
Forskolin weight loss supplements are blowing up and we explain why here. But you have to stick to the good stuff...
Coleus forskohlii, also known as Indian coleus, is an herbal plant that has a long history of use in traditional Ayurvedic medicine, where it’s been extensively used to treat various conditions such as heart disease, pain, and convulsions.[1]
Because of this, a great deal of research has been conducted investigating the benefits from the plants, and several other benefits (that we’re mostly interested in here) were found as well.
In short, this herb is very much the real deal, and 2015 was a breakout year for it in weight loss supplements - where we simply call it Forskolin.
TL;DR
Forskolin is the most underrated stimulant-free ingredient out there, especially for dieters.
- Forskolin's Benefits are primarily for weight loss and building lean muscle tissue, but there are several general health benefits too.
- How it works: Primarily by increasing cAMP levels.
- Dosage: 25mg, twice per day before meals. Note that this is the actual forskolin dose, not the raw coleus forskohlii
-
Best Forskolin Supplement? We like PEScience's Forskolin-95+.
-
Why? Because the high-quality 95% extracts are the only way to go. Buying cheap no-name 10-20% junk on Amazon (or affiliate scam sites) will lead to increased side effects... namely diarrhea.
Seriously -- stick with the good stuff with this herb.
-
- It stacks incredibly well with other fat burners or pre workout supplements.
This article explains why you should expect to see a lot more of this one in the coming years.
Before we get started, you can compare prices and sign up for price drop alerts with PricePlow so that you never miss a great deal:
Forskolin – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.
Forskolin Benefits
The initial studies have shown that forskolin possesses several beneficial properties that may potentially be useful various health issues such as:
- arterial disease,
- heart disease,
- asthma,
- glaucoma, and most importantly to us,
- obesity.[2,3,4,5,6]
Our focus: the diet and athletic benefits
This article will not be covering the pharmacological medical potential of the herb, since that’s beyond the scope of this site (PricePlow). Instead we’ll focus on the use of forskolin in the context of sports nutrition and dieting.
This means we’ll examine the claims on the herb’s ability to help users lose weight, increase testosterone, and support strength and mass gains.[7] Yes - all of these seemingly contrasting effects are possible - it just depends on how you diet and exercise.
Into the deep end we go:
How does Forskolin work?
Forskolin is actually the name of the bioactive ingredient in the coleus forskohlii plant - it’s known as a labdane diterpene. This is a class of natural chemical compounds known to have antibacterial, antifungal, and anti-inflammatory activities.[12]
Forskolin is unique in that it goes a lot further than that.
Stimulating adenylate cyclase
While its exact mechanism of action is still unknown, we do know that forskolin is a potent stimulator of cellular adenylate cyclase (AC).[8,9] When this enzyme (adenylate cyclase) is stimulated, it activates a secondary messenger in hormonal signaling, cyclic AMP (3,5 cyclic adenosine monophosphate) or more commonly referred to as cAMP,[9,10,11] a critically important biological messenger that’s involved in many of our "energy transactions".
In one study, researchers found that forskolin was able to increase cAMP levels 4.82 times more than a placebo.[13]
In fact, this phenomenon of forskolin’s ability to increase levels of cAMP is so established, it (forskolin) is routinely used when researchers are investigating the effects of increased cAMP in cells.[14]
cAMP
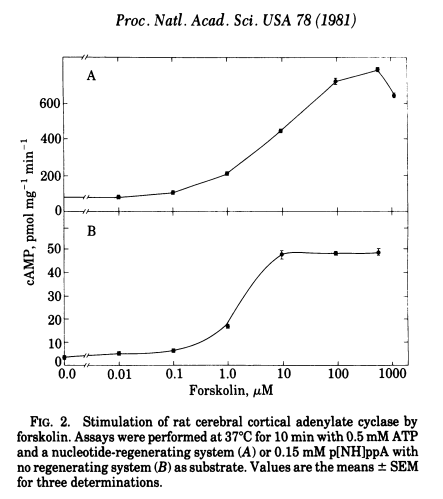
Forskolin stimulates cerebral cortical adenylate cyclase,[10] which leads to various benefits discussed below
There’s no arguing that forskolin is a highly reliable and effective cAMP-increasing agent, but what does that really mean in terms of our athletic and physique endeavors?
cAMP is a cell-regulating compound needed for the regulation of a wide range of cellular actions. The ones we’re most interested in for this article are its potential to
- Stimulate anabolic and anti-catabolic effects,
- promote the oxidation of fatty acids,
- increase the body’s BMR (basal metabolic rates),
- boost levels of testosterone, and
- promote an increase in lean body mass.[6,16]
Exercise also increases cAMP. So what makes forskolin so special?
If you’ve taken an exercise physiology class before, you’ll know that this sounds similar to simply exercising, which can also have the same effects above via cAMP.[17]
There are several ways of activating cAMP (hormones, neurotransmitters, adrenergic receptors, etc), so what makes forskolin unique?
While it’s true that cAMP can get activated in a number of ways, the pathways used to achieve cAMP stimulation might lead to a negative feedback effect. This means that after prolonged or chronic expression of these hormones (or stimulation of these agonists), there may eventually be a down-regulation of the receptor or hormonal agents.
Essentially, your body fights back to achieve homeostasis and stay even-keeled -- it eventually adapts to whatever you throw at it (both good and bad).
But here’s where forskolin supplementation is different - its cAMP processes are not hormone- or receptor-dependent![13] Foskolin has the unique ability to stimulate cAMP completely independently!
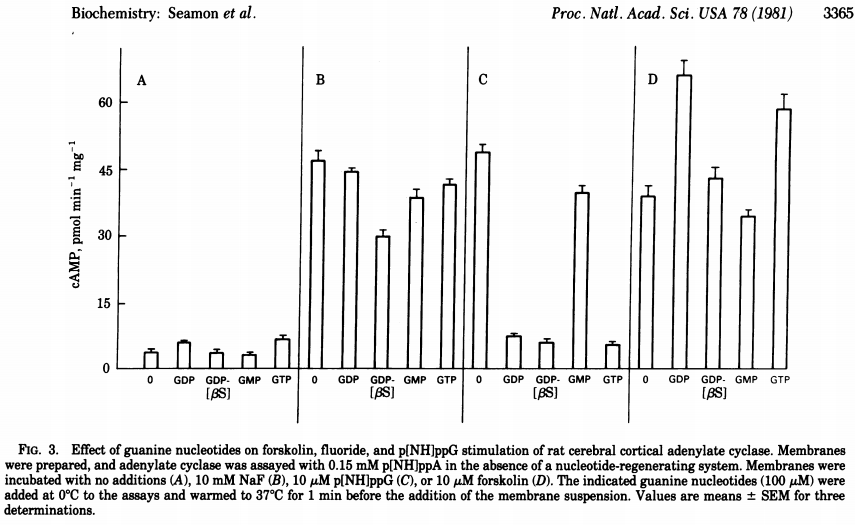
Effects of Forskolin on cAMP-Levels in Intact Cells: "Forskolin elicited a maximal 35-fold increase in the accumulation of cAMP in adenine-labeled rat cerebral cortical slices."[10] Forskolin is in section (D) to the right in this image, and is nearly universally more potent than the other compounds tested.
On top of that, it may also heighten the increase of cAMP when it is paired with a response from hormone or receptor signaling, making it a fantastic workout supplement.
So in short, forskolin is a great way to increase cAMP without the risk of hormonal or receptor down-regulation, yielding all of the benefits in the bullet points above.
This increase in cAMP is believed to be the mechanism behind forskolin’s ability to increase fat loss, act as an anabolic agent, and increase thyroid activity and thermogenesis. Now let’s take a look at those studies.
Weight Loss Effects
Weight loss occurs in 2 parts. First you have lipolysis, which is the liberation of stored fatty acids, and then you have fat oxidation, which is the "burning" of those fatty acids.
The part we’re going to focus on here is the first part -- and arguably the most important part -- lipolysis.
Liberate your stored fat via lipolysis
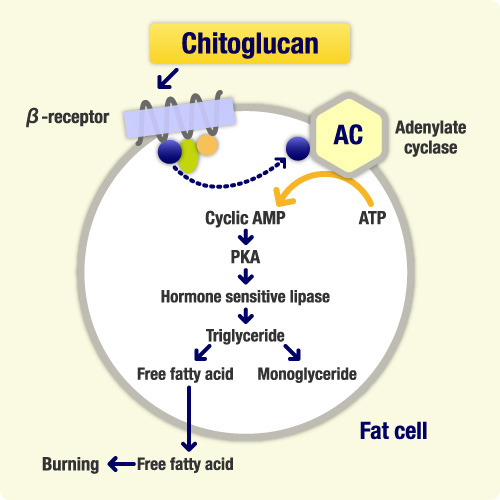
Forskolin causes a chain reaction of events that ultimately lead to fat loss. This is the process of free fatty acid liberation. Then it's up to you burn it with exercise!
Fat is stored all over our body in cells called adipocytes. The fatty acids bind to glycerol to form triglycerides and the accumulation of these results in increased adipose tissue, or fatty tissue. So if you goal is to lose weight, you have to first free those fatty acids from the glycerol first in order to get rid of the fat.
Below is a quick breakdown of the steps surrounding lipolysis:[15]
- The neurotransmitter NE (norepinephrine) binds to a adrenergic receptors (AR) that exist in the plasma membrane of fat cells.
- The binding of NE to AR on fat cells triggers a G-protein release.
- The G protein travels in the cytoplasm to the enzyme adenylate cyclase.
- Adenylate cyclase recruits ATP (the "energy molecule") from within the cell and creates a secondary messenger protein, our friend cyclic adenylate cyclase (cAMP)
- cAMP activates a cytoplasmic enzyme called Protein Kinase A (PKA)
- Now activated PKA goes on to activate Hormone Sensitive Lipase (HSL)
- HSL breaks down triglycerides into free fatty acids.
- The now freed fatty acids can be oxidized for ATP (burned for energy)[15]
In the above steps, adenylate cyclase is hormonally activated, resulting in an elevation of cAMP and cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA), as well as the downstream phosphorylation and activation of enzyme hormone sensitive lipase (HSL).[18]
Forskolin skips the hormones!
As mentioned previously, forskolin possess the unique ability to activate adenylate cyclase directly without the need of the hormonal intervention! It thus increases cAMP levels leading to an increase in the release of fatty acids from adipose stores, and ultimately to thermogenesis and lipolysis in fat cells.[9,19,20,21]
What this means is, forskolin has the potential to increase lipolysis without the need for stimulants. Downright awesome for anyone who either doesn’t want to touch stimulants, or wants to add an even bigger boost to their top fat burner.
A thyroid boost
In addition to the above process (ie forskolin -> increased cAMP -> increased HSL -> increased liberation of fatty acids to be used as energy to burn), forskolin positively affects thyroid activity as well! [23,24]
In this regard, forskolin has been shown to have the potential to stimulate the production of the thyroid hormones T3 and T4. Essentially, forskolin enhances thyroid activity (comparable in strength to thyrotropin or thyroid-stimulating hormone) by its potential to activate adenylate cyclase in the thyroid gland[23,24].
In addition to this, forskolin may also stimulate the conversion of T4 into T3. This thyroid stimulation supports increased basal metabolic rate and promotes thermogenesis.
This could be an area where more research goes, because thyroid boosters are extremely popular, yet not always fully understood. If you are taking thyroid medication, you must speak to your doctor before beginning any new diet or supplementation program - especially with something like forskolin that could enhance your thyroid hormones.
Muscle-Building and Anabolism
As mentioned previously, the benefits of forskolin don’t stop at fat loss. In addition to its ability to promote thermogenesis and increase thyroid activity, forskolin also stimulates increased bone mass and serum free testosterone levels in men, meaning forskolin also possess anti-catabolic and anabolic effects.[6,16].
Once again, the way it accomplishes this is vias increased cAMP.
Remember that cAMP is a secondary messenger. What happens here is not all that different from what happens above in fat cells - the effects are just different.
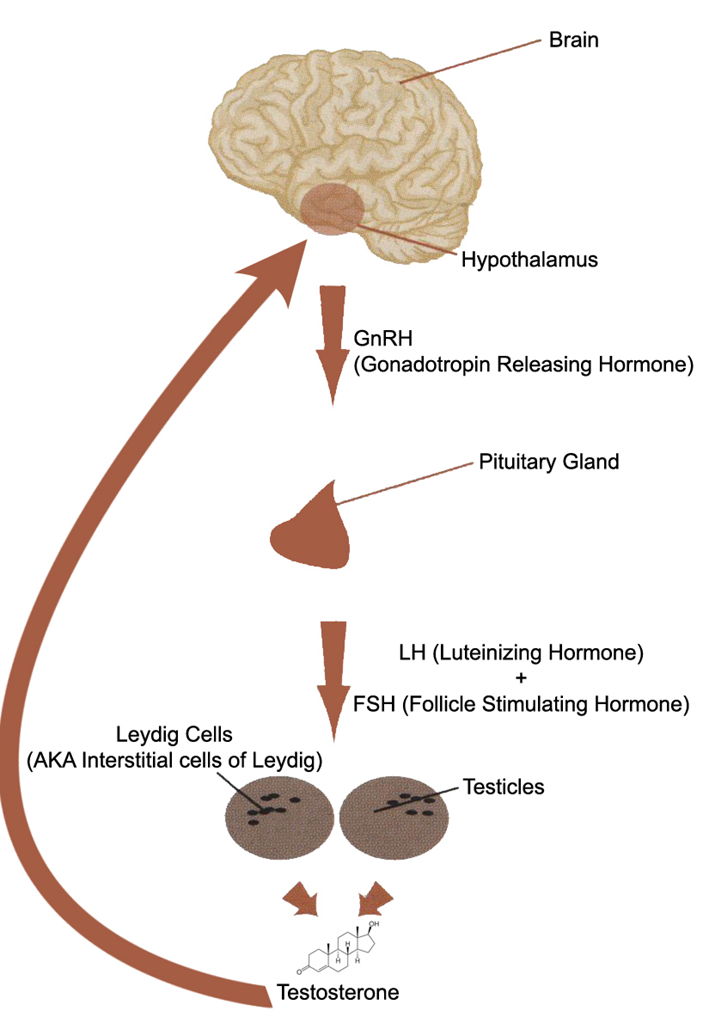
The general process of the HPTA (Hypothalamic Pituitary Testicular Axis). This connection between endocrine glands controls testosterone production. Image Courtesy Sterodal
Like before, forskolin binds and increases cAMP production. This then in turn activates the enzyme protein kinase A, which positively influences androgen receptor binding. Not to mention, cAMP also is a signal for testosterone production (steroidogenesis) in the Leydig cells of the testes.
At face value, this might seem like it’s not that important, but it is. The increase also increases levels of steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR), which is necessary for the stimulation of steroidogenic enzymes involved in the transfer of cholesterol to testosterone.
Essentially, high cAMP leads to a cascade of events from increasing high levels of luteinizing hormone (LH) binding to testosterone production.
Real Results
In a paper published in the Journal of Obesity Research back in 2005, researchers gave participants forskolin over the course of 12 weeks and observed
- an average increase in free testosterone by 33%,
- 10lbs of fat loss, and
- an 8lb increase in lean body mass[6]
Sounds too far fetched? A 2001 study by Badmaev observed similar results![28]
So basically, forskolin-induced elevation of cAMP may stimulate the pituitary gland, in turn increasing LH output, which in turn increases the production of testosterone via stimulation of the StAR protein... which plays a foundational role in the synthesis of testosterone.
It sounds like a long process, but this is often how natural supplementation works. This type of mechanism is exactly what natural athletes need to look for - it’s clearly not marketed to those who are injecting straight testosterone into their bodies.
And on that note, let’s not confuse 33% testosterone increases with steroids, because they’re definitely nowhere near that. Yet the results in the studies are quite nice, considering this is a natural herbal supplement.
Anti-Catabolic Effects
Ultimately, what we’re telling you is this: don’t buy forskolin unless it’s a 95% extract.
The benefits of Forskolin doesn’t stop at muscle-building though -- the compound also has the potential to deliver an anti-catabolic effect. This means that it can help prevent muscle-breakdown, which is often a destroyer of physiques.
Whether you’re a dieter and don’t want to lose your muscle tone (lest you become the dreaded "skinny fat"), or you’re working out hard and don’t want to lose out on your recovery, preventing catabolism as much as possible is extremely important.
Like the previous effects of forskolin, forskolin’s anti-catabolic effects are also cAMP dependent.
So what happens during catabolism / the breakdown of muscle tissue? When under dietary or physical stress, proteins in the muscle undergo hydrolytic degradation partially into peptides or completely into amino acids. This process is called proteolysis. Luckily for us, this process is reversible. Under normal circumstances, our muscle mass is regulated by a balance between protein synthesis and protein degradation, with muscle breakdown occurring when this equilibrium is impaired.[29]
The calpain complication
So where does forskolin come into play here? To understand this we have to first do a real quick overview of the physiology muscle breakdown:
The suggested dose is 25mg of forskolin 30-60 minutes prior to a meal, twice daily.
Calcium-dependent enzymes, known as calpains, govern the breakdown of muscle tissue. When activated, these enzymes are involved in the disassembly of myofibrils (a basic rod-like unit in a muscle cell) and channel the resulting myofibrillar structures into the ubiquitin-proteosome pathway (UPP).[30] In short, say goodbye to some of your beloved muscle fibers when these calpain enzymes get activated.
The activity of these enzymes are regulated by calpastatin. Here’s where forskolin comes in.
Forskolin can prevent this process
As it turns out, the activation of calpastatin is dependent on cAMP. So what this means is that by supplementation with forskolin and activating cAMP, calpastatin gene transcription will be increased, thus inhibiting caplain activity, and ultimately promoting the preservation of lean muscle mass.[31]
Did you follow that? If not, don’t worry: the actual human studies on muscle growth above are what really matters.
Are there any side effects?
The most common side effect in response to consuming forskolin is GI distress, usually in the form of diarrhea. This is the result of increased cAMP within the smooth muscles of the gastrointestinal tract, causing more contractions and motility.
Prevent it with the good stuff

The Coleus Forskohlii plant, which is also known as Plectranthus barbatus. It's highly recommended that you buy well-standardized supplements, not raw or cheap coleus forskohlii. Image courtesy Wikimedia
What this means is that the rate at which things move through your digestive system increases. According to anecdotal reports from users online, this problem can be easily avoided by using a high quality, high standardization extract such as 95% ForsLean from Sabinsa Corp,[32] which uses a patented extraction process.[25] Your chances of experiencing this GI distress is greater when using cheaper less standardized extracts.
Ultimately, what we’re telling you is this: don’t buy forskolin unless it’s a 95% extract. This means staying away from that cheap crap on Amazon or those shady affiliate marketing sites that are looking for pure profit. It’s important to do it right or not do it at all -- more on this in the next section.
Blood pressure effects... as in lower blood pressure
Forskolin also has an effect on blood pressure. Unlike the one above, this side effect isn’t necessarily considered an adverse one. Forskolin has the potential to actually reduce blood pressure. It even has a long history of use in Ayurvedic medicine for this purpose.
Because of this, there are a few contradictions that should be considered. Anyone with diagnosed hypotension, or low blood pressure, and/or gastric ulcers, should avoid taking this supplement.
Individuals who are taking anti-asthmatic and anti‐hypertensive medicine should consult their healthcare provider prior to use of this supplement, and the warning about thyroid medications goes along with this as well.
How to take forskolin?
At this point an "optimal" dose is not yet known, the suggested dose is 25mg of forskolin 30-60 minutes prior to a meal, twice daily.
Remember, this is the amount of the actual active forskolin, not the total coleus forskohlii amount.
This leads us directly into the next question:
What is the best forskolin supplement?
95% is basically the only way to go, and PES is a highly trusted company. We have no affiliation with them, just love their products.
Continuing from the section above, let’s take our current favorite forskolin supplement: PEScience’s Forskolin-95+, available by clicking the image to the right or comparing prices below.
It contains 50mg of ForsLean brand Coleus Forskohlii (Root) Extract, standardized for 95% Forskolin in one "serving" of 2 capsules, which means you are getting a far more pure form than standard / cheaper coleus forskohlii supplements.
With Forskolin-95+, this means you’ll get 0.95 * 50mg = 47.5mg of actual forskolin per day. Nearly perfect. (Also note that Forskolin-95+ includes 200mg Hemerocallis Fulva, which also boosts cAMP levels!)
But beware the cheap / under-labeled stuff...
On the other hand, let’s say you are taking a "forskolin supplement" that is actually only 10% forskolin. In order to get the suggested amount, you’d have to take 250mg twice a day for a 500mg daily total dose. Welcome to diarrhea central.
Worse, some of the cheap forskolin supplements don’t even state their standardization. Those aren’t even worth your time (or money).
So it is important to take into account the percentage of forskolin, dose accordingly, and buy quality. This isn’t a simple herb, as you can imagine from reading this document.
Stacking Forskolin
As you’ve seen, this is a multi-dimensional supplement, and it can be stacked for whatever you need.
For weight loss: Stacking in with fat burners
Human trial after human trial show that forskolin is an effective ingredient.
-- PEScience
Forskolin synergizes amazingly well with beta-agonists,[33] which are popular in several fat burners.
By acting downstream of the b-adrenergic receptor, forskolin increases adenyl cyclase activity and subsequently elevates cAMP. This amplifies the intracellular signal telling the body to "burn fat," in such a way that the body interprets normal beta-receptor stimulation as something greater. This combination works together to maximize fat loss.
If you’re serious about weight loss, our suggestion is to go head over to our Best Fat Burner buyer’s guide, and steer towards what you’d like to take. Find a fat burner without Forskolin, and stack it in as directed above.
For muscle-building
The nearly same advice applies to building muscle, except if you’re not taking a fat burner, you might be taking a pre workout supplement. In that case, check out our Best Pre Workout buyer’s guide, and find something that will work best for your muscle-building goals.
This is no replacement for important supplements like creatine (3-5g per day) or betaine (2.5g per day). Many of the best pre workouts discussed above have one or both of these
As always, you’ll want to get at least 1g of total protein per pound of body weight every single day. Protein shakes help with that, but shouldn’t be relied on. To see what’s hot in the protein world, we have a guide for that too - see our Best Protein Powder buyer’s guide, which will make sure you find the best option for your money.
In conclusion...
You won’t hear us saying this too often, but when it comes to forskolin, Dr. Oz was right. He called it "lightning in a bottle",[34] and although he’s certainly fallen from grace, he’s about right.
What he fails to mention is that you have to get the highly-standardized supplements so that you’re not left with the rest of the low-quality, side-effect causing coleus forskohlii.
Heed those warnings, get the 95% products, and you’ve found yourself a fantastic new stimulant-free supplement that’s actually underrated, for once!
Forskolin – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.


Comments and Discussion (Powered by the PricePlow Forum)