Longtime readers of PricePlow will no doubt be familiar with MuscleTech, an innovative and pioneering brand that has put novel ingredients like paraxanthine on the map with formulas like EuphoriQ.
MuscleTech's parent company, Iovate, also has control over the reins at SIXSTAR, a brand that shoots for exposure and widespread adoption via its extensive distribution with Walmart. While it may appeal to a broader audience, SIXSTAR retains the same focus on manufacturing quality that's made MuscleTech a trusted name for decades.
Today, SIXSTAR's Protein Plus is getting two new collab flavors – and these will have you feeling like a kid again:
SIXSTAR x Kellogg: Frosted Flakes and Froot Loops Protein!
These days, protein powders are a dime a dozen. They all generally use the same ingredients, and are fortunately backed by copious amounts of data surrounding their benefits.
With most whey protein powders in the store more or less the same for the majority of general consumers, what really sets a protein powder apart is flavor. With a supplement like protein – which you'll be taking on a consistent basis – taste is everything.
That's why the two newest flavors are so exciting. SIXSTAR is partnering up with Kellogg to bring two classic cereal flavors to the masses: Froot Loops and Frosted Flakes Protein+!
We're going to dive into how SIXSTAR Whey Protein Plus works, but first, let's check the PricePlow for good SIXSTAR deals, and check out our video review of the new flavors:
Six Star 100% Whey Protein Plus – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.
Update: There's now a Froot Loops RTD Drink flavor too!
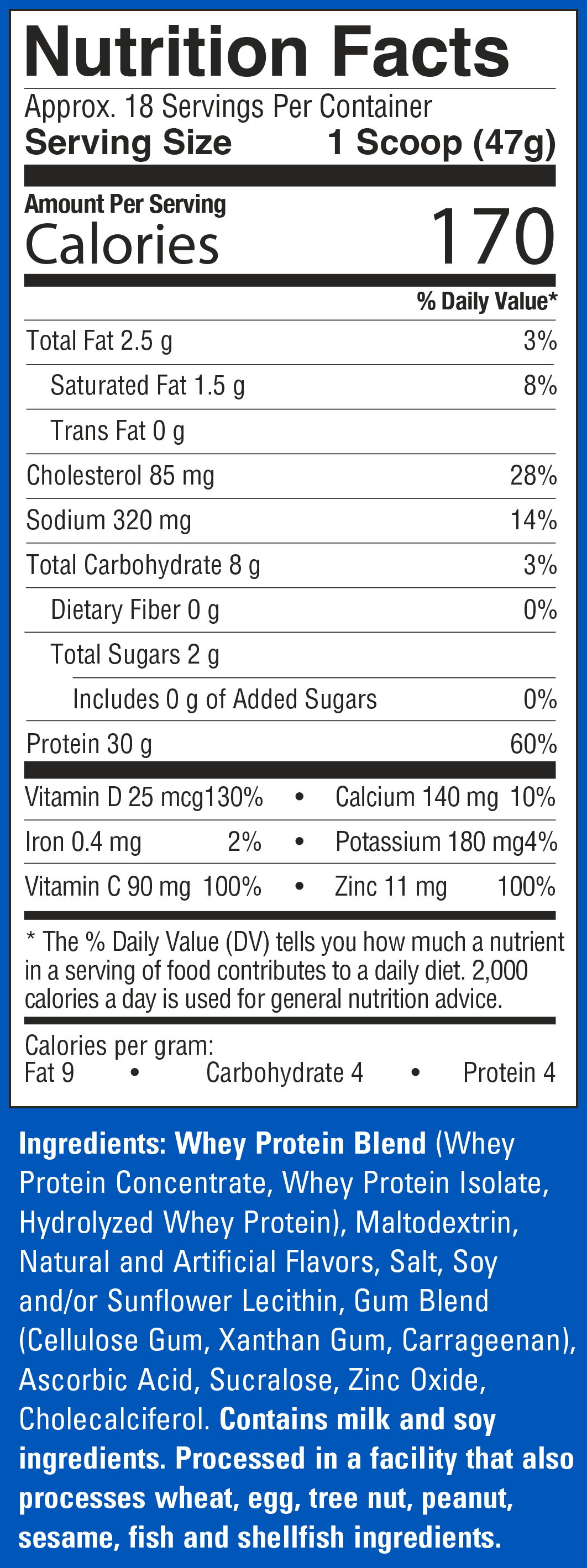
SIXSTAR Whey Protein Plus – Macros
Each scoop (47g) of Protein Plus contains the following macros:
-
Calories: 180
-
Protein: 30g
-
Total Fat: 3g
-
Saturated Fat: 1.5g
-
-
Total Carb: 8g
-
Dietary Fiber: <1g
-
Total Sugars: 2g
-
This is obviously a bit higher in carbs than some of the more premium MuscleTech proteins -- and that's quite alright to anyone who's training even a little bit. Let's see where those macros come from:
Protein Plus – How It Works
Here are the main ingredients inside:
-
Whey Protein Plus Blend
Whey protein, derived from cow's milk, stands as an exceptional source of dairy protein known for its impressive attributes: high bioavailability,[1] rapid action, and robust insulinogenic properties, which are particularly advantageous for post-exercise recovery.
As a complete protein, whey protein contains all nine essential amino acids, which the human body cannot synthesize independently and must acquire through dietary sources.[2] Extensive research indicates that when whey supplements are incorporated into a nutrient-dense, high-protein diet consisting of whole foods, they contribute to enhanced body composition and increased strength in both men and women.[3-6]
Now, let's delve into the distinctions between whey protein concentrate and whey protein isolate.
-
Whey Protein Concentrate
Whey protein concentrate represents a grade of protein powder that can range from 34% to 80% protein content by weight. Consequently, it has undergone some degree of purification and filtration, though not to the same extent as whey protein isolate (see below).
Whey protein concentrate allows for the retention of additional bioactive constituents from dairy, such as lactoglobulins, immunoglobulins, and lactoferrin [7,8]. These components play a vital role in bolstering the immune system.
-
Whey Protein Isolate
Whey protein isolate, on the other hand, undergoes additional filtration steps after the separation process to eliminate as much residual fat and sugar as possible, eventually yielding at least 90% pure protein by weight. This level of purification renders the supplement highly versatile, catering to individuals following dietary strategies aimed at reducing carbohydrates or fat. This pure protein isolate can seamlessly fit into various macro-based diets.
-
Hydrolyzed Whey Protein
Completing the protein composition in Protein Plus is hydrolyzed whey protein. Unlike whey protein isolate, which boasts a higher protein content per gram, hydrolyzed whey undergoes enzymatic breakdown into smaller amino acid chains, greatly enhancing its digestibility.[9] As emphasized earlier, the digestibility factor plays a pivotal role in the realm of protein supplementation.
The expedited digestion of hydrolyzed whey translates into a swifter insulin response,[10] a crucial factor in accelerating recovery times.[11]
-
-
Flavor & Texture
In order to create that classic Kellogg's flavor, Protein Plus incorporates maltodextrin and sucralose as sweeteners along with unnamed natural and artificial flavors. To get that smooth, pleasing texture, SIXSTAR has employed a gum blend consisting of cellulose gum, xanthan gum, and carrageenan.
-
Vitamin and Mineral Fortified
One thing you may also notice is that Whey Protein Plus is fortified with vitamin C (ascorbic acid), vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol), and zinc oxide.
Vitamin C is especially useful for athletes since it can boost endurance when dieting[12] and reduce the biochemical markers of muscle damage (and thus limit soreness) after training.[13,14]
All SIXSTAR Whey Protein Plus flavors
Check out our up-to-date list of Protein Plus flavors below:
Nostalgic Cereal Goodness
SIXSTAR is a brand that appeals to a large swath of consumers, which makes their collaboration with Kellogg seem like a match made in heaven.
We all remember the sugary deliciousness of a big bowl of frosted flakes before heading off to the bus. The problem is, it's not exactly a meal most conducive to maintaining peak physical fitness as an adult. Now, with the flavors distilled down into a protein powder, you can have the best of both worlds: nostalgic, sugary tastes in a shake that packs a whopping thirty grams of protein.
Six Star 100% Whey Protein Plus – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.





Comments and Discussion (Powered by the PricePlow Forum)