The mission of premium supplement manufacturer Alpha Prime Supps is to "always offer the best for every single person." This relentless drive to dominate every category is what's behind AP's gradual expansion from athletic wear into all kinds of other markets, including sports supplements.
Alpha Prime stands behind their Regimen of supplements with an epic Legacy Pre-Workout offering, whose bold formulations made waves in the supplement world. But lately, most know Alpha Prime for their AP Prime Bites Protein Brownies... which have a fair amount of collagen in them.

Alpha Prime Supps has launched three different collagen supplements, including the C3 Collagen that also includes full doses of Carnitine and CLA. But you can also try their Marine Collagen capsules or Pure Collagen if you want to keep it simple!
That's the context for Alpha Prime's collagen line: as we'll see, collagen is perhaps one of the most indispensable health and wellness supplements in existence, and is of particular importance for people who follow a post-industrial eating pattern like the Standard American Diet (aptly abbreviated as SAD!).
So if the 5 grams of collagen in the Prime Bites Brownies aren't enough for you (and for most people, it isn't), the heads up -- Alpha Prime Supps has launched a trifecta of collagen supplements!
Collagen: More Than Just A Beauty Supplement
Most people's first association when they hear the word collagen is skin, as collagen supplementation is most often undertaken to improve a person's skin health, and thus appearance.
But collagen is far, far more than that: it contains a suite of certain amino acids that are absolutely crucial for optimal metabolic and cardiovascular health, and are generally lacking in the SAD.
Alpha Prime Has A Collagen For Everybody
In keeping with the company's mission of offering the best for every single person, Alpha Prime has made a good effort to develop a collagen supplement for everybody - above and beyond the Brownies!
So far, they've launched:
- C3 Collagen: an athletic collagen for rejuvenation, sculpting and performance
- Pure Collagen: a versatile collagen that can be used for many purposes
- Marine Collagen: a capsule-based collagen with superior bioavailability and unique metabolic properties
Each of the three products in Alpha Prime Supps' collagen line does something slightly different: the type of collagen used varies from product to product, as does the secondary ingredients that it's stacked with.
We cover the details below, but first let's check in on PricePlow for availability and prices:
Alpha Prime Supps – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.
Collagen: A Primer
You've probably heard on more than one occasion that the human body consists mostly of water.
Well, your skin is the largest organ in your body, and although it does contain a little water, the vast majority of it – about 80% of it – is actually collagen. In fact, collagenous proteins account for about 25% to 35% of all the protein in your body, making it your body's most common type of protein.
The reason why collagen is so abundant is that it's your body's structural backbone, the extracellular matrix[1] that gives your tissues shape. You can think of collagen as the glue that holds your body together.
The collagen contains a triple helix molecule made up of the amino acids glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline. Together, these three aminos account for nearly 60% of all the amino acids in collagen.
The triple helix molecular structure is what makes collagenous tissue like skin supple and taut: these helices are shaped in such a way that they can fold over each other effortlessly at the structural level, without breaking the bonds between them or degrading the collagen molecule of which they're a part.[1,2]
Dietary Sources of Collagen
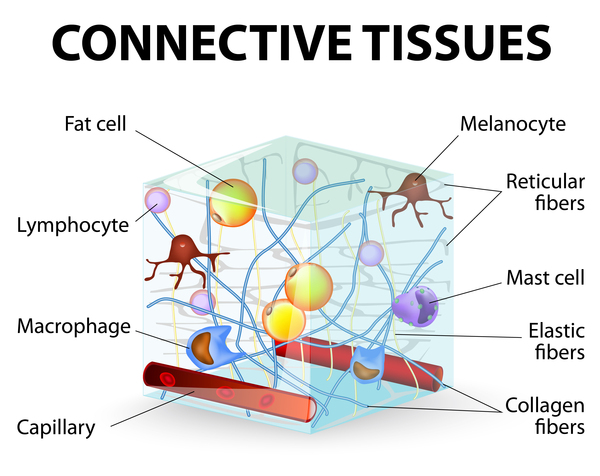
The collagen helps hold it all together - support collagen and support your connective tissues! Image courtesy NIH.
Although people argue endlessly today about what constitutes an optimal diet, the evolutionary record clearly indicates that human beings were omnivorous in our evolutionary past, eating both plant and animal foods in abundance.
When it comes to animal foods, we should think about what kinds of amino acids we were ingesting. Since collagen is the most abundant protein not just in human beings, but in all animals,[3,4] eating animals "nose to tail," as most traditional cultures did, naturally furnished the people in those cultures with a relatively high dietary intake of collagen.
Unfortunately, we do not practice the nose to tail way of eating anymore: meat in the modern American diet consists almost entirely of muscle meats, which have a relatively low collagen content.
Since the amino acid glycine is one of collagen's major constituents, the collagen content of meat is reflected largely by its glycine content. And unfortunately, muscle meats are very low in glycine, compared to organ meats (also known as offal).[5]
Glycine vs. Methionine: The Metabolic Importance of Collagen
We usually think of collagen in cosmetic terms, as something that keeps a healthy sheen in our skin and hair and nails as we age.
But in fact, the importance of collagen goes way beyond merely aesthetic considerations.
Consider the fact that muscle meats are very high in another amino acid called methionine,[5] which balances glycine in certain metabolic processes. Now can see a problem starting to emerge:
The modern diet, with its emphasis on muscle meats over organ meats, pushes our dietary methionine-to-glycine ratio way too far in the direction of methionine.
Too much methionine and not enough glycine can compromise a person's metabolic function, ultimately causing all kinds of second-order health effects.[6]
According to Raymond Peat, Ph.D:
"When only the muscle meats are eaten, the amino acid balance entering our blood stream is the same as that produced by extreme stress, when cortisol excess causes our muscles to be broken down to provide energy and material for repair. The formation of serotonin is increased by the excess tryptophan in muscle, and serotonin stimulates the formation of more cortisol, while the tryptophan itself, along with the excess muscle-derived cysteine, suppresses the thyroid function... A generous supply of glycine/gelatin, against a balanced background of amino acids, has a great variety of antistress actions."[6]
And in fact, a glycine deficiency has been identified as a major risk factor for obesity and the metabolic syndrome,[7] probably because of how a low collagen intake skews the methionine-to-glycine ratio.
Of course, you can attack this ratio from the other end too, which is why some nutritional theorists argue for methionine restriction as a technique to extend lifespan and enhance human health.[8-10]
In any case, collagen supplementation has been shown to improve cardiovascular health, and this is at least partially because the glycine in collagen can help reduce your blood levels of homocysteine, an amino acid that has been identified as an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease.[11,12]
Amazingly, glycine and homocysteine may even play a serious role in mental health: although a causal link has not been proven, it has been observed repeatedly that schizophrenia patients exhibit high levels of homocysteine and low levels of glycine.[13,14]
Additional Benefits of Collagen: Skin, Hair, Nails and Joints
Of course, the reason most people want to take collagen is because it can help improve a person's appearance.
We're interested in this too, but the aesthetic effects of collagen supplementation tend to depend more on the specific type of collagen a person takes, whereas high glycine content is the common denominator for pretty much every type of collagen.
It's worth noting that other studies on collagen -- generally higher-dosed and using generic, non-patented blends -- have also been shown to improve joints and connective tissues[2,11,15,16] and also help hair, skin, and nail health.[3,7,17,18] Cardiovascular health benefits have even been achieved with collagen.[19]
We always make it clear that collagen is not the anabolic "muscle building" kind of protein, even if you see "protein" on the supplement facts label. This is due to the fact that its amino acid ratios are lower in some of the mTOR-stimulating amino acids that drive muscle protein synthesis, so it's not a "complete" protein.[4] If you need to build muscle, eat your steak and add in some Alpha Prime Supps Whey Protein!
Anyway, this is perfectly fine in the case of these supplements - we're using them to build up our joint health and better hair, skin, and nails!
Now let's talk about each of Alpha Prime's collagen products in detail.
First up is C3 collagen.
-
Alpha Prime Supps C3 Collagen
This product is formulated to support the collagen needs of an athlete. It contains the types of collagen you'll need to build and maintain strong tendons, joints, and ligaments, to help your body recover from intense activity (especially load bearing activities such as heavy lifting).
Let's look in detail at how the ingredients in this product work.
C3 Collagen Ingredients
In a single 1 scoop (12 gram) serving of C3 Collagen from Alpha Prime Supps, you get the following:
-
Collagen Types I & III
Collagen type I kicks off the athlete-focused C3 formula, which makes perfect sense since this type of collagen is the most abundant found in mature tendons and ligaments, and gives them their ability to bear heavy loads.[20]
Collagen type III is important for healing injuries caused by inflammation,[21] which is an important consideration for athletes and bodybuilders since exercise actually causes acute inflammation.[22] Although inflammation is a scary word these days, in the case of exercise it's generally a good thing, because it triggers compensatory adaptations in your body in response to exercise. However, your body can only adapt if it has the resources to recover from exercise. That's where a little extra collagen comes in: helping support your body's process of growth and repair.
We like to see type I and type III collagen stacked together because the collagen fibrils in your body need to maintain the right balance between rigidity and elasticity. Since this balance is determined partly by the ratio of type I to type III in your body,[23] we want to make sure that these two types of collagen are consumed in the correct ratio.
These two types of collagen may also synergize in certain bodily processes – for example, collagen types I & III both play an important role in the process of wound healing.[24]
Collagen types I & III are typically taken separately from collagen type II, on the common belief that absorption of collagen type II is impaired by types I & III. However, as of the time of this writing, the PricePlow writing staff is unable to locate peer-reviewed evidence that supports this idea.
-
CLA (Conjugated Linoleic Acid) Matrix – 2500 mg
Conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) is an omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) that occurs naturally in many foods, but is particularly concentrated in meat and dairy products.
It's worth mentioning that grass-fed cows produce meat and milk with naturally higher levels of CLA.[25]
CLA inhibits the action of lipoprotein lipase (LPL), an enzyme that drives fat storage by helping your body's fat cells take in fatty acids from the bloodstream.[26] By inhibiting LPL, the CLA you eat will ultimately increase your body's fatty acid oxidation and, hence, overall metabolic rate (as measured in calories).[26,27]
Alpha Prime Supps also has a separate CLA supplement if you're on a low-fat / low-dairy diet and want to make sure you're not missing any!
The upshot of all this is that CLA can help improve your body composition, by encouraging your body to burn stored fat without replenishing it.[26-29]
Long-term supplementation with CLA seems to have potential benefits for athletic performance, as indicated by one study where student athletes who took CLA for 14 days did better in a test of aerobic fitness than those who took a placebo.[30]
The primary mechanism of action seems to be CLA's ability to improve body composition (thus increasing power to weight ratio), but some evidence suggests CLA might increase testosterone production as well.[31]
CLA may also improve bone strength and density,[32,33] thus decreasing the risk of bones fracturing or breaking during exercise.
We often see very small CLA doses in weight loss supplements - like one softgel containing 500 milligrams. Not the case here, we're getting a more serious dose, and that's important for those who may not be getting the fatty acid naturally (perhaps due to low-dairy or low-fat diets).
-
Carnitine – 2,000 mg
Carnitine is a quaternary ammonium compound (QAC) that supports your body's fat burning metabolism by shuttling fatty acids into your cells, where your cells' mitochondria can convert them into adenosine triphosphate (ATP).[34]
After reading a new review based upon 100 citations, we are finding fewer and fewer reasons not to take ~2g L-Carnitine each day
We at PricePlow love supplements that support cellular energy production. ATP is your body's most basic unit of energy – if your body were an automobile, ATP would be the gasoline.
Your body consumes ATP in the course of performing basically any useful work that you ask your cells to do – including things like muscle protein synthesis, neuromuscular adaptations, and generally speaking all the processes of growth and repair that occur once you finish exercising – to say nothing of the exercise itself, which also consumes your body's ATP stores.[35]
If you want a great physique and to perform at your peak, you absolutely need to be producing lots of ATP.
ATP production is governed by a cluster of intracellular proteins that make up the mitochondrial respiratory chain complex. These proteins (named complexes I, II, III, and IV) control enzymes responsible for converting energy substrates (i.e. oxygen, sugars, and fatty acids) into ATP by subjecting them to the process of oxidative phosphorylation.[36]
Oxidative phosphorylation is responsible for generating most of the energy used by the human body,[37] so supporting this process with adequate carnitine levels is crucial for achieving and maintaining optimal metabolic health.
Carnitine is fairly well-researched (especially at this 2 gram dose), and taking carnitine supplements is associated with fat loss[38,39] as well as better insulin sensitivity and more efficient glucose metabolism.[40]
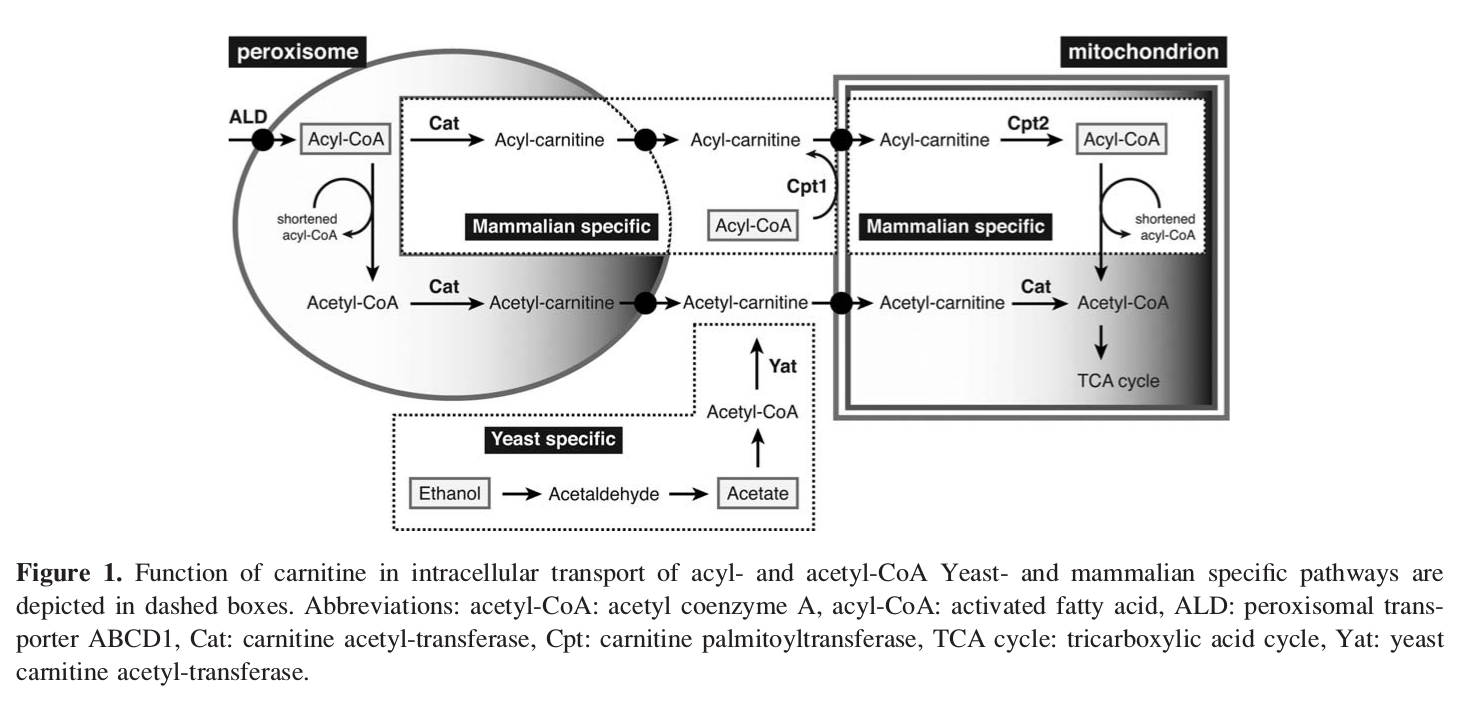
Carnitine's Function in Intracellular Transport.[52] Note how important this molecule is if you plan on delivering fatty acids to cells. You can ignore the bottom yeast section.
Carnitine is capable of converting white adipose tissue (WAT) to brown adipose tissue (BAT). Having more BAT is a good thing because it has a higher mitochondrial density than WAT (in fact, the mitochondria themselves are responsible for staining WAT and giving it a "brown" appearance when viewed under a microscope), which ultimately helps your body burn more calories off as heat in a process called non-shivering thermogenesis.[41]
Overall, this is a very strong sports nutrition supplement with quality clinical doses attached. Carnitine and CLA are far too often underdosed - not a problem here.
Alpha Prime Supps C3 Collagen Carnitine+CLA – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.
-
-
Alpha Prime Supps Pure Collagen
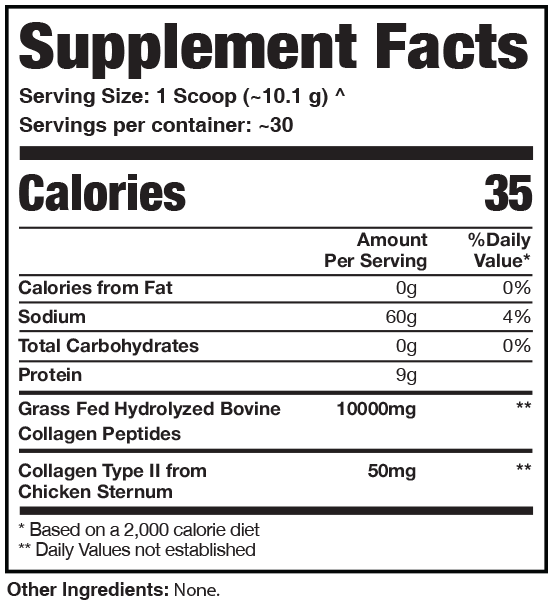
Alpha Prime's Pure Collagen product, as its name implies, gives us just a big serving of collagen types I, II, and III – no secondary ingredients, making this product adaptable to a wide range of individual needs.
Pure Collagen Ingredients
Pure collagen, but not just regular bovine collagen - a bit of extra Type II collagen is also added!
In a single 1 scoop (10.1 g) serving of Pure Collagen from Alpha Prime Supps, you get the following:
-
Grass Fed Hydrolyzed Bovine Collagen Peptides – 10,000 mg
Bovine collagen peptides, i.e. collagens sourced from cows, consist of types I and III, which we discussed extensively above in the section of this article dedicated to C3 Collagen. Although the Pure Collagen product as a whole consists mostly of collagen types I, II and III, the bovine peptides are going to contain some of each type of collagen, making it a kind of "full spectrum" collagen supplement.
In one study, supplementation with bovine collagen significantly improved the skin laxity, repaired collagen fibers, increased collagen content and normalized the ratio of type I to type III collagen in aged mice, showing collagen supplementation's powerful anti-aging effects.[42]
The normalization of the type I to type III collagen ratio is especially interesting – recall our discussion in the C3 section of why it's important to maintain this delicate balance.
Also unsurprising, if you remember what we said about types I and III, is that bovine collagen appears to support skeletal mineralization by supporting the proliferation of osteoblasts, a type of cell responsible for building up your bones.[43]
For this reason, bovine collagen supplementation has been shown to actually prevent bone loss in aging mice.[44]
The research on bovine collagen isn't just limited to animals though – at least one randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in humans has shown that bovine collagen supplements can significantly improve several dimensions of skin quality.[45] In this study, 72 healthy women over the age of 35 took bovine collagen for 12 weeks and saw significant improvements in skin smoothness, hydration, and elasticity.[45]
-
Collagen Type II from Chicken Sternum – 50 mg
Collagen type II is the primary constituent of cartilage,[46] making it especially important for joint health. Research in human subjects indicates that collagen type II supplementation can significantly reduce joint pain in people whose joints are aggravated by physical activity, allowing them to exercise for significantly longer before experiencing any discomfort, as well as improving their range of motion in affected knees.[47]
The ROM-boosting effect of collagen type II is something observed in multiple studies – the effect size seems to range between 3 and 5 degrees of additional flexion.[48]
Collagen type II supplementation can improve joint pain in those suffering from osteoarthritis.[49]
Most other "pure collagen" type supplements only include the bovine collagen, but neglect the added type II -- not Alpha Prime Supps! This is definitely a great reason to consider it over the rest.
Alpha Prime Supps Pure Collagen – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.
-
-
Marine Collagen (capsules)
The Marine Collagen capsules from Alpha Prime Supps comes with all the usual benefits of a collagen supplement – with a couple of twists.
Besides the biochemistry involved here, obviously, there are benefits for consumers with particular concerns about sourcing – such as people who don't want to consume beef products for moral or religious reasons.
Marine Collagen Capsule Ingredients
In three capsules, you get the following:
-
Deep Sea Hydrolyzed Marine Collagen Peptides – 1,500 mg
Marine collagen is most commonly sourced from fish scales. It contains mostly type I collagen, but also a little type III.
In terms of how it functions in your body, marine collagen is pretty similar to bovine collagen and other types of collagen. However, there are some key differences:
First, marine collagen is highly bioavailable compared to other forms of collagen – up to 1.5 times more bioavailable,[50] a pretty significant difference.
But marine collagen also has at least one special metabolic property. It contains collagencin, a peptide unique to marine collagen with powerful antibacterial and possibly antihypertensive properties.[51]
Alpha Prime Supps Marine Collagen – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.
-
Conclusion: Alpha Prime Supps Has Your Collagen Needs Covered
You knew that 5 grams of collagen in AP Prime Bites Protein Brownies wasn't going to be enough for this brand, which is targeting highly-aesthetic, functional, and strength athletes.
While quality collagen is becoming more prevalent in the industry, Alpha Prime Supps has gone further than the vast majority of their competitors to try and tailor collagen supplements to the needs of different consumers.
So after you tear yourself to pieces with those Alpha Prime Supps Legacy Pre-Workouts (available in both stim and stim-free versions), repair some of that soft tissue damage with one or more of these collagen supplements alongside a high-protein diet!
Alpha Prime Supps – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.










Comments and Discussion (Powered by the PricePlow Forum)