As you'd probably guess from their name, Myprotein has historically specialized in protein supplements like powders, bars, and high-protein snacks. In this they differ a bit from most of their industry competitors, where the focus is almost always on performance-boosting ergogenic sports supplements like stimulants and nitric oxide precursors.
Myprotein has plenty of performance-boosters as well, but today, the product we'll be discussing in this article is very on-brand, yet with a twist: a clear whey protein based meal replacement powder. This is no average MRP!

A meal replacement that settles clear?! Myprotein Clear Whey Meal Replacement has done it - not just with hydrolyzed whey protein, but olive oil as well!
In a single serving of Myprotein Clear Whey Meal Replacement, the macro split is as follows:
- 20 grams of protein (80 calories)
- 5 grams of fat (45 calories)
- 10-12 grams of carbs (4-5 grams of fiber)
Overall you're getting about 150 calories per serving, with half the calories coming from protein alone – this is a macro split that can be compatible with a lot of different diets, making Myprotein Clear Whey a pretty versatile product.
Today we'll dive into this unique meal replacement, that's a follow-up to Myprotein's popular Clear Whey Isolate. One major surprise is that it uses olive oil as the fat source, so we'll be digging into its particular benefits, as well as the protein used as well.
Check out PricePlow's listings, and then let's get right into it:
Myprotein Clear Whey Meal Replacement – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.
This area is reserved for Team PricePlow's upcoming videos.
Subscribe to our channel and sign up for notifications so you catch it when it goes live!
Why A Meal Replacement?
We don't get to write about too many meal replacement supplements here at PricePlow, but we're definitely all for them.
Why? It seems like modern life gets faster-paced every passing year. These days, most of us are either spending tons of time outside the home or are simply in circumstances where we don't have access to the best food. We're "runnin and gunnin" far too much, as they say.
A quality meal replacement is a godsend for anybody who's trying to adhere to a diet, but has a busy schedule that places a premium on convenience.
Keeping a meal replacement in your bag, desk, or car means you have consistent access to food that will support your goals – provided you chose the right meal replacement product for your needs.
Industry-wide Meal Replacement Quality Issues
Unfortunately, too many meal replacements are made with ingredients that, to put it mildly, don't meet PricePlow's exacting nutritional standards – there are tons of additives and preservatives that we'd rather our customers don't eat, but here we're mostly referring to cheap filler carbs or dreaded seed oils, which push our omega-3 to omega-6 ratio way in the wrong direction and can become rancid due to their low oxidation temperatures and antinutrient content.
Technically, a meal replacement is a processed food, so a lot can go wrong in making one. It's tough to find a company that does it right.
Myprotein Clear Whey: High Quality Meal Replacement!
That naturally leads us into reason #1 why we're very interested in Myprotein Clear Meal Replacement: the fat base is olive oil, an oil renowned for its health-promoting effects that is free from the nutritional problems that mar cheaper oils like sunflower oil or soybean oil.
So let's talk about the ingredients in greater detail, and help you understand whether this formula can support you as your pursue your goals:
Clear Whey Meal Replacement Ingredients
Here's what's inside Myprotein Clear Whey:
-
Hydrolyzed Whey Protein
No stranger to Myprotein shoppers who've seen hydrolyzed protein in their other Clear products, we have hydrolyzed whey protein, which allows it to settle translucently!
Whey protein is the supplement industry's go-to supplemental protein, and for good reason: whey is extremely bioavailable,[1] takes effect quickly, and creates a lot of insulin, which can help drive recovery and increase your body's anabolic response to exercise.[2]
Whey is also high in the essential amino acids, which are defined as amino acids that your body can't make on its own from other materials, and must obtain whole from the food that you eat.[3]
Research shows whey to be a highly effective protein supplement, capable of improving body composition and strength in obese and athletic individuals alike.[4-7]
Hydrolyzed whey protein is made by taking whey protein isolate and breaking the whey molecules down into smaller protein units. This can be done several different ways, but is most commonly achieved through the use of enzymes that target whey protein.[8]
A closer look at hydrolysis
The name "hydrolysis" comes from the fact that at the molecular level, it's usually water molecules that are actually breaking the chemical bonds holding the whey together.[9]
When whey is hydrolyzed, it effectively gets "pre-digested", which is thought to increase the bioavailability of the whey, although research on this subject shows that hydrolyzed whey doesn't perform better than other types of whey when it comes to affecting long-term body composition.[10]
We love how it's thinner and settles more clearly, but a real health reason to buy hydrolyzed whey is because hydrolysis destroys a lot of allergens,[11,12] meaning that people with intolerances for lactose or other milk allergens can usually tolerate hydrolyzed whey better than non-hydrolyzed whey.
It should go without saying that there are many different types of milk allergy, with varying levels of severity, and that even though hydrolyzed whey might be safer for some, anyone with milk allergy shouldn't assume that he or she will be able to tolerate hydrolyzed whey.
When in doubt, ask your doctor before using hydrolyzed whey and test on tiny doses.
Whey and insulin: little cause for concern
If you're worried about whey protein's insulinogenic effects, don't be – first of all, because all protein is insulinogenic,[13] but also because the research literature on whey indicates that whey actually increases insulin sensitivity and improves several other markers of glycemic control.[14] In metabolically healthy people, whey intake shouldn't be a problem.
Whey's insulin-sensitizing effects seem to hold even in women with PCOS,[15] a condition that is strongly associated with insulin resistance. So even in the case of certain glycemic disorders, whey protein can potentially help – but check with your doctor if you're worried about the insulin stuff.
A word about protein: why do we want to eat a lot of it?
If you're looking at meal replacement supplements, you're probably trying to change your body composition, whether that means building muscle or losing weight.
If that's you, then a high-protein diet offers specific advantages compared to other ways of eating:
The thermic effect of protein promotes a lean body composition
Whenever you eat any kind of food, your body expends energy digesting it, which ultimately subtracts from the net calorie intake you get from eating that food. This phenomenon of burning energy by digesting is called the thermic effect of food. Each food has a different thermic effect – the higher it is, the more calories you burn digesting it.
You can break this down by macronutrient profile: compared to fat and carbohydrates, protein has the highest thermic effect by far.[16]
Research consistently shows that people who eat more protein, as a percentage of their overall calorie intake, have a significantly higher resting metabolic rate (RMR) than those who eat protein.[17]
Protein is the most satiating macronutrient
Because protein is your body's basic building block for all of your cells and tissues, it makes intuitive sense that your appetite would be calibrated largely for protein consumption – and research suggests that it is.
In one study, people who ate a diet with 30% of total calories from protein ate nearly 500 fewer calories per day than a low-protein control group, without trying to eat less.[18] In other words, these people ate less because they weren't as hungry.
Since a pound of body fat theoretically contains 3,500 calories' worth of energy, this reduction in calorie intake should translate to a whole pound of body fat loss per week.
How much protein do I need?
According to the latest research, protein requirements range from 0.8 to 1.6 grams of protein per kilogram of bodyweight, depending on physical activity – the more active you are, the more protein you need.[16]
-
Extra Virgin Olive Oil
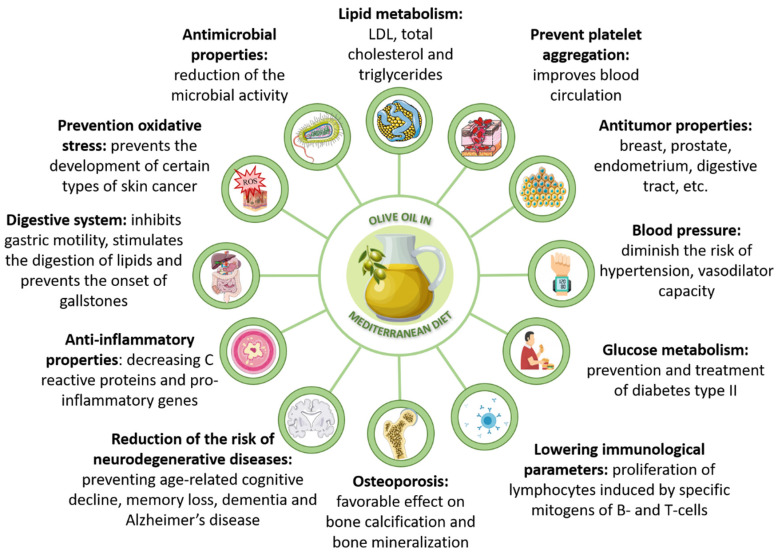
Next up we have arguably the star ingredient of Clear Whey, extra virgin olive oil, the quintessential "healthy fat".
There are so many different nutritional philosophies out there today, and they tend to disagree vociferously on which fats should be eaten, and why – but it's very rare to find a diet that argues against olive oil consumption.
It's really about as close to a universally-respected dietary fat as you're likely to find.
What does “extra virgin” mean?
Extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) is produced by cold pressing olives, meaning that the oil is gently squeezed out of them without being subjected to high temperatures that could denature the bioactive compounds in the oil.
Olive oil produced this way has the highest concentration of nutrients and antioxidants, which is why it's regarded as the healthiest form of olive oil.[17,18]
So right away, you can see that Myprotein is using the good stuff.
EVOO improves cardiovascular health
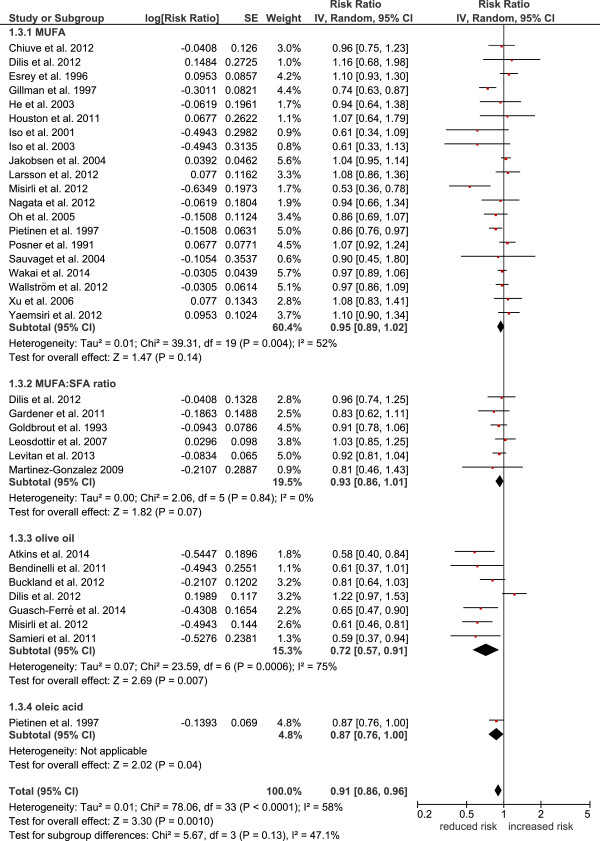
Olive oil is pure fat, and the most abundant type of fat in olive oil by far is oleic acid, a monounsaturated fatty acid (MUFA).
This is the core reason why olive oil is regarded as healthy in so many different nutritional approaches: saturated fats and polyunsaturated fats come with a lot of controversy, but there's not much evidence that MUFA has adverse cardiovascular or metabolic effects.[19-21]
As one study notes, olive oil specifically seems to decrease the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD), whereas other sources of MUFA don't.[19]
This is probably because oleic acid, the specific MUFA in olive oil, is significantly anti-inflammatory. It has been shown in randomized controlled trials to decrease your body's level of C-reactive protein, a marker of systemic inflammation.[22]
Evidence is mounting that chronic inflammation is a risk factor for CVD,[23] so in theory, anything with anti-inflammatory properties should decrease the risk of CVD.
Specific antioxidants in olive oil, namely oleacein and oleocanthal, also appear to have potent anti-inflammatory effects.[24,25]
Besides reducing your body's burden of inflammation – a huge health benefit – olive oil can also:
- Lower levels of oxidized LDL cholesterol[26]
- Improved endothelial function[27]
- Reduced blood clotting (anti-thrombosis)[28]
- Lower blood pressure[29]
Epidemiological studies that track real-world olive oil consumption have largely borne out these theoretical effects, and consistently find that people who regularly consume olive oil have a lower risk of CVD and adverse cardiovascular events.[30-32]
EVOO improves body composition
Despite the fact that dietary fat is the most calorie-dense macronutrient, heavy olive oil consumption is not linked with fat gain,[33] which underscores the metabolic benefits of consuming EVOO.
In fact, eating lots of olive oil may even cause fat loss.[34]
So many clear products! Myprotein Clear Collagen Powder uses hydrolyzed collagen protein to settle more translucently, so you can have thinner, fruity flavors like this one!
Olive oil's ability to improve body composition is explained in large part by its anti-diabetic effects. People who eat olive oil tend to have significantly better glycemic control and insulin sensitivity.[35]
And more!
There's also evidence that olive oil might help prevent Alzheimer's disease,[36] and cancer,[37] and improve symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis.[38]
Olive oil also has strong anti-bacterial properties strong enough to fight Helicobacter pylori infection.[39] Overall, it's an incredibly impressive fat source.
-
Inulin
The last major ingredient we want to discuss is inulin, a prebiotic fiber that can improve the composition of your microbiome, which is unique for a primary carbohydrate source in a meal replacement like Myprotein's Clear Meal Replacement.
Your microbiome is just the collection of microorganisms that inhabit your digestive tract. Although bacteria get most of the attention in discussions of the human microbiome, it technically includes viruses, fungi, and parasites as well.[40]
Myprotein has some fantastic Mike and Ike Clear Whey Isolate flavor collabs: Caribbean Punch & Sour Watermelon Clear Whey Isolate... and these two flavors are (1) insanely good, and (2) insanely sour, respectively!
Among these are the Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli genuses of bacteria, which are symbiotic with human beings. You want lots of these probiotic bacteria species in your gut because they can improve the function of your digestive tract.
They feed largely on certain types of fiber that your body can't digest,[41] so these types of fiber are called "prebiotic" because they are, in a sense, the precursors to probiotic bacteria.
As it turns out, inulin is great food for Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli, so taking inulin can help increase the population of these healthy bacterial species in your gut.[42,43]
Inulin can also help control blood sugar,[44] and generally speaking, dietary fibers like inulin are great for colon health.
-
Other Ingredients
Besides the three major ingredients we've discussed, Clear Whey is also fortified with a ton of essential vitamins and minerals that you'd expect to get from a well-balanced meal.
Supplemental digestive enzymes like bromelain, papain, and the trademarked Digezyme multi-enzyme complex can aid in the digestion of protein, and are included to ensure you absorb as much of the whey that you ingest as possible.
For flavor, we have sucralose and acesulfame potassium, two commonly used zero-calorie artificial sweeteners.
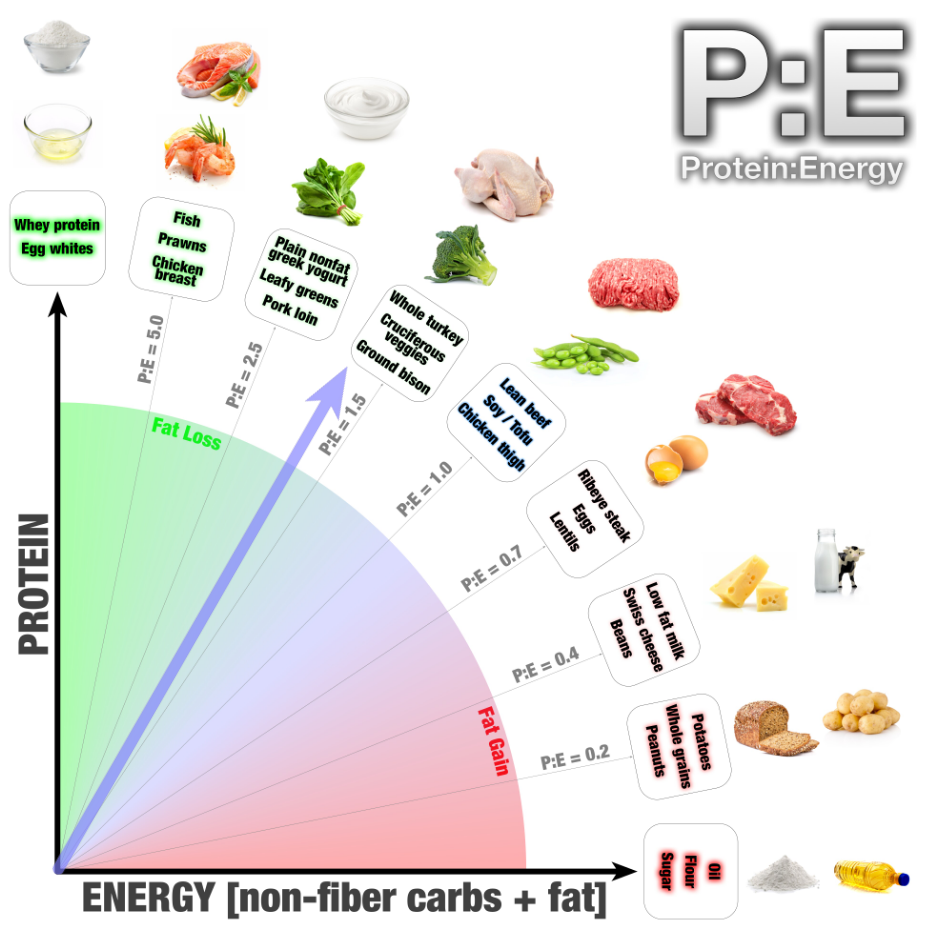
Look at the P:E (Protein:Energy) Ratio
Anytime we see grams of protein greater than the total grams of carbs + fats, we know we're in for a non-obesogenic meal that will satiate! This is based off of the science of Ted Naiman, who wrote the P:E Diet book,[45] based on protein to energy ratios. Long story short: if half or more of your total weight of food is coming from protein, you nearly can't go wrong! And this is something we rarely see in meal replacements, if ever!
Yet with Myprotein Clear Whey Meal Replacement, we have 20 grams of protein to 15-17 grams of carbs+fats, making it a very high-protein meal replacement option. And it's even more impressive if you note that the active carbs are even lower. So consider this a very diet-friendly MRP!
Flavors Available
Conclusion
The use of olive oil instead of cheaper, less nutritious fats may not seem like that big of a deal, but it's the editorial opinion of the PricePlow writing staff that the quality of the fats you consume is the primary determining factor in the overall healthiness of your diet.
The wrong fats can have absolutely terrible effects on human metabolic health, and when it comes to the PricePlow staff's choice of personal supplement consumption, the presence of ingredients like soybean or corn oil is almost always a dealbreaker for us.
Extra virgin olive oil, on the other hand, is pretty much as good as it gets.
Myprotein Clear Whey Meal Replacement – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.







Comments and Discussion (Powered by the PricePlow Forum)