
The Cellucor C4 New Formula (G4) is out!
BIG news everyone!
Cellucor has released several new products, the most important of which is the New Cellucor C4 Formula!
Let's cut to the chase and discuss the changes below:
Cellucor C4 New Formula vs. C4 Extreme - The Comparison
Below you can see the old one (C4 Extreme) is to the left, the new one to the right:

The original formula ingredients. Note vitamin C in the explosive energy blend, which was always a bit odd.
The differences
As you can see, this is very similar to the current version of Cellucor C4 Extreme, except we have more caffeine and a great new ingredient in Theacrine, named TeaCor.
Cellucor C4 Gen 4 – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.
Let's take a look and see if these changes are enough to get Cellucor back onto our Best Pre Workout Buyer's Guide!
The New Formula Ingredients
Our full analysis is in progress below but you can click here to skip to the Theacrine section, since that's the new ingredient everyone's interested in:
-
Beta Alanine: 1.6g
All over this site, we constantly extoll the virtues of beta alanine to all kinds of athletes. This is the ingredient that gives many uses the "tingling" sensation after taking it. That sensation is known as parasthesia, and beta alanine has been shown to be safe.
Beta alanine works by boosting levels of carnosine in your muscles.[1] That carnosine then goes on to buffer fatigue-inducing acids such as lactic acid.[2]
This process works best when performing athletic activities that are between one and four minutes long, and it's hard to find a study that was not successful with beta alanine supplementation.
Some sports where it works, with sources cited, are below:
Beta alanine boosts how long athletes last, which then turns into more overall workload... which, if you eat right, means more gains!
- Rowing[3]
- Wrestling[4]
- Football (the American kind)[4,5]
- Resistance training, including weight lifting[6]
- Cycling (bike)[7,8]
- Standard exercise[9]
- Running[10]
The best studies are at 3.2g per day (every day), which would come from two scoops of the new C4. Otherwise, you can add your own extremely cheap.
Simply put, you should be using beta alanine if you're an athlete no if's, and's, or but's about it.
-
Creatine Nitrate: 1g
Creatine nitrate is a combination of muscle-building creatine and pump-inducing nitrate. It is 32.5% nitrate, and 67.5% creatine, meaning that in each scoop of the new C4, you're only getting 675mg of creatine.
There's good news and bad news here:
First, the good news: 325mg of nitrate is enough to get a decent pump (doubly so when taking two scoops), and it synergizes well with the arginine AKG in the next ingredient.
The benefits of supplemental nitrates
Nitrate provides the following benefits to athletes:
- Increased blood flow[11]
- Less oxygen expense when exercising[11,12,13,14]
- More force production and more power[15,16]
- Nitric oxide pumps![15,17]
- Boosted endurance[13,14]
- Better energy at the cell-level[16]
- Recovery improvements[18]
It's also extremely long-lasting, so the pump goes and goes, which feels great.
We're all about nitrates here on PricePlow, and Cellucor was one of the companies that brought them to the forefront with their "NO3" technology.
Now for the bad news:
This isn't enough creatine.
There's no doubt that creatine has great benefits, like boosting VO2 max here. But is this enough? Not really.
One of the most major, problematic issues with C4 Extreme (and now this new C4 formula) are that inexperienced users don't realize that they're not getting a good enough dosage of creatine when taking it alone.
The best creatine studies for strength and size gains use a minimum of 3-5g per day, even on rest days.[19,20,21,22,23,24,25] It's long been proven safe and effective, even in the long term - anyone who claims it is not safe needs to look at the hundreds of studies that prove them wrong.
In fact, several phenomenal studies utilized a 20g/day "loading" strategy for the first five days. That strategy is now used less, but the fact remains that there is a great deal of science behind higher doses of creatine - but not low doses like this.
Seven such studies are cited above, but there are literally about 750 more and counting.
The point is, if you're going to use this version of C4, realize that you should be taking supplemental creatine alongside it (or post workout). An extra 3-5g is fine, and you can take it however which way you want on off-days.
Don't fall into a false sense of security
Our problem with the micro-dosing of creatine here is that too many users think that they're getting enough creatine in, but if they're not eating a lot of beef, there's a good chance that they're not. Just because it's on the label doesn't mean it's an efficacious amount.
Creatine is too cheap, effective, and safe to skimp on. Don't let this label confuse you - add 3-5g more and get more gains.
-
Arginine AKG: 1g
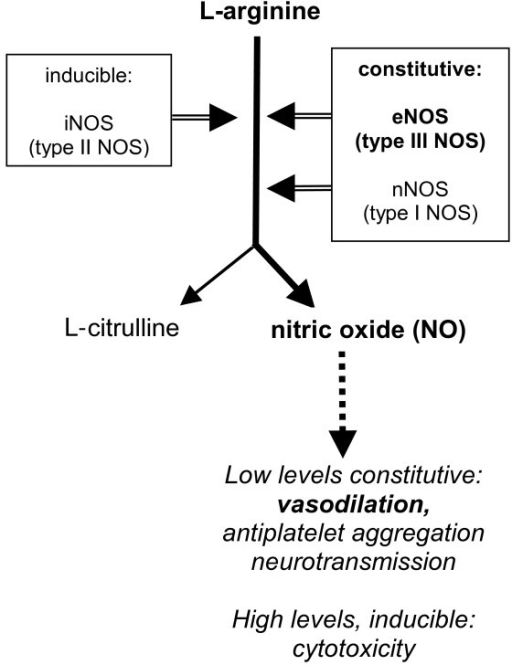
How L-Arginine Works - but the main reason we like it in the new C4 is due to the prevention of nitrate tolerance
Arginine AKG, or AAKG, was formerly popular in pre workouts from roughly 5 years ago, and is helpful in boosting nitric oxide levels a bit and reduces your oxygen expense.[26]
However, it has fallen by the wayside due to other amino acids like l-citrulline and agmatine, which are better at keeping NO levels high. So why is it still in C4? The main reason is that arginine is synergistic with nitrate.[27] It has been shown reduce nitrate tolerance, so when you coingest it with the creatine nitrate above, you won't get "used" to its effects.
So while we'd love to stack in 3g or more l-citrulline or a gram or more of agmatine to get ridiculously ferocious pumps when weightlifting, this isn't that kind of supplement - C4 can be used in all forms of athletic endeavors.
If you need a bigger pump and want to stick with the Cellucor family, you can consider a few capsules of the new NO3 Chrome formula (a pure nitric oxide pill, stimulant free) or even a scoop of the new Alpha Amino (now with HydroMax, which drives water to the muscles).
-
Explosive Energy Blend (371mg):
The main reason this blend has a lower dosage is because vitamin C has been removed. Knowing that, and seeing 150mg of caffeine, we can deduce the doses to a decent degree:
-
N-Acetyl-L-Tyrosine
This is the main focus-booster in the new C4 (as well as the old), and we know that we're getting at least 150mg (but not much more) since it comes before caffeine. At two scoops, that will make for a decent dosage, but nothing out of this world and less than other popular pre workouts.
We're huge fans of L-Tyrosine, and N-Acetyl-L-Tyrosine is the most bioavailable and best-absorbed form.[28]
The studies performed show that it kept members of the military highly focused even when they were very tired.[29,30] Unfortunately, those studies were using higher doses, so we're going to hope that enough was provided here.
Anecdotally, 250-500mg is where it really starts working well, so the focus is going to be felt the most at 1.5 to 2 scoops fo the new C4. It's always recommended that you take your pre workout in terms of caffeine tolerance, however, not by how much creatine or focus enhancers you want to get.
-
Caffeine Anhydrous (150mg)
At this point, we're assuming you know what caffeine does for you and how much you need to get going. This is 15mg more than C4 Extreme... or roughly 10% more if that puts a different perspective on it.
-
Velvet Bean (Mucuna Pruriens) seed extract (standardized for L-Dopa)
L-DOPA is a precursor to dopamine, and when supplementing it, it boosts dopamine[31] and thus the appropriate dosage feels downright good.
Many users are confused to see it in a pre workout supplement, since it's often in nighttime sleep supplements. It may help sleep, but it doesn't make you sleepy. Understand the distinction.
The reason it's in those sleep formulas is because it's to boost growth hormone levels alongside its dopamine boost[32,33], and your GH levels are already being boosted and put to work when sleeping, so it makes sense to include them in those formulas.
At extremely high doses, L-DOPA can improve sexual health[34,35,36], but at this point in the formula, there is not enough room for much of a dosage here - a maximum of 71mg, but likely a bit less.
So you'll get a little dopamine boost (synergistic with the next ingredient), it will feel good, but it likely won't have any massive hormone-boosting effects.
-
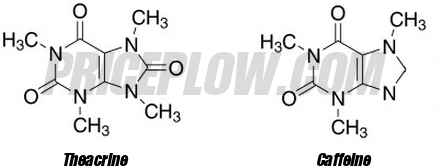
TeaCor Tetramethyluric acid (Theacrine)
We think that Theacrine is going to be hugely popular because it behaves similarly to caffeine, yet has way less tolerance issues, so these tubs will make you feel great all the way through.
Cellucor's hope is that complaints like "two scoops isn't doing it for me anymore" should be a thing of the past.
Looking at the science and origin, Theacrine is an alkaloid that is naturally synthesized from caffeine in certain plants, such as certain Kucha plants[37] (Kucha tea is actually quite popular in some parts of the world).
The best research has been performed on rodents, but Kucha has been studied for a while in humans.
Works similarly to and in parallel with caffeine
Just like caffeine, it's actually a sedative at a very low dosage[38], but stimulatory past a certain threshold dose. We don't know how much is in the new C4 formula, but we hope it is high enough to make this happen.
Adenosine and dopamine signaling
This research shows that its best involved in adenosine and dopamine receptors.[39]
Adenosine is most commonly known for its role in energy transfer in nearly all cells. It is a part of ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, as well as cAMP (cyclic adenosine monophosphate). Some of the best-performing supplements, such as creatine, boost cellucor levels of these hugely important compounds.
When the rats were given an adenosine antagonist, theacrine actually counteracted that antagonist and re-boosted adenosine, making up for "lost" energy.[39]
Meanwhile, the same study showed that it had some level of influence on dopamine signals, working similarly to caffeine. This provides a feel-good boost from caffeine, but one that you won't get used to like you do with caffeine.
Locomotion
The research also showed that rats were active and nimble in their movements - something known as locomotion.[38]
This is good news for athletes who are looking for a new kind of edge, and we hope it translates to speed and basketball-style athleticism.
A lack of tolerance!
The best part of the locomotion study showed that the rats didn't get sensitized to the substance over the course of a week, whereas you do with caffeine![40]
This isn't enough data to completely say that you won't gain tolerance to it, but it's promising, and anecdotally, users are agreeing that the ingredient's effects don't "get old".
Safety and side effects?
It took extremely high amounts of Theacrine to hurt the mice - about 800mg per kg of bodyweight was the LD50 (median lethal) dose.[41]
The total amount in the new C4 won't be anywhere near that much, to say the least. Toxicity generally behaves like caffeine's.[42]
Overall, we're excited to try this out, and we look forward to more research coming over the next year. From what we've heard from users who are taking other Theacrine-based supplements, they absolutely love it.
You can read more about this ingredient on our main Theacrine article
-
The general consensus on these ingredients is that it will definitely be a bit more energetic than caffeine - but it's going to come down to the Theacrine dosage, and how well it works for everyone. We'll need to try it for ourselves to find out.
Compare prices and sign up for price notifications below and we'll let you know as the prices drop:
Cellucor C4 New Formula – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.
How will this perform? Any initial reviews?
It will really come down to how well Theacrine performs, so we must review it soon. Outside of Cellucor's and GNC's corporate headquarters, nobody was given any preview tubs, so we'll have to wait for legit reviews to come out.
Product Availability and Release Schedule
- The new C4 was released on December 11, 2014.
- It will be a GNC-exclusive in December 2014.
- BB.com will get it after that in January 2015.
- After that, all other independent retailers will be able to get it.
We don't expect any massive price drops until more stores have it, but you should sign up for price drops above for when it happens!



Comments and Discussion (Powered by the PricePlow Forum)