones — occurs regardless of your actual blood glucose level, In order words, MCTs give you some of the benefits associated with ketosis, whether or not you to follow a ketogenic diet.
Because of MCTs' ability to provide your body with clean-burning energy that doesn't affect insulin or glucose blood levels, MCT supplementation can increase your metabolic rate, aid fat loss, improve cognition, and reduce appetite.[22-25]
-
Other Ingredients: Added Digestive Enzymes!
Multi-Source Protein from Black Magic Supply contains papain, an important digestive enzyme that helps your body break down and utilize protein.[27] There's also lactase, which helps break down the lactose that's in the whey and casein protein (the whey protein concentrate will have the most lactose).
These should both help with digestion, especially since Multi-Source Protein contains lactose, a milk sugar that may be problematic for people who are intolerant of it. Adding lactase assists with its breakdown and digestion.
Flavors Available
Honey Grahams sound great, but here's what else Black Magic has available out there:
Conclusion: Honey Grahams in a Protein Shake
Multi-Source Protein takes a balanced approach to protein supplementation, blending the three most effective supplemental proteins on the market today. The MCT oil is a nice touch, and its effect on appetite certainly can't hurt your body-composition goals.
We love these protein blends - there's not only science to back them up, but they're generally thicker and tastier than traditional whey proteins as well.
Black Magic Supply has slowly built up quite an arsenal of delicious flavors in Multi-Source Protein, and it's a product that deserves a bit more love. So now if you were looking for a solid post-workout protein after your BZRK and Ecto Plasm fueled pre-workout, the source is Multi-Source.
Black Magic Protein Multi-Source – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.








Comments and Discussion (Powered by the PricePlow Forum)