One of the most established names in the supplement industry, Optimum Nutrition, has just upgraded their supplement line with to include one of the most innovative protein supplements available on the market to date.
Their new product, Protein Energy, combines the well known benefits of whey protein with the powerful effects of caffeine and green tea extract.
While it’s true that whey protein, caffeine, and green tea extract make up the bulk of the formula, the inclusion of vitamins E, B6, and B12 definitely deserves some recognition as well - as all three vitamins were dosed in respectable amounts.
You can compare prices and sign up for price drop notifications below, otherwise, scroll down to read more details behind the ingredients.
Optimum Nutrition Protein Energy – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.
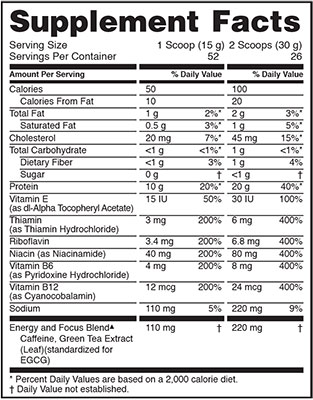
The Protein Energy Ingredients
The ingredient label and nutrition facts are down to the right.
As you can see, the initial release contains 52 servings when taken as one scoop, or 26 servings when taken as two scoops.
Let’s take a closer look at what you're getting in each two scoop serving...
-
20g Whey Protein Blend
Each scoop of the protein blend provides 10g of a well rounded combination of three different forms of whey.
- Whey protein concentrate
- Whey protein isolate
- Whey protein hydrolysate
You can check out our page on whey protein to get a better understanding of each form.
220 mg Energy & Focus Blend
ON kept the energy and focus blend short but sweet.
It contains two ingredients:
- Caffeine
- Green tea extract
For the most part, we all know what caffeine brings to the table - so I’m not going to bore you with a lecture on caffeine’s mode of action or anything of the sorts...
However, I do want to point out something important about the green tea extract, and that’s the fact that it was specifically standardized for epigallocatechin galate (EGCG) content.
What is EGCG?
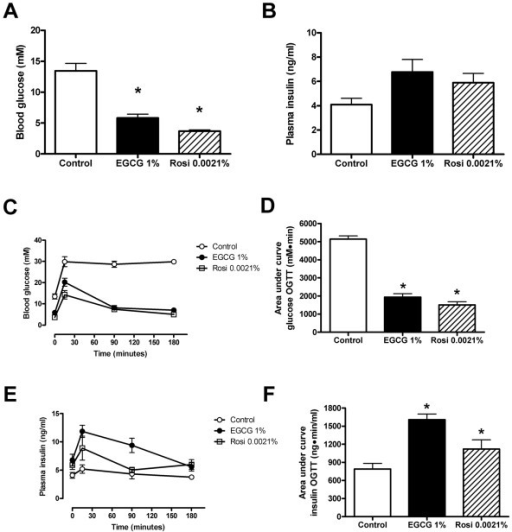
EGCG improved glycemic control in mice. Shown are fasting blood glucose levels (A), fasting plasma insulin levels (B), blood glucose concentrations (C, D) and plasma insulin concentrations (E, F) during an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT).
EGCG is a natural component of green tea that works hand in hand with caffeine, to amplify it’s effect on thermogenesis.
It has this effect because of it’s ability to inhibit the enzyme that breaks down noradrenaline, catechol-O-methyl-transferase.
It’s potent and effective enough that researchers have noted it’s potential use in the management of obesity.[1,2]
-
24 mcg Vitamin B12
24 mcg’s of vitamin B12 provides 400% of your daily value.
Some of the most popular multivitamins on the shelf aren’t even dosing B12 that high.
It works through dozens of pathways, offering a number of benefits.
One of it’s most noteworthy effects (for our purposes at least,) is it’s ability to convert carbohydrates into energy - it also plays an important role in the metabolization of fat and protein.
If you are deficient in B12 your energy levels are probably suffering, one of the most recognizable symptoms of B12 deficiency is fatigue.[3,4]
-
8 mg Vitamin B6
8 mg’s of B6 is going to clock you in at 400% of your daily value...not too shabby, especially for a protein supplement.
Much like B12, vitamin B6 serves a multitude of purposes within the body - too many to discuss in this article.
The most notable thing here - in regards to it’s role in Protein Energy, is probably it’s profound ability to aid in the metabolism of protein.
Numerous sources have stated that “the more protein you consume, the more vitamin B6 you require.”[5,6]
Vitamin B-6 recommended and adequate intake
-
30 IU’s Vitamin E
It’s likely that many of you are familiar with vitamin E in regards to it’s antioxidant properties, but what you probably didn’t know is that if your vitamin E levels are low, you’re going to have a harder time gaining muscle mass and you’re going to be weaker than you should be.
Now here’s the kicker...trusted authorities have reported that many people have low levels of vitamin E.[7,8]
Obviously, this is no bueno for us fitness enthusiasts. With that in mind, ON made sure that you’re getting 100% of your daily value in every two scoop serving of Protein Energy.
Initial Review
Overall, the product looks incredibly promising - for the right person. Obviously you know whether or not you want some caffeine with your protein.
It will ultimately come down to price and taste. Did ON do enough to cover up any of the bitterness that might come with caffeine? Since the caffeine dosage isn't heavy, we don't see that as a problem.
And as for price, you can compare prices to get the best deal online or sign up for price drop updates below and PricePlow will email you when there's a significant discount found at any store.
Optimum Nutrition Protein Energy – Deals and Price Drop Alerts
Get Price Alerts
No spam, no scams.
Disclosure: PricePlow relies on pricing from stores with which we have a business relationship. We work hard to keep pricing current, but you may find a better offer.
Posts are sponsored in part by the retailers and/or brands listed on this page.




Comments and Discussion (Powered by the PricePlow Forum)